Spring听课笔记(tg)AOP
好文:https://blog.csdn.net/javazejian/article/details/56267036
通过一个实例来理解
1. 需求:实现算术计算器,可以加减乘除,同时记录日志
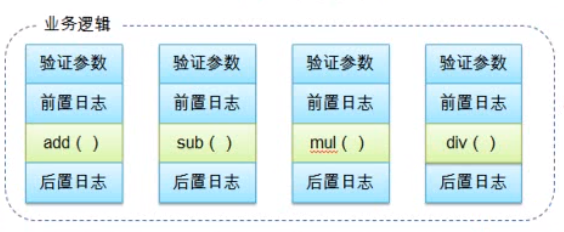
2. 实现方式:
① 高度耦合(直接pass)
② 自己实现动态代理
③ 利用Spring AOP框架
二. 自己实现动态代理
1. 定义接口及实现类:
-- 接口:ArithmeticCalculator
public interface ArithmeticCalculator {
int add(int i, int j);
int sub(int i, int j);
int mul(int i, int j);
int div(int i, int j);
}
-- 接口的实现类
public class ArithmeticCalculatorImpl implements ArithmeticCalculator{
public int add(int i, int j) {
int result = i + j;
System.out.println("[add] " + i + " + " + j + " = " + result);
return result;
}
public int sub(int i, int j) {
int result = i - j;
System.out.println("[sub] " + i + " - " + j + " = " + result);
return result;
}
public int mul(int i, int j) {
int result = i * j;
System.out.println("[mul] " + i + " * " + j + " = " + result);
return result;
}
public int div(int i, int j) {
int result = i / j;
System.out.println("[div] " + i + " / " + j + " = " + result);
return result;
}
}
-- 返回动态代理类
关键代码已经标红,利用JDK的Proxy类,加入参数,返回代理类
try-catch-finally分别对应四种通知
public class ArithmeticCalculatorLoggingProxy {
private ArithmeticCalculator target;
public ArithmeticCalculatorLoggingProxy(ArithmeticCalculator target) {
this.target = target;
}
public ArithmeticCalculator getLoggingProxy() {
ArithmeticCalculator proxy = null;
//代理对象由哪一个类加载器加载
ClassLoader loader = target.getClass().getClassLoader();
//代理对象的类型
Class[] interfaces = new Class[] {ArithmeticCalculator.class};
//调用代理对象的目标方法,并执行的代理方法
InvocationHandler h = new InvocationHandler() {
//proxy: 一般不用proxy中的方法,容易死循环
//method: 目标类中的方法
//args: 目标类方法的参数
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) {
Object result = null;
try {
System.out.println("这是前置通知...");
result = method.invoke(target, args);
System.out.println("这是返回通知,方法正常执行时执行...");
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.println("这是异常通知,方法异常时执行...");
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println("这是后置通知,不论是否异常,都会执行");
}
return result;
}
};
proxy = (ArithmeticCalculator) Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader, interfaces, h);
return proxy;
}
}
-- 调用
public class App
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
ArithmeticCalculator target = new ArithmeticCalculatorImpl();
ArithmeticCalculator proxy = new ArithmeticCalculatorLoggingProxy(target).getLoggingProxy();
proxy.add(1, 3);
System.out.println();
proxy.div(4, 2);
}
}
-- 结果(后置通知的执行顺序好像和spring aop不太一样)

三 通过Spring AOP + AspectJ注解方式
-- 配置文件(利用context和aop命名空间)
<!-- 配置bean自动扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring_1.aop"></context:component-scan> <!-- 配置aspectj起作用 -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
-- 接口,实现类同前,需要注意,实现类要加到spring容器中

-- 日志切面类
需要注意,用@Component 加入到Spring IOC容器中, 用 @Aspect 让AspectJ自动扫描
@Component
@Aspect
public class LogginAspect { /**
* 定义一个方法,用于声明切入点表达式,一般的,方法中不需要其他代码
*/
@Pointcut("execution(* com.atguigu.spring_1.aop.ArithmeticCalculator.*(..))")
public void declareJointPointExpression() {}; /**
* 前置通知
*/
@Before("declareJointPointExpression()")
public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
// JoinPoint:链接点可以访问到方法的具体信息
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
List<Object> args = Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs());
System.out.println("前置通知: method " + methodName + " begin with arguments:" + args +"");
} /**
* 后置通知: 不论是否有异常,都会如期执行
* 但是无法访问到方法的返回值
*/
@After("declareJointPointExpression()")
public void afterMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("后置通知: method " + methodName + " end");
} /**
* 返回通知:只有正常执行时,才可以执行
* 能够访问到方法的返回值
*/
@AfterReturning(value="declareJointPointExpression()",
returning="result")
public void afterReturningMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("返回通知: method " + methodName + " end with result: " + result +"");
} /**
* 异常通知:抛出异常时执行
*/
@AfterThrowing(value="declareJointPointExpression()",
throwing="ex")
public void afterThrowingMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception ex) {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
System.out.println("异常通知: method " + methodName + " throw an exception " + ex +"");
}
}
-- 调用
public class App
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aop.xml");
ArithmeticCalculator target = ctx.getBean(ArithmeticCalculator.class);
target.add(1, 3);
System.out.println();
target.div(4, 2);
}
}
-- 结果

四)四种通知的执行顺序
没有异常:前置通知->目标方法->后置通知->返回通知
有异常: 前置通知->目标方法->后置通知->异常通知
五)后置通知和返回通知的区别
-- 后置通知(@After)不能访问到目标方法的结果,而返回通知(@AfterReturning)则可以
六)切面等基本概念的理解
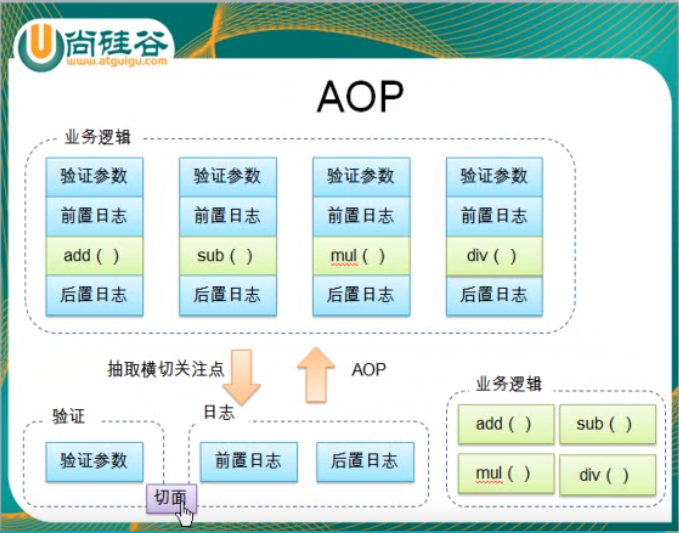

Spring听课笔记(tg)AOP的更多相关文章
- Spring学习笔记之aop动态代理(3)
Spring学习笔记之aop动态代理(3) 1.0 静态代理模式的缺点: 1.在该系统中有多少的dao就的写多少的proxy,麻烦 2.如果目标接口有方法的改动,则proxy也需要改动. Person ...
- Spring学习笔记4——AOP
AOP 即 Aspect Oriented Program 面向切面编程 首先,在面向切面编程的思想里面,把功能分为核心业务功能,和周边功能. 所谓的核心业务,比如登陆,增加数据,删除数据都叫核心业务 ...
- Spring听课笔记(tg)
0. 地址:https://www.bilibili.com/video/av21335209 1.综述,Spring主要的复习要点集中在以下几点 -- Spring的整体结构,Maven依赖(环境搭 ...
- Spring听课笔记(tg)2
配置Bean -- 配置形式:基于XML 文件的方式, 基于注解的方式 -- Bean的配置方式:通过全类名(反射).通过工厂方法(静态工厂方法&实例工厂方法).FactoryBean -- ...
- [Spring学习笔记 4 ] AOP 概念原理以及java动态代理
一.Spring IoC容器补充(1) Spring IoC容器,DI(依赖注入): 注入的方式:设值方法注入setter(属性注入)/构造子注入(构造函数传入依赖的对象)/字段注入Field(注解) ...
- Spring学习笔记2—AOP
1.AOP概念 AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming):面向切面编程,AOP能够将那些与业务无关,却为业务模块所共同调用的应用(例如事务处理.日志管理.权限控制等)封装起来, ...
- Spring听课笔记(专题一)
Spring入门课程:https://www.imooc.com/learn/196 第0章: Spring是为解决企业应用程序开发复杂性而创建的一个Java开源框架,应用非常广泛.业内非常流行的SS ...
- Spring学习笔记之AOP配置篇(一)
[TOC] 1. 创建并声明一个切面 首先,创建一个类,添加@Component注解使其添加到IoC容器 然后,添加@Aspect注解,使其成为一个切面 最后,在配置文件里面,使用<aop:as ...
- Spring听课笔记(专题二下)
第4章 Spring Bean基于注解的装配 4.1 Bean的定义及作用域的注解实现 1. Bean定义的注解 -- @Component是一个通用注解,可用于任何bean -- @Reposito ...
随机推荐
- Echarts数据可视化,easyshu图表集成。
介绍: ECharts,一个使用 JavaScript 实现的开源可视化库,可以流畅的运行在 PC 和移动设备上,兼容当前绝大部分浏览器(IE8/9/10/11,Chrome,Firefox,Sa ...
- linux学习之--虚拟机安装linux【centerOS】
计划把学习中的软件安装使用记录下来,以下是使用VMware 按照 Linux 使用桥接网络虚拟机和windows中都有不同的ip地址
- SpringBoot异常处理(一)
ERROR:严重问题,我们无法处理 EXCEPTION:RuntimeException 编译期不检查,出现问题需要我们修改代码 非RuntimeException(CheckedExceptio ...
- Spark学习进度-RDD
RDD RDD 是什么 定义 RDD, 全称为 Resilient Distributed Datasets, 是一个容错的, 并行的数据结构, 可以让用户显式地将数据存储到磁盘和内存中, 并能控制数 ...
- Ubuntu无法ssh远程连接问题 (转)
[系统]Ubuntu 12.04 server [问题描述]新安装的Ubuntu系统无法直接通过ssh远程连接. [解决办法] 新安装的Ubuntu系统并未安装ssh-server服务,需要自行安装, ...
- (开源项目)abattoir unity游戏
(开源项目)abattoir unity游戏 欢迎各位的改进和提议! 名称: abattoir(角斗场) 版本: v1.0 作者: N-n-N(笔者) 简介: 添加娱乐(冲撞)模式和普通(一般)模式 ...
- 如何使用蓝湖设计稿同时适配PC及移动端
如何使用蓝湖设计稿同时适配PC及移动端 项目需求: 一套代码同时适配PC及移动端 方案: pc端采用px布局,移动端采用rem布局,通过媒体查询(media query)切换 坑: 尝试过使用post ...
- FastApi 进阶
前言 终于有了第一个使用 FastApi 编写的线上服务, 在开发的过程中还是遇到了些问题, 这里记录一下 正文 目录结构 我们知道, FastApi 的启动方式推荐使用 uvicorn, 其启动方式 ...
- 【SpringMVC】SpringMVC 响应数据
SpringMVC 响应数据 文章源码 返回值分类 返回值是字符串 Controller 方法返回字符串可以指定逻辑视图的名称,通过视图解析器解析为物理视图的地址. @Controller @Requ ...
- python模块详解 | shutil
简介: shutil是python的一个内置模块,提供了许多关于文件和文件集合的高级操作,特别提供文件夹与文件操作.归档操作了支持文件复制和删除的功能. 文件夹与文件操作: copyfileobj(f ...
