HDU 4780 Candy Factory(拆点费用流)
There are N candies need to be produced. These candies are also numbered from 1 to N. For each candy i , it can be produced in any machine j. It also has a producing time(si,ti) , meaning that candy i must start producing at time si and will finish at ti. Otherwise if the start time is pi(si < pi < ti) then candy will still finish at ti but need additional K*(pi - si) cost. The candy can’t be produced if pi is greater than or equal to ti. Of course one machine can only produce at most one candy at a time and can’t stop once start producing.
On the other hand, at time 0 all the machines are in their initial state and need to be “set up” or changed before starting producing. To set up Machine j from its initial state to the state which is suitable for producing candiy i, the time required is Cij and cost is Dij. To change a machine from the state suitable for candy i1 into the state suitable for candy i2, time required is Ei1i2 and cost is Fi1i2.
As the manager of the factory you have to make a plan to produce all the N candies. While the sum of producing cost should be minimized.
For each case, the first line contains three integers N(1<=N<=100), M(1<=M<=100), K(1<=K<=100) . The meaning is described above.
Then N lines follow, each line contains 2 integers si and ti(0 <= si < ti <100000).
Then N lines follow, each line contains M integers, the j-th integer of the i-th line indicating Cij(1<=Cij<=100000) .
Then N lines follow, each line contains M integers, the j-th integer of the i-th line indicating Dij(1<=Dij<=100000) .
Then N lines follow, each line contains N integers, the i2-th integer of the i1-th line indicating Ei1i2(1<=Ei1j2<=100000) .
Then N lines follow, each line contains N integers, the i2-th integer of the i1-th line indicating Fi1i2(1 <= Fi1j2<=100000) .
Since the same candy will only be produced once, Eii and Fii are meaningless and will always be -1.
The input ends by N=0 M=0 K=0. Cases are separated with a blank line.
4 7
2 4
8 9
4 4
3 3
3 3
2 8
12 3
14 6
-1 1 1
1 -1 1
1 1 -1
-1 5 5
5 -1 5
5 5 -1
1 1 2
1 5
5
5
-1
-1
0 0 0
-1
For the first example, the answer can be achieved in the following way: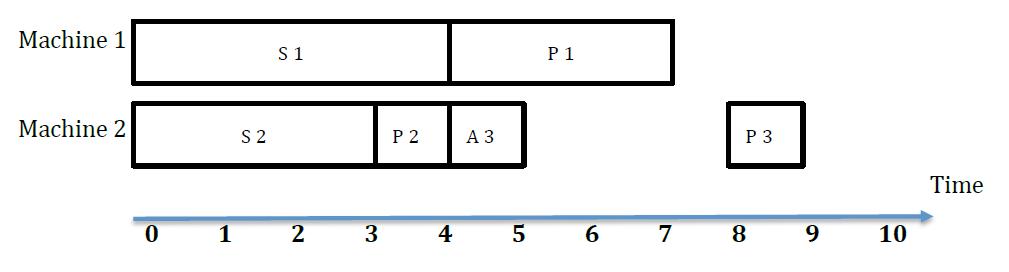
In the picture, S i represents setting up time for candy i, A i represents changing time for candy i and P i represents producing time for candy i .
So the total cost includes:
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std; const int N=1e5+;
const int M=2e5+;
const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f; int FIR[N],FROM[M],TO[M],CAP[M],FLOW[M],COST[M],NEXT[M],tote;
int pre[N],dist[N],q[];
bool vis[N];
int n,m,S,T;
void init()
{
tote=;
memset(FIR,-,sizeof(FIR));
}
void addEdge(int u,int v,int cap,int cost)
{
FROM[tote]=u;
TO[tote]=v;
CAP[tote]=cap;
FLOW[tote]=;
COST[tote]=cost;
NEXT[tote]=FIR[u];
FIR[u]=tote++; FROM[tote]=v;
TO[tote]=u;
CAP[tote]=;
FLOW[tote]=;
COST[tote]=-cost;
NEXT[tote]=FIR[v];
FIR[v]=tote++;
}
bool SPFA(int s, int t)
{
memset(dist,INF,sizeof(dist));
memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis));
memset(pre,-,sizeof(pre));
dist[s] = ;vis[s]=true;q[]=s;
int head=,tail=;
while(head!=tail)
{
int u=q[++head];vis[u]=false;
for(int v=FIR[u];v!=-;v=NEXT[v])
{
if(dist[TO[v]]>dist[u]+COST[v]&&CAP[v]>FLOW[v])
{
dist[TO[v]]=dist[u]+COST[v];
pre[TO[v]]=v;
if(!vis[TO[v]])
{
vis[TO[v]] = true;
q[++tail]=TO[v];
}
}
}
}
return pre[t]!=-;
}
void MCMF(int s, int t, int &cost, int &flow)
{
flow=;
cost=;
while(SPFA(s,t))
{
int Min=INF;
for(int v=pre[t];v!=-;v=pre[TO[v^]])
Min=min(Min,CAP[v]-FLOW[v]);
for(int v=pre[t];v!=-;v=pre[TO[v^]])
{
FLOW[v]+=Min;
FLOW[v^]-=Min;
cost+=COST[v]*Min;
}
flow+=Min;
}
}
int main()
{
int N,M,K,u,ss[],tt[],C[][],D[][],E[][],F[][];
while(scanf("%d%d%d",&N,&M,&K)!=EOF,N||M||K)
{
init();
for(int i=;i<=N;i++)
scanf("%d%d",&ss[i],&tt[i]);
for(int i=;i<=N;i++)for(int j=;j<=M;j++)
scanf("%d",&C[i][j]);
for(int i=;i<=N;i++)for(int j=;j<=M;j++)
scanf("%d",&D[i][j]);
for(int i=;i<=N;i++)for(int j=;j<=N;j++)
scanf("%d",&E[i][j]);
for(int i=;i<=N;i++)for(int j=;j<=N;j++)
scanf("%d",&F[i][j]); S=,u=N+N+M+,T=N+N++M+,n=T;
for(int i=;i<=N;i++)
{
addEdge(S,i,,);
addEdge(N+i,T,,);
for(int j=;j<=N;j++)
{
if(i!=j&&tt[i]+E[i][j]<tt[j])
{
int c=(max(tt[i]+E[i][j],ss[j])-ss[j])*K;
addEdge(i,N+j,,c+F[i][j]);
}
}
}
addEdge(S,u,M,);
for(int i=;i<=M;i++)
{
addEdge(u,N+N+i,,);
for(int j=;j<=N;j++)
{
if(C[j][i]<tt[j])
{
int c=(max(C[j][i],ss[j])-ss[j])*K;
addEdge(N+N+i,N+j,,c+D[j][i]);
}
}
}
int flow,cost;
MCMF(S,T,cost,flow);
if(flow!=N)printf("-1\n");
else printf("%d\n",cost);
}
return ;
}
HDU 4780 Candy Factory(拆点费用流)的更多相关文章
- HDU 4780 Candy Factory
Candy Factory Time Limit: 2000ms Memory Limit: 32768KB This problem will be judged on HDU. Original ...
- BZOJ 1877 晨跑 拆点费用流
题目链接: https://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=1877 题目大意: Elaxia最近迷恋上了空手道,他为自己设定了一套健身计划,比如俯卧 ...
- CF 277E Binary Tree on Plane (拆点 + 费用流) (KM也可做)
题目大意: 平面上有n个点,两两不同.现在给出二叉树的定义,要求树边一定是从上指向下,即从y坐标大的点指向小的点,并且每个结点至多有两个儿子.现在让你求给出的这些点是否能构成一棵二叉树,如果能,使二叉 ...
- HDU 5988 Coding Contest(浮点数费用流)
http://acm.split.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5988 题意:在acm比赛的时候有多个桌子,桌子与桌子之间都有线路相连,每个桌子上会有一些人和一些食物 ...
- HDU 4744 Starloop System(ZKW费用流)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4744 题意:三维空间n个点,每个点有一个wi值.每对点的距离定义为floor(欧拉距离),每对点之间建 ...
- HDU 5644 King's Pliot【费用流】
题目链接: http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=5644 题意: 每天都有p[i]个飞行员进行阅兵,飞行员只工作一天. m个休假公式,花费tt[i]元让 ...
- 【拆点费用流】【HDU1853】【 Cyclic Tour】
题意: 有N个城市,M条单向路,Tom想环游全部城市,每次至少环游2个城市,每个城市只能被环游一次.由于每条单向路都有长度,要求游遍全部城市的最小长度. // 给定一个有向图,必须用若干个环来覆盖整个 ...
- 洛谷P2604 网络扩容 拆点+费用流
原题链接 这题貌似比较水吧,最简单的拆点,直接上代码了. #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define N 1000 #def ...
- HDU - 2732 Leapin' Lizards (拆点最大流)
题意:有N*M的矩形,每个格点有一个柱子,每根柱子有高度c,允许蜥蜴经过这根柱子c次,开始有一些蜥蜴在某些柱子上,它们要跳出这个矩形,每步最大能跳d个单位,求最少有多少蜥蜴不能跳出这个矩形. 分析:转 ...
随机推荐
- 记一次Chrome冒充QQ浏览器领取奖励之行
DNF游戏十周年活动,但是看到活动页面竟然是QQ浏览器专属活动,可是对于QQ浏览器,我内心是拒绝的,所以本着能不下载就不下载的原则,当然是选择放弃它了..... 开玩笑,看到这一活动,虽然奖励不高 ...
- CRM项目之stark组件
. stark也是一个app(用startapp stark创建),目标时把这个做成一个可以拔插的组件 . setting文件下INSTALLED_APPS 路径要配置好(app的注册) . 写好si ...
- C++ 是 编程界 的 背锅侠
C++ 是 编程界 的 背锅侠, C++ 背的包袱 之 庞大复杂, 举世瞩目, 令人感动 . C++ 标准 委员会 俨然 已成了一个 职业 . C++ 把 静态编译 体系 发展到 庞大复杂, C ...
- nginx实现按日期进行日志分割
1:nginx的访问日志按日期分割,也就是每天的零点把前一天的访问日志以日期的形式备份,然后重新打开一份访问日志,这里的kill -USR1 $pid 重新打开访问日志,必须得把原来的mv,如果存在的 ...
- LDAP学习总结
一.简介: LDAP(Light Directory Access Portocol),它是基于X.500标准的轻量级目录访问协议.目录是一个为查询.浏览和搜索而优化的数据库,它成树状结构组织数据,类 ...
- Azure VMSS (1) 入门
<Windows Azure Platform 系列文章目录> 在使用云计算服务的时候,我们经常需要有自动横向扩展的功能.比如: 1.在业务高峰期,根据负载的增加,自动打开若干台VM 2. ...
- Android Dialog.dismiss()与Activity.finish()顺序
activity.finish() 和dialog.show() 同时调用的时候, 需要先调用dialog.dismiss() 后activity.finish() 如果先直接finish()后,再触 ...
- Bootstrap 插件收集
Bootstrap-Mutilselect 将下拉选项扩展支持多选以及多种选择方式 http://davidstutz.de/bootstrap-multiselect/ Bootstrap Sel ...
- [sharepoint]Rest api相关知识(转)
写在前面 最近又开始弄rest api了,通过sharepoint rest api获取站点信息,Items,fields非常方便,再结合OData查询,更是得心应手.这里记录学习的时候用到的知识点, ...
- 实验五:Xen环境下多虚拟机的桥接配置
实验名称: Xen环境下多虚拟机的桥接配置 实验环境: 这里我们首先需要有一台已经安装好的虚拟机机,能够正常运行,且网卡正常,如下图: 实验需求: 进行虚拟机的复制,并添加新的网桥配置,然后将两台虚拟 ...
