[matlab] 7.快速搜索随机树(RRT---Rapidly-exploring Random Trees) 路径规划
RRT是一种多维空间中有效率的规划方法。它以一个初始点作为根节点,通过随机采样增加叶子节点的方式,生成一个随机扩展树,当随机树中的叶子节点包含了目标点或进入了目标区域,便可以在随机树中找到一条由从初始点到目标点的路径。RRT方法是概率完备且不最优的。
function BuildRRT(qinit, K, Δq)
T.init(qinit)
for k = 1 to K
qrand = Sample() -- chooses a random configuration
qnearest = Nearest(T, qrand) -- selects the node in the RRT tree that is closest to qrand
if Distance(qnearest, qgoal) < Threshold then
return true
qnew = Extend(qnearest, qrand, Δq) -- moving from qnearest an incremental distance in the direction of qrand
if qnew ≠ NULL then
T.AddNode(qnew)
return false function Sample() -- Alternatively,one could replace Sample with SampleFree(by using a collision detection algorithm to reject samples in C_obstacle
p = Random(0, 1.0)
if 0 < p < Prob then
return qgoal
elseif Prob < p < 1.0 then
return RandomNode()
RRT 伪代码
初始化时随机树T只包含一个节点:根节点qinit。首先Sample函数从状态空间中随机选择一个采样点qrand(4行);然后Nearest函数从随机树中选择一个距离qrand最近的节点qnearest(5行);最后Extend函数通过从qnearest向qrand扩展一段距离,得到一个新的节点qnew(8行)。如果qnew与障碍物发生碰撞,则Extend函数返回空,放弃这次生长,否则将qnew加入到随机树中。重复上述步骤直到qnearest和目标点qgaol距离小于一个阈值,则代表随机树到达了目标点,算法返回成功(6~7行)。为了使算法可控,可以设定运行时间上限或搜索次数上限(3行)。如果在限制次数内无法到达目标点,则算法返回失败。
为了加快随机树到达目标点的速度,简单的改进方法是:在随机树每次的生长过程中,根据随机概率来决定qrand是目标点还是随机点。在Sample函数中设定参数Prob,每次得到一个0到1.0的随机值p,当0<p<Prob的时候,随机树朝目标点生长行;当Prob<p<1.0时,随机树朝一个随机方向生长。
上述算法的效果是随机采样点会“拉着”树向外生长,这样能更快、更有效地探索空间(The effect is that the nearly uniformly distributed samples “pull” the tree toward them, causing the tree to rapidly explore C-Space)。随机探索也讲究策略,如果我们从树中随机取一个点,然后向着随机的方向生长,那么结果是什么样的呢?见下图(Left: A tree generated by applying a uniformly-distributed random motion from a randomly chosen tree node does not explore very far. Right: A tree generated by the RRT algorithm using samples drawn randomly from a uniform distribution. Both trees have 2000 nodes )。可以看到,同样是随机树,但是这棵树并没很好地探索空间。


下面是具体的代码
%% RRT parameters
map=im2bw(imread('map.bmp')); % input map read from a bmp file. for new maps write the file name here
source=[490 490]; % source position in Y, X format
goal=[10 900]; % goal position in Y, X format
stepsize = 20; % size of each step of the RRT
threshold = 20; % nodes closer than this threshold are taken as almost the same
maxFailedAttempts = 10000;
display = true; % display of RRT if ~feasiblePoint(source,map), error('source lies on an obstacle or outside map'); end
if ~feasiblePoint(goal,map), error('goal lies on an obstacle or outside map'); end
if display,imshow(map);rectangle('position',[1 1 size(map)-1],'edgecolor','k'); end tic; % tic-toc: Functions for Elapsed Time RRTree = double([source -1]); % RRT rooted at the source, representation node and parent index
failedAttempts = 0;
counter = 0;
pathFound = false; while failedAttempts <= maxFailedAttempts % loop to grow RRTs
%% chooses a random configuration
if rand < 0.5
sample = rand(1,2) .* size(map); % random sample
else
sample = goal; % sample taken as goal to bias tree generation to goal
end %% selects the node in the RRT tree that is closest to qrand
[A, I] = min( distanceCost(RRTree(:,1:2),sample) ,[],1); % find the minimum value of each column
closestNode = RRTree(I(1),1:2); %% moving from qnearest an incremental distance in the direction of qrand
theta = atan2(sample(1)-closestNode(1),sample(2)-closestNode(2)); % direction to extend sample to produce new node
newPoint = double(int32(closestNode(1:2) + stepsize * [sin(theta) cos(theta)]));
if ~checkPath(closestNode(1:2), newPoint, map) % if extension of closest node in tree to the new point is feasible
failedAttempts = failedAttempts + 1;
continue;
end if distanceCost(newPoint,goal) < threshold, pathFound = true; break; end % goal reached [A, I2] = min( distanceCost(RRTree(:,1:2),newPoint) ,[],1); % check if new node is not already pre-existing in the tree
if distanceCost(newPoint,RRTree(I2(1),1:2)) < threshold, failedAttempts = failedAttempts + 1; continue; end RRTree = [RRTree; newPoint I(1)]; % add node
failedAttempts = 0;
if display, line([closestNode(2);newPoint(2)],[closestNode(1);newPoint(1)]);counter = counter + 1; M(counter) = getframe; end % Capture movie frame
end % getframe returns a movie frame, which is a structure having two fields
if display && pathFound, line([closestNode(2);goal(2)],[closestNode(1);goal(1)]); counter = counter+1;M(counter) = getframe; end if display, disp('click/press any key'); waitforbuttonpress; end
if ~pathFound, error('no path found. maximum attempts reached'); end %% retrieve path from parent information
path = [goal];
prev = I(1);
while prev > 0
path = [RRTree(prev,1:2); path];
prev = RRTree(prev,3);
end pathLength = 0;
for i=1:length(path)-1, pathLength = pathLength + distanceCost(path(i,1:2),path(i+1,1:2)); end % calculate path length
fprintf('processing time=%d \nPath Length=%d \n\n', toc, pathLength);
imshow(map);rectangle('position',[1 1 size(map)-1],'edgecolor','r');
line(path(:,2),path(:,1));
rrt_main.m
%% distanceCost.m
function h=distanceCost(a,b)
h = sqrt(sum((a-b).^2, 2));
distanceCost.m
%% checkPath.m
function feasible=checkPath(n,newPos,map)
feasible=true;
dir=atan2(newPos(1)-n(1),newPos(2)-n(2));
for r=0:0.5:sqrt(sum((n-newPos).^2))
posCheck=n+r.*[sin(dir) cos(dir)];
if ~(feasiblePoint(ceil(posCheck),map) && feasiblePoint(floor(posCheck),map) && ...
feasiblePoint([ceil(posCheck(1)) floor(posCheck(2))],map) && feasiblePoint([floor(posCheck(1)) ceil(posCheck(2))],map))
feasible=false;break;
end
if ~feasiblePoint(newPos,map), feasible=false; end
end
checkPath.m
%% feasiblePoint.m
function feasible=feasiblePoint(point,map)
feasible=true;
% check if collission-free spot and inside maps
if ~(point(1)>=1 && point(1)<=size(map,1) && point(2)>=1 && point(2)<=size(map,2) && map(point(1),point(2))==1)
feasible=false;
end
feasiblePoint.m
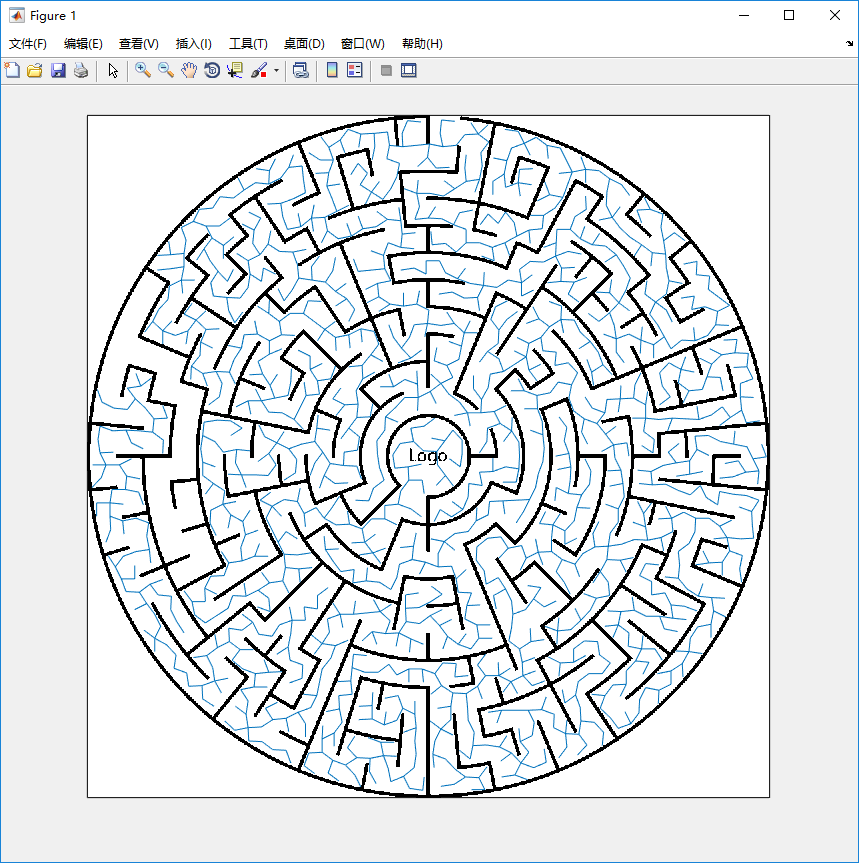
结果如图
[matlab] 7.快速搜索随机树(RRT---Rapidly-exploring Random Trees) 路径规划的更多相关文章
- matlab练习程序(快速搜索随机树RRT)
RRT快速搜索随机树英文全称Rapid-exploration Random Tree,和PRM类似,也是一种路径规划算法. 和PRM类似,算法也需要随机撒点,不过不同的是,该算法不是全局随机撒点,而 ...
- [python] RRT快速拓展随机树
""" version1.1,2018-05-09 <基于智能优化与RRT算法的无人机任务规划方法研究>博士论文 <基于改进人工势场法的路径规划算法研究 ...
- RRT路径规划算法(matlab实现)
基于快速扩展随机树(RRT / rapidly exploring random tree)的路径规划算法,通过对状态空间中的采样点进行碰撞检测,避免了对空间的建模,能够有效地解决高维空间和复杂约束的 ...
- RRT路径规划算法
传统的路径规划算法有人工势场法.模糊规则法.遗传算法.神经网络.模拟退火算法.蚁群优化算法等.但这些方法都需要在一个确定的空间内对障碍物进行建模,计算复杂度与机器人自由度呈指数关系,不适合解决多自由度 ...
- 「干货」面试官问我如何快速搜索10万个矩形?——我说RBush
「干货」面试官问我如何快速搜索10万个矩形?--我说RBUSH 前言 亲爱的coder们,我又来了,一个喜欢图形的程序员,前几篇文章一直都在教大家怎么画地图.画折线图.画烟花,难道图形就是这样嘛,当 ...
- 使用脚本自动配置matlab安装libsvm和随机森林工具箱
前言 支持向量机(SVM)和随机森林 都是用于分类的机器学习算法. 这里我需要对网上的工具箱在matlab中进行配置. 效果演示: 1.双击运行“自动配置.bat” 2.matlab会自动启动,手动配 ...
- 为什么要进行傅立叶变换?傅立叶变换究竟有何意义?如何用Matlab实现快速傅立叶变换
写在最前面:本文是我阅读了多篇相关文章后对它们进行分析重组整合而得,绝大部分内容非我所原创.在此向多位原创作者致敬!!!一.傅立叶变换的由来关于傅立叶变换,无论是书本还是在网上可以很容易找到关于傅立叶 ...
- 修正magento快速搜索返回结果不准确
有时候发现用magento的mini 快速搜索搜出来的结果一点都不准确,跟实际结果相差甚大,这里发现修改一个地方即可修复这个问题. 打开app/code/core/Mage/CatalogSearch ...
- 【阿里云产品公测】大数据下精确快速搜索OpenSearch
[阿里云产品公测]大数据下精确快速搜索OpenSearch 作者:阿里云用户小柒2012 相信做过一两个项目的人都会遇到上级要求做一个类似百度或者谷歌的站内搜索功能.传统的sql查询只能使用like ...
随机推荐
- GA中的术语及经常分析的指标
GA中的术语 跳出客流:只浏览了网站的一个页面,并且没有进一步动作的访客目标转化:通常缩写为目标或转化,这是网站上面的一个预期或动作,通常被认为比标准网页更有价值,例如:"确认购买" ...
- phpstudy 产生You don't have permission to access / on this server.解决
phpstudy配置好访问目录时候有时候会产生You don't have permission to access / on this server. 解决办法: 修改服务器httpd.conf配置 ...
- JavaScript中判断整字类型最简洁的实现方法
这篇文章主要介绍了JavaScript中判断整字类型最简洁的实现方法,本文给出多个判断整数的方法,最后总结出一个最短.最简洁的实现方法,需要的朋友可以参考下 我们知道JavaScript提供了type ...
- module.js:549 throw err;
解决方法: 1.有可能是拼写错误 2.未明原因. (1)删除 node_modules 文件夹 (2)cnpm cache clean,不过提示错误就用 cnpm cache clean --forc ...
- 2018-08-06 在Office的VBA代码里中文命名
在Excel处理数据时, 顺便试了一下VBA代码编辑器里输入中文, 结果显示为乱码. 查了一下发现VBA本身支持Unicode, 但需要设置系统配置使编辑器能够正常显示, 即设置简体中文为Curren ...
- iPhone X手机投屏电脑无线连接教程
iPhone X手机是一款非常有气场的手机,独特的设计,展现手机的独特魅力,手机外观让人一眼就爱上,手感也是超级的舒适,真的是堪称完美,但是iPhone X手机投屏电脑怎么无线连接呢? 使用工具: 电 ...
- ACL技术总结
1.ACL的全称是访问控制列表,本质上是定义一组策略,以便指导报文在交换机内部的转发行为. 2.要配置策略,首先要明确ACL应用的对象,可以是针对端口,也可以是针对特殊的一条流. 针对端口,就是指端口 ...
- PyCharm 在PyCharm中使用GitHub
PyCharm是当前进行Python开发,尤其是Django开发最好的IDE,GitHub是程序员的圣地,几乎人人都在用,就不详细介绍两者了. 本文假设你对PyCharm和Github都有一定的了解, ...
- Linux中Root密码破解
1.开机后在选择菜单时按下e进入编辑模式 2.选择linux16这一行,在行末尾添加 rd.break 3.然后Ctrl+x执行.然后进入shell界面: 4.设置密码: 1.重新挂载根目录为读写模式 ...
- ssh-keygen的学习总结
ssh-keygen介绍 维基百科上关于ssh-keygen的介绍如下: ssh-keygen is a standard component of the Secure Shell (S ...
