009.Ansible模板管理 Jinja2
一 Jinja2简介
Jinja2是基于python的模板引擎。
假设说现在我们需要一次性在10台主机上安装redis,这个通过playbook现在已经很容易实现。默认情况下,所有的redis安装完成之后,我们可以统一为其分发配置文件。这个时候就面临一个问题,这些redis需要监听的地址各不相同,我们也不可能为每一个redis单独写一个配置文件。因为这些配置文件中,绝大部分的配置其实都是相同的。这个时候最好的方式其实就是用一个通用的配置文件来解决所有的问题。将所有需要修改的地方使用变量替换
二 模板使用
playbook使用template模块来实现模板文件的分发,其用法与copy模块基本相同,唯一的区别是,copy模块会将原文件原封不动的复制到被控端,而template会将原文件复制到被控端,并且使用变量的值将文件中的变量替换以生成完整的配置文件。
2.1 redis模板配置
创建一个模板目录
[root@node1 ansible]# mkdir template
为了方便区分,模板文件最好使用.j2结尾,就知道是模板文件,在复制时需要使用template模块
[root@node1 ansible]# vim template/redis.conf.j2
daemonize yes
pidfile /var/run/redis.pid
port
logfile "/var/log/redis/redis.log"
dbfilename dump.rdb
dir /data/redis maxmemory {{redismem }} bind {{ ansible_ens33.ipv4.address }} 127.0.0.1 timeout
loglevel notice databases
save
save
save rdbcompression yes maxclients
appendonly yes
appendfilename appendonly.aof
appendfsync everysec
[root@node1 ansible]# vim redis_config.yml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: set redis-server
set_fact: redismem="{{ ansible_memtotal_mb/2|int }}"
- name: install redis
yum:
name: redis
state: present
- name: ensure sest direectory exists
file:
path: "{{ item }}"
state: directory
mode:
recurse: yes
owner: redis
group: redis
with_items:
- "/var/log/redis"
- "/data/redis"
- name: cp redis.conf to /etc
template:
src: template/redis.conf.j2
dest: /etc/redis.conf
mode:
notify: restart redis
- name: start redis
systemd:
name: redis
state: restarted
handlers:
- name: restart redis
systemd:
name: redis
state: restarted
关于template模块的更多参数说明:
- backup:如果原目标文件存在,则先备份目标文件
- dest:目标文件路径
- force:是否强制覆盖,默认为yes
- group:目标文件属组
- mode:目标文件的权限
- owner:目标文件属主
- src:源模板文件路径
- validate:在复制之前通过命令验证目标文件,如果验证通过则复制
执行
[root@node1 ansible]# ansible-playbook redis_config.yml
PLAY [all] ************************************************************************************************************************************ TASK [set redis-server] ***********************************************************************************************************************
ok: [demo4.example.com]
ok: [demo5.example.com]
ok: [demo1.example.com]
ok: [demo2.example.com]
ok: [demo3.example.com] TASK [install redis] **************************************************************************************************************************
ok: [demo5.example.com]
ok: [demo2.example.com]
ok: [demo3.example.com]
ok: [demo1.example.com]
ok: [demo4.example.com] TASK [ensure sest direectory exists] **********************************************************************************************************
changed: [demo1.example.com] => (item=/var/log/redis)
changed: [demo5.example.com] => (item=/var/log/redis)
changed: [demo2.example.com] => (item=/var/log/redis)
changed: [demo3.example.com] => (item=/var/log/redis)
changed: [demo4.example.com] => (item=/var/log/redis)
changed: [demo5.example.com] => (item=/data/redis)
changed: [demo2.example.com] => (item=/data/redis)
changed: [demo1.example.com] => (item=/data/redis)
changed: [demo3.example.com] => (item=/data/redis)
changed: [demo4.example.com] => (item=/data/redis) TASK [cp redis.conf to /etc] ******************************************************************************************************************
ok: [demo1.example.com]
ok: [demo4.example.com]
ok: [demo5.example.com]
ok: [demo3.example.com]
ok: [demo2.example.com] TASK [start redis] ****************************************************************************************************************************
changed: [demo5.example.com]
changed: [demo1.example.com]
changed: [demo4.example.com]
changed: [demo2.example.com]
changed: [demo3.example.com] PLAY RECAP ************************************************************************************************************************************
demo1.example.com : ok= changed= unreachable= failed= skipped= rescued= ignored=
demo2.example.com : ok= changed= unreachable= failed= skipped= rescued= ignored=
demo3.example.com : ok= changed= unreachable= failed= skipped= rescued= ignored=
demo4.example.com : ok= changed= unreachable= failed= skipped= rescued= ignored=
demo5.example.com : ok= changed= unreachable= failed= skipped= rescued= ignored=
[root@node1 ansible]# ansible all -m shell -a "cat /etc/redis.conf|grep bind"
demo2.example.com | CHANGED | rc= >>
bind 192.168.132.132 127.0.0.1
demo1.example.com | CHANGED | rc= >>
bind 192.168.132.131 127.0.0.1
demo3.example.com | CHANGED | rc= >>
bind 192.168.132.133 127.0.0.1
demo5.example.com | CHANGED | rc= >>
bind 192.168.132.135 127.0.0.1
demo4.example.com | CHANGED | rc= >>
bind 192.168.132.134 127.0.0.1
使用条件判断
2.2 条件语句
在上面的示例中,我们直接取了被控节点的ens33网卡的ip作为其监听地址。那么假如有些机器的网卡是bond0,这种做法就会报错。这个时候我们就需要在模板文件中定义条件语句如下:
[root@node1 ansible]# cat template/redis.conf.j2
daemonize yes
pidfile /var/run/redis.pid
port
logfile "/var/log/redis/redis.log"
dbfilename dump.rdb
dir /data/redis maxmemory {{redismem }}
{% if ansible_bond0 is defined %}
bind {{ ansible_bind0.ipv4.address }} 127.0.0.1
{% elif ansible_ens33 is defined %}
bind {{ ansible_ens33.ipv4.address }} 127.0.0.1
{% else %}
bind 0.0.0.0
{% endif %}
timeout
loglevel notice databases
save
save
save rdbcompression yes maxclients
appendonly yes
appendfilename appendonly.aof
appendfsync everysec
You have new mail in /var/spool/mail/root
让redis主从角色都可以使用该文件:
配置主从条件
[root@node1 ansible]# vim inventory
[redis]
demo3.example.com
demo4.example.com masterip=demo3.example.com
模板文件
[root@node1 ansible]# vim template/redis.conf.j2
daemonize yes
pidfile /var/run/redis.pid
port
logfile "/var/log/redis/redis.log"
dbfilename dump.rdb
dir /data/redis maxmemory {{redismem }}
{% if ansible_bond0 is defined %}
bind {{ ansible_bind0.ipv4.address }} 127.0.0.1
{% elif ansible_ens33 is defined %}
bind {{ ansible_ens33.ipv4.address }} 127.0.0.1
{% else %}
bind 0.0.0.0
{% endif %} {% if masterip is defined %}
slaveof {{ masterip }} {{ materport|default() }}
{% endif %}
timeout
loglevel notice databases
save
save
save rdbcompression yes maxclients
appendonly yes
appendfilename appendonly.aof
appendfsync everysec
[root@node1 ansible]# vim redis_config.yml
- hosts: redis
tasks:
- name: set redis-server
set_fact: redismem="{{ ansible_memtotal_mb/2|int }}"
- name: install redis
yum:
name: redis
state: present
- name: ensure sest direectory exists
file:
path: "{{ item }}"
state: directory
mode:
recurse: yes
owner: redis
group: redis
with_items:
- "/var/log/redis"
- "/data/redis"
- name: cp redis.conf to /etc
template:
src: template/redis.conf.j2
dest: /etc/redis.conf
mode:
notify: restart redis
- name: start redis
systemd:
name: redis
state: restarted
handlers:
- name: restart redis
systemd:
name: redis
state: restarted
节点查看
[root@node4 ~]# redis-cli -h 127.0.0.1 -p
127.0.0.1:> info replication
# Replication
role:slave
master_host:demo3.example.com
master_port:
master_link_status:up
master_last_io_seconds_ago:
master_sync_in_progress:
slave_repl_offset:
slave_priority:
slave_read_only:
connected_slaves:
master_repl_offset:
repl_backlog_active:
repl_backlog_size:
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:
repl_backlog_histlen:
[root@node3 ~]# redis-cli -h 127.0.0.1 -p
127.0.0.1:> info replication
# Replication
role:master
connected_slaves:1
slave0:ip=192.168.132.134,port=6379,state=online,offset=421,lag=0
master_repl_offset:
repl_backlog_active:
repl_backlog_size:
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:
repl_backlog_histlen:
2.3 jinj2的循环语句
现在把proxy主机组中的主机作为代理服务器,安装nginx做反向代理,将请求转发至后面的两台webserver,即webserver组的服务器。
[root@node1 ansible]# vim inventory
[webserver]
demo1.example.com
demo2.example.com
demo3.example.com [proxy]
demo5.example.com [redis]
demo3.example.com
demo4.example.com masterip=demo3.example.com
[root@node1 ansible]# vim systeminit.yml
- hosts: all
tasks:
- name: ipatbles flush filter
iptables:
chain: "{{ item }}"
flush: yes
with_items: ['INPUT','FORWARD','OUTPUT']
[root@node1 ansible]# ansible-playbook systeminit.yml
部署httpd
[root@node1 ansible]# vim config_httpd.yml
- hosts: webserver
tasks:
- name: install httpd
yum:
name: httpd
state: present
- name: start httpd
systemd:
name: httpd
state: started
enabled: yes
daemon_reload: yes
[root@node1 ansible]# ansible-playbook config_httpd.yml
配置nginxproxy
[root@node1 ansible]# vim config_proxy.yml
- name: gather facts #这里需要配置缓存,触发setup,把facts参数缓存到本地,否则在下面获取到的fact将是nginx proxy的fact值,就不会有结果
gather_facts: False
hosts: webserver
tasks:
- name: gather facts
setup:
- name: Configue Nginx
hosts: proxy
tasks:
- name: install nginx
yum:
name: nginx
state: present
- name: copy nginx.conf to dest
template:
src: template/nginx.conf.j2
dest: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
notify: reload nginx
- name: start nginx
systemd:
name: nginx
enabled: yes
daemon_reload: yes
handlers:
- name: reload nginx
systemd:
name: nginx
state: reloaded
[root@node1 ansible]# vim template/nginx.conf.j2
user nginx;
worker_processes {{ ansible_processor_vcpus }};
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /var/run/nginx.pid;
include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf;
events {
worker_connections 65535;
use epoll;
}
http {
map $http_x_forwarded_for $clientRealIP {
"" $remote_addr;
~^(?P<firstAddr>[0-9\.]+),?.*$ $firstAddr;
}
log_format real_ip '{ "datetime": "$time_local", '
'"remote_addr": "$remote_addr", '
'"source_addr": "$clientRealIP", '
'"x_forwarded_for": "$http_x_forwarded_for", '
'"request": "$request_uri", '
'"status": "$status", '
'"request_method": "$request_method", '
'"request_length": "$request_length", '
'"body_bytes_sent": "$body_bytes_sent", '
'"request_time": "$request_time", '
'"http_referrer": "$http_referer", '
'"user_agent": "$http_user_agent", '
'"upstream_addr": "$upstream_addr", '
'"upstream_status": "$upstream_status", '
'"upstream_http_header": "$upstream_http_host",'
'"upstream_response_time": "$upstream_response_time", '
'"x-req-id": "$http_x_request_id", '
'"servername": "$host"'
' }';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log real_ip;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; upstream web {
{% for host in groups['webserver'] %}
{% if hostvars[host]['ansible_bond0']['ipv4']['address'] is defined %}
server {{ hostvars[host]['ansible_bond0']['ipv4']['address'] }}:80;
{% elif hostvars[host]['ansible_ens33']['ipv4']['address'] is defined %}
server {{ hostvars[host]['ansible_ens33']['ipv4']['address'] }}:80;
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
}
server {
listen 80 default_server;
server_name _;
location / {
proxy_pass http://web;
}
}
}
执行验证
[root@node1 ansible]# ansible-playbook config_proxy.yml
[root@node5 ~]# vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
user nginx;
worker_processes ;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log;
pid /var/run/nginx.pid;
include /usr/share/nginx/modules/*.conf;
events {
worker_connections 65535;
use epoll;
}
http {
map $http_x_forwarded_for $clientRealIP {
"" $remote_addr;
~^(?P<firstAddr>[0-9\.]+),?.*$ $firstAddr;
}
log_format real_ip '{ "datetime": "$time_local", '
'"remote_addr": "$remote_addr", '
'"source_addr": "$clientRealIP", '
'"x_forwarded_for": "$http_x_forwarded_for", '
'"request": "$request_uri", '
'"status": "$status", '
'"request_method": "$request_method", '
'"request_length": "$request_length", '
'"body_bytes_sent": "$body_bytes_sent", '
'"request_time": "$request_time", '
'"http_referrer": "$http_referer", '
'"user_agent": "$http_user_agent", '
'"upstream_addr": "$upstream_addr", '
'"upstream_status": "$upstream_status", '
'"upstream_http_header": "$upstream_http_host",'
'"upstream_response_time": "$upstream_response_time", '
'"x-req-id": "$http_x_request_id", '
'"servername": "$host"'
' }';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log real_ip;
sendfile on;
tcp_nopush on;
tcp_nodelay on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
types_hash_max_size 2048;
include /etc/nginx/mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; upstream web {
server 192.168.132.131:80;
server 192.168.132.132:80;
server 192.168.132.133:80;
}
server {
listen 80 default_server;
server_name _;
location / {
proxy_pass http://web;
}
}
}
域名解析服务bind的配置文件 named.conf的jinja2模板示例:
[root@node1 ansible]# vim inventory
[dnsmaster]
demo2.example.com
demo3.example.com [dnsslave]
demo4.example.com
demo5.example.com
[root@node1 ansible]# vim config_dns.yml
- hosts: dnsmaster,dnsslave
tasks:
- template:
src: template/named.conf.j2
dest: /tmp/named.conf
[root@node1 ansible]# vim template/named.conf.j2
options {
listen-on port {
127.0.0.1;
{% for ip in ansible_all_ipv4_addresses %}
{{ ip }};
{% endfor %}
};
listen-on-v6 port { ::; };
directory "/var/named";
dump-file "/var/named/data/cache_dump.db";
statistics-file "/var/named/data/named_stats.txt";
memstatistics-file "/var/named/data/named_mem_stats.txt";
};
zone "." IN {
type hint;
file "named.ca";
};
include "/etc/named.rfc1912.zones";
include "/etc/named.root.key";
{% if 'dnsmaster' in group_names %} #设置变量,属于这个组设为master
{% set zone_type = 'master' %}
{% set zone_dir = 'data' %}
{% else %}
{% set zone_type = 'slave' %} #否则设为salve
{% set zone_dir = 'slaves' %}
{% endif %}
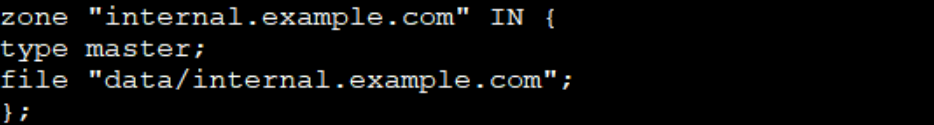
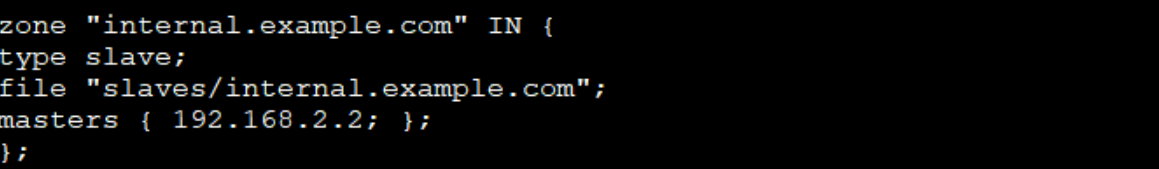
zone "internal.example.com" IN {
type {{ zone_type }};
file "{{ zone_dir }}/internal.example.com"; #引用变量
{% if 'dnsmaster' not in group_names %}
masters { 192.168.2.2; };
{% endif %}
};
执行anslibe查看主从
node2和node3
node4和node5
三 Jinja2过滤器
3.1 default过滤器
例如上一个redis案例
{% if masterip is defined %}
slaveof {{ masterip }} {{ materport|default() }}
{% endif %}
另一个示例
- hosts:
gather_facts: false
vars:
- path: /tmp/test
mode:
- path: /tmp/foo
- path: /tmp/bar
tasks:
- file:
dest: {{item}}
state: touch
mode: {{ item.mode|default(omit) }} #如果存在设置,不存在忽略
with_items: '{{ paths }}'
3.2 字符串相关过滤器
- upper:将所有字符串转换为大写
- |ower:将所有字宇符串转换为小写
- capitalize:将字符串的首字母大写,其他字母小写
- reverse:将宇符串倒序排列
- first:返回字符串的第一个宇符
- last:返回字符串的最后一个字符
- trim:将宇符串开头和结尾的空格去掉
- center(30):将宇符串放在中间,并且字符串两边用空格补齐30位
- length:返回字符串的长度,与 count等价
- |ist:将宇符串转换为列表
- shuffle:list将宇符串转换为列表,但是顺序排列, shuffle同样将宇符串转换为列表,但是会随机打乱宇符串顺序
3.3 数字相关操作
- int:将对应的值转换为整数
- float:好对应的值转换为浮点数
- abs:获取绝对值
- round:小数点四舍五入
- randon:从一个给定的范围中获取随机值
- hosts: demo2.example.com
gather_facts: no
vars:
testnum: -
tasks:
- debug:
msg: "{{ 8+('8'|int) }}"
- debug:
msg: "{{ 'a'|int(default=6) }}"
- debug:
msg: "{{ '8'|float }}"
- debug:
msg: "{{ testnum|abs }}"
- debug:
msg: "{{ 12.5|round }}"
- debug:
msg: "{{ 3.1415926|round(5) }}"
- debug:
#从0到100随即返回一个数字
msg: "{{ 100|random }}"
- debug:
#从5到10中随机返回一个数字
msg: "{{ 10|random(start=5) }}"
- debug:
#从4到15随机返回一个数字,步长为3
#返回的随机数这只可能是: 13中的一个
msg: "{{ 15|random(start=5,step=3) }}"
- debug:
#从0到15随机返回一个数字,步长为4
msg: "{{ 15|random(step=4) }}"
执行结果
TASK [debug] **************************************************************************************************************************************
ok: [demo2.example.com] => {
"msg": ""
}
TASK [debug] **************************************************************************************************************************************
ok: [demo2.example.com] => {
"msg": ""
}
TASK [debug] **************************************************************************************************************************************
ok: [demo2.example.com] => {
"msg": "8.0"
}
TASK [debug] **************************************************************************************************************************************
ok: [demo2.example.com] => {
"msg": ""
}
TASK [debug] **************************************************************************************************************************************
ok: [demo2.example.com] => {
"msg": "13.0"
}
TASK [debug] **************************************************************************************************************************************
ok: [demo2.example.com] => {
"msg": "3.14159"
}
TASK [debug] **************************************************************************************************************************************
ok: [demo2.example.com] => {
"msg": ""
}
TASK [debug] **************************************************************************************************************************************
ok: [demo2.example.com] => {
"msg": ""
}
TASK [debug] **************************************************************************************************************************************
ok: [demo2.example.com] => {
"msg": ""
}
TASK [debug] **************************************************************************************************************************************
ok: [demo2.example.com] => {
"msg": ""
}
3.4 列表过滤器
- length:返回列表长度
- first:返回列表的第一个值
- last:返回列表的最后一个值
- min:返回列表中最小的值
- max:返回列表中最大的值
- sort:重新排列列表,默认为升序排列, sort(reverse=true)为降序
- sum:返回皱教宁非嵌套列表中所有数字的和I
- flatten:如果列表中包含列表,则 flatten可拉平嵌套的列表 levels参数可用于指定被拉平的层级
- join:将列表中的元素合并为一个字符串
- random:从列表中随机返回一个元素
- shuffle
- upper
- lower
- union:将两个列表合并,如果元素有重复,则只留下一个
- intersect:获取两个列表的交集
- difference:获取存在于第一个列表中,但不存在于第二个列表中的元素
- symmetric difference:取出两个列表中各自独立的元素,如果重复则只留一个
3.5 应用于文件路径的过滤器
- basename:返回文件路径中的文件名部分
- dirname:返回文件路径中的目录部分
- expanduser:将文件路径中的~替换为用户目录
- realpath:处理符号链接后的文件实际路径
示例:
- name: test basename
hosts: test
vars:
homepage: /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
tasks:
- name: copy homepage
copy:
src: files/index.html
dest: {{ homepage }}
改写
- name: test basename
hosts: test
vars:
homepage: /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
tasks:
- name: copy homepage
copy:
src: files/{{ homepage | basename }}
dest: {{ homepage }}
3.6 自定义过滤器
举个简单的例子,现在有一个playbook如下:
- name: test filter
hosts: demo2.example.com
vars:
domains: ["www.example.com","example.com"]
tasks:
- template:
src: template/test.conf.j2
dest: /tmp/test.conf
template/test.conf.j2如下:
hosts = [{{ domains | join(',') }}]
执行playbook后,在目标机上的test.conf如下:
[root@node1 ansible]# ansible demo2.example.com -m shell -a "cat /tmp/test.conf"
demo2.example.com | CHANGED | rc= >>
hosts = [www.example.com,example.com]
现在如果希望目标机上的test.conf文件返回结果如下:
hosts = ["www.example.com","example.com"]
没有现成的过滤器来帮我们做这件事情。我们可以自己简单写一个surround_by_quote.py内容如下:
我们需要开启ansible.cfg的配置项:
filter_plugins = /etc/ansible/plugins/filter
[root@node1 ansible]# mkdir -p /etc/ansible/plugins/filter
[root@node1 ansible]# vim /etc/ansible/plugins/filter/surround_by_quote.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
def surround_by_quote(a_list):
# return ['"%s"' % an_element for an_element in a_list] #这个是下面的简写,python语法
lst = []
for index in a_list:
lst.append('"%s"' %index)
return lst
class FilterModule(object):
def filters(self):
return {'surround_by_quote': surround_by_quote}
将刚刚编写的代码文件放入/etc/ansible/plugins/filter目录下,然后修改templates/test.conf.j2如下:
hosts = [{{ domains |surround_by_quote|join(',') }}]
执行查看
[root@node1 ansible]# ansible demo2.example.com -m shell -a "cat /tmp/test.conf"

博主声明:本文的内容来源主要来自誉天教育晏威老师,由本人实验完成操作验证,需要的博友请联系誉天教育(http://www.yutianedu.com/),获得官方同意或者晏老师(https://www.cnblogs.com/breezey/)本人同意即可转载,谢谢!
009.Ansible模板管理 Jinja2的更多相关文章
- Ansible状态管理
转载自:http://xdays.me/ansible状态管理.html 简介 就像所有服务器批量管理工具(puppet有DSL,salt有state)一样,ansible也有自己的状态管理组件 ...
- Ansible 批量管理Windows Server服务器
Ansible批量管理Windows Server Ansible是一款为类Unix系统开发的自由开源的配置和自动化工具, 它用Python写成,类似于saltstack和Puppe ...
- ansible批量管理服务 下
1 ansible-playbook 任务剧本 1.1 剧本文件概念 (1)playbook可以将多个批量操作模块功能整合,完成一件事情.(2)简化运维工作复杂度(3)playbook通过yaml语法 ...
- 六.ansible批量管理服务
期中集群架构-第六章-ansible批量管理服务介绍====================================================================== 01. ...
- web 框架的本质及自定义web框架 模板渲染jinja2 mvc 和 mtv框架 Django框架的下载安装 基于Django实现的一个简单示例
Django基础一之web框架的本质 本节目录 一 web框架的本质及自定义web框架 二 模板渲染JinJa2 三 MVC和MTV框架 四 Django的下载安装 五 基于Django实现的一个简单 ...
- Django + Ansible 主机管理(有源码)
本文给大家介绍如何利用 Django + Ansible 进行 Web 项目管理. Django介绍 一个可以使 Web 开发工作愉快并且高效的 Web 开发框架,能够以最小的代价构建和维护高质量 ...
- ansible批量管理常见的配置方法
第7章 ansible的管理 7.1 ansible概念的介绍 ansible-playbook –syntax 检查语法 ansible-playbook -C ...
- 【Ansible】记一次技术博客害死人的经历——ansible模板变量注入探究
风和日丽,夏天的北京湿热并举,睁不开的眼睛里,横竖都看着是“吃人”. 带薪学习的日子不好过,要在几天内迅速掌握导师下发要求学习的技能,看着以前一起蹲IT坑的同事人来人往,用隔壁同性黄同学的话来说,就是 ...
- 使用ansible批量管理远程服务器
使用ansible批量管理远程服务器 背景 本地需要管理远程的一批服务器,主要执行以下任务: 1) 将本地的文件复制到远端所有服务器: 2) 需要在远程服务器中执行一个个命令: 远端服务器路径并非完全 ...
随机推荐
- 华为五年自动化测试工程详细解说:unittest单元测试框架
一.单元测试框架说明 单元测试是指在编程中,针对程序模块的最小单元(类中的方法)进行正确性检验的测试工作.python+selenium自动化测试中通常使用unittest或者pytest作为单元 ...
- 001_Three.js中的跨域问题
001_Three.js中的跨域问题 [情景描述]: 在初始化模型,引入字体和纹理皮肤图片的时候,由于跨域问题,出现了以下提示: Access to image at 'file:///F:/User ...
- 使用 Spring data redis 结合 Spring cache 缓存数据配置
使用 JavaConfig 方式配置 依赖 jar 包: jedis.spring-data-redis 首先需要进行 Redis 相关配置 @Configuration public class R ...
- Shell:homework
1.判断/etc/inittab文件是否大于100行,如果大于,则显示”/etc/inittab is a big file.”否则显示”/etc/inittab is a small file.”# ...
- 关于web数据库的相关知识点的操作
主要是怎样建立与数据库的连接.对于框架是固定的: 下面是对于数据库的连接操作: package com.DBU; //数据库连接 import java.sql.Connection; import ...
- (js描述的)数据结构[双向链表](5)
(js描述的)数据结构[双向链表](5) 一.单向链表的缺点 1.只能按顺序查找,即从上一个到下一个,不能反过来. 二.双向链表的优点 1.可以双向查找 三.双向链表的缺点 1.结构较单向链表复杂. ...
- 用robotframework 标准库String解决由于存在千分位分隔符导致两个数值不相等的问题。
在编写robotframework自动化断言的过程中,我遇到了如下问题: 我想写一个两个金额判断是否相等的断言,其中一个金额是展示字段存在千分位分隔符,另一个金额是input带入字段,没有千分位分隔符 ...
- Python设计模式(5)-代理模式
# coding=utf-8 # 代理模式:# * 代理类成为实际想调用对象的中间件,可以控制对实际调用对象的访问权限# * 可以维护实际对象的引用 class DbManager: def __in ...
- 一个不错的java学习博客
http://iteye.blog.163.com/blog/static/18630809620131484835129/
- CentOS8.1.1911正式发布!
前阵子,CentOS官方宣布:CentOS8.1.1911正式发布!已经安装CentOS8.0的朋友,可以执行yum update更新(笔者更新了2次),体验下新版本!如是新安装,可以从官方网站下载h ...
