【Android开发学习笔记之一】5大布局方式详解
Android中常用的5大布局方式有以下几种:
- 线性布局(LinearLayout):按照垂直或者水平方向布局的组件。
- 帧布局(FrameLayout):组件从屏幕左上方布局组件。
- 表格布局(TableLayout):按照行列方式布局组件。
- 相对布局(RelativeLayout):相对其它组件的布局方式。
- 绝对布局(AbsoluteLayout):按照绝对坐标来布局组件。
1. 线性布局
线性布局是Android开发中最常见的一种布局方式,它是按照垂直或者水平方向来布局,通过“android:orientation”属性可以设置线性布局的方向。属性值有垂直(vertical)和水平(horizontal)两种。
常用的属性:
android:orientation:可以设置布局的方向
android:gravity:用来控制组件的对齐方式
layout_weight:控制各个组件在布局中的相对大小
第一个实例
①效果图:
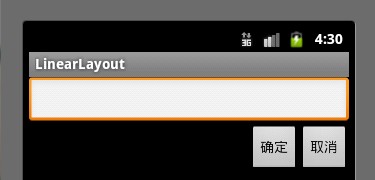
②核心代码如下:
main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
>
<EditText
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
/>
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:gravity="right"
>
<!-- android:gravity="right"表示Button组件向右对齐 -->
<Button
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text="确定"
/>
<Button
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text="取消"
/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
第二个实例
①效果图:
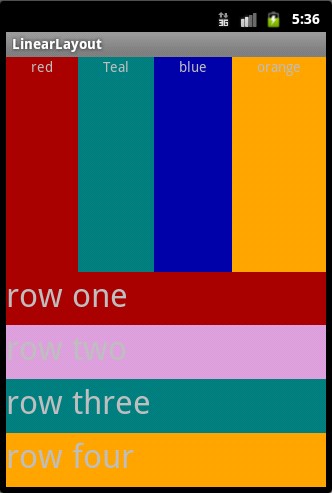
②核心代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <LinearLayout
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"> <TextView
android:text="red"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:background="#aa0000"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
/>
<!--android:gravity="center_horizontal"水平居中 -->
<!--layout_weight属性以控制各个控件在布局中的相对大小。layout_weight属性是一个非负整数值。
线性布局会根据该控件layout_weight值与其所处布局中所有控件layout_weight值之和的比值为该控件分配占用的区域。
例如,在水平布局的LinearLayout中有两个Button,这两个Button的layout_weight属性值都为1,
那么这两个按钮都会被拉伸到整个屏幕宽度的一半。如果layout_weight指为0,控件会按原大小显示,不会被拉伸;
对于其余layout_weight属性值大于0的控件,系统将会减去layout_weight属性值为0的控件的宽度或者高度,
再用剩余的宽度或高度按相应的比例来分配每一个控件显示的宽度或高度-->
<TextView
android:text="Teal"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:background="#008080"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"/> <TextView
android:text="blue"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:background="#0000aa"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
/> <TextView
android:text="orange"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:background="#FFA500"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
/> </LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"> <TextView
android:text="row one"
android:textSize="15pt"
android:background="#aa0000"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
/>
<!-- -->
<TextView
android:text="row two"
android:textSize="15pt"
android:background="#DDA0DD"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
/> <TextView
android:text="row three"
android:textSize="15pt"
android:background="#008080"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
/>
<TextView
android:text="row four"
android:textSize="15pt"
android:background="#FFA500"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_weight="1"
/>
</LinearLayout>
</LinearLayout>
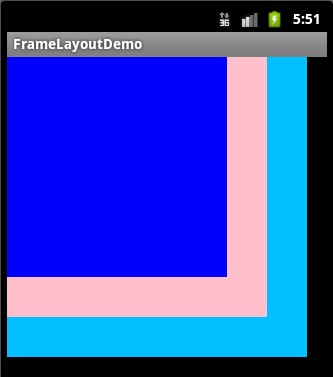
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="300dp"
android:layout_height="300dp"
android:background="#00BFFF"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="260dp"
android:layout_height="260dp"
android:background="#FFC0CB"
/>
<TextView
android:layout_width="220dp"
android:layout_height="220dp"
android:background="#0000FF"
/>
</FrameLayout>
android:shrinkColumns:收缩指定的列以适合屏幕,不会挤出屏幕
android:stretchColumns:尽量把指定的列填充空白部分
android:layout_column:控件放在指定的列
android:layout_span:该控件所跨越的列数
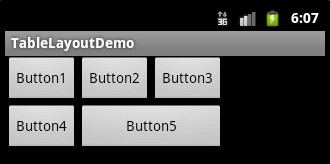
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<TableRow>
<Button
android:text="Button1"
/>
<Button
android:text="Button2"
/>
<Button
android:text="Button3"
/>
</TableRow>
<TableRow>
<Button
android:text="Button4"
/>
<Button
android:layout_span="2"
android:text="Button5"
/>
</TableRow> </TableLayout>
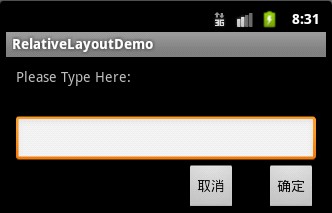
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:padding="10px"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tev1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="30dp"
android:text="Please Type Here:"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/tx1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/tev1"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/tx1"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:text="确定"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/tx1"
android:layout_toLeftOf="@id/btn1"
android:layout_marginRight="30dp"
android:text="取消"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
【Android开发学习笔记之一】5大布局方式详解的更多相关文章
- 【转】Android开发学习笔记:5大布局方式详解
Android中常用的5大布局方式有以下几种: 线性布局(LinearLayout):按照垂直或者水平方向布局的组件. 帧布局(FrameLayout):组件从屏幕左上方布局组件. 表格布局(Tabl ...
- Android开发5大布局方式详解
Android中常用的5大布局方式有以下几种: 线性布局(LinearLayout):按照垂直或者水平方向布局的组件. 帧布局(FrameLayout):组件从屏幕左上方布局组件. 表格布局(Tabl ...
- Android开发之5大布局方式详解
Android中常用的5大布局方式有以下几种: 线性布局(LinearLayout):按照垂直或者水平方向布局的组件. 帧布局(FrameLayout):组件从屏幕左上方布局组件. 表格布局(Tabl ...
- android开发学习笔记000
使用书籍:<疯狂android讲义>——李刚著,2011年7月出版 虽然现在已2014,可我挑来跳去,还是以这本书开始我的android之旅吧. “疯狂源自梦想,技术成就辉煌.” 让我这个 ...
- Linux防火墙iptables学习笔记(三)iptables命令详解和举例[转载]
Linux防火墙iptables学习笔记(三)iptables命令详解和举例 2008-10-16 23:45:46 转载 网上看到这个配置讲解得还比较易懂,就转过来了,大家一起看下,希望对您工作能 ...
- (转)live555学习笔记10-h264 RTP传输详解(2)
参考: 1,live555学习笔记10-h264 RTP传输详解(2) http://blog.csdn.net/niu_gao/article/details/6936108 2,H264 sps ...
- 【Android开发学习笔记】【第八课】五大布局-下
概念 五大布局上一篇文章已经介绍了 LinearLayout RelativeLayout 这一篇我们介绍剩下的三种布局 FrameLayout 五种布局中最佳单的一种布局.在这个布局在整个界面被当成 ...
- 【Android开发学习笔记】【第七课】五大布局-上
概念 Android程序各式各样,依靠的就是布局,先来看看布局都是怎么来的: 白色部分就是我们经常用的几种布局,主要说说介绍下面五大布局 FrameLayout AbsoluteLayout Line ...
- 【转】Android开发学习笔记(一)——初识Android
对于一名程序员来说,“自顶向下”虽然是一种最普通不过的分析问题和解决问题的方式,但其却是简单且较为有效的一种.所以,将其应用到Android的学习中来,不至于将自己的冲动演变为一种盲目和不知所措. 根 ...
随机推荐
- 使用Xshell5连接虚拟机VMware中安装的CentOS7系统
使用Xshell5连接VMware中安装的CentOS7系统 准备材料 Xshell 下载地址 VMware Workstation 12 Pro 下载地址 CentOS 7 64位系统 下载地址 安 ...
- 长话短说 之 js的原型和闭包
原型链:undefined, number, string, boolean 属于简单的值类型,函数.数组.对象.null.new obj()都是引用类型.检测值类型用typeof x 即可,检测引用 ...
- json_encode()中文不转码
php使用json_encode()把数组转换为json的时候,总会把中文进行转码,转码后从json数据上我们无法看出其中的中文文字.php5.4以后,当json_encode()的第二个参数赋值为J ...
- Python Fabric远程自动部署简介
Fabric是一个Python(2.5-2.7)库,用于简化使用SSH的应用程序部署或系统管理任务. 它提供的操作包括:执行本地或远程shell命令,上传/下载文件,以及其他辅助功能,如提示用户输入. ...
- 给资源文件添加指纹(Gulp版)
至于为什么要费尽心思地给文件添加指纹,请参看前端静态资源缓存控制策略.这次要达到的小目标就是生成的资源文件能够被客户端缓存,而在文件内容变化后,能够请求到最新的文件. 需要用到的 gulp 插件是 g ...
- 安装PyQt5之后mayavi和VTK不能使用
mayavi在显示数据的过程中需要调用PyQt4的GUI方法产生应用框架.但是新发布的PyQt5和PyQt4在很多方面都是不兼容的,这也就导致了用mayavi编写的程序运行失败.在实践之后,我的解决方 ...
- vim基本命令(转载自网络)
来源于<Unix初级教程(第四版)>. 命令模式切换到文本输入模式: 键 功能 i 在光标左侧输入文本 I 在当前行的行首输入文本 a 在光标右侧输入文本 A 在当前行的行尾输入文本 o ...
- Leetcode题解(十一)
31.Next Permutation 题目 这道题目的意思是给定一个序列,找出其按照字典顺序的下一个顺序,如果给定顺序是字典中的最后一个顺序,其下一个顺序则为字典中的第一个顺序.比如: 1,2,3, ...
- Problem M
Problem Description Accounting for Computer Machinists (ACM) has sufferred from the Y2K bug and lost ...
- PHP(一)OOP基础
[面向过程&面向对象] 1.面向过程:专注于解决一件事情的过程.最大的特点,是有一个个函数来实现功能需求 2.面向对象:专注于有哪一个对象来实现这个功能,最大的特点,时产生一个个具有属性和方法 ...
