浅谈Android系统进程间通信(IPC)机制Binder中的Server和Client获得Service Manager接口之路
文章转载至CSDN社区罗升阳的安卓之旅,原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6627260
在前面一篇文章浅谈Service Manager成为Android进程间通信(IPC)机制Binder守护进程之路中,介绍了Service Manager是如何成为Binder机制的守护进程的。既然作为守护进程,Service Manager的职责当然就是为Server和Client服务了。那么,Server和Client如何获得Service Manager接口,进而享受它提供的服务呢?本文将简要分析Server和Client获得Service Manager的过程。
在阅读本文之前,希望读者先阅读Android进程间通信(IPC)机制Binder简要介绍和学习计划一文提到的参考资料Android深入浅出之Binder机制,这样可以加深对本文的理解。
我们知道,Service Manager在Binder机制中既充当守护进程的角色,同时它也充当着Server角色,然而它又与一般的Server不一样。对于普通的Server来说,Client如果想要获得Server的远程接口,那么必须通过Service Manager远程接口提供的getService接口来获得,这本身就是一个使用Binder机制来进行进程间通信的过程。而对于Service Manager这个Server来说,Client如果想要获得Service Manager远程接口,却不必通过进程间通信机制来获得,因为Service Manager远程接口是一个特殊的Binder引用,它的引用句柄一定是0。
获取Service Manager远程接口的函数是defaultServiceManager,这个函数声明在frameworks/base/include/binder/IServiceManager.h文件中:
- sp<IServiceManager> defaultServiceManager();
实现在frameworks/base/libs/binder/IServiceManager.cpp文件中:
- sp<IServiceManager> defaultServiceManager()
- {
- if (gDefaultServiceManager != NULL) return gDefaultServiceManager;
- {
- AutoMutex _l(gDefaultServiceManagerLock);
- if (gDefaultServiceManager == NULL) {
- gDefaultServiceManager = interface_cast<IServiceManager>(
- ProcessState::self()->getContextObject(NULL));
- }
- }
- return gDefaultServiceManager;
- }
gDefaultServiceManagerLock和gDefaultServiceManager是全局变量,定义在frameworks/base/libs/binder/Static.cpp文件中:
- Mutex gDefaultServiceManagerLock;
- sp<IServiceManager> gDefaultServiceManager;
从这个函数可以看出,gDefaultServiceManager是单例模式,调用defaultServiceManager函数时,如果gDefaultServiceManager已经创建,则直接返回,否则通过interface_cast<IServiceManager>(ProcessState::self()->getContextObject(NULL))来创建一个,并保存在gDefaultServiceManager全局变量中。
在继续介绍interface_cast<IServiceManager>(ProcessState::self()->getContextObject(NULL))的实现之前,先来看一个类图,这能够帮助我们了解Service Manager远程接口的创建过程。
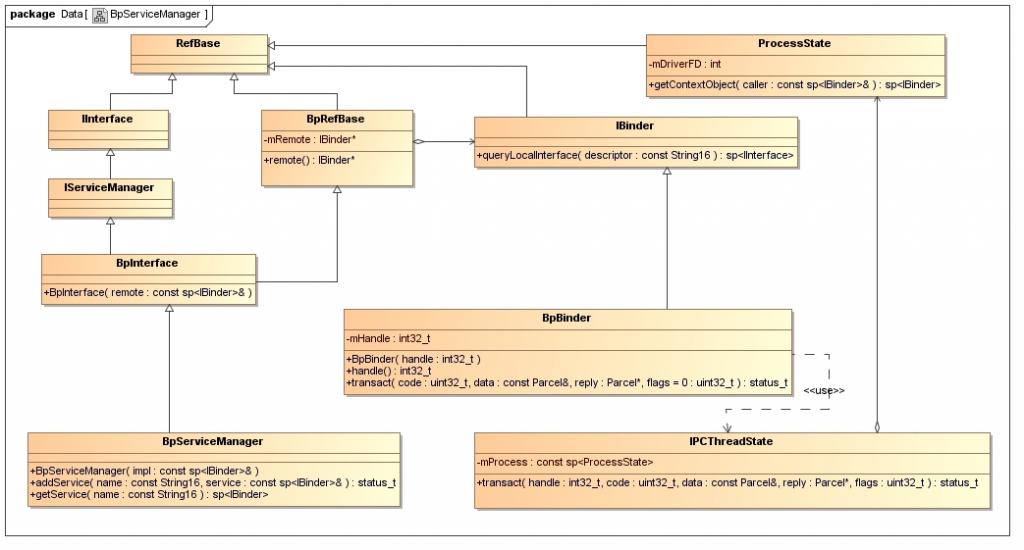
参考资料Android深入浅出之Binder机制一文的读者,应该会比较容易理解这个图。这个图表明了,BpServiceManager类继承了BpInterface<IServiceManager>类,BpInterface是一个模板类,它定义在frameworks/base/include/binder/IInterface.h文件中:
- template<typename INTERFACE>
- class BpInterface : public INTERFACE, public BpRefBase
- {
- public:
- BpInterface(const sp<IBinder>& remote);
- protected:
- virtual IBinder* onAsBinder();
- };
IServiceManager类继承了IInterface类,而IInterface类和BpRefBase类又分别继承了RefBase类。在BpRefBase类中,有一个成员变量mRemote,它的类型是IBinder*,实现类为BpBinder,它表示一个Binder引用,引用句柄值保存在BpBinder类的mHandle成员变量中。BpBinder类通过IPCThreadState类来和Binder驱动程序并互,而IPCThreadState又通过它的成员变量mProcess来打开/dev/binder设备文件,mProcess成员变量的类型为ProcessState。ProcessState类打开设备/dev/binder之后,将打开文件描述符保存在mDriverFD成员变量中,以供后续使用。
理解了这些概念之后,就可以继续分析创建Service Manager远程接口的过程了,最终目的是要创建一个BpServiceManager实例,并且返回它的IServiceManager接口。创建Service Manager远程接口主要是下面语句:
- gDefaultServiceManager = interface_cast<IServiceManager>(
- ProcessState::self()->getContextObject(NULL));
看起来简短,却暗藏玄机,具体可阅读Android深入浅出之Binder机制这篇参考资料,这里作简要描述。
首先是调用ProcessState::self函数,self函数是ProcessState的静态成员函数,它的作用是返回一个全局唯一的ProcessState实例变量,就是单例模式了,这个变量名为gProcess。如果gProcess尚未创建,就会执行创建操作,在ProcessState的构造函数中,会通过open文件操作函数打开设备文件/dev/binder,并且返回来的设备文件描述符保存在成员变量mDriverFD中。
接着调用gProcess->getContextObject函数来获得一个句柄值为0的Binder引用,即BpBinder了,于是创建Service Manager远程接口的语句可以简化为:
- gDefaultServiceManager = interface_cast<IServiceManager>(new BpBinder(0));
再来看函数interface_cast<IServiceManager>的实现,它是一个模板函数,定义在framework/base/include/binder/IInterface.h文件中:
- template<typename INTERFACE>
- inline sp<INTERFACE> interface_cast(const sp<IBinder>& obj)
- {
- return INTERFACE::asInterface(obj);
- }
这里的INTERFACE是IServiceManager,于是调用了IServiceManager::asInterface函数。IServiceManager::asInterface是通过DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(ServiceManager)宏在IServiceManager类中声明的,它位于framework/base/include/binder/IServiceManager.h文件中:
- DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(ServiceManager);
展开即为:
- #define DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(ServiceManager) \
- static const android::String16 descriptor; \
- static android::sp<IServiceManager> asInterface( \
- const android::sp<android::IBinder>& obj); \
- virtual const android::String16& getInterfaceDescriptor() const; \
- IServiceManager(); \
- virtual ~IServiceManager();
IServiceManager::asInterface的实现是通过IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE(ServiceManager, "android.os.IServiceManager")宏定义的,它位于framework/base/libs/binder/IServiceManager.cpp文件中:
- IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE(ServiceManager, "android.os.IServiceManager");
展开即为:
- #define IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE(ServiceManager, "android.os.IServiceManager") \
- const android::String16 IServiceManager::descriptor("android.os.IServiceManager"); \
- const android::String16& \
- IServiceManager::getInterfaceDescriptor() const { \
- return IServiceManager::descriptor; \
- } \
- android::sp<IServiceManager> IServiceManager::asInterface( \
- const android::sp<android::IBinder>& obj) \
- { \
- android::sp<IServiceManager> intr; \
- if (obj != NULL) { \
- intr = static_cast<IServiceManager*>( \
- obj->queryLocalInterface( \
- IServiceManager::descriptor).get()); \
- if (intr == NULL) { \
- intr = new BpServiceManager(obj); \
- } \
- } \
- return intr; \
- } \
- IServiceManager::IServiceManager() { } \
- IServiceManager::~IServiceManager() { }
估计写这段代码的员工是从Microsoft跳槽到Google的。这里我们关注IServiceManager::asInterface的实现:
- android::sp<IServiceManager> IServiceManager::asInterface(const android::sp<android::IBinder>& obj)
- {
- android::sp<IServiceManager> intr;
- if (obj != NULL) {
- intr = static_cast<IServiceManager*>(
- obj->queryLocalInterface(IServiceManager::descriptor).get());
- if (intr == NULL) {
- intr = new BpServiceManager(obj);
- }
- }
- return intr;
- }
这里传进来的参数obj就则刚才创建的new BpBinder(0)了,BpBinder类中的成员函数queryLocalInterface继承自基类IBinder,IBinder::queryLocalInterface函数位于framework/base/libs/binder/Binder.cpp文件中:
- sp<IInterface> IBinder::queryLocalInterface(const String16& descriptor)
- {
- return NULL;
- }
由此可见,在IServiceManager::asInterface函数中,最终会调用下面语句:
- intr = new BpServiceManager(obj);
即为:
- intr = new BpServiceManager(new BpBinder(0));
回到defaultServiceManager函数中,最终结果为:
- gDefaultServiceManager = new BpServiceManager(new BpBinder(0));
这样,Service Manager远程接口就创建完成了,它本质上是一个BpServiceManager,包含了一个句柄值为0的Binder引用。
在Android系统的Binder机制中,Server和Client拿到这个Service Manager远程接口之后怎么用呢?
对Server来说,就是调用IServiceManager::addService这个接口来和Binder驱动程序交互了,即调用BpServiceManager::addService 。而BpServiceManager::addService又会调用通过其基类BpRefBase的成员函数remote获得原先创建的BpBinder实例,接着调用BpBinder::transact成员函数。在BpBinder::transact函数中,又会调用IPCThreadState::transact成员函数,这里就是最终与Binder驱动程序交互的地方了。回忆一下前面的类图,IPCThreadState有一个PorcessState类型的成中变量mProcess,而mProcess有一个成员变量mDriverFD,它是设备文件/dev/binder的打开文件描述符,因此,IPCThreadState就相当于间接在拥有了设备文件/dev/binder的打开文件描述符,于是,便可以与Binder驱动程序交互了。
对Client来说,就是调用IServiceManager::getService这个接口来和Binder驱动程序交互了。具体过程上述Server使用Service Manager的方法是一样的,这里就不再累述了。
IServiceManager::addService和IServiceManager::getService这两个函数的具体实现,在下面两篇文章中,会深入到Binder驱动程序这一层,进行详细的源代码分析,以便更好地理解Binder进程间通信机制,敬请关注。
老罗的新浪微博:http://weibo.com/shengyangluo,欢迎关注!
浅谈Android系统进程间通信(IPC)机制Binder中的Server和Client获得Service Manager接口之路的更多相关文章
- Android系统进程间通信(IPC)机制Binder中的Server启动过程源代码分析
文章转载至CSDN社区罗升阳的安卓之旅,原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6629298 在前面一篇文章浅谈Android系 ...
- 浅谈Android系统开发中LOG的使用
文章转载至CSDN社区罗升阳的安卓之旅,原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6581828 在程序开发过程中,LOG是广泛使用 ...
- 浅谈Android系统开发中LOG的使用【转】
本文转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6581828 在程序开发过程中,LOG是广泛使用的用来记录程序执行过程的机制,它既可以 ...
- 浅谈Android系统移植、Linux设备驱动
一.Android系统架构 第一层:Linux内核 包括驱动程序,管理内存.进程.电源等资源的程序 第二层:C/C++代码库 包括Linux的.so文件以及嵌入到APK程序中的NDK代码 第三层:An ...
- 浅谈Android系统的图标设计规范
http://homepage.yesky.com/89/11620089.shtml 目前移动平台的竞争日益激烈,友好的用户界面可以帮助提高用户体验满意度,图标Icon是用户界面中一个重要的组成部分 ...
- 浅谈Android View事件分发机制
引言 前面的文章介绍了View的基础知识和View的滑动,今天我们来介绍View的另一个核心知识,View的事件分发机制. 点击事件的传递规则 所谓的点击事件的分发机制,其实就是对MotionEven ...
- Android系统进程间通信(IPC)机制Binder中的Client获得Server远程接口过程源代码分析
文章转载至CSDN社区罗升阳的安卓之旅,原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6633311 在上一篇文章中,我 们分析了And ...
- Android系统进程间通信Binder机制在应用程序框架层的Java接口源代码分析
文章转载至CSDN社区罗升阳的安卓之旅,原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/luoshengyang/article/details/6642463 在前面几篇文章中,我们详细介绍了A ...
- 浅谈Android五大布局
Android的界面是有布局和组件协同完成的,布局好比是建筑里的框架,而组件则相当于建筑里的砖瓦.组件按照布局的要求依次排列,就组成了用户所看见的界面.Android的五大布局分别是LinearLay ...
随机推荐
- HDU--1584--蜘蛛牌--深搜版本号
蜘蛛牌 Time Limit: 10000/5000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others) Total Submi ...
- Hacker(19)----检测Windows系统漏洞
想完全掌握Windows中存在的漏洞需要使用专业的漏洞扫描软件.目前常用的有MBSA(MircosoftBaselineSecurityAnalyzer).360安全卫士等. 一.使用MBSA检测系统 ...
- Hacker(17)----认识Windows系统漏洞
Windows系统是迄今为止使用频率最高的操作系统,虽然其安全性随着版本的更新不断提高,但由于人为编写的缘故始终存在漏洞和缺陷.但Mircosoft公司通过发布漏洞补丁来提高系统的安全性,使Windo ...
- (转)Web.config配置文件详解(新手必看)
花了点时间整理了一下ASP.NET Web.config配置文件的基本使用方法.很适合新手参看,由于Web.config在使用很灵活,可以自定义一些节点.所以这里只介绍一些比较常用的节点. <? ...
- (转)WCF中调用WebService出错,大家帮忙看看,回答就有分
http://bbs.csdn.net/topics/390542345 在WCF项目里面添加了一个WebService引用,然后在我们调用这个WCF服务时,老出错,提示在 ServiceModel ...
- Android ----------获取各种路径(更新中。。。。。。)
##在手机中的路径 *获取应用的路径,形式:/data/data/包名 String appDataDir = getApplicationInfo().dataDir; *获取手机数据存储路径,即/ ...
- .net 将xml转换成DateSet
/// <summary> /// 将XML字符串转换成DATASET /// </summary> /// <param name="xmlStr" ...
- WCF入门教程系列六
一.前言 前面的几个章节介绍了很多理论基础,如:什么是WCF.WCF中的A.B.C.WCF的传输模式.本文从零开始和大家一起写一个小的WCF应用程序Demo. 大多框架的学习都是从增.删.改.查开始来 ...
- C++中的类指针
代码: #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <cstdio> using namespace std; c ...
- 对面向对象程序设计(OOP)的认识
前言 本文主要介绍面向对象(OO)程序设计,以维基百科的解释: 面向对象程序设计(英语:Object-oriented programming,缩写:OOP),指一种程序设计范型,同时也是一种程序开发 ...
