The Preliminary Contest for ICPC China Nanchang National Invitational and International Silk-Road Programming Contest
打网络赛
比赛前的准备工作要做好
确保 c++/java/python的编译器能用
打好模板,放在桌面
A. PERFECT NUMBER PROBLEM
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; #define ll long long const int maxn=1e8+;
const int inf=1e9;
const double eps=1e-; int sum[maxn]; int main()
{
int n=,i,j;
for (i=;i<n;i++)
for (j=i;j<n;j+=i)
sum[j]+=i;
for (i=;i<n;i++)
if (sum[i]==i+i)
printf("%d ",i);
return ;
}
/*
6 28 496 8128 33550336
Process returned 0 (0x0) execution time : 24.646 s
*/
较差的打表方法
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; #define ll long long const int maxn=1e4+;
const int inf=1e9;
const double eps=1e-; int main()
{
///我相信很大一部分同学是网上找答案的,这不好
// printf("6\n28\n496\n8128\n33550336");
ll sum,i,j,k;
for (i=;i<=;i++)
{
sum=;
k=sqrt(i);
for (j=;j<=k;j++)
if (i%j==)
sum+=j+i/j;
if (k*k==i)
sum-=i;
sum-=i;
if (sum==i)
printf("%d ",i);
if (i%==)
printf("i=%d\n",i);
}
return ;
}
/*
6 28 496 8128 33550336
18 min
*/
C. Angry FFF Party
fib(x) 逐渐变得很大
而fib(fib(x))更是如此,
感觉可以打表
于是用python打表验证一下
import math
a=/math.sqrt()
b=(+math.sqrt())/
c=(-math.sqrt())/
a
0.4472135954999579
a
for n in range(,):
print(n)
x=a*(pow(b,n) - pow(c,n))
x=round(x)
print(x)
y=a*(pow(b,x) - pow(c,x))
print(y)
print()
1.0
1.0
1.0
2.0
5.000000000000001
21.000000000000004
233.00000000000006
10946.000000000007
5702887.0000000065
139583862445.00024
1.7799794160047194e+18
5.555654042242954e+29
2.2112364063039317e+48
2.746979206949977e+78
1.3582369791278544e+127
开始用java写 BigInteger
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.Scanner; public class Main {
static class mat {
BigInteger [][]a=new BigInteger[][];
mat() {
a[][]=a[][]=a[][]=a[][]=BigInteger.ZERO;
}
static mat mul(mat a,mat b) {
mat c=new mat();
for (int k=;k<;k++)
for (int i=;i<;i++)
for (int j=;j<;j++)
c.a[i][j]=c.a[i][j].add(a.a[i][k].multiply(b.a[k][j]));
return c;
}
void print() {
for (int i=;i<;i++) {
for (int j=;j<;j++)
System.out.print(a[i][j]+" ");
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
} static BigInteger _pow(int n) {
mat a=new mat();
mat b=new mat();
a.a[][]=BigInteger.ONE;
a.a[][]=BigInteger.ZERO;
a.a[][]=BigInteger.ZERO;
a.a[][]=BigInteger.ONE; b.a[][]=BigInteger.ONE;
b.a[][]=BigInteger.ONE;
b.a[][]=BigInteger.ONE;
b.a[][]=BigInteger.ZERO; while (n>) {
if (n%==)
a=mat.mul(a,b);
b=mat.mul(b,b);
// b.print();
n>>=;
}
return a.a[][];
} public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { int i,len=;//
int []a=new int[];
BigInteger []b=new BigInteger[];
StringBuffer s=new StringBuffer("");
for (i=;i<len;i++)
s=s.append("");
String ss=new String(s);
BigInteger maxb=new BigInteger(ss);
// System.out.println(maxb); // _pow(10); a[]=a[]=;
mat ma = new mat();
for (i=;i<;i++) {
if (i<)
a[i]=;
else
a[i]=a[i-]+a[i-];
// System.out.println(a[i]);
b[i]=_pow(a[i]);
// if (i<10)
// System.out.println(b[i]);
if (b[i].compareTo(maxb)>=)
break;
}
// System.out.println("i="+i);
int maxg=i; Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
int t=in.nextInt();
BigInteger m; int []num=new int[];
int g=;
BigInteger[] bb=new BigInteger[];
for (i=;i<=;i++)
bb[i]=new BigInteger(Integer.toString(i));
String []pr=new String[]; /*
1 1 1 2 5 21
*/
pr[]="";
pr[]="1 2";
pr[]="1 2 3";
pr[]="1 2 4";
pr[]="1 2 3 4";
for (i=;i<=;i++)
pr[i]=pr[i-]+""; while (t-->) {
m=in.nextBigInteger(); g=;
if (m.compareTo(bb[])>) {
for (i=maxg;i>;i--)
if (m.compareTo(b[i])>=) {
m=m.subtract(b[i]);
g=g+;
num[g]=i;
}
}
if (m.compareTo(bb[])>)
System.out.println(-);
else {
for (i=;i<=;i++)
if (m.compareTo(bb[i])==)
System.out.print(pr[i]);
if (m.compareTo(bb[])!= && g!=)
System.out.print(" ");
if (g==)
System.out.println();
for (i=g;i>=;i--) {
System.out.print(num[i]);
if (i==)
System.out.println();
else
System.out.print(" ");
}
}
}
}
}
/*
1 1 1 2 5 21 1
1
1
2
5
21
233
10946
5702887 100
1-10
11
21
27
*/
H. Coloring Game
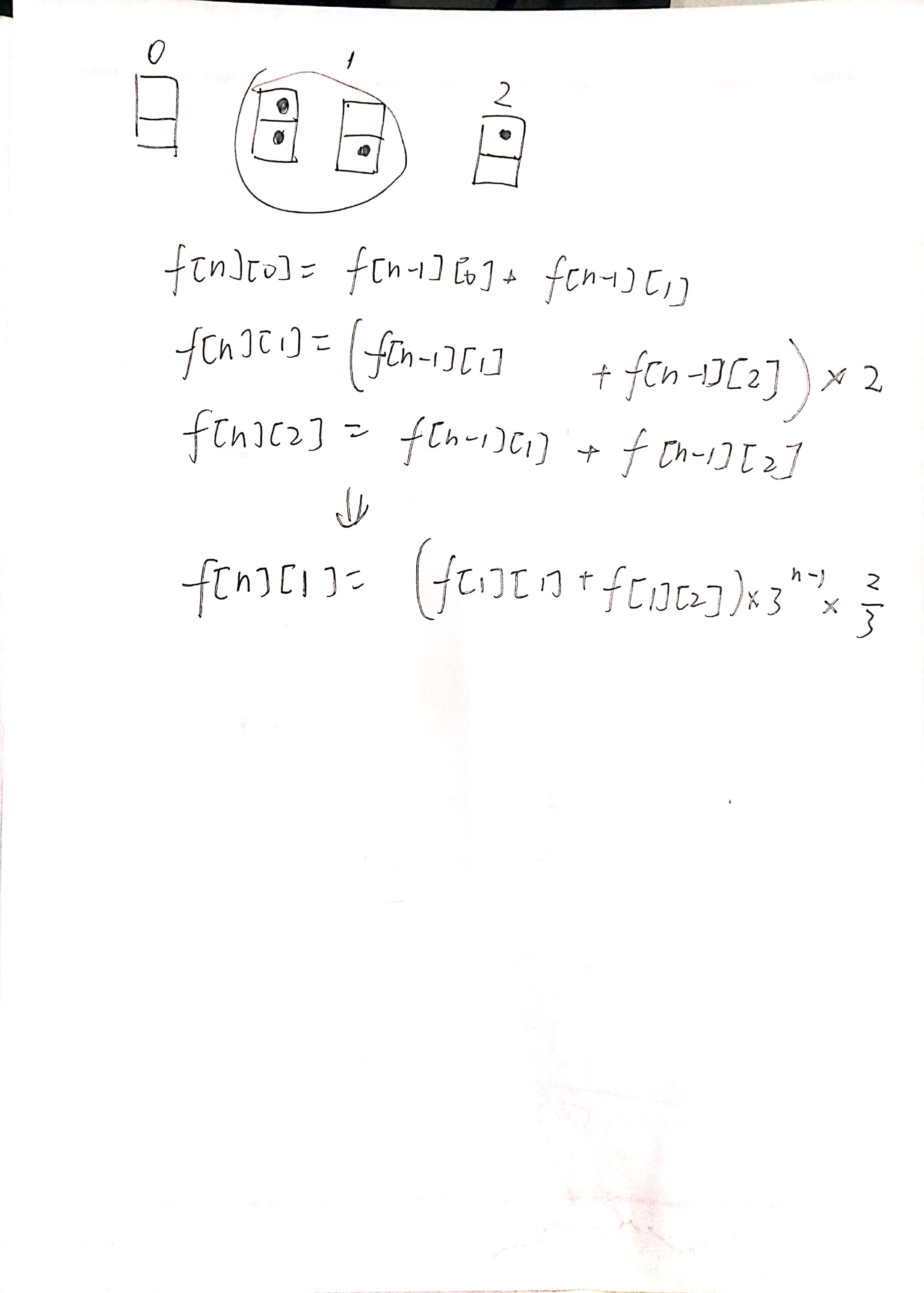
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; #define ll long long const int maxn=1e4+;
const int inf=1e9;
const double eps=1e-;
const ll mod=1e9+; ll mul(ll a,ll b)
{
ll y=;
while (b)
{
if (b&)
y=y*a%mod;
a=a*a%mod;
b>>=;
}
return y;
} int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
if (n==)
printf("");
else
printf("%lld",mul(,n-)*%mod);
return ;
}
/*
1000000000
*/
K. MORE XOR
找规律
推公式较为复杂,据说用插板法
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; #define ll long long const int maxn=1e5+;
const int inf=1e9;
const double eps=1e-; int f[][maxn],a[maxn]; int main()
{
// printf("%d",1^2^5^6^9^10);
int T,n,q,i,j,k,x,y,s,t,v;
scanf("%d",&T);
while (T--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for (i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]); for (k=;k<;k++)
for (i=(k==)?:k,j=;i<=n;i+=,j++)
f[k][j]=f[k][j-]^a[i]; scanf("%d",&q);
while (q--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&i,&j);
y=(j-i+)%;
if (y==)
{
///i,i+4,i+8 ...
x=i%;
s=(i+)/;
t=s+(j-i)/;
printf("%d\n",f[x][t]^f[x][s-]);
}
else if (y==)
{
x=i%;
s=(i+)/;
t=s+(j-i)/;
v=f[x][t]^f[x][s-]; i++;
x=i%;
s=(i+)/;
t=s+(j-i)/;
printf("%d\n",v^f[x][t]^f[x][s-]);
}
else if (y==)
{
i++;
x=i%;
s=(i+)/;
t=s+(j-i)/;
printf("%d\n",f[x][t]^f[x][s-]);
}
else
printf("0\n");
}
}
return ;
}
/*
1
10
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
100
1 7
*/
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; #define ll long long const int maxn=1e4+;
const int inf=1e9;
const double eps=1e-; int n=; struct node
{
int a[];
node operator+(const node &y)
{
node z;
for (int i=;i<=n;i++)
z.a[i]=a[i]+y.a[i];
return z;
}
}f[][][]; int main()
{
int i,j,k,l;
int x=;
for (i=;i<=n;i++)
f[][i][i].a[i]=;
for (l=;l<=x;l++)
{
// for (i=1;i<n;i++)
// {
// f[l][i][i]=f[l-1][i][i];
// for (j=i+1;j<=n;j++)
// f[l][i][j]=f[l][i][j-1]+f[l-1][j][j];
// } for (i=;i<=n;i++)
for (j=i;j<=n;j++)
{
if (i!=j)
f[l][i][j]=f[l][i][j-];
for (k=i;k<=j;k++)
f[l][i][j]=f[l][i][j]+f[l-][k][j];
}
}
int y=;
for (i=;i<=n;i++)
{
for (j=;j<=n;j++)
// printf("%d%c",f[y][1][i].a[j],j==n?'\n':' ');
printf("%d%c",f[y][][i].a[j] &,j==n?'\n':' ');
}
return ;
}
/*
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0
1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
*/
M. Subsequence
序列自动机
非正统的写法:
1.从后往前,记录每一个字符最新出现的位置
2.贪心,找到第一个字符,在第一个字符位置之后找第二个字符,...
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; #define ll long long const int maxn=1e5+;
const int inf=1e9;
const double eps=1e-; int f[maxn][],pre[maxn];
char s[maxn]; int main()
{
int i,j,len,t;
memset(pre,0xff,sizeof(pre));
s[]='a';
scanf("%s",s+);
len=strlen(s+);
for (i=len;i>=;i--)
{
for (j=;j<;j++)
f[i][j]=pre[j];
pre[s[i]]=i;
}
scanf("%d",&t);
while (t--)
{
scanf("%s",s);
len=strlen(s);
j=f[][s[]];
for (i=;i<len;i++)
{
if (j==-)
break;
j=f[j][s[i]];
}
if (j!=-)
printf("YES\n");
else
printf("NO\n");
}
return ;
}
/* */
C. Angry FFF Party
数位dp
原来的数据是完全无用的,
只需要火柴棒总数保持一致,
只需要对于每一位,火柴棒加的次数完全一样
不用考虑前导0
+0 -> +9
-0 -> +5
w为数字的位数,y使用的火柴数
f[w][y] 的最大值
f[w][y]=max(f[w-1][y-g[i]]+i*10^(w-1)) i=0..9
w<10,y<w*7+2
-11..1 无法改变
f[1][3]=-1
f[p][p*2+1]=-11..1
其它时候不用减法(至少可以节省一根火柴,使负号变为加号)
这个不成立,在第一个数时(潜在加法)
预处理
对于当前的前x个数字,y为使用的火柴棒总数,以此最大的值
对于第x个数字,位数为w
a[x][y]=max(a[x-1][z]+f[w][z-y])
x<=50,y<=7*50+2*49=448
[49个加号,50个数]
易错点:
+/- 不能单独每一位,而要整体求
| 正确通过 | 2019-04-21 00:57 | 5ms | 448kB | c++14 |
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; #define ll long long const int maxn=1e4+;
const int inf=1e9;
const double eps=1e-; /**
其实最多只有9位,
是小于10^9,没有等于 999999999+999999999+...
超过int
**/ int g[]={,,,,,,,,,};
int f[][];
int mul[];
ll a[][];
int fv[];
int add[];
char s[]; int main()
{
bool vis;
int i,j,k,l,maxw,w,t,n,tot,sum,c; // printf("%d\n",'+');///43
// printf("%d\n",'-');///45
add[]=,add[]=;
for (i=;i<+;i++)
add[i]=g[i-]; mul[]=;
for (i=;i<=;i++)
mul[i]=mul[i-]*; fv[]=-;
for (i=;i<=;i++)
fv[i]=fv[i-]*-; memset(f,0x8f,sizeof(f));
f[][]=;///+
for (i=;i<=;i++)
{
maxw=(i-)*+;
for (j=;j<=maxw;j++)
for (l=;l<=;l++) ///或者只要用火柴数在一个数量时最大的数即可
f[i][j+g[l]]=max(f[i][j+g[l]],f[i-][j]+l*mul[i]);
} scanf("%d",&t);
while (t--)
{
memset(a,0x8f,sizeof(a));
scanf("%d",&n);
scanf("%s",s);
tot=;
vis=;
sum=;
a[][]=;
i=;
c=;
for (w=;w<=n;w++)
{
tot+=add[s[w]];
if (s[w]=='+' || s[w]=='-' || w==n)
{
c++;
maxw=i*+;
for (j=;j<=sum;j++)
for (k=;k<=maxw;k++)
///f[i][k](int memset)相比a[j](ll memset)小很多,减很多次,仍不会到达下界
a[c][j+k]=max(a[c][j+k],a[c-][j]+f[i][k]); ///可以使用滚动数组 if (vis)
for (j=;j<=sum;j++)
a[c][j+*i+]=max(a[c][j+*i+],a[c-][j]+fv[i]); sum+=maxw; ///当然也可以求出tot后再求
vis=;
i=;
continue;
}
else
i++;
}
printf("%lld\n",a[c][tot+]); ///第一个加号是没有的
}
return ;
}
/*
10
11
100000000+9
13
111-111111-11
20
100000000-99999999+1
36
10000000+12345+0+1+2+3+4+5+6+7+8+9 */
I. Max answer
单调栈+线段树
单调栈
找到一个数左边/右边的第一个大于其的数
把数列出来,容易找到方法
7 8 9 5(则9 8 7 出栈并赋值)
线段树
[l,r]区间 数为d 包含d的最大区间
sum[query_max(d,r)] - sum[query_min(l,d-1)]
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <list>
#include <queue>
#include <vector>
#include <bitset>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long const double eps=1e-;
const int maxn=5e5+;
const ll inf=1e18; int a[maxn],lef[maxn],rig[maxn],st[maxn],maxnum[maxn<<],minnum[maxn<<];
ll sum[maxn]; void build(int ind,int l,int r)
{
if (l==r)
maxnum[ind]=minnum[ind]=l;
else
{
int m=(l+r)>>;
build(ind<<,l,m);
build(ind<<|,m+,r);
if (sum[ maxnum[ind<<] ] > sum[ maxnum[ind<<|] ])
maxnum[ind]=maxnum[ind<<];
else
maxnum[ind]=maxnum[ind<<|]; if (sum[ minnum[ind<<] ] < sum[ minnum[ind<<|] ])
minnum[ind]=minnum[ind<<];
else
minnum[ind]=minnum[ind<<|];
}
} int query_max(int ind,int l,int r,int x,int y)
{
if (x>y)
return ;
if (x<=l && r<=y)
return maxnum[ind];
int m=(l+r)>>,b=-;
if (x<=m)
b=query_max(ind<<,l,m,x,y);
if (m<y)
{
if (b==-)
return query_max(ind<<|,m+,r,x,y);
else
{
int c=query_max(ind<<|,m+,r,x,y);
if (sum[b]>sum[c])
return b;
return c;
}
}
return b; ///
} int query_min(int ind,int l,int r,int x,int y)
{
if (x>y)
return ;
if (x<=l && r<=y)
return minnum[ind];
int m=(l+r)>>,b=-;
if (x<=m)
b=query_min(ind<<,l,m,x,y);
if (m<y)
{
if (b==-)
return query_min(ind<<|,m+,r,x,y);
else
{
int c=query_min(ind<<|,m+,r,x,y);
if (sum[b]<sum[c])
return b;
return c;
}
}
return b; ///
} int main()
{
int n,i,g;
ll r;
scanf("%d",&n);
for (i=;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]); g=;
for (i=;i<=n;i++)
{
while (g> && a[st[g]]>a[i])
{
rig[st[g]]=i;
g--;
}
st[++g]=i;
sum[i]=sum[i-]+a[i];
} g=;
for (i=n;i>=;i--)
{
while (g> && a[st[g]]>a[i])
{
lef[st[g]]=i;
g--;
}
st[++g]=i;
} build(,,n);
r=-inf;
for (i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if (rig[i]==)
rig[i]=n+;
if (a[i]>=)
r=max(r,a[i]*(sum[rig[i]-]-sum[lef[i]]));
else
r=max(r,a[i]*(sum[query_min(,,n,i,rig[i]-)]-max(0ll,sum[query_max(,,n,lef[i]+,i-)])));///<
}
printf("%lld",r);
return ;
}
/*
5
-2 1 -3 -4 3 6
-1 -2 -3 -4 -5 -6 3
-1 -3 -2 1
-3
*/
J. Distance on the tree
1.树剖
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
const double eps=1e-;
const int maxn=1e5+; ///°´ÕձߵĴóСÅÅÐò
///树剖: 边 而不是 点 struct node
{
int d;
node *to;
}*e[maxn]; struct rec
{
int u,v,w,num,mode;
bool operator<(const rec &y) const
{
if (w==y.w)
return mode<y.mode;
return w<y.w;
}
}b[maxn+maxn]; int sum[maxn]; int fa[maxn],dep[maxn],siz[maxn],son[maxn];
int id[maxn],top[maxn];
int n,num;
bool vis[maxn];
int tr[maxn<<]; void dfs1(int d)
{
int dd;
node* p=e[d];
vis[d]=;
siz[d]=;
while (p)
{
dd=p->d;
if (!vis[dd])
{
fa[dd]=d;
dep[dd]=dep[d]+;
dfs1(dd);
siz[d]+=siz[dd];
if (siz[dd]>siz[son[d]])
son[d]=dd;
}
p=p->to;
}
} void dfs2(int d,int topd)
{
id[d]=++num;
top[d]=topd;
if (son[d]!=)
{
int dd;
node *p;
dfs2(son[d],topd); p=e[d];
while (p)
{
dd=p->d;
if (dd!=son[d] && dd!=fa[d])
dfs2(dd,dd);
p=p->to;
}
}
} void update(int ind,int l,int r,int x)
{
tr[ind]++;
if (l==r)
return;
int m=(l+r)>>;
if (x<=m)
update(ind<<,l,m,x);
else
update(ind<<|,m+,r,x);
} int query(int ind,int l,int r,int x,int y)
{
if (x<=l && r<=y)
return tr[ind];
int m=(l+r)>>,sum=;
if (x<=m)
sum+=query(ind<<,l,m,x,y);
if (m<y)
sum+=query(ind<<|,m+,r,x,y);
return sum;
} int cal(int x,int y)
{
int sum=;
while (top[x]!=top[y])
{
if (dep[top[x]]<dep[top[y]])
swap(x,y);
sum+=query(,,n,id[top[x]],id[x]);
x=fa[top[x]];
} if (dep[x]<dep[y])
swap(x,y);
///u,v not the same
///减去根节点
return sum+query(,,n,id[y]+,id[x]);
} int main()
{
node *p;
int m,i,u,v;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for (i=;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&b[i].u,&b[i].v,&b[i].w);
b[i].num=i;
b[i].mode=; p=new node();
p->d=b[i].v;
p->to=e[b[i].u];
e[b[i].u]=p; p=new node();
p->d=b[i].u;
p->to=e[b[i].v];
e[b[i].v]=p;
}
for (i=n;i<n+m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&b[i].u,&b[i].v,&b[i].w);
b[i].num=i;
b[i].mode=;
}
sort(b+,b+n+m); fa[]=;
dfs1(); dfs2(,); for (i=;i<n+m;i++)
{
u=b[i].u;
v=b[i].v;
if (dep[u]<dep[v])
swap(u,v); ///往距离远的点加值
if (b[i].num<n)
update(,,n,id[u]);
else
sum[b[i].num-n+]=cal(u,v);
} for (i=;i<=m;i++)
printf("%d\n",sum[i]);
return ;
}
2.主席树
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; #define ll long long
const double eps=1e-;
const int maxn=1e5+;
const int maxv=1e9; ///1-i中的所有数 1-fa(j) -> 1-j 链 主席树 struct node
{
int d,len,num;
node *to;
node *opp;
int c;
}*e[maxn],*point[maxn]; struct rec
{///any d,dd 经历两次 可以选择d中加入编号比其大的
int l,r,sum;
}tr[maxn*]; int sum[maxn],fa[maxn],be[maxn],num;
bool vis[maxn]; void build(int ind_old,int ind,int l,int r,int x)
{
if (l==r) ///single
{
tr[ind].sum=tr[ind_old].sum+;
return;
}
int m=(l+r)>>;
if (x<=m)
{
tr[ind].r=tr[ind_old].r;
tr[ind].l=++num;
build(tr[ind_old].l,tr[ind].l,l,m,x);
}
else
{
tr[ind].l=tr[ind_old].l;
tr[ind].r=++num;
build(tr[ind_old].r,tr[ind].r,m+,r,x);
}
tr[ind].sum=tr[tr[ind].l].sum + tr[tr[ind].r].sum;
} int query(int ind,int l,int r,int k) ///[1,k]
{
if (r<=k)
return tr[ind].sum;
int m=(l+r)>>,sum=;
if (tr[ind].l!=) ///存在(该点在线段树中被创建)
sum+=query(tr[ind].l,l,m,k);
if (m<k && tr[ind].r!=)
sum+=query(tr[ind].r,m+,r,k);
return sum;
} void dfs(int d)
{
node *p=e[d];
int dd;
vis[d]=;
while (p)
{
dd=p->d;
if (!vis[dd])
{
be[dd]=++num;
build(be[d],be[dd],,maxv,p->len);
dfs(dd);
}
p=p->to;
}
} int getf(int d)
{
if (fa[d]==d)
return d;
fa[d]=getf(fa[d]);
return fa[d];
} void lca(int d)
{
int dd,x,y;
node *p=e[d];
vis[d]=;
while (p)
{
dd=p->d;
if (!vis[dd])
{
lca(dd);
x=getf(d);
y=getf(dd);
fa[y]=x;
}
p=p->to;
} p=point[d];
while (p)
{
dd=p->d;
///也许出现一次,也许出现两次
if (vis[dd] && p->opp->c==)
{
sum[p->num]-=query(be[getf(dd)],,maxv,p->len)*;
p->c=;
} p=p->to;
}
} int main()
{
node *p,*pp;
int n,m,u,v,w,k,i;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for (i=;i<=n;i++)
fa[i]=i; for (i=;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&u,&v,&w); p=new node();
p->d=v;
p->len=w;
p->to=e[u];
e[u]=p; p=new node();
p->d=u;
p->len=w;
p->to=e[v];
e[v]=p;
} num=;
be[]=; dfs(); for (i=;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&u,&v,&k); p=new node();
pp=new node(); p->d=v;
p->len=k;
p->num=i;
p->to=point[u];
p->opp=pp;
p->c=;
point[u]=p; pp->d=u;
pp->len=k;
pp->num=i;
pp->to=point[v];
pp->opp=p;
pp->c=;
point[v]=pp; sum[i]=query(be[u],,maxv,k) + query(be[v],,maxv,k); // printf("%d %d\n",query(be[u],1,maxv,k),query(be[v],1,maxv,k));
} memset(vis,,sizeof(vis));
lca(); for (i=;i<=m;i++)
printf("%d\n",sum[i]);
return ;
}
The Preliminary Contest for ICPC China Nanchang National Invitational and International Silk-Road Programming Contest的更多相关文章
- 2019The Preliminary Contest for ICPC China Nanchang National Invitational
The Preliminary Contest for ICPC China Nanchang National Invitational 题目一览表 考察知识点 I. Max answer 单调栈+ ...
- 计蒜客 38229.Distance on the tree-1.树链剖分(边权)+可持久化线段树(区间小于等于k的数的个数)+离散化+离线处理 or 2.树上第k大(主席树)+二分+离散化+在线查询 (The Preliminary Contest for ICPC China Nanchang National Invitational 南昌邀请赛网络赛)
Distance on the tree DSM(Data Structure Master) once learned about tree when he was preparing for NO ...
- The Preliminary Contest for ICPC China Nanchang National Invitational
目录 Contest Info Solutions A. PERFECT NUMBER PROBLEM D. Match Stick Game G. tsy's number H. Coloring ...
- The Preliminary Contest for ICPC China Nanchang National Invitational I. Max answer (单调栈+线段树)
题目链接:https://nanti.jisuanke.com/t/38228 题目大意:一个区间的值等于该区间的和乘以区间的最小值.给出一个含有n个数的序列(序列的值有正有负),找到该序列的区间最大 ...
- The Preliminary Contest for ICPC China Nanchang National Invitational I题
Alice has a magic array. She suggests that the value of a interval is equal to the sum of the values ...
- Max answer(The Preliminary Contest for ICPC China Nanchang National Invitational)
Alice has a magic array. She suggests that the value of a interval is equal to the sum of the values ...
- The Preliminary Contest for ICPC China Nanchang National Invitational I.Max answer单调栈
题面 题意:一个5e5的数组,定义一个区间的值为 这个区间的和*这个区间的最小值,注意数组值有负数有正数,求所有区间中最大的值 题解:如果全是正数,那就是原题 POJ2796 单调栈做一下就ok 我们 ...
- 2019 The Preliminary Contest for ICPC China Nanchang National Invitational(A 、H 、I 、K 、M)
A. PERFECT NUMBER PROBLEM 题目链接:https://nanti.jisuanke.com/t/38220 题意: 输出前五个完美数 分析: 签到.直接百度完美数输出即可 #i ...
- 计蒜客 38228. Max answer-线段树维护单调栈(The Preliminary Contest for ICPC China Nanchang National Invitational I. Max answer 南昌邀请赛网络赛) 2019ICPC南昌邀请赛网络赛
Max answer Alice has a magic array. She suggests that the value of a interval is equal to the sum of ...
随机推荐
- Python HTML解析器BeautifulSoup(爬虫解析器)
BeautifulSoup简介 我们知道,Python拥有出色的内置HTML解析器模块——HTMLParser,然而还有一个功能更为强大的HTML或XML解析工具——BeautifulSoup(美味的 ...
- Spring 事务与脏读、不可重复读、幻读
索引: 目录索引 参看代码 GitHub: 1.Spring 事务 2.事务行为 一.Spring 事务: Spring 的事务机制是用统一的机制来处理不同数据访问技术的事务处理. Spring 的事 ...
- django源码分析 请求流程
一.从浏览器发出一个请求,到返回响应内容,这个过程是怎么样的? 1. 浏览器解析输入的url 2. 查找url对应的ip地址 3. 通过ip地址访问我们的服务器 1. 请求进入wsgi服务器(我在这 ...
- sql 语句-初级进阶(二)
1.insert插入数据时注意事项: 每次插入一整行,不能半行或者是几列数据. 值与列数必须相同,包括数据类型也必须匹配. 不能为标识列指定值(就是最前面的那一序号列),它是自动增长的 列的数据类型为 ...
- Spring MVC中用@ResponseBody转json,对json进行处理方法汇总
<mvc:annotation-driven> <mvc:message-converters register-defaults="true"> < ...
- logback日志配置
第一步:加入jar包.要加入slf4j和logback的jar包,slf4j需要的jar包为slf4j-api,logback需要2个jar包(logback-classic.logback-core ...
- Linux Shell 返回值之 PIPESTATUS
BASH SHELL中,通常使用 $? 来获取上一条命令的返回码,对于管道中的命令,使用$?只能获取管道中最后一条命令的返回码,例如: 下面的例子 /djdjal/dajiojidksj.file是一 ...
- 一致性哈希算法----nginx负载均衡器配置之一
一直性Hash算法在很多场景下都有应用,尤其是在分布式缓存系统中,经常用其来进行缓存的访问的负载均衡,比如:redis等<k,v>非关系数据库作为缓存系统.我们首先来看一下采用取模方式进行 ...
- GMM算法的matlab程序
GMM算法的matlab程序 在“GMM算法的matlab程序(初步)”这篇文章中已经用matlab程序对iris数据库进行简单的实现,下面的程序最终的目的是求准确度. 作者:凯鲁嘎吉 - 博客园 h ...
- c++中 . 和 -> 的区别是什么?
主要用于访问类的成员,->主要用于类类型的指针访问类的成员,而.运算符,主要用于类类型的对象访问类的成员. 例如: class A { public :int a } A ma; A *p=&a ...
