一元回归_R相关系数_多重检验
python机器学习-乳腺癌细胞挖掘(博主亲自录制视频)https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005269003&utm_campaign=commission&utm_source=cp-400000000398149&utm_medium=share
文件夹需要两个包


normality_check.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
'''
Author:Toby
QQ:231469242,all right reversed,no commercial use
normality_check.py
正态性检验脚本 ''' import scipy
from scipy.stats import f
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy.stats as stats
# additional packages
from statsmodels.stats.diagnostic import lillifors #正态分布测试
def check_normality(testData):
#20<样本数<50用normal test算法检验正态分布性
if 20<len(testData) <50:
p_value= stats.normaltest(testData)[1]
if p_value<0.05:
print"use normaltest"
print "data are not normal distributed"
return False
else:
print"use normaltest"
print "data are normal distributed"
return True #样本数小于50用Shapiro-Wilk算法检验正态分布性
if len(testData) <50:
p_value= stats.shapiro(testData)[1]
if p_value<0.05:
print "use shapiro:"
print "data are not normal distributed"
return False
else:
print "use shapiro:"
print "data are normal distributed"
return True if 300>=len(testData) >=50:
p_value= lillifors(testData)[1]
if p_value<0.05:
print "use lillifors:"
print "data are not normal distributed"
return False
else:
print "use lillifors:"
print "data are normal distributed"
return True if len(testData) >300:
p_value= stats.kstest(testData,'norm')[1]
if p_value<0.05:
print "use kstest:"
print "data are not normal distributed"
return False
else:
print "use kstest:"
print "data are normal distributed"
return True #对所有样本组进行正态性检验
def NormalTest(list_groups):
for group in list_groups:
#正态性检验
status=check_normality(group)
if status==False :
return False '''
group1=[2,3,7,2,6]
group2=[10,8,7,5,10]
group3=[10,13,14,13,15]
list_groups=[group1,group2,group3]
list_total=group1+group2+group3
#对所有样本组进行正态性检验
NormalTest(list_groups)
'''
correlalion_multiple.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
#斯皮尔曼等级相关(Spearman’s correlation coefficient for ranked data)
import math,pylab,scipy
import numpy as np
import scipy.stats as stats
from scipy.stats import t
from scipy.stats import f
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from statsmodels.stats.diagnostic import lillifors
import normality_check
import statsmodels.formula.api as sm
x=[40,42,50,55,65,78,84,100,116,125,130,140]
y=[130,150,155,140,150,154,165,170,167,180,175,185] list_group=[x,y]
sample=len(x)
#显著性
a=0.05 #数据可视化
plt.plot(x,y,'ro')
#斯皮尔曼等级相关,非参数检验
def Spearmanr(x,y):
print("use spearmanr,Nonparametric tests")
#样本不一致时,发出警告
if len(x)!=len(y):
print ("warming,the samples are not equal!")
r,p=stats.spearmanr(x,y)
print("spearman r**2:",r**2)
print("spearman p:",p)
if sample<500 and p>0.05:
print("when sample < 500,p has no mean(>0.05)")
print("when sample > 500,p has mean") #皮尔森 ,参数检验
def Pearsonr(x,y):
print("use Pearson,parametric tests")
r,p=stats.pearsonr(x,y)
print("pearson r**2:",r**2)
print("pearson p:",p)
if sample<30:
print("when sample <30,pearson has no mean") #皮尔森 ,参数检验,带有详细参数
def Pearsonr_details(x,y,xLabel,yLabel,formula):
n=len(x)
df=n-2
data=pd.DataFrame({yLabel:y,xLabel:x})
result = sm.ols(formula, data).fit()
print(result.summary()) #模型F分布显著性分析
print('\n')
print("linear relation Significant test:...................................")
#如果F检验的P值<0.05,拒绝H0,x和y无显著关系,H1成立,x和y有显著关系
if result.f_pvalue<0.05:
print ("P value of f test<0.05,the linear relation is right.") #R的显著检验
print('\n')
print("R significant test:...................................")
r_square=result.rsquared
r=math.sqrt(r_square)
t_score=r*math.sqrt(n-2)/(math.sqrt(1-r**2))
t_std=t.isf(a/2,df)
if t_score<-t_std or t_score>t_std:
print ("R is significant according to its sample size")
else:
print ("R is not significant") #残差分析
print('\n')
print("residual error analysis:...................................")
states=normality_check.check_normality(result.resid)
if states==True:
print("the residual error are normal distributed")
else:
print("the residual error are not normal distributed") #残差偏态和峰态
Skew = stats.skew(result.resid, bias=True)
Kurtosis = stats.kurtosis(result.resid, fisher=False,bias=True)
if round(Skew,1)==0:
print("residual errors normality Skew:in middle,perfect match")
elif round(Skew,1)>0:
print("residual errors normality Skew:close right")
elif round(Skew,1)<0:
print("residual errors normality Skew:close left") if round(Kurtosis,1)==3:
print("residual errors normality Kurtosis:in middle,perfect match")
elif round(Kurtosis,1)>3:
print("residual errors normality Kurtosis:more peak")
elif round(Kurtosis,1)<3:
print("residual errors normality Kurtosis:more flat") #自相关分析autocorrelation
print('\n')
print("autocorrelation test:...................................")
DW = np.sum( np.diff( result.resid.values )**2.0 )/ result.ssr
if round(DW,1)==2:
print("Durbin-Watson close to 2,there is no autocorrelation.OLS model works well")
else:
print("there may be autocorrelation")
#共线性检查
print('\n')
print("multicollinearity test:")
conditionNumber=result.condition_number
if conditionNumber>30:
print("conditionNumber>30,multicollinearity exists")
else:
print("conditionNumber<=30,multicollinearity not exists") #绘制残差图,用于方差齐性检验
Draw_residual(list(result.resid))
'''
result.rsquared
Out[28]: 0.61510660055413524
''' #kendalltau非参数检验
def Kendalltau(x,y):
print("use kendalltau,Nonparametric tests")
r,p=stats.kendalltau(x,y)
print("kendalltau r**2:",r**2)
print("kendalltau p:",p) #选择模型
def R_mode(x,y,xLabel,yLabel,formula):
#正态性检验
Normal_result=normality_check.NormalTest(list_group)
print ("normality result:",Normal_result)
if len(list_group)>2:
Kendalltau(x,y)
if Normal_result==False:
Spearmanr(x,y)
Kendalltau(x,y)
if Normal_result==True:
Pearsonr_details(x,y,xLabel,yLabel,formula) #调整的R方
def Adjust_Rsquare(r_square,n,k):
adjust_rSquare=1-((1-r_square)*(n-1)*1.0/(n-k-1))
return adjust_rSquare
'''
n=len(x)
n=10
k=1
r_square=0.615
Adjust_Rsquare(r_square,n,k)
Out[11]: 0.566875
''' #绘图
def Plot(x,y,yLabel,xLabel,Title):
plt.plot(x,y,'ro')
plt.ylabel(yLabel)
plt.xlabel(xLabel)
plt.title(Title)
plt.show() #绘图参数
yLabel='Alcohol'
xLabel='Tobacco'
Title='Sales in Several UK Regions'
Plot(x,y,yLabel,xLabel,Title)
formula='Alcohol ~ Tobacco' #绘制残点图
def Draw_residual(residual_list):
x=[i for i in range(1,len(residual_list)+1)]
y=residual_list
pylab.plot(x,y,'ro')
pylab.title("draw residual to check wrong number") # Pad margins so that markers don't get clipped by the axes,让点不与坐标轴重合
pylab.margins(0.3) #绘制网格
pylab.grid(True) pylab.show() R_mode(x,y,xLabel,yLabel,formula)
sklearn r平方计算
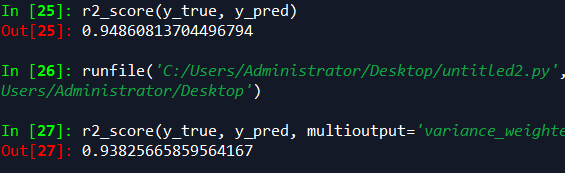
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
y_true = [3, -0.5, 2, 7]
y_pred = [2.5, 0.0, 2, 8]
r2_score(y_true, y_pred) y_true = [[0.5, 1], [-1, 1], [7, -6]]
y_pred = [[0, 2], [-1, 2], [8, -5]]
r2_score(y_true, y_pred, multioutput='variance_weighted')
https://study.163.com/provider/400000000398149/index.htm?share=2&shareId=400000000398149( 欢迎关注博主主页,学习python视频资源,还有大量免费python经典文章)
一元回归_R相关系数_多重检验的更多相关文章
- Python_sklearn机器学习库学习笔记(一)_一元回归
一.引入相关库 %matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from matplotlib.font_manager import FontP ...
- 一元回归1_基础(python代码实现)
python机器学习-乳腺癌细胞挖掘(博主亲自录制视频) https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005269003&u ...
- 机器学习(2):简单线性回归 | 一元回归 | 损失计算 | MSE
前文再续书接上一回,机器学习的主要目的,是根据特征进行预测.预测到的信息,叫标签. 从特征映射出标签的诸多算法中,有一个简单的算法,叫简单线性回归.本文介绍简单线性回归的概念. (1)什么是简单线性回 ...
- 标准方程法_岭回归_LASSO算法_弹性网
程序所用文件:https://files.cnblogs.com/files/henuliulei/%E5%9B%9E%E5%BD%92%E5%88%86%E7%B1%BB%E6%95%B0%E6%8 ...
- 零相关|回归|相关|相关系数|回归解释相关|r判断相关性|相关系数的区间估计|数据类型|非线性回归
零相关是什么? 零相关亦称“不相关”.相关的一种.两个变量的相关系数r=0时的相关.零相关表示两个变量非线性相关,这时两个变量可能相互独立,也可能曲线相关.对于正态变量,两个变量零相关与两个变量相互独 ...
- 一元回归_ols参数解读(推荐AAA)
sklearn实战-乳腺癌细胞数据挖掘(博客主亲自录制视频教程) https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005269003&a ...
- Linear regression with multiple variables(多特征的线型回归)算法实例_梯度下降解法(Gradient DesentMulti)以及正规方程解法(Normal Equation)
,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, ,, , ...
- R 分析回归(一元回归)
x <- c(,,,,,,,,,) # build X(predictor) y <- c(,,,,,,,,,) # build Y(dependent variable) mode(x) ...
- 回归分析法&一元线性回归操作和解释
用Excel做回归分析的详细步骤 一.什么是回归分析法 "回归分析"是解析"注目变量"和"因于变量"并明确两者关系的统计方法.此时,我们把因 ...
随机推荐
- 【Alpha】阶段第五次Scrum Meeting
[Alpha]阶段第五次Scrum Meeting 工作情况 团队成员 今日已完成任务 明日待完成任务 刘峻辰 增加课程接口 增加教师接口 赵智源 整合前端进行部署 构建后端测试点测试框架 肖萌威 编 ...
- Alpha事后诸葛(团队)
[设想和目标] Q1:我们的软件要解决什么问题?是否定义得很清楚?是否对典型用户和典型场景有清晰的描述? "小葵日记"是为了解决18-30岁年轻用户在记录生活时希望得到一美体验友好 ...
- rfid工作原理
RFID的工作原理是:标签进入磁场后,如果接收到阅读器发出的特殊射频信号,就能凭借感应电流所获得的能量发送出存储在芯片中的产品信息(即Passive Tag,无源标签或被动标签),或者主动发送某一频率 ...
- jQuery的滚动监听
jQuery的滚动监听 1.当前滚动的地方的窗口顶端到整个页面顶端的距离: var winPos = $(window).scrollTop(); 2.获取指定元素的页面位置: $(val).offs ...
- Sass & Scss & CSS3
Sass & Scss & CSS3 Sass & Scss @mixin & @include & @import & variable https: ...
- JavaScript常用方法(工具类的封装)
日期格式化 function formatDateTime(timeStamp) { var date = new Date(); date.setTime(timeStamp); var y = d ...
- 【EF】EF Code First Migrations数据库迁移
1.EF Code First创建数据库 新建控制台应用程序Portal,通过程序包管理器控制台添加EntityFramework. 在程序包管理器控制台中执行以下语句,安装EntityFramewo ...
- FZU2121_神庙逃亡
水题.直接解二次方程判断点的高度即可. #include <iostream> #include <cstring> #include <cstdio> #incl ...
- HDU4786_Fibonacci Tree
题目很新颖的,略带智商,很好. 题目的意思是给你一些白色边和黑色边,现在问你能否用两色边构造出一颗生成树,且树中白色边的数量为一个Fibonacci数. 其实在没做题目之前我就已经听说了这个题目的解题 ...
- kettle、Oozie、camus、gobblin
kettle简介 http://www.cnblogs.com/limengqiang/archive/2013/01/16/KettleApply1.html Oozie介绍 http://blog ...