C++fread/fwrite的基础用法
前言
fread是吼东西
应某人要求(大概)科普一下
fread
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#define fo(a,b,c) for (a=b; a<=c; a++)
#define fd(a,b,c) for (a=b; a>=c; a--)
using namespace std;
char st[233];
char *Ch=st;
int main()
{
fread(st,1,233,stdin);
cout<<st<<endl;
cout<<*Ch<<endl;
}
可以用文件输入,也可以直接输并在最后加Ctrl+Z
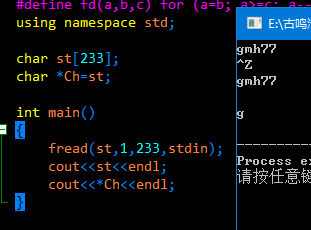
(下面的空行是因为读入了一个换行符)
fread基本格式:
fread(字符串,1,字符串大小,stdin);
*Ch一开始指向的是st[0],之后可以不断*++Ch来往后跳
快速读入
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#define fo(a,b,c) for (a=b; a<=c; a++)
#define fd(a,b,c) for (a=b; a>=c; a--)
using namespace std;
char st[233];
char *Ch=st;
int getint()
{
int x=0;
while (*Ch<'0' || *Ch>'9') *++Ch;
while (*Ch>='0' && *Ch<='9') x=x*10+(*Ch-'0'),*++Ch;
return x;
}
int main()
{
fread(st,1,233,stdin);
cout<<getint()<<endl;
}
fwrite
用处并不是很大
fwrite(字符串,1,字符串长度,stdout);
快速输出
把数字转成字符串再反过来加进去(要加上空格/换行符)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
#define fo(a,b,c) for (a=b; a<=c; a++)
#define fd(a,b,c) for (a=b; a>=c; a--)
using namespace std;
char st[233];
int Len;
void putint(int x)
{
int a[233];
int i,len=0;
if (!x) len=1;
while (x)
{
a[++len]=x%10;
x/=10;
}
fd(i,len,1)
st[++Len]=a[i]+'0';
st[++Len]=' ';
}
int main()
{
Len=-1;
putint(1);
putint(2);
putint(233);
fwrite(st,1,Len,stdout);
}
真正的fread/fwrite
其实上面的都是假的
但是上面的很好写
下面的不需要额外空间,但不能关文件
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
namespace io
{
const int SIZE = 1 << 22 | 1;
char iBuf[SIZE], *iS, *iT, c;
char oBuf[SIZE], *oS = oBuf, *oT = oBuf + SIZE;
#define gc() (iS == iT ? iT = iBuf + fread(iS = iBuf, 1, SIZE, stdin), (iS == iT ? EOF : *iS++) : *iS++)
template<class I> void gi(I &x)
{
int f = 1;
for(c = gc(); c < '0' || c > '9'; c = gc())
if(c == '-') f = -1;
for(x = 0; c >= '0' && c <= '9'; c = gc())
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (c & 15);
x *= f;
}
inline void flush()
{
fwrite(oBuf, 1, oS - oBuf, stdout);
oS = oBuf;
}
inline void putc(char x)
{
*oS++ = x;
if(oS == oT) flush();
}
template<class I> void print(I x)
{
if(x < 0) putc('-'), x = -x;
static char qu[55];
char *tmp = qu;
do *tmp++ = (x % 10) ^ '0'; while(x /= 10);
while(tmp-- != qu) putc(*tmp);
}
struct flusher{ ~flusher() { flush(); } }_;
}
using io :: gi;
using io :: putc;
using io :: print;
int main()
{
int x;
gi(x);
print(x);
putc('\n');
return 0;
}
C++fread/fwrite的基础用法的更多相关文章
- PropertyGrid控件由浅入深(二):基础用法
目录 PropertyGrid控件由浅入深(一):文章大纲 PropertyGrid控件由浅入深(二):基础用法 控件的外观构成 控件的外观构成如下图所示: PropertyGrid控件包含以下几个要 ...
- 那些年,坑死自己的事之fread/fwrite
今天继续看牛人做过的东西,这个小程序并不大,加上相当多的注释行,才5000多行.这个小程序是在linux下实现的,之前自己也一直用vi来看并加以更加详细的注释,但是效率实在太低.于是将其转移到wind ...
- logstash安装与基础用法
若是搭建elk,建议先安装好elasticsearch 来自官网,版本为2.3 wget -c https://download.elastic.co/logstash/logstash/packag ...
- elasticsearch安装与基础用法
来自官网,版本为2.3 注意elasticsearch依赖jdk,2.3依赖jdk7 下载rpm包并安装 wget -c https://download.elastic.co/elasticsear ...
- BigDecimal最基础用法
BigDecimal最基础用法 用字符串生成的BigDecimal是不会丢精度的. 简单除法. public class DemoBigDecimal { public static void mai ...
- linux缓冲的概念fopen /open,read/write和fread/fwrite区别
fopen /open区别 UNIX环境下的C 对二进制流文件的读写有两套班子:1) fopen,fread,fwrite ; 2) open, read, write这里简单的介绍一下他们的区别.1 ...
- Linux read/write fread/fwrite两者区别
Linux read/write fread/fwrite两者区别 1,fread是带缓冲的,read不带缓冲. 2,fopen是标准c里定义的,open是POSIX中定义的. 3,fread可以读一 ...
- Vue组件基础用法
前面的话 组件(Component)是Vue.js最强大的功能之一.组件可以扩展HTML元素,封装可重用的代码.根据项目需求,抽象出一些组件,每个组件里包含了展现.功能和样式.每个页面,根据自己所需, ...
- Smarty基础用法
一.Smarty基础用法: 1.基础用法如下 include './smarty/Smarty.class.php';//引入smarty类 $smarty = new Smarty();//实例化s ...
随机推荐
- js监听当前页面再次加载
document.addEventListener("visibilitychange", function () { if (!document.hidden) { //处于当前 ...
- 乱入Spring+Mybatis
新进入一个项目,写了一个功能,就是提供一个服务(service),该服务能够查询和插入.完成后,想要用junit测试一下:发现到了DAO底层注入的SqlSession字段为空:才意识到这是一个Spri ...
- HttpClient设置忽略SSL,实现HTTPS访问, 解决Certificates does not conform to algorithm constraints
话不多说,直接上代码. 测试API: https://api.k780.com/?app=life.time&appkey=10003&sign=b59bc3ef6191eb9f7 ...
- proteus 与 keil 的安装及联调
proteus 安装 Win10 系统的下载链接可以参考这里:https://tieba.baidu.com/p/5644915130?traceid= 百度网盘地址 链接1: http://pan. ...
- 003-Django创建模版配置流程
创建一个页面,简单的 templates/新建home.html,首页展示个人信息,发现我们需要四个参数 <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en&qu ...
- 【BZOJ2622】[2012国家集训队测试]深入虎穴
虎是中国传统文化中一个独特的意象.我们既会把老虎的形象用到喜庆的节日装饰画上,也可能把它视作一种邪恶的可怕的动物,例如“武松打虎”或者“三人成虎”.“不入虎穴焉得虎子”是一个对虎的威猛的形象的极好体现 ...
- 20191127 Spring Boot官方文档学习(6-8)
6.部署Spring Boot应用程序 在部署应用程序时,Spring Boot的灵活打包选项提供了很多选择.您可以将Spring Boot应用程序部署到各种云平台,容器映像(例如Docker)或虚拟 ...
- 堆排序 && Kth Largest Element in an Array
堆排序 堆节点的访问 通常堆是通过一维数组来实现的.在数组起始位置为0的情形中: 父节点i的左子节点在位置(2*i+1); 父节点i的右子节点在位置(2*i+2); 子节点i的父节点在位置floor( ...
- centos6.9 安装mysql8
centos6.9 安装 mysql8 # 安装mysql8 1.下载https://cdn.mysql.com//Downloads/MySQL-8.0/mysql-8.0.16-2.el6.x86 ...
- spring cloud gateway自定义过滤器
在API网关spring cloud gateway和负载均衡框架ribbon实战文章中,主要实现网关与负载均衡等基本功能,详见代码.本节内容将继续围绕此代码展开,主要讲解spring cloud g ...
