ARM32 Linux kernel virtual address space
http://thinkiii.blogspot.jp/2014/02/arm32-linux-kernel-virtual-address-space.html
In Linux kernel implementation, user space and kernel must coexist in the same 4GB virtual address space. It means both user space and kernel can use less than 4GB virtual address space.
Linux kernel provides 3 different split of virtual address spaces: VMSPLIT_3G, VMSPLIT_2G, VMSPLIT_1G.
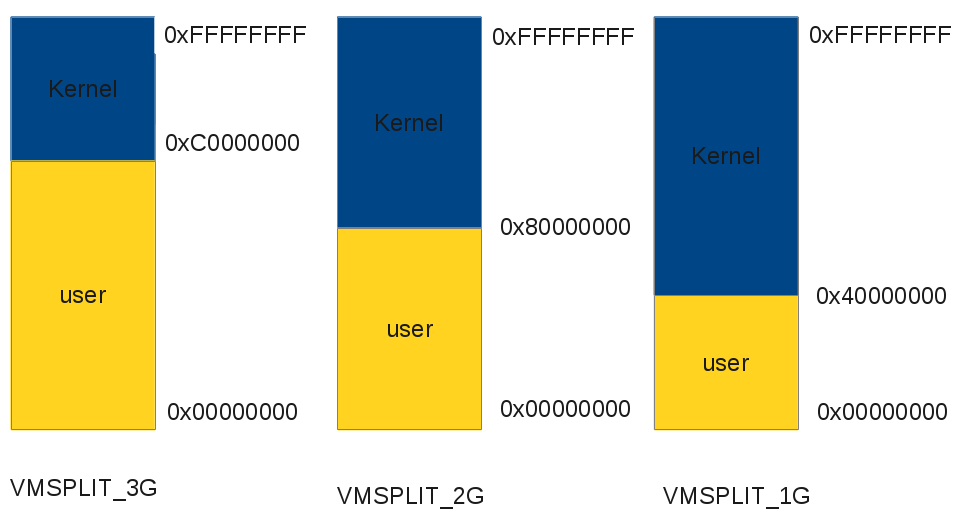
|
| Linux virtual address space options |
The default configuration is VMSPLIT_3G, as you can see, kernel space starts from 0xC0000000 to 0xFFFFFFFF and user space starts from 0x00000000 to 0xC0000000.
Let's take a closer look of the VMSPLIT_3G mapping:
The code for deterring user space virtual address is in arch/arm/mm/mmap.c
The user space have two different kind of mmap layout: legacy and non-legacy. Legacy layout sets the base of mmap(TASK_UNMAPPED_BASE) and the mmap grows in bottom-up manner; on the other case, non-legacy set the mmap base from TASK_SIZE - 128MB with some random shift for security reasons).
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
void arch_pick_mmap_layout(struct mm_struct *mm){ unsigned long random_factor = 0UL; /* 8 bits of randomness in 20 address space bits */ if ((current->flags & PF_RANDOMIZE) && !(current->personality & ADDR_NO_RANDOMIZE)) random_factor = (get_random_int() % (1 << 8)) << PAGE_SHIFT; if (mmap_is_legacy()) { mm->mmap_base = TASK_UNMAPPED_BASE + random_factor; mm->get_unmapped_area = arch_get_unmapped_area; } else { mm->mmap_base = mmap_base(random_factor); mm->get_unmapped_area = arch_get_unmapped_area_topdown; } |
The user space virtual address layout looks like:
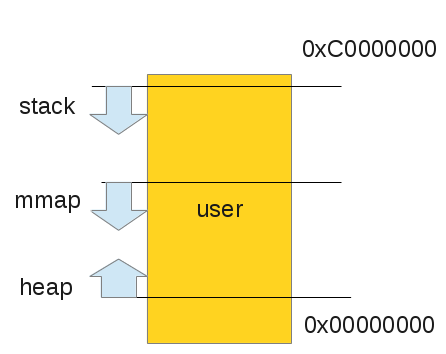
|
| 32-bit user virtual address space layout |
*ARM has LPAE (Large Physical Address Extension) mode that can address up to 1TB.
ARM32 Linux kernel virtual address space的更多相关文章
- ARM64 Linux kernel virtual address space
墙外通道:http://thinkiii.blogspot.com/2014/02/arm64-linux-kernel-virtual-address-space.html Now let's ta ...
- Memory Layout (Virtual address space of a C process)
Memory Layout (Virtual address space of a C process) 分类: C语言基础2012-12-06 23:16 2174人阅读 评论(0) 收藏 举报 f ...
- linux内核可以接受的参数 | Linux kernel启动参数 | 通过grub给内核传递参数
在Linux中,给kernel传递参数以控制其行为总共有三种方法: 1.build kernel之时的各个configuration选项. 2.当kernel启动之时,可以参数在kernel被GRUB ...
- Linux kernel学习-内存管理【转】
转自:https://zohead.com/archives/linux-kernel-learning-memory-management/ 本文同步自(如浏览不正常请点击跳转):https://z ...
- Linux kernel Programming - Allocating Memory
kmalloc #include <linux/slab.h> void *kmalloc(size_t size,int flags); void kfree(void *addr); ...
- Linux kernel学习-内存管理
转自:https://zohead.com/archives/linux-kernel-learning-memory-management/ 本文同步自(如浏览不正常请点击跳转):https://z ...
- Android linux kernel privilege escalation vulnerability and exploit (CVE-2014-4322)
In this blog post we'll go over a Linux kernel privilege escalation vulnerability I discovered which ...
- Linux Kernel - Debug Guide (Linux内核调试指南 )
http://blog.csdn.net/blizmax6/article/details/6747601 linux内核调试指南 一些前言 作者前言 知识从哪里来 为什么撰写本文档 为什么需要汇编级 ...
- Linux kernel memory-faq.txt
## Linux kernel memory-faq.txt What is some existing documentation on Linux memory management? Ulric ...
随机推荐
- 爬虫:Scrapy14 - Telnet 终端(Telnet Console)
Scrapy 提供了内置的 Telnet 终端,以供检查,控制 Scrapy 运行的进程.Telnet 仅仅是一个运行在 Scrapy 进程中的普通 Python 终端.因此你可以在其中做任何是. T ...
- Android通过onDraw实现在View中绘图操作
Android绘图操作,通过继承View实现,在onDraw函数中实现绘图. 下面是一个简单的例子: public class AndroidTest extends Activity { /** C ...
- 贪吃蛇StringBuilder 和 定时器
ConsoleKeyInfo info = Console.ReadKey(); while (true) { if (info.Key == ConsoleKey.UpArrow)//只能输入一次但 ...
- 简单的JS钟表计时
思路:先写出简单的数字计时,根据时分秒的数值转换成度数,使用CSS3的transform进行div倾斜. 知识点:transform可以对div进行倾斜或旋转等效果.但是根据浏览器不同代码也不同,本代 ...
- Java服务器端消息队列实战
服务端口监听--报文接收--报文解码--业务处理--报文编码--写回客户端 从服务端与客户端成功握手并产生一个socket后,为了提高吞吐能力,接下来的事情就可以交给多线程去处理. 为了对接入的请求做 ...
- python代理池的实现
https://github.com/wangqifan/ProxyPool http://python.jobbole.com/86994/
- Audio Unit 介绍
关于 Audio Unit iOS 提供了音频处理插件,支持混音,声音均衡,格式转化,以及用于录音,回放,离线渲染,实时对话的输入输出.可以动态载入和使用这些强大而灵活的插件,在 iOS 应用中这些插 ...
- Windows7下的Run运行命令一览表
按住Windows键(就是左边Ctrl和Alt之间那个印windows徽标的键,简称Win键)+R,即可弹出运行对话框,在里面输入黑体字符即可运行相应程序.相比XP这次新增了不少新东西. 添加/删除程 ...
- POST JSON fails with 415 Unsupported media type, SpringMVC
网上的解决办法非常多,但是大多不靠谱. 归结原因:SpringMVC 无法通过 httprequest headers 中的 Content-Type 和 Accept 匹配到对应的HttpMessa ...
- AGC023E - Inversion
Description \(n \le 2*10^5\) 给定限制序列 \(A\) 求满足 \(P_i\le A_i\) 的所有排列中 逆序对个数的和 Solution 考虑知道一个 \(A\) 序列 ...
