爬虫利器BeautifulSoup模块使用
| 一、简介 |
BeautifulSoup 是一个可以从HTML或XML文件中提取数据的Python库.它能够通过你喜欢的转换器实现惯用的文档导航,查找,修改文档的方式,同时应用场景也是非常丰富,你可以使用它进行XSS过滤,也可以是使用它来提取html中的关键信息。
官方文档:https://www.crummy.com/software/BeautifulSoup/bs4/doc/
| 二、安装 |
1.安装模块
easy_install beautifulsoup4
pip3 install beautifulsoup4
2.安装解析器(可以使用内置的解析器)
#Ubuntu
$ apt-get install Python-lxml
#centos/redhat
$ easy_install lxml
$ pip install lxml
3.各个解释器优缺点比较
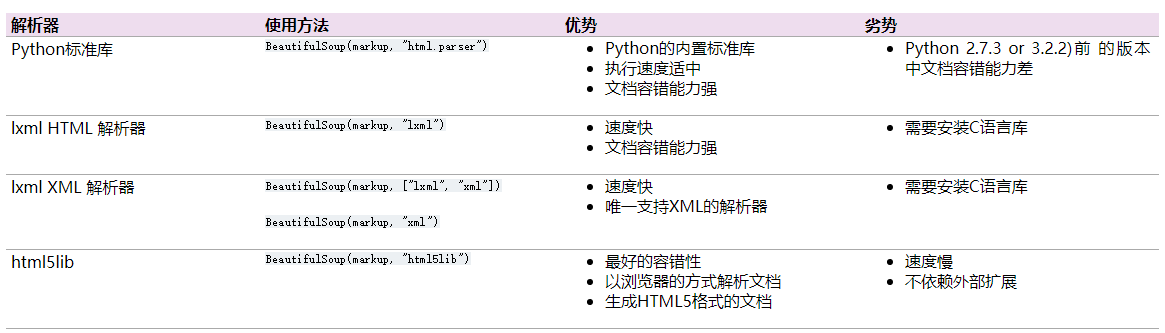
| 三、开始使用,基本属性介绍 |
创建对象
将一段文档传入BeautifulSoup 的构造方法,就能得到一个文档的对象, 可以传入一段字符串或一个文件句柄。
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(open("index.html"))
soup = BeautifulSoup("<html><body>...</body></html>")
###使用解释器###
soup = BeautifulSoup(open("index.html"), features="lxml")
基本使用
使用html示例
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>test</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>wd</b></p>
<p class="story">
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
</body>
</html>
""" soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,features="html.parser")
print(soup.head)#获取head标签
print(soup.head.title)#获取title
print(soup.body.a)
tips:通过soup.方式获取的标签如果标签有多个,只返回第一个标签
1.name:标签名称,如:<a>标签的名称为a,<span>标签名称为span
操作方式:获取、设置,设置以后会使得原文档标签改变
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#_*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
#Author:wd from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>test</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>wd</b></p>
<p class="story">
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
</body>
</html>
"""
soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,features="html.parser")
print(soup.body.name)#获取标签名称
soup.body.p.name='span'#设置标签名称
print(soup)
2.attrs:标签属性(如id,class,style等)
操作方式:获取、设置
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#_*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
#Author:wd
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>test</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>wd</b></p>
<p class="story">
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
</body>
</html>
"""
soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,features="html.parser")
print(soup.body.p.attrs)#获取标签所有属性
soup.body.p.attrs['id']='user'#设置/添加属性
print(soup.body.p.attrs.get('class'))#获取标签具体的某个属性,当然可以通过soup.body.p.attrs['class']获取
soup.body.p.attrs['class']=["hide","a1"]#设置多个属性
print(soup)
3.string:标签内容(类似js中的innertext),该属性只能适用于标签中只有一个内容,若有多个子标签都有内容则返回None
操作方式:获取、设置
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#_*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
#Author:wd
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>test</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>wd</b></p>
<p class="story">
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
</body>
</html>
"""
soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,features="html.parser")
print(soup.head.title.string)#获取内容
soup.head.title.string='name'#设置内容
print(soup)
4.contents:将子节点以列表方式输出,返回list(),列表中仅仅含有子标签
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#_*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
#Author:wd
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>test</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><a>wd</a></p>
<p class="story">
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
</body>
</html>
"""
soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,features="html.parser")
a=soup.body.contents
print(a)
print(type(a))
5.childen:和contents不同,它返回列表生成器,使用循环获取,生成器中只含有子标签
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#_*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
#Author:wd
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>test</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><a>wd</a></p>
<p class="story">
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
</body>
</html>
"""
soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,features="html.parser")
a=soup.body.children
print(type(a))
for item in a:
print(item)
6.descendants:返回子子孙孙标签,返回迭代器
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#_*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
#Author:wd
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>test</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><a>wd</a></p>
<p class="story">
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
</body>
</html>
"""
soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,features="html.parser")
a=soup.body.descendants
print(type(a))
for k,v in enumerate(a):
print(k,v)
7.strings&stripped_strings:返回所有子子孙孙标签内容生成器,stripped_strings和strings区别是,stripped_strings输出的是去掉空格的内容。
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#_*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
#Author:wd
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>test</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>wd</b></p>
<p class="story">
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
</body>
</html>
""" soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,features="html.parser")
for k,v in enumerate(soup.body.strings):
print(k,v)
for k1,v1 in enumerate(soup.body.stripped_strings):
print(k1,v1)
复制代码
8.parent&parents:父标签(节点)和祖辈节点,父标签一般只有一个,祖辈节点可能很多,parents返回生成器。
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#_*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
#Author:wd
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>test</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><a>wd</a></p>
<p class="story">
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
</body>
</html>
""" soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,features="html.parser")
print(soup.a.parent)#a标签的父节点
b=list(enumerate(soup.a.parents))
print(b)
for k,v in enumerate(soup.a.parents): #a标签的祖辈节点
print(k,v)
9.next_sibling&previous_sibling:兄弟标签(节点),一般只有一个,没有返回none
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#_*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
#Author:wd
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>test</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><a>wd</a></p>
<p class="story">
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
</body>
</html>
""" soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,features="html.parser")
print(soup.p.next_sibling)
print(soup.p.previous_sibling)
for k,v in enumerate(soup.p.next_siblings):
print(k,v)
10.next_siblings&previous_siblings:返回所有兄弟标签的生成器。
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#_*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
#Author:wd
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>test</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><a>wd</a></p>
<p class="story">
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
</body>
</html>
""" soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,features="html.parser")
for k,v in enumerate(soup.p.next_siblings):
print(k,v)
for k1,v1 in enumerate(soup.p.previous_siblings):
print(k1,v1)
11.hidden:隐藏或显示当前标签,只会把当前标签隐藏,子孙标签不变
soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,features="html.parser")
tag = soup.find('body')
tag.hidden=True#设置body标签隐藏
print(tag)
print(soup)
12.is_empty_element,是否是空标签(是否可以是空)或者自闭合标签
# tag = soup.find('br')
# v = tag.is_empty_element
# print(v)
| 四、强大的过滤器 |
这里所说的过滤器可以理解为查找文档的参数,可以是字符串,可以是name,可以是正则表达式等等,过滤器依赖于过滤方法,下面介绍常用过滤方法。
1.find_all(self, name=None, attrs={}, recursive=True, text=None, limit=None, **kwargs): 获取匹配的所有标签(节点),返回列表
- name:标签名,字符串对象会被忽略,可以是字符串、正则、列表、方法或者True
- attrs:标签属性,字典形式,用于查找标签的特殊属性
- recursive:是否递归查找,设置Flase,只查找子节点.
- text:文档中的字符串内容,与name参数一样,可接受字符串、正则、列表、或者True
- limit:限制列表中个数,如limit=3只返回前三个
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#_*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
#Author:wd
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
asdf
<div class="title">
<b>The Dormouse's story总共</b>
<h1>f</h1>
</div>
<div class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister0" id="link1">Els<span>f</span>ie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</div>
ad<br/>sf
<p class="story">...</p>
</body>
</html>
"""
soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,features="html.parser")
# tags = soup.find_all('a')
# print(tags) # tags = soup.find_all('a',limit=1)
# print(tags) # tags = soup.find_all(name='a', attrs={'class': 'sister'}, recursive=True, text='Lacie')
# # tags = soup.find(name='a', class_='sister', recursive=True, text='Lacie')
# print(tags) # ####### 列表 #######
# v = soup.find_all(name=['a','div'])
# print(v) # v = soup.find_all(class_=['sister0', 'sister'])
# print(v) # v = soup.find_all(text=['Tillie'])
# print(v, type(v[0])) # v = soup.find_all(id=['link1','link2'])
# print(v) # v = soup.find_all(href=['link1','link2'])
# print(v) # ####### 正则 #######
import re
# rep = re.compile('p')
# rep = re.compile('^p')
# v = soup.find_all(name=rep)
# print(v) # rep = re.compile('sister.*')
# v = soup.find_all(class_=rep)
# print(v) # rep = re.compile('http://www.oldboy.com/static/.*')
# v = soup.find_all(href=rep)
# print(v) # ####### 方法筛选 #######
# def func(tag):
# return tag.has_attr('class') and tag.has_attr('id')
# v = soup.find_all(name=func)
# print(v) # ## get,获取标签属性
# tag = soup.find('a')
# v = tag.get('id')
# print(v)
2.find_all(self, name=None, attrs={}, recursive=True, text=None, limit=None, **kwargs): 获取匹配的一个(节点),返回tag对象,用法与find_all相同
#!/usr/bin/env python3
#_*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
#Author:wd
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
asdf
<div class="title">
<b>The Dormouse's story总共</b>
<h1>f</h1>
</div>
<div class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister0" id="link1">Els<span>f</span>ie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</div>
ad<br/>sf
<p class="story">...</p>
</body>
</html>
"""
soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,features="html.parser")
tag = soup.find('a')
print(tag.name)
3.其他过滤方法:
tag.find_next(...) #返回后面第一个符合条件的节点
tag.find_all_next(...) #返回后面所有符合条件的节点
tag.find_next_sibling(...) #返回后面第一个兄弟节点
tag.find_next_siblings(...) #返回后面所有兄弟节点 tag.find_previous(...) #返回前面一个符合条件的节点
tag.find_all_previous(...) #返回前面所有符合条件的节点
tag.find_previous_sibling(...) #返回前面第一个兄弟节点
tag.find_previous_siblings(...) #返回前面所有兄弟节点 tag.find_parent(...) #返回所有祖先节点
tag.find_parents(...) #返回直接父节点 # 参数同find_all
| 五、CSS选择器 |
BeautifulSoup不仅提供了筛选器,也提供了选择器,用法和前端css一样,其中.代表class,#代表id
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
asdf
<div class="title">
<b>The Dormouse's story总共</b>
<h1>f</h1>
</div>
<div class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a class="sister0" id="link1">Els<span>f</span>ie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</div>
ad<br/>sf
<p class="story">...</p>
</body>
</html>
""" soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, features="lxml")
soup.select("title") soup.select("p nth-of-type(3)") soup.select("body a") soup.select("html head title") tag = soup.select("span,a") soup.select("head > title") soup.select("p > a") soup.select("p > a:nth-of-type(2)") soup.select("p > #link1") soup.select("body > a") soup.select("#link1 ~ .sister") soup.select("#link1 + .sister") soup.select(".sister") soup.select("[class~=sister]") soup.select("#link1") soup.select("a#link2") soup.select('a[href]') soup.select('a[href="http://example.com/elsie"]') soup.select('a[href^="http://example.com/"]') soup.select('a[href$="tillie"]') soup.select('a[href*=".com/el"]') from bs4.element import Tag def default_candidate_generator(tag):
for child in tag.descendants:
if not isinstance(child, Tag):
continue
if not child.has_attr('href'):
continue
yield child tags = soup.find('body').select("a", _candidate_generator=default_candidate_generator)
print(type(tags), tags) from bs4.element import Tag
def default_candidate_generator(tag):
for child in tag.descendants:
if not isinstance(child, Tag):
continue
if not child.has_attr('href'):
continue
yield child tags = soup.find('body').select("a", _candidate_generator=default_candidate_generator, limit=1)
print(type(tags), tags)
| 六、tag对象常用方法 |
1.clear():将标签的所有子标签全部清空(保留标签名)
# tag = soup.find('body')
# tag.clear()
# print(soup)
2.decompose():递归的删除所有的标签
soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,features="html.parser")
body = soup.find('body')
body.decompose()#body自身标签也会删除
print(soup)
3.extract():递归的删除所有的标签,并获取删除的标签
soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,features="html.parser")
body = soup.find('body')
a=body.extract()
print(a)
print(soup)
4.decode()&decode_contents():decode,转换为字符串(含当前标签),decode_contents(不含当前标签)
soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,features="html.parser")
body = soup.find('body')
a=body.decode()
b=body.decode_contents()
print(type(a))
print(type(b))
5.encode()&encode_contents():encode,转换为bytes类型(含当前标签),encode_contents(不含当前标签)
soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,features="html.parser")
body = soup.find('body')
a=body.encode()
b=body.encode_contents()
print(type(a))
print(type(b))
6. has_attr():检查标签是否具有该属性,返回布尔类型
soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,features="html.parser")
tag = soup.find('a')
print(tag.has_attr('id'))
7. get_text():获取标签内部文本内容
soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,features="html.parser")
tag = soup.find('a')
print(tag.get_text())
8.index():检查标签在某标签中的索引位置
# tag = soup.find('body')
# v = tag.index(tag.find('div'))
# print(v)
# tag = soup.find('body')
# for i,v in enumerate(tag):
# print(i,v)
9.append():在当前标签内部追加一个标签
# tag = soup.find('body')
# tag.append(soup.find('a'))
# print(soup)
#
# from bs4.element import Tag
# obj = Tag(name='i',attrs={'id': 'it'})
# obj.string = '我是一个新来的'
# tag = soup.find('body')
# tag.append(obj)
# print(soup)
10.insert():在当前标签内部指定位置插入一个标签
# from bs4.element import Tag
# obj = Tag(name='i', attrs={'id': 'it'})
# obj.string = '我是一个新来的'
# tag = soup.find('body')
# tag.insert(2, obj)
# print(soup)
11.insert_after()&insert_before(): 在当前标签后面或前面插入
# from bs4.element import Tag
# obj = Tag(name='i', attrs={'id': 'it'})
# obj.string = '我是一个新来的'
# tag = soup.find('body')
# # tag.insert_before(obj)
# tag.insert_after(obj)
# print(soup)
12.replace_with(): 在当前标签替换为指定标签
# from bs4.element import Tag
# obj = Tag(name='i', attrs={'id': 'it'})
# obj.string = '我是一个新来的'
# tag = soup.find('div')
# tag.replace_with(obj)
# print(soup)
13.setup():设置标签之间关系
# tag = soup.find('div')
# a = soup.find('a')
# tag.setup(previous_sibling=a)
# print(tag.previous_sibling)
14.wrap():将指定标签把当前标签包裹起来
# from bs4.element import Tag
# obj1 = Tag(name='div', attrs={'id': 'it'})
# obj1.string = '我是一个新来的'
#
# tag = soup.find('a')
# v = tag.wrap(obj1)
# print(soup) # tag = soup.find('a')
# v = tag.wrap(soup.find('p'))
# print(soup)
15. unwrap():去掉当前标签,将保留其包裹的标签
# tag = soup.find('a')
# v = tag.unwrap()
# print(soup)
爬虫利器BeautifulSoup模块使用的更多相关文章
- 【爬虫入门手记03】爬虫解析利器beautifulSoup模块的基本应用
[爬虫入门手记03]爬虫解析利器beautifulSoup模块的基本应用 1.引言 网络爬虫最终的目的就是过滤选取网络信息,因此最重要的就是解析器了,其性能的优劣直接决定这网络爬虫的速度和效率.Bea ...
- 【网络爬虫入门03】爬虫解析利器beautifulSoup模块的基本应用
[网络爬虫入门03]爬虫解析利器beautifulSoup模块的基本应用 1.引言 网络爬虫最终的目的就是过滤选取网络信息,因此最重要的就是解析器了,其性能的优劣直接决定这网络爬虫的速度和效率.B ...
- Python 爬虫三 beautifulsoup模块
beautifulsoup模块 BeautifulSoup模块 BeautifulSoup是一个模块,该模块用于接收一个HTML或XML字符串,然后将其进行格式化,之后遍可以使用他提供的方法进行快速查 ...
- Python爬虫之Beautifulsoup模块的使用
一 Beautifulsoup模块介绍 Beautiful Soup 是一个可以从HTML或XML文件中提取数据的Python库.它能够通过你喜欢的转换器实现惯用的文档导航,查找,修改文档的方式.Be ...
- Python网络爬虫之BeautifulSoup模块
一.介绍: Beautiful Soup 是一个可以从HTML或XML文件中提取数据的Python库.它能够通过你喜欢的转换器实现惯用的文档导航,查找,修改文档的方式.Beautiful Soup会帮 ...
- 爬虫五 Beautifulsoup模块
一 介绍 Beautiful Soup 是一个可以从HTML或XML文件中提取数据的Python库.它能够通过你喜欢的转换器实现惯用的文档导航,查找,修改文档的方式.Beautiful Soup会帮你 ...
- 爬虫五 Beautifulsoup模块详细
一.基本使用 from bs4 import BeautifulSoup htmlCharset = "GB2312" soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,'l ...
- python爬虫主要就是五个模块:爬虫启动入口模块,URL管理器存放已经爬虫的URL和待爬虫URL列表,html下载器,html解析器,html输出器 同时可以掌握到urllib2的使用、bs4(BeautifulSoup)页面解析器、re正则表达式、urlparse、python基础知识回顾(set集合操作)等相关内容。
本次python爬虫百步百科,里面详细分析了爬虫的步骤,对每一步代码都有详细的注释说明,可通过本案例掌握python爬虫的特点: 1.爬虫调度入口(crawler_main.py) # coding: ...
- SuperSpider——打造功能强大的爬虫利器
SuperSpider——打造功能强大的爬虫利器 1.爬虫的介绍 图1-1 爬虫(spider) 网络爬虫(web spider)是一个自动的通过网络抓取互联网 上的网页的程序,在当今互联网 中 ...
随机推荐
- Linux重启后raid5的名字发生变化
Linux重启后raid5的名字发生变化 使用raid,每次重启后,都会变换设备路径 比如原来为/dev/md0 重启一次变成了/dev/md127 这个问题,可以使用修改配置文件来解决. 1.mda ...
- Python day02 三元运算
type 查看数据类型.2 **32 :2的32次方 .浮点的表示类型是小数,但是小数不仅仅包括浮点 浮点数用来处理实数,即带有小数的数字 三元运算: result = 值1 if 条件 el ...
- 基于vue2+vuex+vue-router+sass+webpack的网易云音乐
[本博客为原创:http://www.cnblogs.com/HeavenBin/] 前言: 这段时间写的一个项目,供给大家互相学习,有什么疑问可以issues我. 源码地址:https://git ...
- linux系统编程:IO读写过程的原子性操作实验
所谓原子性操作指的是:内核保证某系统调用中的所有步骤(操作)作为独立操作而一次性加以执行,其间不会被其他进程或线程所中断. 举个通俗点的例子:你和女朋友OOXX的时候,突然来了个电话,势必会打断你们高 ...
- 使用Xamarin实现跨平台移动应用开发(转载)
刚在朋友圈看到张善友,转发的一条分享“使用Xamarin实现跨平台移动应用开发”,写的确实很详细得体,从收费到开源,这段时间xamarin受到不少质疑,如此文http://blog.csdn.net/ ...
- 大话命令之--ss
大话命令之-ss ss是Socket Statistics的缩写.顾名思义,ss命令可以用来获取socket统计信息,它可以显示和netstat类似的内容. 优势: (1)显示更多更详细的有关TCP和 ...
- 积累jquery一些有意思的函数
$("#btn").unbind("click"); // 让btn这个元素的点击事件失效 $("#btn").unbind(); // 让 ...
- 解决前端开发sublime text 3编辑器无法安装插件的问题
今天在笔记本电脑上安装了个sublime,但是却出现无法装插件的问题.于是稍微在网上查了些资料,并试验了一番,写了如下文章. 安装插件的步骤: 弹出 选中install package 如果出现如下问 ...
- Eclipse中使用Maven新建 Servlet 2.5的 SpringMVC项目
1.前言: 最近在学习SpringMVC框架,由于使用Eclipse创建的webAPP项目默认使用的还是比较旧的servlet2.3,而且默认使用的还是JDK1.5,所以便有一次开始了我的配置之路 2 ...
- 阿里云Centos 7.4 mssql-server
1.阿里云服务器控制台,开启1433端口(出入方向都要开).自从微软发布linux版本后,控制台常用端口下拉列表也增加了1433. 2.如果你没配置阿里云yum源,可参照配置一下.http://www ...
