[乱搞]hdu 6406 Taotao picks apples 笛卡尔树+倍增
When Taotao picks apples, Taotao scans these apples from the first one to the last one. If the current apple is the first apple, or it is strictly higher than the previously picked one, then Taotao will pick this apple; otherwise, he will not pick.
Given the heights of these apples h1,h2,⋯,hn, you are required to answer some independent queries. Each query is two integers p,q, which asks the number of apples Taotao would pick, if the height of the p-th apple were q (instead of hp). Can you answer all these queries?
Each test case begins with a line of two integers n,m (1≤n,m≤105), denoting the number of apples and the number of queries. It is then followed by a single line of n integers h1,h2,⋯,hn (1≤hi≤109), denoting the heights of the apples. The next m lines give the queries. Each of these m lines contains two integers p (1≤p≤n) and q (1≤q≤109), as described in the problem statement.
5 3
1 2 3 4 4
1 5
5 5
2 3
5
3
For the first query, the heights of the apples were 5, 2, 3, 4, 4, so Taotao would only pick the first apple.
For the second query, the heights of the apples were 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, so Taotao would pick all these five apples.
For the third query, the heights of the apples were 1, 3, 3, 4, 4, so Taotao would pick the first, the second and the fourth apples.
无论用哪一种算法,对于这道题目,最重要的就是高效的完成从一个苹果找到下一个苹果,那么笛卡尔树用来处理这样的操作是否足够呢?(笛卡尔树的解释可以参考这篇博客)
把一个数组按笛卡尔树的方式组织,根节点是整个数组最大的节点,然后以这个节点把数组划分为两部分,左右子结点分别又是左右部分的最大节点,以此类推。这样处理以后,从根节点一直向左走的路径,就是从第一个苹果出发将得到的递增序列。因此,我们只用考虑每次询问以后,这条路径会发生怎样的变化,而不必考虑整棵树的变化(如果树在不断更新就得考虑,只是需要进行非常细致的讨论)。询问大致可以分为4类:路径上的点变大/变小,非路径上的点变大/变小。
情况一:路径上的点变大
因为是增大,所以不会有新的点出现,只会覆盖已有的点。只需要从当前节点出发找到第一个比q大的节点就可以了。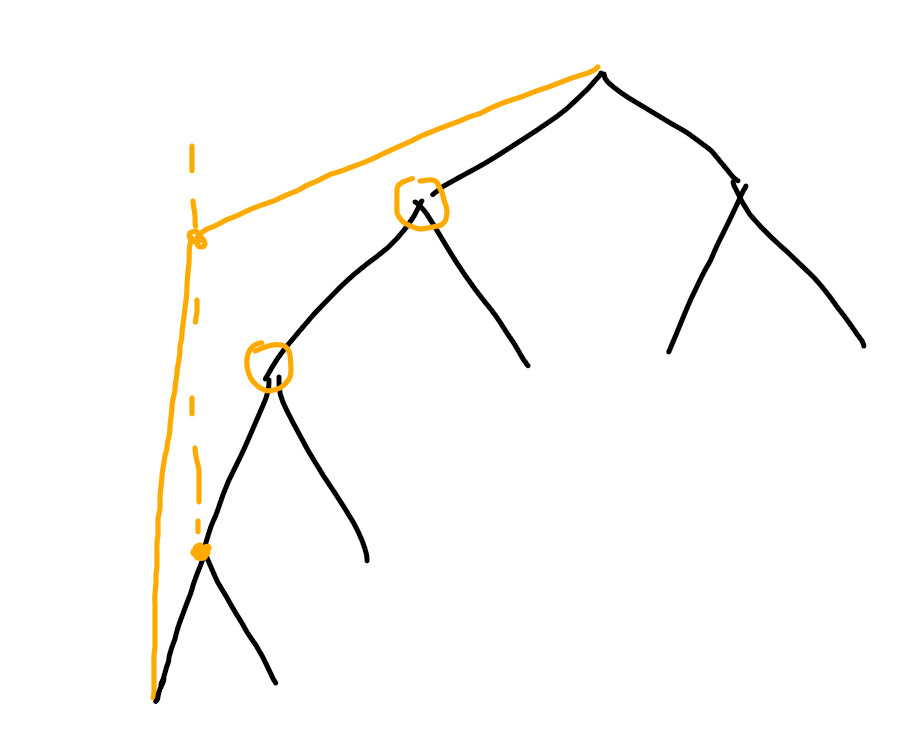
情况二:路径上的点变小
假设这个点是a,路径上的下一个点是b,那么当a变为a1的时候,在a,b之间本来被a覆盖的数字,就需要重新考虑。也就是从这个点右边的第一个数开始寻找,一直向上直到第一个比a1大的数。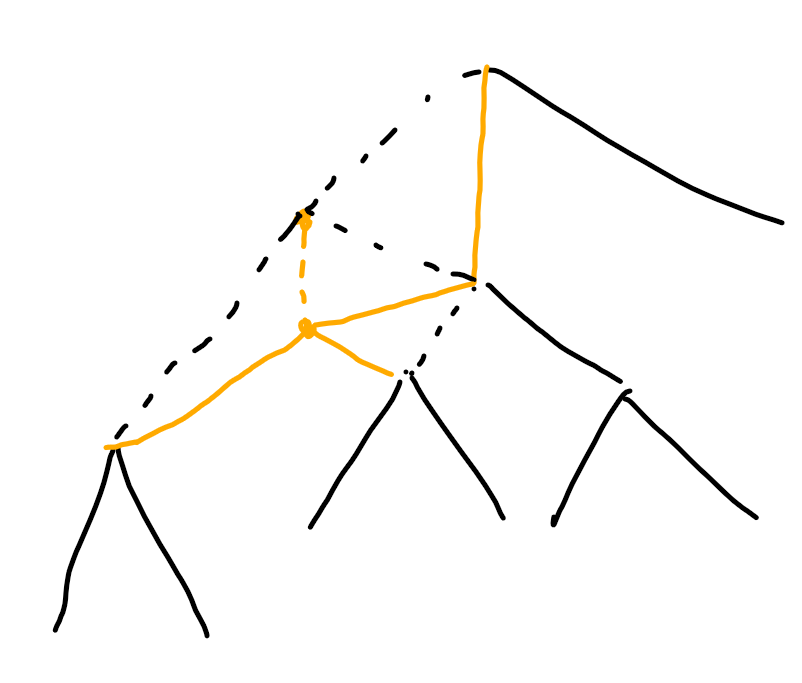
但是当a继续变小的时候,它将被路径上的前一个点c覆盖,而下一个点就应该是到第一个比c大的数
情况三:非路径上的点变大
考虑这个点在路径上的最近祖先。只有当它的变得比它的祖先还大,才会影响路径。而且它只会覆盖这个祖先的祖先。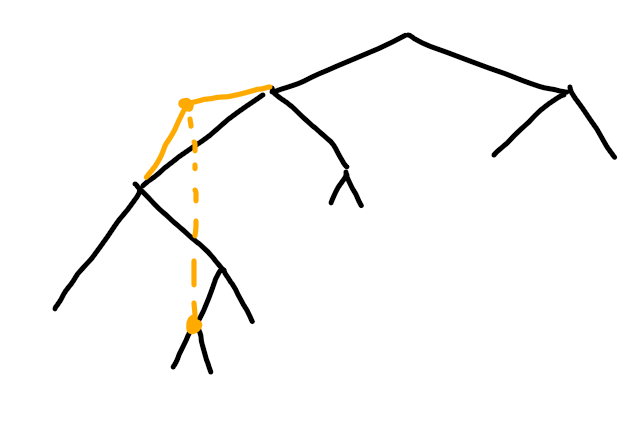
情况四:非路径上的点变小
对路径无影响
根据上面四个情况的分析,看似有很多边的变化,但最终只需要考虑有多少点要添加到路径上,其余的怎么变化不必考虑。
接下来就是终于到了算法的核心了,使用笛卡尔树只是将数组整理了成了一个比较好的结构,还需要一个高效寻找节点的方法。因为笛卡尔树的性质,向上走永远是在变大,每一个向上的过程都是单调的,可以用倍增的思想去寻找,每次尝试走1步,2步,4步,8步,直到遇到大的节点。
算法的复杂度不会算了,当时是这样分析的:建笛卡尔树为O(n),每次查询找下一个节点的复杂度在O(log(n))以内,如果建出来的笛卡尔树比较平衡的话,甚至可能接近O(log(log(n))),但因为数据随机以及可能有专门卡的数据,一次询问复杂度大致为O(log(n)),总共m次询问,最坏情况下也为O(mlogn)。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<memory.h>
#define N_max 100005
int n, m, ipt[N_max];
//#define debug there_is_no_bug_at_all_and_you_should_not_be_able_to_see_these_words_:( /*手动简易栈*/
int slen, stackhelp[N_max];
inline void push(int x) { stackhelp[slen++] = x; }
inline void pop() { slen--; }
inline int top() { return slen> ? stackhelp[slen - ] : -; }
inline void clear() { slen = ; } //笛卡尔树
typedef struct {
int l, r, p, v;
void newnode() { l = -; r = -; p = -; v = ; }
}node;
node tree[N_max];
int g[N_max][];
int on[N_max]; int lay[N_max];
void treeinit() {
clear();
memset(g, , sizeof g);
memset(lay, , sizeof lay);
memset(on, , sizeof on);
tree[].newnode();
tree[].v = 0x3f3f3f3f;
push();
} void add(int id, int v) {
tree[id].newnode();//准备好节点
while (slen > && tree[top()].v < v)pop();
int rt = top();
tree[id].v = v;
if (tree[rt].r > ) {/*子树挂到id左边*/
tree[tree[rt].r].p = id;
tree[id].l = tree[rt].r;
}
//id挂到根右边
tree[rt].r = id;
tree[id].p = rt;
push(id);//入栈
} int fb;
void dfs1(int cur){/*求倍增数组,顺带标记一下节点的层数*/
if (cur == -)return;
lay[cur] = (cur==?:(lay[tree[cur].p] + ));
g[cur][] = tree[cur].p;
for (int i = ;; ++i) {
fb = g[cur][i - ]; if (fb == )break;
g[cur][i] = g[fb][i - ];
}
dfs1(tree[cur].l);
dfs1(tree[cur].r);
} int key;
int find(int cur) {//利用倍增的思想查找第一个比key大的节点
if (cur == -)return -;
if (tree[cur].v>key)return cur; int fb = g[cur][];
if (tree[fb].v>key)return fb;
int jmp = fb;
for (int i = ;; ++i) {//向上试探
fb = g[cur][i]; if (fb == )break;
if (tree[fb].v>key)break;
jmp = fb;
}
return find(jmp);//可能没有一次找到,继续向上试探
} void color(int cur){//把一颗子树完全涂色为根节点
if (cur == -)return;
on[cur] = on[tree[cur].p];
color(tree[cur].l);
color(tree[cur].r);
} void geton() {//从根节点出发,把路径标记出来,并把路径上节点的右子树涂色为该节点
int cur = tree[].r;
do { on[cur] = cur;color(tree[cur].r); cur = tree[cur].l; } while (cur != -);
} int sol(int p,int q){
int x,y;
if(on[p]==p){//在路径上的操作
if(tree[p].v<q){//变大,考虑将被覆盖的点的个数
key = q; x = find(p);
return lay[] - lay[p] + + lay[x];
}
else{//变小
if(tree[p].r==-){
//没有右子树,则一定不会出现新的点,只考虑当前点是否会被前一个点覆盖
return (lay[]- ((tree[p].l==-)?:(q <= tree[tree[p].l].v)));
}
//考虑将从右子树新增几个点到路径上
key = q;
if(tree[p].l!=-&&q<=tree[tree[p].l].v)
//左边有点并且更新后比前一个点更小
key = tree[tree[p].l].v;
y = find(p + );
return lay[] - (q <= tree[tree[p].l].v) + lay[y] - lay[p];
}
}
else{//操作非路径上的点
if (tree[p].v<q){//变大
key = q; x = find(p);
if(on[x]==x)//变大到足够影响原序列,考虑将被覆盖的点的个数
return (lay[] - lay[on[p]] + lay[x]+(x!=on[p])+(q>tree[on[p]].v));
}
return (lay[]);//不足以影响,无变化
}
return ;//正常情况下不该出现的返回值(误
} int main()
{
int kase, p, q;
scanf("%d", &kase);
while (kase--) {
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
treeinit();
for (int i = ; i <= n; ++i){
scanf("%d", ipt + i);
add(i, ipt[i]);
}
lay[] = ;
dfs1();
geton();
for (int i = ; i<m; ++i) {
scanf("%d %d", &p, &q);
printf("%d\n",sol(p,q));
}
}
return ;
}
[乱搞]hdu 6406 Taotao picks apples 笛卡尔树+倍增的更多相关文章
- hdu 6406 Taotao Picks Apples (线段树)
Problem Description There is an apple tree in front of Taotao's house. When autumn comes, n apples o ...
- hdu 6406 Taotao Picks Apples 线段树 单点更新
Taotao Picks Apples Time Limit: 2000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 131072/131072 K (Java/Ot ...
- hdu 6406 Taotao Picks Apples (2018 Multi-University Training Contest 8 1010)(二分,前缀和)
链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6406 思路: 暴力,预处理三个前缀和:[1,n]桃子会被摘掉,1到当前点的最大值,1到当前点被摘掉的桃子的 ...
- HDU 6406 Taotao Picks Apples & FJUT3592 做完其他题后才能做的题(线段树)题解
题意(FJUT翻译HDU): 钱陶陶家门前有一棵苹果树. 秋天来了,树上的n个苹果成熟了,淘淘会去采摘这些苹果. 到园子里摘苹果时,淘淘将这些苹果从第一个苹果扫到最后一个. 如果当前的苹果是第一个苹果 ...
- HDU 6406 Taotao Picks Apples 线段树维护
题意:给个T,T组数据: 每组给个n,m:n个数,m个操作: (对序列的操作是,一开始假设你手上东西是-INF,到i=1时拿起1,之后遍历,遇到比手头上的数量大的数时替换(拿到手的算拿走),问最后拿走 ...
- HDU - 6406 Taotao Picks Apples (RMQ+dp+二分)
题意:N个高度为hi的果子,摘果子的个数是从位置1开始从左到右的严格递增子序列的个数.有M次操作,每次操作对初始序列修改位置p的果子高度为q.每次操作后输出修改后能摘到得数目. 分析:将序列分为左.右 ...
- hdu6406 Taotao Picks Apples(线段树)
Taotao Picks Apples 题目传送门 解题思路 建立一颗线段树,维护当前区间内的最大值maxx和可摘取的苹果数num.最大值很容易维护,主要是可摘取的苹果数怎么合并.合并左右孩子时,左孩 ...
- 【杂题总汇】HDU-6406 Taotao Picks Apples
[HDU 6406]Taotao Picks Apples 多校赛的时候多写了一行代码就WA了……找了正解对拍,在比赛结束后17分钟AC了
- HDU - 6305 RMQ Similar Sequence(笛卡尔树)
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=6305 题目 对于A,B两个序列,任意的l,r,如果RMQ(A,l,r)=RMQ(B,l,r),B序列里的数为[0 ...
随机推荐
- 【MongoDB】NoSQL Manager for MongoDB 教程(进阶篇)
项目做完,有点时间,接着写下第二篇吧.回顾戳这里 基础篇:安装.连接mongodb.使用shell.增删改查.表复制 本文属于进阶篇,为什么叫进阶篇,仅仅是因为这些功能属于DB范畴,一般使用的不多, ...
- 【MYSQL安装】mysql 5.6在centos6.4上的安装
1.卸载系统自带的mysql [root@zhangmeng ~]# rpm -qa |grep mysql mysql-libs--.el6_3.x86_64 [root@zhangmeng ~]# ...
- SQL基本的45题
-- 查询Student表中的所有记录的Sname.Ssex和Class列.SELECT Sname,Ssex,Class from student -- 查询教师所有的单位即不重复的Depart列. ...
- 我们一起学习WCF 第五篇数据协定和消息协定
A:数据协定(“数据协定”是在服务与客户端之间达成的正式协议,用于以抽象方式描述要交换的数据. 也就是说,为了进行通信,客户端和服务不必共享相同的类型,而只需共享相同的数据协定. 数据协定为每个参数或 ...
- 牛客小白月赛9 A签到(分数取模,逆元)
传送门 对分母求一下逆元,把除法取模变成乘法取模,逆元介绍看这里 这种方法只适合模为质数的情况 #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; ; ...
- 解析build.gradle文件
Gradle是一个非常先进的项目构建工具,它使用了一种基于Groovy的领域特定语言DSL来声明项目设置,摒弃了传统XML(如Ant和Maven)的各种繁琐配置 项目结构如上图: 1.最外层目录下的b ...
- PaaSoo云通讯-印度市场机遇与挑战并存
2019年4月16日,由白鲸出海举办的2019中印互联网大会(Global Connects India)在印度新德里举行,这次的大会主要涵盖了出海主题峰会.B2B展会.中印互联网高层圆桌等模块. 众 ...
- 关于cisco路由器配置的一些参数
单臂路由设置 Switch(config-if)#no switchport Switch(config)#ip routingSwitch(config)#interface FastEtherne ...
- Masha and Bears(翻译+思维)
Description A family consisting of father bear, mother bear and son bear owns three cars. Father bea ...
- Beta发布——视频博客
1.视频链接 视频上传至优酷自频道,地址链接:http://v.youku.com/v_show/id_XMzkzNzAxNDk2OA==.html?spm=a2hzp.8244740.0.0 2.视 ...
