C++复数四则运算的实现
程序主要实现复数的加减乘,数乘,取共轭功能。
将所有函数都定义为了成员函数。
使用库函数atof将字符串转换为浮点型数据。
函数主要难点在于处理输入。由于需要判断输入是选择退出还是继续,所以用字符串来接收输入,判断是否为q或Q后将字符串转换为double型。
由于库函数中定义了complex类,因此,这里的类名改为comple。
类声明
#ifndef COMPLEX_H_
#define COMPLEX_H_ #include<iostream>
using namespace std; class comple
{
private:
double re;
double im;
public:
comple(double r=0.0, double i=0.0);
~comple();
comple operator+(const comple & a) const;
comple operator-(const comple & a) const;
comple operator*(const comple & a) const;
comple operator~() const;
comple operator*(const double x) const;
friend ostream & operator<<(ostream & os, const comple & b);
friend int operator>>(istream & is, comple & b);
friend comple operator*(const double x, const comple & b); }; #endif
方法定义
#include"complex0.h"
#include<iostream>
#include<math.h> //strlen函数头文件
#include"string.h"
#include<cstdlib>//atof函数头文件
using namespace std; comple::comple(double r, double i)
{
re=r;
im=i;
} comple::~comple()
{ } comple comple::operator+(const comple & a) const
{
comple temp;
temp.re=re+a.re;
temp.im=im+a.im;
return temp;
} comple comple::operator-(const comple & a) const
{
comple temp;
temp.re=re-a.re;
temp.im=im-a.im;
return temp;
} comple comple::operator*(const comple & a) const
{
comple temp;
temp.re=re*a.re-im*a.im;
temp.im=re*a.im+im*a.re;
return temp;
} comple comple::operator~() const
{
comple temp;
temp.re=re;
temp.im=-im;
return temp;
} comple comple::operator*(const double x ) const
{
return comple(x*re,x*im);
} ostream & operator<<(ostream & os, const comple & b)
{
os << "(" <<b.re <<"," <<b.im << "i)";
return os;
} int operator>>(istream & is, comple & b)
{
double c1,c2;
char s[],*str;
int c,i;
cout << "real:";
is >> s;
c=strlen(s);
str=s;
for(i=;i<c;i++)
if(s[i]=='q'||s[i]=='Q')
return ; if((s[]>'')&&(s[]<''))
c1=atof(str); cout << "imaginary:";
is >> s;
c=strlen(s);
str=s;
for(i=;i<c;i++)
{
if(s[i]=='q'||s[i]=='Q')
return ;
} if(s[]>''&&s[]<'')
c2=atof(str); b=comple(c1,c2);
return ; } comple operator*(double x, const comple & b)
{
return b*x;
}
测试程序
#include<iostream>
#include"complex0.h" using namespace std; int main()
{
comple a(3.0,4.0);
comple c; cout << "Enter a complex number (q to quit):\n";
while(cin >> c)
{
cout << "c is " << c << endl;
cout << "complex conjugate is " << ~c <<endl;
cout << "a is " << a << endl;
cout << "a+c is " << a+c << endl;
cout << "a-c is " << a-c << endl;
cout << "a*c is " << a*c << endl;
cout << "2*c is " << *c << endl;
cout << "Enter a complex number (q to quit):\n";
}
cout << "Done!\n";
return ;
}
测试结果
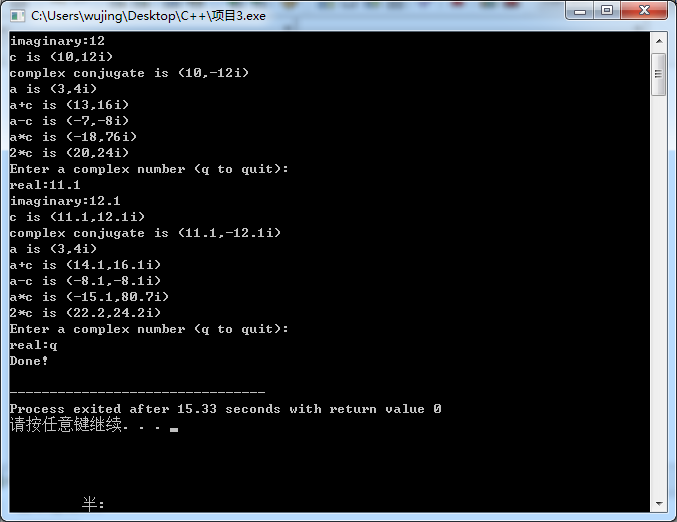
atof函数补充
包含的头文件在c中为#include<stdlib.h>,c++中为include<cstdlib>
http://www.cppblog.com/cxiaojia/archive/2012/02/24/166436.html
http://my.oschina.net/Tsybius2014/blog/338234
http://www.cnblogs.com/lidabo/archive/2012/07/10/2584706.html
http://blog.csdn.net/cxh342968816/article/details/6627768
标准c++库函数中复数四则运算程序
#ifndef __MYCOMPLEX__
#define __MYCOMPLEX__ class complex;
complex&
__doapl (complex* ths, const complex& r);
complex&
__doami (complex* ths, const complex& r);
complex&
__doaml (complex* ths, const complex& r); class complex
{
public:
complex (double r = , double i = ): re (r), im (i) { }
complex& operator += (const complex&);
complex& operator -= (const complex&);
complex& operator *= (const complex&);
complex& operator /= (const complex&);
double real () const { return re; }
double imag () const { return im; }
private:
double re, im; friend complex& __doapl (complex *, const complex&);
friend complex& __doami (complex *, const complex&);
friend complex& __doaml (complex *, const complex&);
}; inline complex&
__doapl (complex* ths, const complex& r)
{
ths->re += r.re;
ths->im += r.im;
return *ths;
} inline complex&
complex::operator += (const complex& r)
{
return __doapl (this, r);
} inline complex&
__doami (complex* ths, const complex& r)
{
ths->re -= r.re;
ths->im -= r.im;
return *ths;
} inline complex&
complex::operator -= (const complex& r)
{
return __doami (this, r);
} inline complex&
__doaml (complex* ths, const complex& r)
{
double f = ths->re * r.re - ths->im * r.im;
ths->im = ths->re * r.im + ths->im * r.re;
ths->re = f;
return *ths;
} inline complex&
complex::operator *= (const complex& r)
{
return __doaml (this, r);
} inline double
imag (const complex& x)
{
return x.imag ();
} inline double
real (const complex& x)
{
return x.real ();
} inline complex
operator + (const complex& x, const complex& y)
{
return complex (real (x) + real (y), imag (x) + imag (y));
} inline complex
operator + (const complex& x, double y)
{
return complex (real (x) + y, imag (x));
} inline complex
operator + (double x, const complex& y)
{
return complex (x + real (y), imag (y));
} inline complex
operator - (const complex& x, const complex& y)
{
return complex (real (x) - real (y), imag (x) - imag (y));
} inline complex
operator - (const complex& x, double y)
{
return complex (real (x) - y, imag (x));
} inline complex
operator - (double x, const complex& y)
{
return complex (x - real (y), - imag (y));
} inline complex
operator * (const complex& x, const complex& y)
{
return complex (real (x) * real (y) - imag (x) * imag (y),
real (x) * imag (y) + imag (x) * real (y));
} inline complex
operator * (const complex& x, double y)
{
return complex (real (x) * y, imag (x) * y);
} inline complex
operator * (double x, const complex& y)
{
return complex (x * real (y), x * imag (y));
} complex
operator / (const complex& x, double y)
{
return complex (real (x) / y, imag (x) / y);
} inline complex
operator + (const complex& x)
{
return x;
} inline complex
operator - (const complex& x)
{
return complex (-real (x), -imag (x));
} inline bool
operator == (const complex& x, const complex& y)
{
return real (x) == real (y) && imag (x) == imag (y);
} inline bool
operator == (const complex& x, double y)
{
return real (x) == y && imag (x) == ;
} inline bool
operator == (double x, const complex& y)
{
return x == real (y) && imag (y) == ;
} inline bool
operator != (const complex& x, const complex& y)
{
return real (x) != real (y) || imag (x) != imag (y);
} inline bool
operator != (const complex& x, double y)
{
return real (x) != y || imag (x) != ;
} inline bool
operator != (double x, const complex& y)
{
return x != real (y) || imag (y) != ;
} #include <cmath> inline complex
polar (double r, double t)
{
return complex (r * cos (t), r * sin (t));
} inline complex
conj (const complex& x)
{
return complex (real (x), -imag (x));
} inline double
norm (const complex& x)
{
return real (x) * real (x) + imag (x) * imag (x);
} #endif //__MYCOMPLEX__
测试程序
#include <iostream>
#include "complex.h" using namespace std; ostream&
operator << (ostream& os, const complex& x)
{
return os << '(' << real (x) << ',' << imag (x) << ')';
} int main()
{
complex c1(, );
complex c2(, ); cout << c1 << endl;
cout << c2 << endl; cout << c1+c2 << endl;
cout << c1-c2 << endl;
cout << c1*c2 << endl;
cout << c1 / << endl; cout << conj(c1) << endl;
cout << norm(c1) << endl;
cout << polar(,) << endl; cout << (c1 += c2) << endl; cout << (c1 == c2) << endl;
cout << (c1 != c2) << endl;
cout << +c2 << endl;
cout << -c2 << endl; cout << (c2 - ) << endl;
cout << ( + c2) << endl; return ;
}
C++复数四则运算的实现的更多相关文章
- C语言 · 复数四则运算
算法提高 6-17复数四则运算 时间限制:1.0s 内存限制:512.0MB 设计复数库,实现基本的复数加减乘除运算. 输入时只需分别键入实部和虚部,以空格分割,两个复数之间用运算符 ...
- Java实现 蓝桥杯 算法提高 复数四则运算
算法提高 6-17复数四则运算 时间限制:1.0s 内存限制:512.0MB 提交此题 设计复数库,实现基本的复数加减乘除运算. 输入时只需分别键入实部和虚部,以空格分割,两个复数之间用运算符分隔:输 ...
- PTA 复数四则运算
本题要求编写程序,计算2个复数的和.差.积.商. 输入格式: 输入在一行中按照a1 b1 a2 b2的格式给出2个复数C1=a1+b1i和C2=a2+b2i的实部和虚部.题目保证C2不为0. 输出格式 ...
- 算法笔记_156:算法提高 6-17复数四则运算(Java)
目录 1 问题描述 2 解决方案 1 问题描述 设计复数库,实现基本的复数加减乘除运算. 输入时只需分别键入实部和虚部,以空格分割,两个复数之间用运算符分隔:输出时按a+bi的格式在屏幕上打印结果 ...
- [C++][重载]
运算符重载 C++中预定义的运算符的操作对象只能是基本数据类型,实际上,对于很多用户自定义类型,也需要有类似的运算操作.例如: class complex { public: complex(d ...
- 基于C++任意点数的FFT/IFFT(时域和频域)实现
函数说明:更改主函数体中的N和length(=log2(N))既可以实现任意点数(2的幂次)的FFT/ IFFT的实现,fft函数中flag标志位控制是正变换还是逆变换. 1.复数操作类 定 ...
- C++运算符重载讲解与经典实例
最近在学C++,找到一篇详细讲解运算符重载的文章,贴在这里分享和收藏. C++中预定义的运算符的操作对象只能是基本数据类型,实际上,对于很多用户自定义类型,也需要有类似的运算操作.例如: class ...
- [Swift]复数的表示和四则运算
我们把形如z=a+bi(a,b均为实数)的数称为复数,其中a称为实部,b称为虚部,i称为虚数单位. 当虚部等于零时,这个复数可以视为实数:当z的虚部不等于零时,实部等于零时,常称z为纯虚数. 复数域是 ...
- C复数的四则运算
#include<stdio.h> void judge(int True,int Fake) { if (True == 0) { if (Fake == ...
随机推荐
- 曲线行驶s弯道技巧图解【转】
s弯道怎么走?在走S弯的时候,最主要的就是控制车的速度,在做每个动作的时候要保持一样的速度,不要一会快一会慢的,在开的时候,因为每个人的身高,体型不一样,每个人看的点位都是不一样的,每次在开的时候要找 ...
- 42.Android之ListView中ArrayAdapter简单学习
今天学习下Android中ListView关于ArrayAdapter数据绑定, 废话少说直接上代码. 改下布局文件: <?xml version="1.0" encodin ...
- 22.Android之ExpandableListView树形列表学习
Android经常用到树形菜单,一般ExpandableListView可以满足这个需要,今天学习下. XML代码: <?xml version="1.0" encoding ...
- ubuntu设置屏幕亮度
楼主的本本是acer4750g ,系统是ubuntu kylin 14.04 原 笔记本ubuntu14.04无法调节屏幕亮度 http://my.oschina.net/lhplj/blog/397 ...
- poj 1006 中国剩余定理解同余方程
其实画个图就明白了, 该问题就是求同余方程组的解: n+d≡p (mod 23) n+d≡e (mod 28) n+d≡i (mod 33) #include "iostream" ...
- poj 3683 2-SAT入门
原题模型:两者(A,B)不能同时取 #include "cstdio" #include "vector" #include "stack" ...
- POJ2263 Heavy Cargo
Heavy Cargo Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 4004 Accepted: 2124 Descr ...
- Syntax error, annotations are only available if source level is 1.5
在项目上右键 -> Properties -> Java Compiler
- Modular Query
Solution F(L, R) 就是在A[L]在[L+1, R]内从左模到右. 首先应当注意到: 对$a, b > 0$ \[a \mod b \begin{cases} = a, & ...
- ExtJS入门教程06,grid分页的实现
前面两篇内容分别介绍了extjs grid的基本用法和extjs grid异步加载数据,这篇文章将介绍extjs grid的分页. 数据量大的时候我们必须用到分页,结合上一篇的异步加载数据,今天我们就 ...
