JavaPersistenceWithHibernate第二版笔记-第六章-Mapping inheritance-004Table per class hierarchy(@Inheritance..SINGLE_TABLE)、@DiscriminatorColumn、@DiscriminatorValue、@DiscriminatorFormula)
一、结构
You can map an entire class hierarchy to a single table. This table includes columns for all properties of all classes in the hierarchy. The value of an extra type discriminator column or formula identifies the concrete subclass represented by a particular row. Figure 6.2 shows this approach.
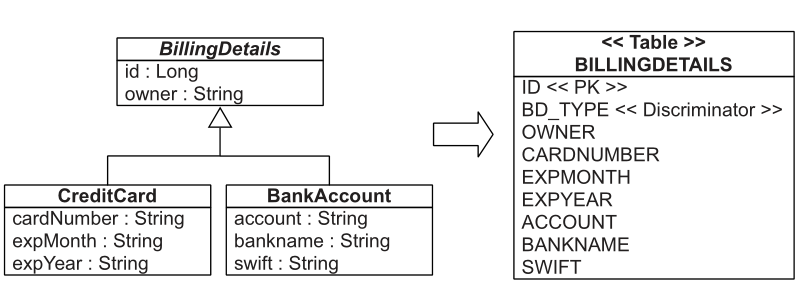
二、代码
1.
package org.jpwh.model.inheritance.singletable; import org.jpwh.model.Constants; import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.DiscriminatorColumn;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Inheritance;
import javax.persistence.InheritanceType;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull; @Entity
@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.SINGLE_TABLE)
@DiscriminatorColumn(name = "BD_TYPE")
public abstract class BillingDetails { @Id
@GeneratedValue(generator = Constants.ID_GENERATOR)
protected Long id; @NotNull // Ignored by Hibernate for schema generation!
@Column(nullable = false)
protected String owner; // ... protected BillingDetails() {
} protected BillingDetails(String owner) {
this.owner = owner;
} public Long getId() {
return id;
} public String getOwner() {
return owner;
} public void setOwner(String owner) {
this.owner = owner;
}
}
2.
package org.jpwh.model.inheritance.singletable; import javax.persistence.DiscriminatorValue;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull; @Entity
@DiscriminatorValue("BA")
public class BankAccount extends BillingDetails { @NotNull
protected String account; @NotNull
protected String bankName; @NotNull
protected String swift; public BankAccount() {
super();
} public BankAccount(String owner, String account, String bankName, String swift) {
super(owner);
this.account = account;
this.bankName = bankName;
this.swift = swift;
} public String getAccount() {
return account;
} public void setAccount(String account) {
this.account = account;
} public String getBankName() {
return bankName;
} public void setBankName(String bankName) {
this.bankName = bankName;
} public String getSwift() {
return swift;
} public void setSwift(String swift) {
this.swift = swift;
}
}
3.
package org.jpwh.model.inheritance.singletable; import javax.persistence.DiscriminatorValue;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull; @Entity
@DiscriminatorValue("CC")
public class CreditCard extends BillingDetails { @NotNull // Ignored by Hibernate for DDL generation!
protected String cardNumber; @NotNull
protected String expMonth; @NotNull
protected String expYear; // ... public CreditCard() {
super();
} public CreditCard(String owner, String cardNumber, String expMonth, String expYear) {
super(owner);
this.cardNumber = cardNumber;
this.expMonth = expMonth;
this.expYear = expYear;
} public String getCardNumber() {
return cardNumber;
} public void setCardNumber(String cardNumber) {
this.cardNumber = cardNumber;
} public String getExpMonth() {
return expMonth;
} public void setExpMonth(String expMonth) {
this.expMonth = expMonth;
} public String getExpYear() {
return expYear;
} public void setExpYear(String expYear) {
this.expYear = expYear;
}
}
4.在无法改变表结构增加discriminator的情况下,可以使用Hibernate的扩展注解@DiscriminatorFormula,底层是利用数据库的case when 语句
package org.jpwh.model.inheritance.singletableformula; import org.jpwh.model.Constants; import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Inheritance;
import javax.persistence.InheritanceType;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotNull; @Entity
@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.SINGLE_TABLE)
@org.hibernate.annotations.DiscriminatorFormula(
"case when CARDNUMBER is not null then 'CC' else 'BA' end"
)
public abstract class BillingDetails {
// ...
@Id
@GeneratedValue(generator = Constants.ID_GENERATOR)
protected Long id; @NotNull
protected String owner; protected BillingDetails() {
} protected BillingDetails(String owner) {
this.owner = owner;
} public Long getId() {
return id;
} public String getOwner() {
return owner;
} public void setOwner(String owner) {
this.owner = owner;
}
}
三、SINGLE_TABLE的优缺点
1.优点
(1)This mapping strategy is a winner in terms of both performance and simplicity. It’s the best-performing way to represent polymorphism—both polymorphic and non-polymorphic queries perform well—and it’s even easy to write queries by hand. Ad hoc reporting is possible without complex joins or unions. Schema evolution is straightforward.
Hibernate generates the following SQL for select bd from BillingDetails bd :
select
ID, OWNER, EXPMONTH, EXPYEAR, CARDNUMBER,
ACCOUNT, BANKNAME, SWIFT, BD_TYPE
from
BILLINGDETAILS
To query the CreditCard subclass, Hibernate adds a restriction on the discriminator column:
select
ID, OWNER, EXPMONTH, EXPYEAR, CARDNUMBER
from
BILLINGDETAILS
where
BD_TYPE='CC'
2.缺点
(1)the loss of NOT NULL constraints may be a serious problem from the point of view of data correctness. Imagine that an expiration date for credit cards is required, but your database schema can’t enforce this rule because all columns of the table can be NULL .
(2)Another important issue is normalization. You’ve created functional dependencies between non-key columns, violating the third normal form. As always, denormalization for performance reasons can be misleading, because it sacrifices long-term stability,maintainability, and the integrity of data for immediate gains that may be also achieved
by proper optimization of the SQL execution plans (in other words, ask your DBA ).
(3)considering denormalized schemas can become a major burden in the long term. Your DBA may not like it at all
(4)An implementation quirk of Hibernate requires that you declare nullability with @Column because Hibernate
ignores Bean Validation’s @NotNull when it generates the database schema.Hibernate ignores the @NotNull for schema DDL generation, but it observes it at runtime, before inserting a row.
JavaPersistenceWithHibernate第二版笔记-第六章-Mapping inheritance-004Table per class hierarchy(@Inheritance..SINGLE_TABLE)、@DiscriminatorColumn、@DiscriminatorValue、@DiscriminatorFormula)的更多相关文章
- JavaPersistenceWithHibernate第二版笔记-第六章-Mapping inheritance-005Table per subclass with joins(@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.JOINED)、@PrimaryKeyJoinColumn、)
一.结构 The fourth option is to represent inheritance relationships as SQL foreign key associations. Ev ...
- JavaPersistenceWithHibernate第二版笔记-第六章-Mapping inheritance-008Polymorphic many-to-one associations(@ManyToOne、@Inheritance、)
一.结构 二.代码 1. package org.jpwh.model.inheritance.associations.manytoone; import org.jpwh.model.Consta ...
- JavaPersistenceWithHibernate第二版笔记-第六章-Mapping inheritance-006Mixing inheritance strategies(@SecondaryTable、@PrimaryKeyJoinColumn、<join fetch="select">)
一.结构 For example, you can map a class hierarchy to a single table, but, for a particular subclass, s ...
- JavaPersistenceWithHibernate第二版笔记-第六章-Mapping inheritance-003Table per concrete class with unions(@Inheritance(strategy = InheritanceType.TABLE_PER_CLASS)、<union-subclass>)
一.代码 1. package org.jpwh.model.inheritance.tableperclass; import org.jpwh.model.Constants; import ja ...
- JavaPersistenceWithHibernate第二版笔记-第六章-Mapping inheritance-002Table per concrete class with implicit polymorphism(@MappedSuperclass、@AttributeOverride)
一.结构 二.代码 1. package org.jpwh.model.inheritance.mappedsuperclass; import javax.persistence.MappedSup ...
- JavaPersistenceWithHibernate第二版笔记-第六章-Mapping inheritance-001Hibernate映射继承的方法
There are four different strategies for representing an inheritance hierarchy: Use one table per co ...
- JavaPersistenceWithHibernate第二版笔记-第六章-Mapping inheritance-009Polymorphic collections(@OneToMany(mappedBy = "user")、@ManyToOne、)
一.代码 1. package org.jpwh.model.inheritance.associations.onetomany; import org.jpwh.model.Constants; ...
- JavaPersistenceWithHibernate第二版笔记-第六章-Mapping inheritance-007Inheritance of embeddable classes(@MappedSuperclass、@Embeddable、@AttributeOverrides、、)
一.结构 二.代码 1. package org.jpwh.model.inheritance.embeddable; import javax.persistence.MappedSuperclas ...
- JavaPersistenceWithHibernate第二版笔记-第五章-Mapping value types-007UserTypes的用法(@org.hibernate.annotations.Type、@org.hibernate.annotations.TypeDefs、CompositeUserType、DynamicParameterizedType、、、)
一.结构 二.Hibernate支持的UserTypes接口 UserType —You can transform values by interacting with the plain JD ...
随机推荐
- MySQL分片 --转自Peter Zaitsev对MySQL分片的建议
本文作者Peter Zaitsev是知名数据库专家,2006年联合创立了Percona.负责维护网站“MySQL性能”.同时,他也是<高性能MySQL>一书的联合作者.以下是他对MySQL ...
- HttpClient与Spring RestTemplate
需要的包 ,除了Spring的基础包外还用到json的包,这里的数据传输使用json格式 客户端和服务端都用到一下的包 <!-- Spring --> <dependency> ...
- C++中string的常见用法
在ACM中主要用到string的这几个功能:赋值,添加,删除,替换,查找,比较,反向排序. 1.赋值 直接来就行: string ss; ss="aaa"; 或者 string s ...
- SVN客户端与服务器端搭建
一.客户端安装 1.点击安装程序 2.修改svn安装位置 3.开始安装 4.安装完成 5.回到左面 右键出现svn检出 tortoiSVN 表示安装成功 二.SVN服务端安装 1.点击服务端安装 ...
- ERR_PTR PTR_ERR IS_ERR ERROR
在linux-x.xx/include/uapi/asm-generic/errno-base.h和errno.h里分别定义了返回错误的信息. errno-base.h: #ifndef _ASM_G ...
- C++对C语言的拓展(3)—— 默认参数和占位参数
通常情况下,函数在调用时,形参从实参那里取得值.对于多次调用同一函数同一 实参时,C++给出了更简单的处理办法.给形参以默认值,这样就不用从实参那里取值了. 1.单个默认参数 若填写参数,使用你填写的 ...
- 软件架构设计 ADMEMS方法体系
ADMEMS是Architecture Design Method has been Extended to Method System的简称,是由CSAI顾问团架构设计专家组于2009年11月在第六 ...
- nodejs渲染到页面的理解
一般逻辑都是: 打开页面,前端发请求到服务端,服务端返回数据到前端,前端根据数据生成DOM节点,然后append到DOM中. 如果是nodejs渲染到页面,我的理解是: 打开页面,服务端直接把数据查询 ...
- springboot实现定时任务的一种方式
参考:https://www.yoodb.com/news/detail/1205 目前觉得这种还是很好用,所以就记录. 最好新建一个项目测试: 1. pom中添加 <dependency> ...
- [置顶]
strcpy()与strncpy()的区别
头文件:#include <string.h> strcpy() 函数用来复制字符串,其原型为: char *strcpy(char *dest, const char *src); [参 ...
