SpringMVC执行流程源码分析
SpringMVC执行流程源码分析
我们先来看张图片,帮助我们理解整个流程
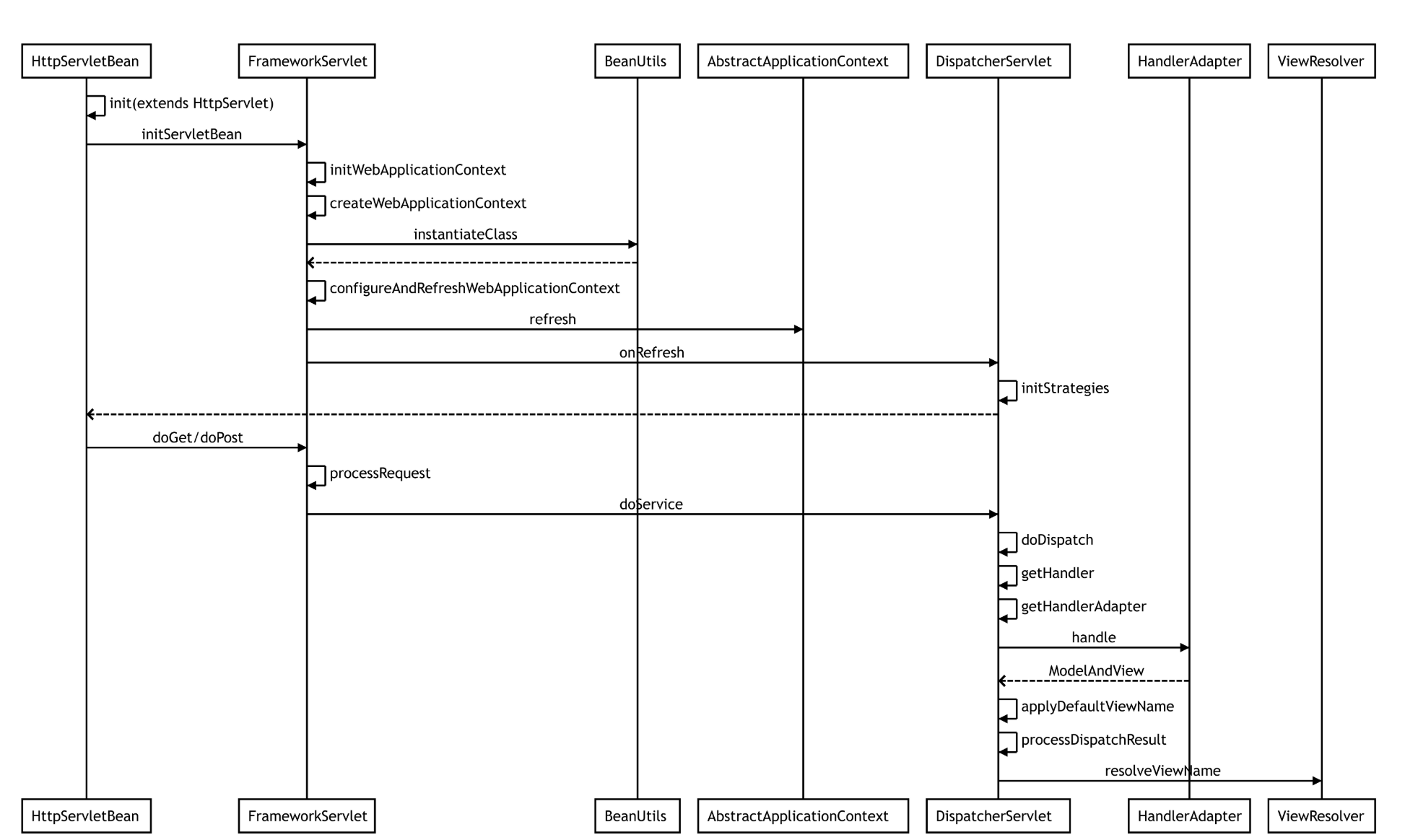
然后我们开始来解析
首先SpringMVC基于Servlet来运行 那么我们首先来看HttpServletBean这个类 他继承HttpServlet,所以这个HttpServletBean为一个Servlet,我们直接看Init方法,因为init方法在Servlet初始化的时候会执行的一个方法
public final void init() throws ServletException {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Initializing servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
// 在Web.xml中读取配置文件.
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
//通过BeanWrapper代理器创建DispatcherServlet
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
//设置DispatcherServlet属性
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// 该类为空实现,由他的子类实现也就是FrameworkServlet
initServletBean();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Servlet '" + getServletName() + "' configured successfully");
}
}
那我们来看FrameworkServlet里的实现
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " +
elapsedTime + " ms");
}
}
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
可以看到在这里进行webApplicationContext的初始化,initFrameworkServlet()也可也为空方法,此方法将在设置任何bean属性之后调用,已加载WebApplicationContext,默认实现为空,子类可以覆盖此方法来执行它们需要的任何初始化.
我们点进initWebApplicationContext详细来看
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +
"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
}
}
return wac;
}
可以看到这里有个 onRefresh(wac);方法 他就是初始化我们SpringMVC的九大组件 他在DispatcherServlet核心类里,等会我们在细说,我们继续看这里有个createWebApplicationContext方法创建实例
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) {
Class<?> contextClass = getContextClass();
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"' will try to create custom WebApplicationContext context of class '" +
contextClass.getName() + "'" + ", using parent context [" + parent + "]");
}
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
wac.setParent(parent);
wac.setConfigLocation(getContextConfigLocation());
//刷新并配置web应用上下文
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
可以看到通过反射实例化Web上下文,我们继续来看configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
if (this.contextId != null) {
wac.setId(this.contextId);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(getServletContext().getContextPath()) + '/' + getServletName());
}
}
wac.setServletContext(getServletContext());
wac.setServletConfig(getServletConfig());
wac.setNamespace(getNamespace());
wac.addApplicationListener(new SourceFilteringListener(wac, new ContextRefreshListener()));
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(getServletContext(), getServletConfig());
}
postProcessWebApplicationContext(wac);
applyInitializers(wac);
wac.refresh();
}
我们注意最后一个调用方法 wac.refresh(); 在这里面可以看到IOC的初始化流程 。我们现在继续回到刚刚说的onRefresh他没有实现 而让他的子类DispatchServlet实现
//DispatchServlet
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
// 初始化文件上传处理
initMultipartResolver(context);
//初始化本地化处理
initLocaleResolver(context);
//初始化主题处理
initThemeResolver(context);
// 初始化处理器映射器(用来保存controller中配置的RequestMapping与Method对应关系)
initHandlerMappings(context);
// 初始化处理器适配器(用来动态匹配Method参数 包括类转换 动态赋值)
initHandlerAdapters(context);
// 初始化处理器异常处理
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
// 初始化请求至视图名转换
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
// 初始化视图解析器
initViewResolvers(context);
// 初始化flash映射管理器
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
我们再来看DispatcherServlet的配置文件DispatcherServlet.properties
org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.ThemeResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerExceptionResolver,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver org.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMapManager=org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager
这个是DispatcherServlet策略接口的默认实现类。
那我们再捋一次执行过程,我们回到FrameworkServlet 比如用户在前台发送一个请求POST或GET,会调用 FrameworkServlet的doPost/doGet方法,这里以 post请求为例
protected final void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException { processRequest(request, response);
}
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Throwable failureCause = null; LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext();
LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request); RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes); WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor()); initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes); try {
//执行请求
doService(request, response);
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
failureCause = ex;
throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex);
} finally {
resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes);
if (requestAttributes != null) {
requestAttributes.requestCompleted();
} if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (failureCause != null) {
this.logger.debug("Could not complete request", failureCause);
}
else {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
logger.debug("Leaving response open for concurrent processing");
}
else {
this.logger.debug("Successfully completed request");
}
}
} publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause);
}
}
我们点进doService(request, response);这时又到我们的DispatcherServlet类
protected void doService(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String resumed = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).hasConcurrentResult() ? " resumed" : "";
logger.debug("DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'" + resumed +
" processing " + request.getMethod() + " request for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "]");
}
// Keep a snapshot of the request attributes in case of an include,
// to be able to restore the original attributes after the include.
Map<String, Object> attributesSnapshot = null;
if (WebUtils.isIncludeRequest(request)) {
attributesSnapshot = new HashMap<String, Object>();
Enumeration<?> attrNames = request.getAttributeNames();
while (attrNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String attrName = (String) attrNames.nextElement();
if (this.cleanupAfterInclude || attrName.startsWith(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PREFIX)) {
attributesSnapshot.put(attrName, request.getAttribute(attrName));
}
}
}
// Make framework objects available to handlers and view objects.
request.setAttribute(WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, getWebApplicationContext());
request.setAttribute(LOCALE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.localeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE, this.themeResolver);
request.setAttribute(THEME_SOURCE_ATTRIBUTE, getThemeSource());
FlashMap inputFlashMap = this.flashMapManager.retrieveAndUpdate(request, response);
if (inputFlashMap != null) {
request.setAttribute(INPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, Collections.unmodifiableMap(inputFlashMap));
}
request.setAttribute(OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE, new FlashMap());
request.setAttribute(FLASH_MAP_MANAGER_ATTRIBUTE, this.flashMapManager);
try {
doDispatch(request, response);
}
finally {
if (!WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Restore the original attribute snapshot, in case of an include.
if (attributesSnapshot != null) {
restoreAttributesAfterInclude(request, attributesSnapshot);
}
}
}
}
我们点进 doDispatch(request, response);
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request;
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null;
boolean multipartRequestParsed = false;
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
try {
ModelAndView mv = null;
Exception dispatchException = null;
try {
// 如果是MultipartContent类型则转换为MultiHttpServletRequest类型的request
processedRequest = checkMultipart(request);
multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request);
// 确定当前请求的处理程序,根据request寻找对应的handler
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);
if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) {
noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response);
return;
}
// // 根据处理器获取handler适配器
HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());
// Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler.
String method = request.getMethod();
boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method);
if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) {
long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified);
}
if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) {
return;
}
}
// 拦截器postHandle方法处理
if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) {
return;
}
// Actually invoke the handler.
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
return;
}
// 结果视图对象的处理
applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv);
// 拦截器postHandle方法处理
mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
dispatchException = ex;
}
catch (Throwable err) {
// As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well,
// making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios.
dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err);
}
// 处理最终结果 渲染视图等
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex);
}
catch (Throwable err) {
triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler,
new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err));
}
finally {
if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// 请求成功响应之后的方法
if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response);
}
}
else {
// Clean up any resources used by a multipart request.
if (multipartRequestParsed) {
cleanupMultipart(processedRequest);
}
}
}
}
我们来看getHandler()方法
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(
"Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request);
if (handler != null) {
return handler;
}
}
return null;
}
我们继续看hm.getHandler(request);方法的实现来自于HandlerMapping这个接口由AbstractHandlerMapping来实现
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 根据request获取handler
Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);
// 没有查找到使用默认handler
if (handler == null) {
handler = getDefaultHandler();
}
if (handler == null) {
return null;
}
// 如果handler是字符串类型 说明是bean名称 需要获取handler bean对象
if (handler instanceof String) {
String handlerName = (String) handler;
handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);
}
// 封装handler执行链
HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);
if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) {
CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.globalCorsConfigSource.getCorsConfiguration(request);
CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);
CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);
executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);
}
return executionChain;
}
我们继续来看getHandlerInternal
//AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
// 获取request中的url 用来匹配handler
String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking up handler method for path " + lookupPath);
}
this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();
try {
// 根据路径寻找handler
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (handlerMethod != null) {
logger.debug("Returning handler method [" + handlerMethod + "]");
}
else {
logger.debug("Did not find handler method for [" + lookupPath + "]");
}
}
return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);
}
finally {
this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();
}
}
protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {
List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<Match>();
// 直接匹配
List<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);
// 存在匹配 则添加到匹配列表中
if (directPathMatches != null) {
addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);
}
// 没有匹配 遍历所有处理方法查找
if (matches.isEmpty()) {
// No choice but to go through all mappings...
addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request);
}
// 存在匹配
if (!matches.isEmpty()) {
Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));
Collections.sort(matches, comparator);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Found " + matches.size() + " matching mapping(s) for [" +
lookupPath + "] : " + matches);
}
// 排序之后获取第一个
Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);
// 有多个匹配 会找出第二个进行比较
if (matches.size() > 1) {
if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) {
return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;
}
Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);
if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) {
Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod();
throw new IllegalStateException("Ambiguous handler methods mapped for HTTP path '" +
request.getRequestURL() + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");
}
}
// 设置request参数
handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);
// 返回匹配的url处理方法
return bestMatch.handlerMethod;
}
else {
return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request);
}
}
我们回到 getHandlerExecutionChain继续来看
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandlerExecutionChain(Object handler, HttpServletRequest request) {
// // 如果当前handler不是执行链类型 则创建一个新的执行链封装
HandlerExecutionChain chain = (handler instanceof HandlerExecutionChain ?
(HandlerExecutionChain) handler : new HandlerExecutionChain(handler));
// 当前url
String lookupPath = this.urlPathHelper.getLookupPathForRequest(request);
// 遍历拦截器 与当前url匹配的添加至执行链中
for (HandlerInterceptor interceptor : this.adaptedInterceptors) {
if (interceptor instanceof MappedInterceptor) {
MappedInterceptor mappedInterceptor = (MappedInterceptor) interceptor;
if (mappedInterceptor.matches(lookupPath, this.pathMatcher)) {
chain.addInterceptor(mappedInterceptor.getInterceptor());
}
}
else {
chain.addInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
return chain;
}
private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, ModelAndView mv, Exception exception) throws Exception { boolean errorView = false; if (exception != null) {
if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) {
logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception);
mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView();
}
else {
Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null);
mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception);
errorView = (mv != null);
}
} // Did the handler return a view to render?
if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) {
//渲染
render(mv, request, response);
if (errorView) {
WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request);
}
}
else {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Null ModelAndView returned to DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': assuming HandlerAdapter completed request handling");
}
} if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) {
// Concurrent handling started during a forward
return;
} if (mappedHandler != null) {
mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null);
}
}
点进render来看
protected void render(ModelAndView mv, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception {
// Determine locale for request and apply it to the response.
Locale locale = this.localeResolver.resolveLocale(request);
response.setLocale(locale);
View view;
if (mv.isReference()) {
// 解析视图名获取视图对象
view = resolveViewName(mv.getViewName(), mv.getModelInternal(), locale, request);
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("Could not resolve view with name '" + mv.getViewName() +
"' in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
else {
// No need to lookup: the ModelAndView object contains the actual View object.
view = mv.getView();
if (view == null) {
throw new ServletException("ModelAndView [" + mv + "] neither contains a view name nor a " +
"View object in servlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
}
// Delegate to the View object for rendering.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
try {
if (mv.getStatus() != null) {
response.setStatus(mv.getStatus().value());
}
view.render(mv.getModelInternal(), request, response);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Error rendering view [" + view + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" +
getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
那我们总结一个核心问题?请求如何路由到具体的Controller上的方法进行处理? 根据请求路径,与已知的handlerMapping进行匹配,并加入interceptors,dispatcherServlet.getHandler()最终调用AbstracteHandlerMapping.getHandlerExecutionChain(..)中进行url与handlerMapping进行匹配,并加入interceptors;
好的 到这里我们解析结束.
SpringMVC执行流程源码分析的更多相关文章
- Mybatis执行流程源码分析
第一部分:项目结构 user_info表:只有id和username两个字段 User实体类: public class User { private String username; private ...
- SpringMVC流程源码分析及DispatcherServlet核心源码
一.源码分析前还是需要一张流程图作为指导,如下: 二.简单介绍以及源码定位 DispatcherServlet其实就是一个HttpServlet,他是HttpServlet的子类,所以它和普通的Htt ...
- mybatis-sql执行流程源码分析
1. SqlSessionFactory 与 SqlSession. 通过前面的章节对于mybatis 的介绍及使用,大家都能体会到SqlSession的重要性了吧, 没错,从表面上来看,咱们都是通过 ...
- Spring Cloud学习 之 Spring Cloud Ribbon(执行流程源码分析)
Spring Boot版本:2.1.4.RELEASE Spring Cloud版本:Greenwich.SR1 文章目录 分析: 总结: 分析: 在上篇文章中,我们着重分析了RestTempla ...
- Spring aop(1)--- 寻找切面和代理对象执行流程源码分析
1.基于注解,首先我们是通过@EnableAspectJAutoProxy()这个注解开起AOP功能,这个注解会导入AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar组件从而将AnnotationAw ...
- SpringBoot中Tomcat和SpringMVC整合源码分析
概述 SpringBoot中集成官方的第三方组件是通过在POM文件中添加组件的starter的Maven依赖来完成的.添加相关的Maven依赖之后,会引入具体的jar包,在SpringBoot启动 ...
- [Android]从Launcher开始启动App流程源码分析
以下内容为原创,欢迎转载,转载请注明 来自天天博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/tiantianbyconan/p/5017056.html 从Launcher开始启动App流程源码 ...
- [Android]Android系统启动流程源码分析
以下内容为原创,欢迎转载,转载请注明 来自天天博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/tiantianbyconan/p/5013863.html Android系统启动流程源码分析 首先 ...
- Android系统默认Home应用程序(Launcher)的启动过程源码分析
在前面一篇文章中,我们分析了Android系统在启动时安装应用程序的过程,这些应用程序安装好之后,还须要有一个Home应用程序来负责把它们在桌面上展示出来,在Android系统中,这个默认的Home应 ...
随机推荐
- 你真的理解索引吗?从数据结构层面解析mysql索引原理
从<mysql存储引擎InnoDB详解,从底层看清InnoDB数据结构>中,我们已经知道了数据页内各个记录是按主键正序排列并组成了一个单向链表的,并且各个数据页之间形成了双向链表.在数据页 ...
- java web应用启动报错:Several ports (8080, 8009) required by Tomcat v6.0 Server at localhost are already in use.
Several ports (8080, 8009) required by Tomcat v6.0 Server at localhost are already in use. The serve ...
- DB2 SQLCODE=-206, SQLSTATE=42703 定义表字段问题
>[错误] 脚本行:1-1 --------------------------------------- "STATUS" is not valid in the cont ...
- C#LeetCode刷题之#605-种花问题( Can Place Flowers)
问题 该文章的最新版本已迁移至个人博客[比特飞],单击链接 https://www.byteflying.com/archives/3724 访问. 假设你有一个很长的花坛,一部分地块种植了花,另一部 ...
- CTF bossplayers 靶机
WAYs: robots.txt文件提供线索,命令执行漏洞获得反弹shell suid命令提升权限 1:netdiscover 发现主机地址192.168.1.109 2:使用namp进行端口扫描发现 ...
- Spring Boot 2.x基础教程:使用集中式缓存Redis
之前我们介绍了两种进程内缓存的用法,包括Spring Boot默认使用的ConcurrentMap缓存以及缓存框架EhCache.虽然EhCache已经能够适用很多应用场景,但是由于EhCache是进 ...
- 实战分享丨MySQL 与Django版本匹配相关经验
摘要:关于MySQL 与Django版本匹配相关知识的经验分享. run: (env) E:\PythonPro\PyDjangoProDemo011\xuanyuaniotpro>python ...
- Jmeter 常用函数(21)- 详解 __char
如果你想查看更多 Jmeter 常用函数可以在这篇文章找找哦 https://www.cnblogs.com/poloyy/p/13291704.htm 作用 根据给定的字符值转换成 Unicode ...
- 第2章 RDD编程(2.1-2.2)
第2章 RDD编程 2.1 编程模型 在Spark中,RDD被表示为对象,通过对象上的方法调用来对RDD进行转换.经过一系列的transformations定义RDD之后,就可以调用actions触发 ...
- Jenkins(1)—— 部署安装
最近有聊到接口自动化,持续集成这方面,所以想从持续集成工具Jenkins作为切入点来学习一下 一.jenkins概念 Jenkins是一个开源的.可扩展的持续集成.交付.部署(软件/代码的编译.打包. ...
