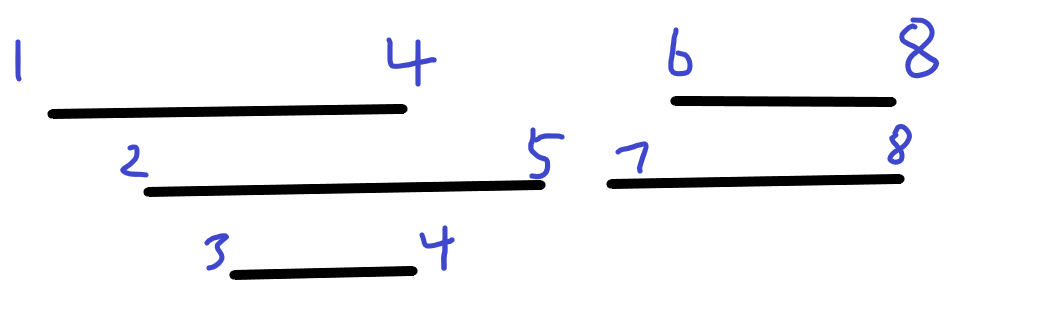Mayor's posters (线段树+离散化)
Mayor's posters
Description
The citizens of Bytetown, AB, could not stand that the candidates in the mayoral election campaign have been placing their electoral posters at all places at their whim. The city council has finally decided to build an electoral wall for placing the posters and introduce the following rules:
- Every candidate can place exactly one poster on the wall.
- All posters are of the same height equal to the height of the wall; the width of a poster can be any integer number of bytes (byte is the unit of length in Bytetown).
- The wall is divided into segments and the width of each segment is one byte.
- Each poster must completely cover a contiguous number of wall segments.
They have built a wall 10000000 bytes long (such that there is enough place for all candidates). When the electoral campaign was restarted, the candidates were placing their posters on the wall and their posters differed widely in width. Moreover, the candidates started placing their posters on wall segments already occupied by other posters. Everyone in Bytetown was curious whose posters will be visible (entirely or in part) on the last day before elections.
Your task is to find the number of visible posters when all the posters are placed given the information about posters' size, their place and order of placement on the electoral wall.
Input
The first line of input contains a number c giving the number of cases that follow. The first line of data for a single case contains number 1 <= n <= 10000. The subsequent n lines describe the posters in the order in which they were placed. The i-th line among the n lines contains two integer numbers li and ri which are the number of the wall segment occupied by the left end and the right end of the i-th poster, respectively. We know that for each 1 <= i <= n, 1 <= li <= ri <= 10000000. After the i-th poster is placed, it entirely covers all wall segments numbered li, li+1 ,... , ri.
Output
For each input data set print the number of visible posters after all the posters are placed.
The picture below illustrates the case of the sample input.

Sample Input
1
5
1 4
2 6
8 10
3 4
7 10
Sample Output
4 这是一道很经典的线段树离散化问题,题目中给出的区间[li,ri]的数据都很大,直接用线段树做的话至少需要10000000*4的空间,因此,我们首先要对数据进行离散化处理
首先,我们要弄清楚离散化的概念,我们根据题目样例进行分析,可以看到[1,4],[2,6],[8,10],[3,4],[7,10]这五个区间,我们将这10个数都拿出来排个序,创建序列a
1 2 3 4 4 6 7 8 10 10
接下来我们对序列a去下重
1 2 3 4 6 7 8 10
然后我们用他们的相对大小(例如:6在这个序列中是第5大,10在这个序列中是第8大)建立另一个序列b
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
最后我们用每个数对应的相对大小来替换原来的区间就变成了这样
[1,4],[2,5],[7,8],[3,4],[6,8]
我们用这个区间来计算一下最后能观察到的海报数的话会发现,结果仍然是4
我个人对离散化的理解就是用数字的相对大小来替换他的实际大小从而达到减小其值,却不破坏它的位置关系的目的
这道题我们利用这样的方法就能将li,ri这么大的数缩小到最大只有20000(因为最多有20000个点)
理解题意后我们直接看代码,至于线段树部分就是普通的区间修改而已
#pragma GCC optimize("Ofast")
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
#define ll long long
struct node
{
int l, r, flag;
} tree[];
int base[], ls[];
set<int> s;
void tree_build(int i, int l, int r)
{
tree[i].l = l;
tree[i].r = r;
tree[i].flag = ;
if (l == r)
{
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> ;
tree_build(i << , l, mid);
tree_build(i << | , mid + , r);
}
void push_down(int i)
{
if (tree[i].flag)
{
tree[i << ].flag = tree[i].flag;
tree[i << | ].flag = tree[i].flag;
tree[i].flag = ;
}
}
void update(int i, int l, int r, int num)
{
if (tree[i].l >= l && tree[i].r <= r)
{
tree[i].flag = num;
return;
}
if (tree[i].r < l || tree[i].l > r)
{
return;
}
push_down(i);
if (tree[i << ].r >= l)
{
update(i << , l, r, num);
}
if (tree[i << | ].l <= r)
{
update(i << | , l, r, num);
}
}
void search(int i, int l, int r)
{
if (tree[i].flag)
{
s.insert(tree[i].flag);//利用set自动去重的性质来记录海报数量
return;
}
if (l == r)
{
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> ;
search(i << , l, mid);
search(i << | , mid + , r);
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio();
cin.tie();
cout.tie();
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
int n, x, y, pos = ;
cin >> n;
s.clear();
tree_build(, , );
for (int i = ; i <= n; ++i)
{
//这地方我们开两个数组,base用与计算每个数的相对位置,ls是离散化后的数组
cin >> x >> y;
base[pos] = x;
ls[pos++] = x;
base[pos] = y;
ls[pos++] = y;
}
//无论是sort还是unique还是lower_bound区间设定都是左闭右开的形式,品,你细细的品
sort(base + , base + pos);
int num = unique(base + , base + pos) - base;//对base排序并去重,必须排序后才能用unique
for (int i = ; i < pos; ++i)
{
ls[i] = lower_bound(base + , base + num, ls[i]) - base;
}
for (int i = ; i < pos; i += )
{
update(, ls[i - ], ls[i], i);
}
search(, , );
cout << s.size() << endl;
}
return ;
}
你以为这就完事了?其实这样离散化在这道题中会有一些bug,我们看这组数据[1,10],[1,3],[6,10],很明显答案是3
但是离散化之后为[1,4],[1,2],[3,4],答案变成了2
为解决这种问题,我们可以在更新线段树的时候将区间从[l,r]变成[l,r-1],就将区间转化成了[1,3],[1,1],[3,3]这样的树
但是当我们遇到这样的数据[1,3],[1,1],[2,2],[3,3],就会导致区间更新时出错,我们可以将初始数据的r都加上1,就排除了li和ri相等的情况,如果没有这种情况,离散化后的区间也都是一样的
其实这道题数据很弱,不管这样的情况也能过(逃
#pragma GCC optimize("Ofast")
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
using namespace std;
#define endl '\n'
#define ll long long
struct node
{
int l, r, flag;
} tree[];
int base[], ls[];
set<int> s;
void tree_build(int i, int l, int r)
{
tree[i].l = l;
tree[i].r = r;
tree[i].flag = ;
if (l == r)
{
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> ;
tree_build(i << , l, mid);
tree_build(i << | , mid + , r);
}
void push_down(int i)
{
if (tree[i].flag)
{
tree[i << ].flag = tree[i].flag;
tree[i << | ].flag = tree[i].flag;
tree[i].flag = ;
}
}
void update(int i, int l, int r, int num)
{
if (tree[i].l >= l && tree[i].r <= r)
{
tree[i].flag = num;
return;
}
if (tree[i].r < l || tree[i].l > r)
{
return;
}
push_down(i);
if (tree[i << ].r >= l)
{
update(i << , l, r, num);
}
if (tree[i << | ].l <= r)
{
update(i << | , l, r, num);
}
}
void search(int i, int l, int r)
{
//cout << tree[i].flag << " " << tree[i].l << " " << tree[i].r << endl;
if (tree[i].flag)
{
//cout << tree[i].flag << " " << tree[i].l << " " << tree[i].r << endl;
s.insert(tree[i].flag);
return;
}
if (l == r)
{
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> ;
search(i << , l, mid);
search(i << | , mid + , r);
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio();
cin.tie();
cout.tie();
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
int n, x, y, pos = ;
cin >> n;
s.clear();
tree_build(, , );
for (int i = ; i <= n; ++i)
{
cin >> x >> y;
base[pos] = x;
ls[pos++] = x;
base[pos] = y + ;
ls[pos++] = y + ;
}
sort(base + , base + pos);
int num = unique(base + , base + pos) - base;
for (int i = ; i < pos; ++i)
{
ls[i] = lower_bound(base + , base + num, ls[i]) - base;
}
for (int i = ; i < pos; i += )
{
update(, ls[i - ], ls[i] - , i);
}
search(, , );
cout << s.size() << endl;
}
return ;
}
Mayor's posters (线段树+离散化)的更多相关文章
- POJ 2528 Mayor's posters(线段树+离散化)
Mayor's posters 转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/winddreams/article/details/38443761 [题目链接]Mayor's posters [ ...
- poj 2528 Mayor's posters 线段树+离散化技巧
poj 2528 Mayor's posters 题目链接: http://poj.org/problem?id=2528 思路: 线段树+离散化技巧(这里的离散化需要注意一下啊,题目数据弱看不出来) ...
- [poj2528] Mayor's posters (线段树+离散化)
线段树 + 离散化 Description The citizens of Bytetown, AB, could not stand that the candidates in the mayor ...
- Mayor's posters(线段树+离散化POJ2528)
Mayor's posters Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 51175 Accepted: 14820 Des ...
- POJ 2528 Mayor's posters (线段树+离散化)
Mayor's posters Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions:75394 Accepted: 21747 ...
- poj 2528 Mayor's posters 线段树+离散化 || hihocode #1079 离散化
Mayor's posters Description The citizens of Bytetown, AB, could not stand that the candidates in the ...
- POJ.2528 Mayor's posters (线段树 区间更新 区间查询 离散化)
POJ.2528 Mayor's posters (线段树 区间更新 区间查询 离散化) 题意分析 贴海报,新的海报能覆盖在旧的海报上面,最后贴完了,求问能看见几张海报. 最多有10000张海报,海报 ...
- poj-----(2528)Mayor's posters(线段树区间更新及区间统计+离散化)
Mayor's posters Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 65536K Total Submissions: 43507 Accepted: 12693 ...
- POJ2528:Mayor's posters(线段树区间更新+离散化)
Description The citizens of Bytetown, AB, could not stand that the candidates in the mayoral electio ...
随机推荐
- 2018-2-13-win10-uwp-绑定静态属性
title author date CreateTime categories win10 uwp 绑定静态属性 lindexi 2018-2-13 17:23:3 +0800 2018-2-13 1 ...
- Git 删除大文件的方法
git 仓库中删除历史大文件 git 仓库中删除历史大文件 在git中增加了一个很大的文件,而且被保存在历史提交记录中,每次拉取代码都很大,速度很慢.而且用删除 提交历史记录的方式不是很实际. 以 ...
- web应用中web.xml文件的解释
一.web.xml配置文件常用元素及其意义预览 1 <web-app> 2 3 <!--定义了WEB应用的名字--> 4 <display-name></di ...
- vagrant在windows下的安装和配置(二)
在(一)中安装和配置好后 框框中的信息是登录vagrant up后的系统用的 我这里登录用的是xshell-----下载一个xshell然后安装 打开xshell 按确定之后生成一个新的会话,然后登录 ...
- 0014 标签显示模式:display(重点)
目标: 理解 标签的三种显示模式 三种显示模式的特点以及区别 理解三种显示模式的相互转化 应用 实现三种显示模式的相互转化 2.1 什么是标签显示模式 什么是标签的显示模式? 标签以什么方式进行显示, ...
- starUml破解
在安装目录的:StarUML\www\license\node 找到LicenseManagerDomain.js 在 try 前面加上: return { name:"0xcb" ...
- CodeForces - 1228D
乍一看,嗯,图论题,不错: 结果,这尼玛是模拟???? 传送链接:https://codeforces.com/contest/1228/problem/D 看了大佬的代码瞬间就明白了许多!!! #i ...
- java之set接口
1.set集合不能存储重复的元素, 2.HashSet集合不能保证的迭代顺序与元素存储顺序相同. 3.HashSet集合,采用哈希表结构存储数据,保证元素唯一性的方式依赖于:hashCode()与eq ...
- loongson编译所遇问题
环境:虚拟机VMware +Ubuntu18.04+gcc4.9.3 使用gcc4.9.3编译时出错,提示需要运行命令:make -C /work/loongson0103/vUDK2018-loon ...
- Django 链接MySQL及数据操作
Django 链接MySQL Django创建的项目自带的数据库是SQLite3,我们想要链接MySQL的话,需要更改settings.py中的配置 1.在MySQL中创建好数据库,Django项目不 ...