组合数们&&错排&&容斥原理
最近做了不少的组合数的题
这里简单总结一下下
1.n,m很大p很小 且p为素数
p要1e7以下的 可以接受On的时间和空间
然后预处理阶乘 Lucas定理来做
以下是代码
/*Hdu3037 Saving Beans*/
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#define ll long long
#define maxn 1000010
using namespace std;
ll T,n,m,p,f[maxn];
void Get(){
f[]=;
for(int i=;i<=p;i++)
f[i]=f[i-]*i%p;
}
ll qm(ll a,ll b){
a%=p;ll r=;
while(b){
if(b&)r=r*a%p;
b>>=;a=a*a%p;
}
return r;
}
ll C(ll a,ll b){
if(b>a)return ;
return f[a]*qm(f[b]*f[a-b],p-)%p;
}
ll Lcs(ll a,ll b){
if(b==)return ;
return C(a%p,b%p)*Lcs(a/p,b/p)%p;
}
int main(){
cin>>T;
while(T--){
cin>>n>>m>>p;Get();
cout<<Lcs(n+m,n)<<endl;
}
return ;
}
2.n很大,m很小,p很大,且p为素数p>m
m很小我们可以直接暴力,保证了p大于m,也就是pm互质,保证存在逆元
/*[FZU 2020] 组合*/
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#define ll long long
#define maxn 1000010
using namespace std;
ll T,n,m,p;
ll qm(ll a,ll b){
a%=p;ll r=;
while(b){
if(b&)r=r*a%p;
b>>=;a=a*a%p;
}
return r;
}
ll C(ll a,ll b){
if(b>a)return ;ll res=;
for(ll i=a,j=;j<=b;i--,j++){
res*=i%p;res%=p;res*=qm(j,p-);res%=p;
}
return res;
}
int main(){
cin>>T;
while(T--){
cin>>n>>m>>p;
cout<<C(n,m)<<endl;
}
return ;
}
3.n很大,m很小,p很大,且p为素数
同上可用暴力,但是p虽然会prime但是可能m是p的倍数逆元可能不存在
所以我们用Lucas定理,把m分解成一个p进制数,保证比p小,就可以同上了
/*ZOJ 3557 How Many Sets II */
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
ll T,n,m,p;
ll qm(ll a,ll b){
a%=p;ll r=;
while(b){
if(b&)r=r*a%p;
b>>=;a=a*a%p;
}
return r;
}
ll C(ll a,ll b){
if(b>a)return ;ll res=;
for(ll i=a,j=;j<=b;i--,j++){
res*=i%p;res%=p;res*=qm(j,p-);res%=p;
}
return res;
}
ll Lcs(ll a,ll b){
if(b==)return ;
return C(a%p,b%p)*Lcs(a/p,b/p)%p;
} int main(){
while(cin>>n>>m>>p)
cout<<Lcs(n-m+,m)<<endl;
return ;
}
下面是几个性质
1.C(n,0),C(n,1),,,,,C(n,n)里面奇数的个数
= 2^(n二进制表示下的1的个数) (好像有组合数的做法,这个是打表找的规律)
2.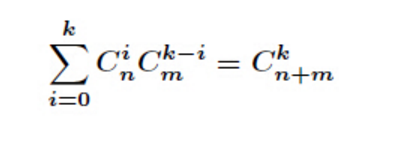
范德莫恒等式
错排问题&&容斥原理
Ai表示i在i位置的序列个数,显然 Ai=(n-1)! Ai∩Aj=(n-2)!
Ai的反也就是i不在i位置的序列个数,
所以A1反∩A2反∩.....∩An反 = ( A1∪A2∪....∪An )反=U- ( A1∪A2∪....∪An )
U=n!,所以ans=n!-C(n,1)*(n-1)!+C(n,2)*(n-2)!......
代码
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
int n;ll f[],ans;
int main(){
f[]=;for(int i=;i<=;i++)f[i]=f[i-]*i;
while(~scanf("%d",&n)){
ans=f[n];for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
if(i&)ans-=f[n]/f[i];
else ans+=f[n]/f[i];
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return ;
}
这个是比较裸地,然后我们看一个题目
HDU 2068
题意:满足a[i]=i的个数一般或以上的序列个数
我们就枚举有x个a[i]=i,然后剩下的就是n-x错排了 乘法原理乘一下
高中用的为数不多的组合数的题目就是隔板法,还有一种模型就是解的个数
x1+x2+x3....+xm=n 问合法的x1x2x3....个数,若保证是正整数就是C(n-1,m-1),可能为0 那就每个x都加一 右边变成n+m,答案就是C(n+m-1,m-1)
看这样一道题 HDU6397
题意:x1+x2+x3....+xm=k 0<=xi<=n
先不管<=n这个条件,我们先转化成正整数:x1+x2+x3....+xm=k+m
考虑<=n这件事: 我们能求出来的是没有上界的模型,倘若我们知道只有x1>n,那我们用x1-n替换x1,就把这个变成了我们可以解决的模型(注意右边-n)
然后就可以想到容斥原理,就是看有几个xi>n,我们剪掉一个x大于n的时候会多剪掉两个的,就是简单的+-+-的容斥模型了
然后注意特殊的数据
#include<cstdio>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
int T,n,m,k;
const ll mod=;
ll ans,f[],inv[];
void extgcd(ll a,ll b,ll& d,ll& x,ll& y){
if(!b){
d=a;x=;y=;
}
else{
extgcd(b,a%b,d,y,x);
y-=x*(a/b);
}
}
ll inverse(ll a,ll n){
ll d,x,y;
extgcd(a,n,d,x,y);
return d==?(x+n)%n:;
}
ll C(int x,int y){
return f[x]*inv[y]%mod*inv[x-y]%mod;
}
int main(){ scanf("%d",&T);f[]=;inv[]=;
for(int i=;i<=;i++){
f[i]=f[i-]*i%mod;
inv[i]=inverse(f[i],mod);
}
while(T--){
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&m,&k);
if((n-)*(ll)m<k){
printf("0\n");continue;
}
int x=k-+m,y=m-;ans=;f[]=;
for(int i=;i<=m&&x>=y;i++,x-=n){
if(i&)ans+=C(m,i-)*C(x,y)%mod;
else ans-=C(m,i-)*C(x,y)%mod;
ans+=mod;ans%=mod;
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return ;
}
再看个稍微麻烦一点的
cf451E
题意同上,只不过上界不是固定的n,是一个ai
乍一看好像挺难得因为上面的状态的是 几个不合法的, 而现在是 哪几个不合法的
不过好在m很小,我们可以利用状丫确定状态,然后容斥的时候就不能 x个不合法的一起算了
而是奇数个不合法的话,就对答案贡献为-,偶数为正.
#include<iostream>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
const ll mod=;
int n,cnt;
ll f[],ans,s,k;
void extgcd(ll a,ll b,ll& d,ll& x,ll& y){
if(!b){
d=a;x=;y=;
}
else{
extgcd(b,a%b,d,y,x);
y-=x*(a/b);
}
}
ll inverse(ll a,ll n){
ll d,x,y;
extgcd(a,n,d,x,y);
return d==?(x+n)%n:;
}
ll C(ll x,ll y){
ll res=;
for(ll i=x,j=;j<=y;i--,j++){
res*=i%mod;res%=mod;res*=inverse(j,mod);res%=mod;
}
return res;
}
int main(){
cin>>n>>s;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
cin>>f[i];
for(int S=;S<(<<n);S++){
cnt=;k=s;
for(int j=;j<=n;j++)
if(S&(<<j-)){
cnt++;k-=f[j]+;
}
if(k<)continue;
if(cnt&)ans-=C(k+n-,n-);
else ans+=C(k+n-,n-);
ans+=mod;ans%=mod;
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return ;
}
然后是一个比较emmmmm好像也不是很简单的容斥原理
UVAlive 5846
题意:一个圈上有很多点,两两连边,每条边是红/蓝,然后问形成的同色三角形的个数
ans=总三角形的个数-异色三角形的个数
tot=C(n,3),下面考虑异色三角形个数
以为只有两种颜色,所以异色三角形的构成是112或者 122
也就是说,有两个顶点连出去的边异色,我们转而研究点,对于每个点,选两条异色边,就一定构成一个异色三角形
然后每个三角形统计了两边,在/2就好了
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#define maxn 1010
using namespace std;
int T,n,a[maxn],b[maxn];
long long ans;
int main(){
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--){
memset(a,,sizeof(a));
memset(b,,sizeof(b));
scanf("%d",&n);int x;ans=;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
for(int j=;j<=n-i;j++){
scanf("%d",&x);
if(x)a[i]++,a[i+j]++;
else b[i]++,b[i+j]++;
}
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
ans-=a[i]*b[i];
ans/=;ans+=(long long)n*(n-)*(n-)/;
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return ;
}
组合数们&&错排&&容斥原理的更多相关文章
- bzoj4517[Sdoi2016]排列计数(组合数,错排)
4517: [Sdoi2016]排列计数 Time Limit: 60 Sec Memory Limit: 128 MBSubmit: 1792 Solved: 1111[Submit][Stat ...
- HDU2048 HDU2049 组合数系列 错排
HDU1465HDU2048HDU2049#include<cstdio> #include<cstdlib> #include<iostream> #includ ...
- K - Wand(组合数+错排公式)
N wizards are attending a meeting. Everyone has his own magic wand. N magic wands was put in a line, ...
- HDU1465 第六周L题(错排组合数)
L - 计数,排列 Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:32768KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u Descrip ...
- 容斥原理--计算错排的方案数 UVA 10497
错排问题是一种特殊的排列问题. 模型:把n个元素依次标上1,2,3.......n,求每一个元素都不在自己位置的排列数. 运用容斥原理,我们有两种解决方法: 1. 总的排列方法有A(n,n),即n!, ...
- Codeforces 888D: Almost Identity Permutations(错排公式,组合数)
A permutation \(p\) of size \(n\) is an array such that every integer from \(1\) to \(n\) occurs exa ...
- 【BZOJ4517】[Sdoi2016]排列计数 组合数+错排
[BZOJ4517][Sdoi2016]排列计数 Description 求有多少种长度为 n 的序列 A,满足以下条件: 1 ~ n 这 n 个数在序列中各出现了一次 若第 i 个数 A[i] 的值 ...
- BZOJ 4517 组合数+错排
思路: 预处理错排 然后C(n,m)*s[n-m-1]就是答案了 特判n-m-1<0 //By SiriusRen #include <cstdio> using namespace ...
- HDU 2068 RPG的错排
要求答对一半或以上就算过关,请问有多少组答案能使他顺利过关. 逆向思维,求答错一半或以下的组数 1,错排 错排公式的由来 pala提出的问题: 十本不同的书放在书架上.现重新摆放,使每本书都不在原来放 ...
随机推荐
- Android项目实战_手机安全卫士进程管理
###1.设备进程信息获取获取设备运行进程 ActivityManager am = (ActivityManager) context.getSystemService(Context.ACTIVI ...
- cmd 切换目录和配置环境变量
记录一下: 在用cmd进行切换盘符的时候, 如果是从 C盘切换到其他盘的话: D:直接回车就行了. 如果是在同一个盘符内切换文件夹的话,cd D:\ComputerSoft\curl\curl-7.6 ...
- C#——数据库的访问
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.T ...
- 【译】x86程序员手册02 - 基本的程序模式
Chapter 2 -- Basic Programming Model: 基本的程序模式 Introduces the models of memory organization. Defines ...
- WinForm窗体中窗口控件的生成
1:button控件的生成方式 Button button = new Button(); button.Size = new Size(80, 80); button.Location = new ...
- ESX/ESXi 主机的某些存储阵列可能存在读取或写入性能问题 (1002598)
Last Updated: 12/14/2018Categories: Troubleshooting Details 免责声明:本文为 ESX/ESXi hosts might experienc ...
- python str操作
1. str.format():使用“{}”占位符格式化字符串(占位符中的索引号形式和键值对形式可以混合使用). 1 >>> string = 'python{}, django{} ...
- Day 11 文件和异常
文件和异常 在实际开发中,常常需要对程序中的数据进行持久化操作,而实现数据持久化最直接简单的方式就是将数据保存到文件中.说到“文件”这个词,可能需要先科普一下关于文件系统的知识,对于这个概念,维基百科 ...
- Django - 数据获取
Django - 数据获取 1.radio值获取 2.checkbox获取 3.select 获取 select 获取值,需要根据前端multiple来获取,get or getlist; 4.上传文 ...
- stress工具使用指南和结果分析
stress介绍 #stress `stress' imposes certain types of compute stress on your system Usage: stress [OPTI ...
