tensorflow GPU版本配置加速环境
import tensorflow as tf
tf.test.is_gpu_available()
- 背景
环境:Anaconda 、tensorflow_gpu==1.4.0 (这里就用1.4.0版本做演示了,虽然现在的已经是2.0版本了)
如下图是各个版本的cuda版本信息,在安装时需要看清楚,并不是所有的gpu版本都是cuda_8.0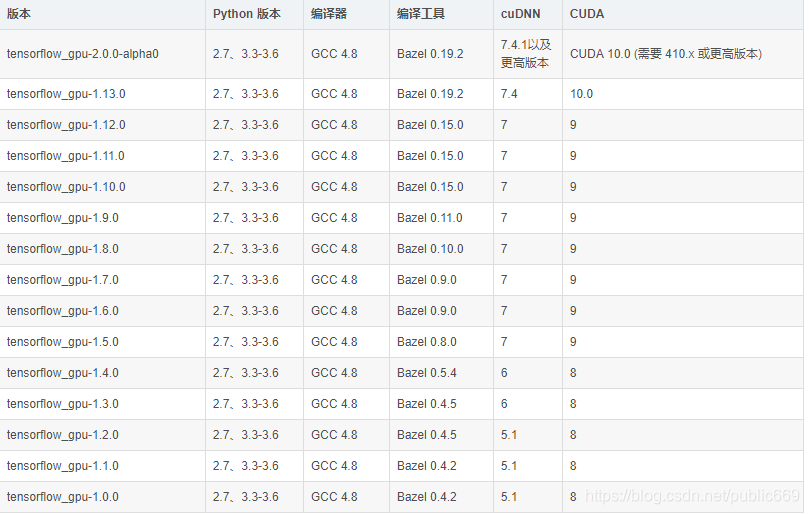
材料:cuda_8.0版本链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1lzKSWRLl5lYMrYcLjGbVXw
提取码:2p9i - 安装cuda
下载之后点击执行cuda
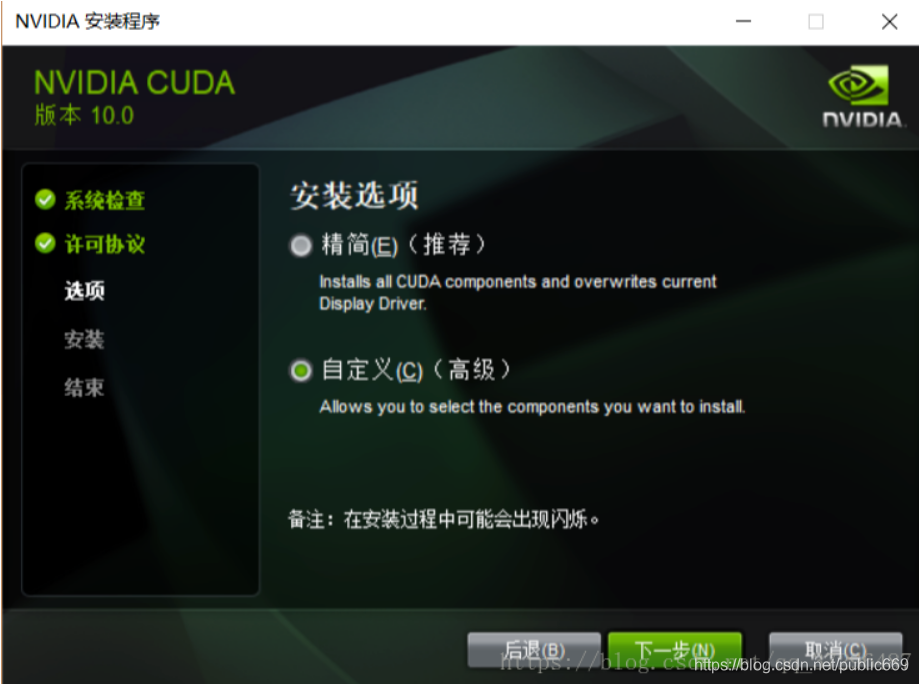
这里可以选择安装的模式:精简也可以选择自定义
安装路径可以自定义,也可以默认。选择自定义得记住安装的路径(后面配置环境变量)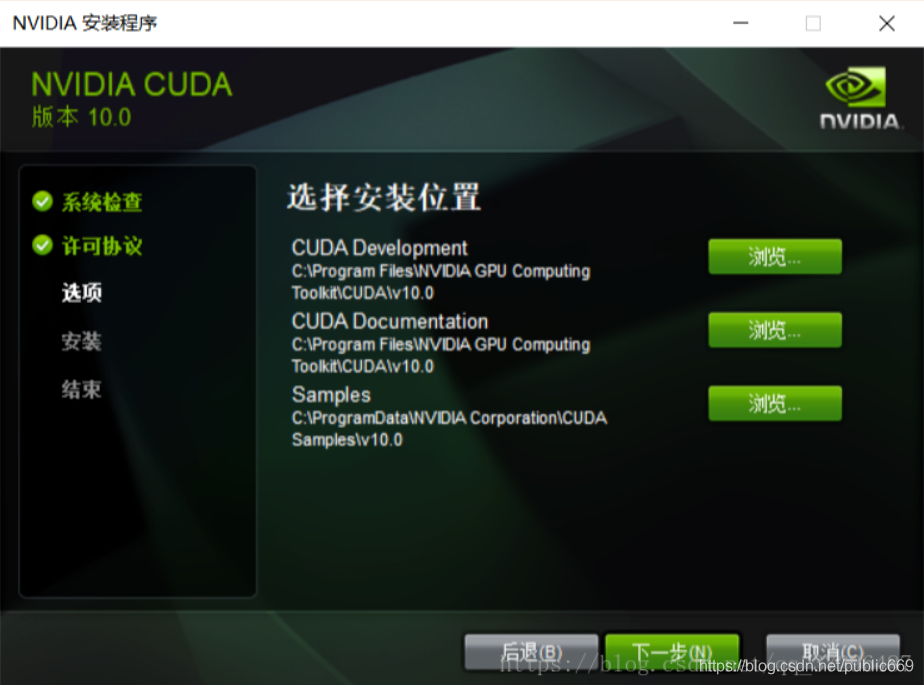
后面的就是一键Next,完成即可 - 配置系统环境变量
在系统环境变量中配置环境变量,在cuda安装好时会自动的配置两个,另外两个需要自己配置(ps:如果安装路径是自定义的话,需要根据情况自行变动)
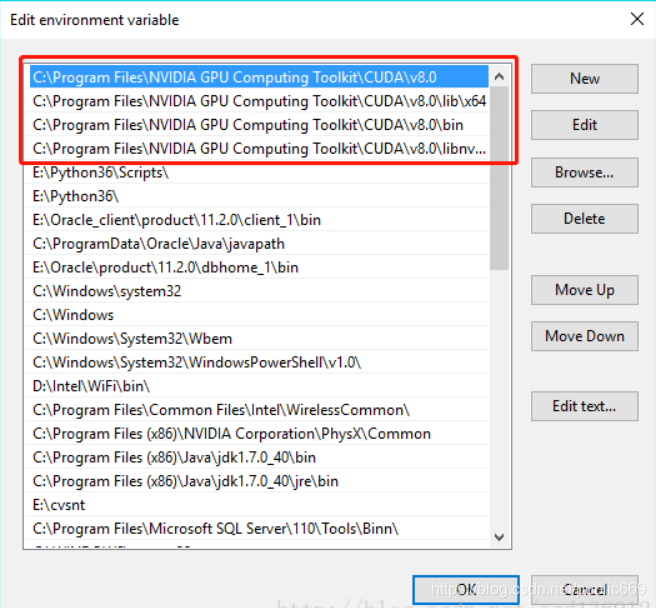
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v8.0
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v8.0\bin
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v8.0\lib\x64
C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing Toolkit\CUDA\v8.0\libnvvp
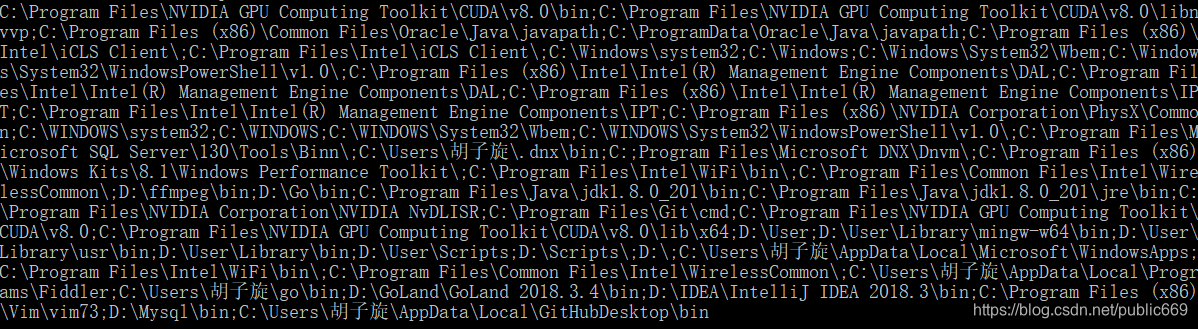
在完成了上述的配置后,可以验证一下是否配置成功:
在cmd中输入如下的代码:
echo %path%
执行结果如下:
4.配置cudnn:
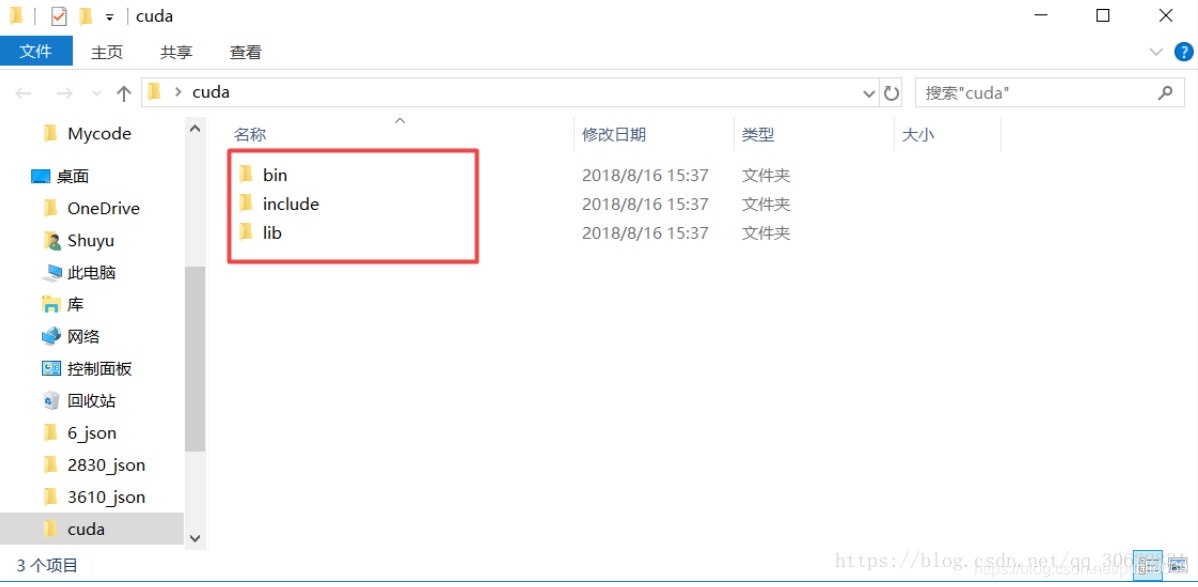
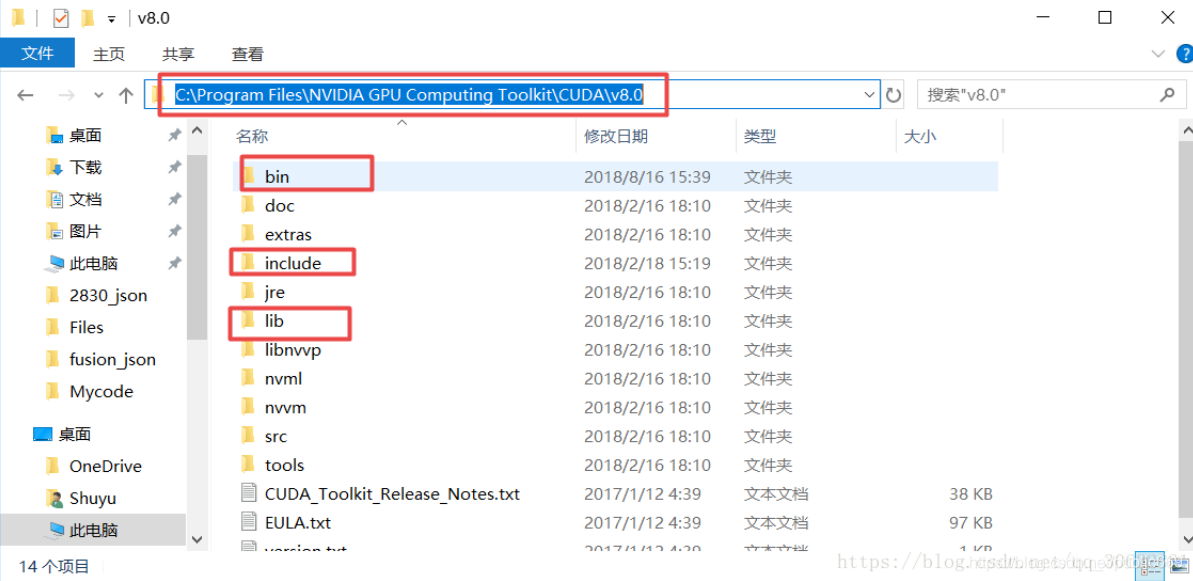
在分享的安装包中有一个压缩包,将其解压会出现三个文件夹:
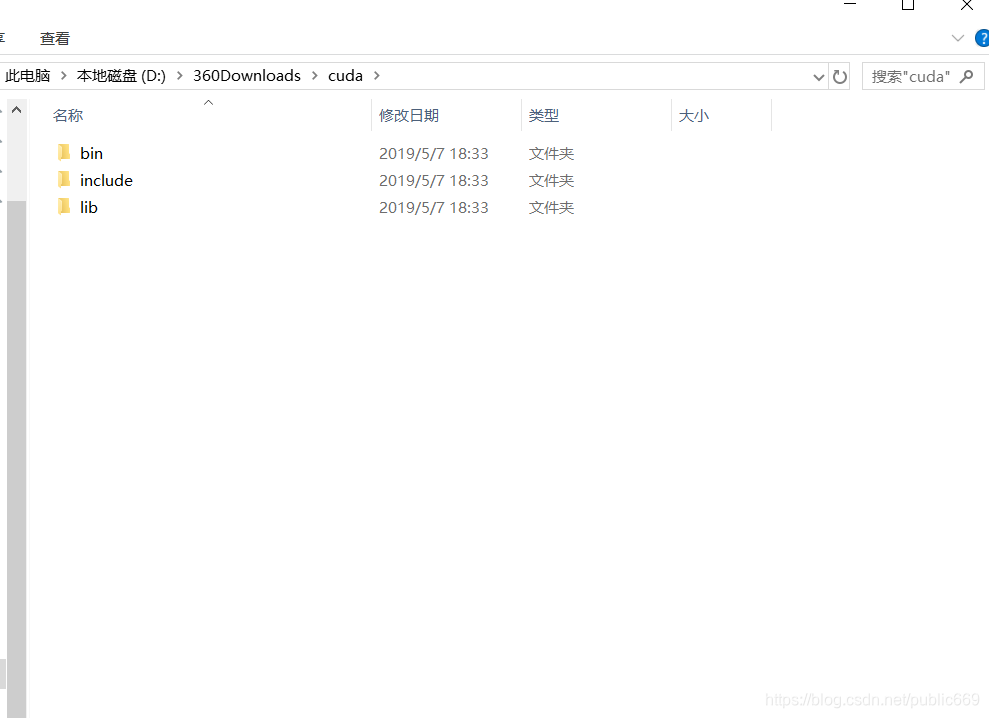
将这三个文件夹里面的文件对应的复制到cuda文件下:
(注意这里是将文件下的文件复制到cuda对应的文件夹里面,而不是将文件夹直接替代cuda下的文件夹(这步特别重要))
4.验证:
完成上述的所有步骤后,基本上就完成了大部分了!!!
验证是否成功:
打开pycharm,在里面输入如下测试代码:(前提是已经安装了相应版本tensorflow_gpu,这里给出1.4.0安装方法:在cmd中输入pip install -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple tensorflow-gpu==1.4.0)
import ctypes
import imp
import sys
def main():
try:
import tensorflow as tf
print("TensorFlow successfully installed.")
if tf.test.is_built_with_cuda():
print("The installed version of TensorFlow includes GPU support.")
else:
print("The installed version of TensorFlow does not include GPU support.")
sys.exit(0)
except ImportError:
print("ERROR: Failed to import the TensorFlow module.")
candidate_explanation = False
python_version = sys.version_info.major, sys.version_info.minor
print("\n- Python version is %d.%d." % python_version)
if not (python_version == (3, 5) or python_version == (3, 6)):
candidate_explanation = True
print("- The official distribution of TensorFlow for Windows requires "
"Python version 3.5 or 3.6.")
try:
_, pathname, _ = imp.find_module("tensorflow")
print("\n- TensorFlow is installed at: %s" % pathname)
except ImportError:
candidate_explanation = False
print("""
- No module named TensorFlow is installed in this Python environment. You may
install it using the command `pip install tensorflow`.""")
try:
msvcp140 = ctypes.WinDLL("msvcp140.dll")
except OSError:
candidate_explanation = True
print("""
- Could not load 'msvcp140.dll'. TensorFlow requires that this DLL be
installed in a directory that is named in your %PATH% environment
variable. You may install this DLL by downloading Microsoft Visual
C++ 2015 Redistributable Update 3 from this URL:
https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=53587""")
try:
cudart64_80 = ctypes.WinDLL("cudart64_80.dll")
except OSError:
candidate_explanation = True
print("""
- Could not load 'cudart64_80.dll'. The GPU version of TensorFlow
requires that this DLL be installed in a directory that is named in
your %PATH% environment variable. Download and install CUDA 8.0 from
this URL: https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-toolkit""")
try:
nvcuda = ctypes.WinDLL("nvcuda.dll")
except OSError:
candidate_explanation = True
print("""
- Could not load 'nvcuda.dll'. The GPU version of TensorFlow requires that
this DLL be installed in a directory that is named in your %PATH%
environment variable. Typically it is installed in 'C:\Windows\System32'.
If it is not present, ensure that you have a CUDA-capable GPU with the
correct driver installed.""")
cudnn5_found = False
try:
cudnn5 = ctypes.WinDLL("cudnn64_5.dll")
cudnn5_found = True
except OSError:
candidate_explanation = True
print("""
- Could not load 'cudnn64_5.dll'. The GPU version of TensorFlow
requires that this DLL be installed in a directory that is named in
your %PATH% environment variable. Note that installing cuDNN is a
separate step from installing CUDA, and it is often found in a
different directory from the CUDA DLLs. You may install the
necessary DLL by downloading cuDNN 5.1 from this URL:
https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn""")
cudnn6_found = False
try:
cudnn = ctypes.WinDLL("cudnn64_6.dll")
cudnn6_found = True
except OSError:
candidate_explanation = True
if not cudnn5_found or not cudnn6_found:
print()
if not cudnn5_found and not cudnn6_found:
print("- Could not find cuDNN.")
elif not cudnn5_found:
print("- Could not find cuDNN 5.1.")
else:
print("- Could not find cuDNN 6.")
print("""
The GPU version of TensorFlow requires that the correct cuDNN DLL be installed
in a directory that is named in your %PATH% environment variable. Note that
installing cuDNN is a separate step from installing CUDA, and it is often
found in a different directory from the CUDA DLLs. The correct version of
cuDNN depends on your version of TensorFlow:
* TensorFlow 1.2.1 or earlier requires cuDNN 5.1. ('cudnn64_5.dll')
* TensorFlow 1.3 or later requires cuDNN 6. ('cudnn64_6.dll')
You may install the necessary DLL by downloading cuDNN from this URL:
https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn""")
if not candidate_explanation:
print("""
- All required DLLs appear to be present. Please open an issue on the
TensorFlow GitHub page: https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues""")
sys.exit(-1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
如果出现以下结果则表明已经配置成功了:
TensorFlow successfully installed.
The installed version of TensorFlow includes GPU support.
若是出现以下问题则表明环境配置出错了:
Could not load ‘cudart64_80.dll’. The GPU version of TensorFlow
requires that this DLL be installed in a directory that is named in
your %PATH% environment variable. Download and install CUDA 8.0 from
this URL: https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-toolkit
5.模型gpu加速训练:
# 测试tensorflow_gpu版本加速效果代码
from datetime import datetime
import math
import time
import tensorflow as tf
import os
#os.environ["CUDA_DEVICE_ORDER"] = "PCI_BUS_ID"
#os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "-1"
batch_size = 32
num_batches = 100
# 该函数用来显示网络每一层的结构,展示tensor的尺寸
def print_activations(t):
print(t.op.name, ' ', t.get_shape().as_list())
# with tf.name_scope('conv1') as scope # 可以将scope之内的variable自动命名为conv1/xxx,便于区分不同组件
def inference(images):
parameters = []
# 第一个卷积层
with tf.name_scope('conv1') as scope:
# 卷积核、截断正态分布
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([11, 11, 3, 64],
dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(images, kernel, [1, 4, 4, 1], padding='SAME')
# 可训练
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[64], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv1 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
print_activations(conv1)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
# 再加LRN和最大池化层,除了AlexNet,基本放弃了LRN,说是效果不明显,还会减速?
lrn1 = tf.nn.lrn(conv1, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9, beta=0.75, name='lrn1')
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(lrn1, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='VALID', name='pool1')
print_activations(pool1)
# 第二个卷积层,只有部分参数不同
with tf.name_scope('conv2') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 64, 192], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(pool1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[192], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
print_activations(conv2)
# 稍微处理一下
lrn2 = tf.nn.lrn(conv2, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9, beta=0.75, name='lrn2')
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(lrn2, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='VALID', name='pool2')
print_activations(pool2)
# 第三个
with tf.name_scope('conv3') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 192, 384], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(pool2, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[384], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv3 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
print_activations(conv3)
# 第四层
with tf.name_scope('conv4') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 384, 256], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(conv3, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[256], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv4 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
print_activations(conv4)
# 第五个
with tf.name_scope('conv5') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 256, 256], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(conv4, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[256], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv5 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
print_activations(conv5)
# 之后还有最大化池层
pool5 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv5, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='VALID', name='pool5')
print_activations(pool5)
return pool5, parameters
# 全连接层
# 评估每轮计算时间,第一个输入是tf得Session,第二个是运算算子,第三个是测试名称
# 头几轮有显存加载,cache命中等问题,可以考虑只计算第10次以后的
def time_tensorflow_run(session, target, info_string):
num_steps_burn_in = 10
total_duration = 0.0
total_duration_squared = 0.0
# 进行num_batches+num_steps_burn_in次迭代
# 用time.time()记录时间,热身过后,开始显示时间
for i in range(num_batches + num_steps_burn_in):
start_time = time.time()
_ = session.run(target)
duration = time.time() - start_time
if i >= num_steps_burn_in:
if not i % 10:
print('%s:step %d, duration = %.3f' % (datetime.now(), i - num_steps_burn_in, duration))
total_duration += duration
total_duration_squared += duration * duration
# 计算每轮迭代品均耗时和标准差sd
mn = total_duration / num_batches
vr = total_duration_squared / num_batches - mn * mn
sd = math.sqrt(vr)
print('%s: %s across %d steps, %.3f +/- %.3f sec / batch' % (datetime.now(), info_string, num_batches, mn, sd))
def run_benchmark():
# 首先定义默认的Graph
with tf.Graph().as_default():
# 并不实用ImageNet训练,知识随机计算耗时
image_size = 224
images = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([batch_size, image_size, image_size, 3], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1))
pool5, parameters = inference(images)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True, log_device_placement=False))
sess.run(init)
# 下面直接用pool5传入训练(没有全连接层)
# 只是做做样子,并不是真的计算
time_tensorflow_run(sess, pool5, "Forward")
# 瞎弄的,伪装
objective = tf.nn.l2_loss(pool5)
grad = tf.gradients(objective, parameters)
time_tensorflow_run(sess, grad, "Forward-backward")
run_benchmark()
好啦,到这里就大功告成啦~~~~
可以体会gpu给你带来训练时的高速了,个人觉得还是得有一块好的显卡,这样加速效果会更好,速度更快。。。。
6.结束:
有什么问题和建议欢迎给我发邮件:1017190168@qq.com
或者直接联系我:1017190168
tensorflow GPU版本配置加速环境的更多相关文章
- 【转】Ubuntu 16.04安装配置TensorFlow GPU版本
之前摸爬滚打总是各种坑,今天参考这篇文章终于解决了,甚是鸡冻\(≧▽≦)/,电脑不知道怎么的,安装不了16.04,就安装15.10再升级到16.04 requirements: Ubuntu 16.0 ...
- Eclipse(非J2EE版本)配置Extjs环境以及安装部署Tomcat
Eclipse(非J2EE版本)配置Extjs环境(Spket) 1. 安装spket插件,帮助->安装新软件->http://www.agpad.com/update. 2. 设置Spk ...
- 通过Anaconda在Ubuntu16.04上安装 TensorFlow(GPU版本)
一. 安装环境 Ubuntu16.04.3 LST GPU: GeForce GTX1070 Python: 3.5 CUDA Toolkit 8.0 GA1 (Sept 2016) cuDNN v6 ...
- Windows7 64bits下安装TensorFlow GPU版本(图文详解)
不多说,直接上干货! Installing TensorFlow on Windows的官网 https://www.tensorflow.org/install/install_windows 首先 ...
- win10系统下安装TensorFlow GPU版本
首先要说,官网上的指南是最好的指南. https://www.tensorflow.org/install/install_windows 需要FQ看. 想要安装gpu版本的TensorFlow.我们 ...
- Win10上安装Keras 和 TensorFlow(GPU版本)
一. 安装环境 Windows 10 64bit 家庭版 GPU: GeForce GTX1070 Python: 3.5 CUDA: CUDA Toolkit 8.0 GA1 (Sept 2016 ...
- tensorflow 一些好的blog链接和tensorflow gpu版本安装
pading :SAME,VALID 区别 http://blog.csdn.net/mao_xiao_feng/article/details/53444333 tensorflow实现的各种算法 ...
- windows下caffe GPU版本配置
由于项目需要,所以在自己本子上配置了一下windows下GPU版本的caffe; 硬件: win10 ; gtx1070独显(计算能力6.1): 安装软件: cudnn-8. ...
- 说说Windows7 64bits下安装TensorFlow GPU版本会遇到的一些坑
不多说,直接上干货! 再写博文,回顾在Windows7上安装TensorFlow-GPU的一路坑 Windows7上安装TensorFlow的GPU版本后记 欢迎大家,加入我的微信公众号:大数据躺过的 ...
- tensorflow GPU版本安装及配置
经检测速度大幅度上升,不枉费我折腾了这么久,最坑的就是网上教程.书都没有写将cuda的bin加入全局变量,还是根据报错信息推出来的. 1.cuda9.0下载安装 https://developer.n ...
随机推荐
- 吃透单调栈(2)——解两道Hard题:接雨水、柱状图中最大的矩形问题
怎么想到要用单调栈的? 这类题目的数据通常是一维数组,要寻找任一个元素的右边或者左边第一个比自己大或者小的元素的位置(寻找边界),此时我们就要想到可以用单调栈了. 42. 接雨水 这道题就是要求解每一 ...
- numpy_tricks
Numpy Tricks 这篇文章不定期更新,主要是记录在使用numpy过程中一些有效的tricks(或者重要的API) import numpy as np numpy.where() numpy. ...
- SpringBoot 后端配置 Https 教程
以阿里云为例子 1. 申请 SSL 证书 1. 注册域名 打开阿里云官网,搜索域名 点击域名注册,输入域名,点击搜索 选择心仪的域名,点击购买,打钱 进入域名控制台,进行实名认证 2. 申请 SSL ...
- RK3568开发笔记(十):开发板buildroot固件移植开发的应用Demo,启动全屏显示
前言 上一篇,移植应用前的通讯接口工作和全屏工作都已经完成了.本篇移植开发的商业应用. 交叉编译好应用 (略),参照<RK3568开发笔记(八):开发板烧写buildroot固件(支 ...
- 文心一言 VS 讯飞星火 VS chatgpt (101)-- 算法导论9.3 7题
七.用go语言,设计一个 O(n)时间的算法,对于一个给定的包含n个互异元素的集合 S 和一个正整数k≤n,该算法能够确定 S 中最接近中位数的k个元素. 文心一言: 要设计一个 O(n) 时间的算法 ...
- Strimzi Kafka Bridge(桥接)实战之一:简介和部署
欢迎访问我的GitHub 这里分类和汇总了欣宸的全部原创(含配套源码):https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos 关于<Strimzi Kafka Bridge( ...
- Python网络编程——基于tcp协议实现远程执行命令、udp协议没有粘包问题、解决粘包问题、socketserver模块的基本使用(基于tcp协议、基于udp协议的使用)
文章目录 基于tcp协议实现远程执行命令 udp协议没有粘包问题 解决粘包问题 解决粘包问题(终极版) socketserver模块的基本使用 基于tcp协议的使用 基于udp协议的使用 基于tcp协 ...
- 创建vue项目并搭建JSONSERVER
1.该前提是你已经搭建好vue-cli脚手架,开始创建一个新项目,输入 vue init webpack demo(demo是自定义项目名). 2.cd demo 进入项目安装依赖 3.在已经创建的项 ...
- 如何在 Vue.js 中引入原子设计?
本文为翻译文章,原文链接: https://medium.com/@9haroon_dev/introducing-atomic-design-in-vue-js-a9e873637a3e 前言 原子 ...
- [数据分析与可视化] 基于Python绘制简单动图
动画是一种高效的可视化工具,能够提升用户的吸引力和视觉体验,有助于以富有意义的方式呈现数据可视化.本文的主要介绍在Python中两种简单制作动图的方法.其中一种方法是使用matplotlib的Anim ...
