android界面设计之布局管理
谈到android界面设计,各种布局样式不得不提!传统的布局方式有6种,我们会一一介绍。
在android studio2.2版本之后出现了一款超棒的布局方式,真正意义上的所见即所得,后面我们也会讲到!
1.LinearLayout:线性布局:线性布局又有两种,“垂直布局”和“水平布局”。
垂直布局每一行只能有一个控件(自己嵌套的不算);
水平布局只有一行,所有的控件依次从左向右排列;
linearLayout中有一个重要的属性 android:layout_weight="",这个weight在垂直布局时,代表行距;水平的时候代表列宽;weight值越大就越大,当把所有控件的weight都设置为相同值,比如1的时候,这些控件会平分父类控件的区域。
举个栗子:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"> <Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:text="button2"
android:textSize="60dp"
android:background="#1188aa"
android:enabled="false"/> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="button1"
android:textSize="50dp"
android:enabled="false"/> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="textview1"
android:textSize="50dp"
android:textColor="#991111"/> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="textview2"
android:textSize="60dp"
android:textColor="#119911"/> </LinearLayout>
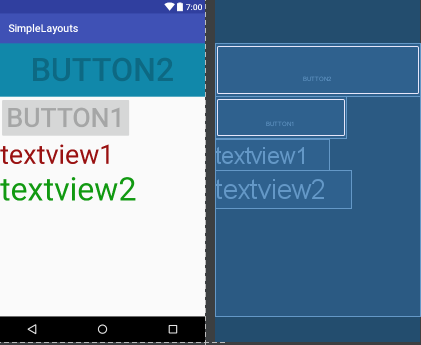
以上代码运行结果如下图:
2.FrameLayout:帧布局:这个比较简单,说白了就是在屏幕上定义一块空白的区域(当然也可以是整个屏幕)。
在这个空白的区域中,所有的控件都是在区域的左上角排列的,也就是说你没有办法指定这个区域里面控件的位置,后一个控件会一个接着一个的顶到左上角,这样就会覆盖前面的控件。
举个栗子:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<FrameLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"> <Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:text="button2"
android:textSize="60dp"
android:background="#1188aa"
android:enabled="false"/> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="button1"
android:textSize="50dp"
android:enabled="false"/> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="textview1"
android:textSize="50dp"
android:textColor="#991111"/> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="textview2"
android:textSize="60dp"
android:textColor="#119911"/> </FrameLayout>
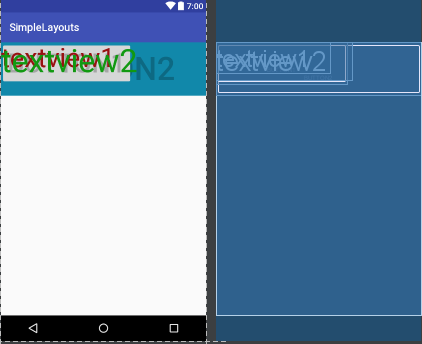
以上代码运行如下图,细心的你可能会发现上述的button中有一个enable属性,如果把这行代码去掉,那么button就会覆盖textview,这与我们之前讲的后一个组件会覆盖前一个组件是相违背的,你问我为什么,我也不知道,如知内情,望相告之:
3.RelativeLayout:相对布局:相对布局可以理解为某一个元素为参照物,来定位的布局方式,这个稍微复杂一些,因为其属性比较多,一个一个来看:
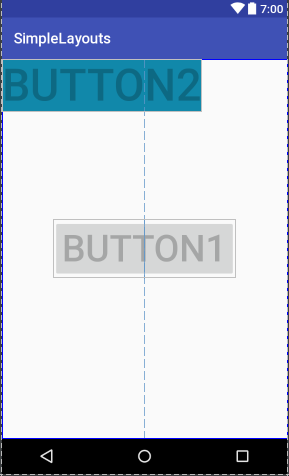
首先,我们定义两个button,并且把btn1放在屏幕的最中间,如图1,
我们在btn2中添加一行代码:android:layout_below="@+id/btn1",如图2,
把这行代码换成:android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/btn1",如图3,
再换一下:android:layout_alignParentBottom="true",如图4,
再换一下:android:layout_marginRight="200dp",如图5,连btn2的形状都挤变形了,是不是很神奇,想要真正领悟,必须上代码亲自试探试探!
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:text="button1"
android:textSize="50dp"
android:enabled="false"/> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/btn2" android:layout_marginRight="200dp" android:text="button2"
android:textSize="60dp"
android:background="#1188aa"
android:enabled="false"/> <!--<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/tv1"
android:text="textview1"
android:textSize="50dp"
android:textColor="#991111"/> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/tv2"
android:text="textview2"
android:textSize="60dp"
android:textColor="#119911"/>--> </RelativeLayout>



4.AbsoluteLayout:绝对布局:这个也很简单,主要属性就两个 layout_x 和 layout_y 分别定义 这个组件的绝对位置。 即,以屏幕左上角为(0,0)的坐标轴的x,y值,当向下或向右移动时,坐标值将变大。这个使用较少,因为其在不同设备上的显示大相径庭。但我还是举例说明吧!
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<AbsoluteLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:text="button1"
android:textSize="50dp" android:layout_x="100dp"
android:layout_y="50dp"/> <Button
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:text="button2"
android:textSize="50dp" android:textColor="#ff1111" android:layout_x="100dp"
android:layout_y="150dp"/> </AbsoluteLayout>
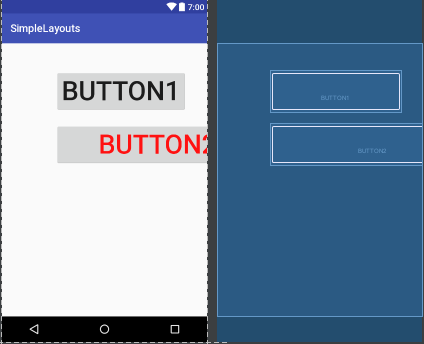
我们把btn2的宽度设置为填满整个父控件,可以发现结果如上图,看来,这个x和y针对的是控件的左上定点,并非控件中心点,这个需要注意。
5.TableLayout:表格布局:表格布局类似Html里面的Table。每一个TableLayout里面有表格行TableRow,TableRow里面可以具体定义每一个元素。
表格由列和行组成许多的单元格。表格允许单元格为空。单元格不能跨列,这与HTML 中的不一样。TabRow只论行,不论列(列自定义)。
举例说明:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<TableLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"> <TableRow>
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:text="button1"
android:textSize="30dp" android:layout_x="100dp"
android:layout_y="50dp"/> <Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:text="button2"
android:textSize="20dp"
android:textColor="#ff1111"
android:layout_x="100dp"
android:layout_y="150dp"/> </TableRow> <TableRow> <TextView android:text="第一行第0列"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<TextView android:text="第一行第1列"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
<TextView android:text="第一行第2列"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> </TableRow> </TableLayout>
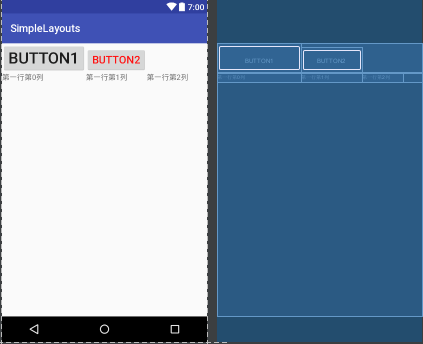
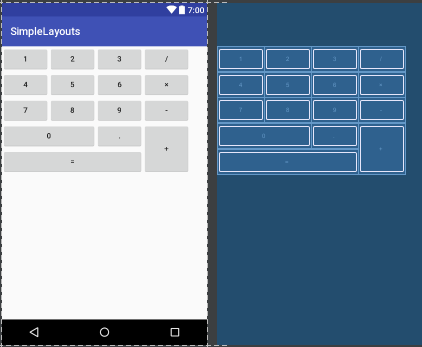
6.GridLayout:网格布局:网格布局是android4.0之后提出来的一种布局方式,使用它的理由有两个:1,减少布局嵌套层次从而提高性能;2,对需要复杂对齐的布局,非他莫属。不使用它的理由:由于太灵活导致学习难度比较大。在这里就不详细解释了,大家可以参考文档:http://www.jianshu.com/p/441d60be7d8a。
举个栗子吧:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<GridLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal"
android:rowCount="5"
android:columnCount="4"> <Button
android:id="@+id/one"
android:text="1"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/two"
android:text="2"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/three"
android:text="3"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/devide"
android:text="/"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/four"
android:text="4"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/five"
android:text="5"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/six"
android:text="6"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/multiply"
android:text="×"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/seven"
android:text="7"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/eight"
android:text="8"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/nine"
android:text="9"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/minus"
android:text="-"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/zero"
android:layout_columnSpan="2"
android:layout_gravity="fill"
android:text="0"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/point"
android:text="."/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/plus"
android:layout_rowSpan="2"
android:layout_gravity="fill"
android:text="+"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/equal"
android:layout_columnSpan="3"
android:layout_gravity="fill"
android:text="="/> </GridLayout>
7.ConstraintLayout:谷歌在2016年的IO大会上推出的一种新的布局方式—-ConstraintLayout,这局是一种约束型的布局方式。这绝对是你最应该了解的神器,有了它,天黑都不怕!这里隆重献上一个大神的作品,必须要读,必须要读,必须要读啊!
这个讲的非常清晰,我就不多废话了:
Android新特性介绍,ConstraintLayout完全解析
android界面设计之布局管理的更多相关文章
- Android界面设计适配不同屏幕的尺寸和密度解读
Android是运行在各种提供不同的屏幕尺寸和密度的设备.Android系统提供跨设备的统一开发环境和处理大部分的工作,以调整每个应用程序的用户界面,以在其上显示的画面. 同时,该系统提供了API,允 ...
- android 界面设计基本知识Ⅲ
本章继续讲述在android界面设计中相关的知识点.介绍内容包括BroadcastReceiver(广播),Service(服务),Widget(小部件),WebView(网页加载控件). 1.Bro ...
- Android UI组件:布局管理器
为了更好的管理Android应用的用户界面中的组件,Android提供了布局管理器.通过使用布局管理器,Android应用的图形用户界面具有良好的平台无关性.通常,推荐使用布局管理器来管理组件的分布. ...
- 【Android 应用开发】AndroidUI设计之 布局管理器 - 详细解析布局实现
写完博客的总结 : 以前没有弄清楚的概念清晰化 父容器与本容器属性 : android_layout...属性是本容器的属性, 定义在这个布局管理器的LayoutParams内部类中, 每个布局管理器 ...
- 让你大开眼界的10款Android界面设计
根据调查显示, iOS与Android的市场份额差距正越来越大.Android设备正在成为手机应用市场的主力军.如何从设计层面创造一个优美的app界面来吸引用户已然成为广大App开发者们必做的功课之一 ...
- android 界面设计基本知识Ⅱ
上一章讲述了Android界面设计时,一些基本控件的使用,本章主要讲述自定义控件,Fragment和Headler线程机制. 1.自定义控件 (1)基本知识 dp.sp和dx px:像素点 ...
- android 界面设计基本知识
一个好的APP不仅有美观,好看的界面,更需要良好的性能和稳定性.作为一名开发人员,需要理解界面设计原则并写出优秀的界面设计代码. 本章主要讲述基本控件的使用,界面布局及一些常用的界面设计属性. 1.常 ...
- AndroidUI设计之 布局管理器 - 详细解析布局实现
写完博客的总结 : 以前没有弄清楚的概念清晰化 父容器与本容器属性 : android_layout...属性是本容器的属性, 定义在这个布局管理器的LayoutParams内部类中, 每个布局管理器 ...
- android中常用的布局管理器(二)
接上篇博客 (3)LinearLayout 线性布局管理器 线性布局管理器是将放入其中的组件按照垂直或水平方向来布局,每一行或每一列只能放一个组件,并且不会换行,当组件排列到窗体的边缘后,后面 ...
随机推荐
- asp.net 文件上传 Uploadify HTML5 带进度条
参考的https://www.cnblogs.com/lvdabao/p/3452858.html这位,在此基础上略有修改: 1.根据Layer,将上传附件做成弹窗显示,引入frame弹窗,在项目当中 ...
- 使用json文件给es中导入数据
使用json文件可以给es中导入数据,10万条左右的数据可以一次导入,数量太大时导入就会报错.大数量的到导入还是需要用bulk方式. accounts.json文件格式如下: {"index ...
- UOJ#77. A+B Problem [可持久化线段树优化建边 最小割]
UOJ#77. A+B Problem 题意:自己看 接触过线段树优化建图后思路不难想,细节要处理好 乱建图无果后想到最小割 白色和黑色只能选一个,割掉一个就行了 之前选白色必须额外割掉一个p[i], ...
- Chrome Stylist 插件 (CSS备份)
Stylist 插件还是很好用的,可以给网站自定义CSS样式,(还有个插件叫"油猴子",可以给网页加载自定义JS): 不过麻烦的是,现在的最新版360浏览器不能显示这个插件(这个浏 ...
- 【实用】需要收藏备用的JQuery代码片段
1 元素屏幕居中 jQuery.fn.center = function () { this.css("position","absolute"); this. ...
- 【Unity3D技术文档翻译】第1.6篇 使用 AssetBundle Manager
上一章:[Unity3D技术文档翻译]第1.5篇 使用 AssetBundles 本章原文所在章节:[Unity Manual]→[Working in Unity]→[Advanced Develo ...
- spark RDD,DataFrame,DataSet 介绍
弹性分布式数据集(Resilient Distributed Dataset,RDD) RDD是Spark一开始就提供的主要API,从根本上来说,一个RDD就是你的数据的一个不可变的分布式元素集合,在 ...
- Eclipse搭建Maven项目之准备工作
Maven是优秀的Java项目对象模型解决方案,意为知识的积累(意地绪文),Maven可以方便的解决Java项目包依赖问题,通过配置pom.xml引入依赖,并自动引入其他依赖. 操作系统版本:wind ...
- php 网络爬虫2种方法
1,通过curl进行抓取再进行写入文件当中: $curlobj = curl_init(); // 初始化curl_setopt($curlobj, CURLOPT_URL, "https: ...
- poj 3278 简单BFS
题意:给定农夫和奶牛的初始位置,农夫可以当前位置+1.-1.*2三种移动方式,问最少需要多少分钟抓住奶牛 AC代码: #include<cstdio> #include<cstrin ...
