Lombok认知
Lombok的简介
Lombok是一款Java开发插件,公司项目到处使用,整体效果很棒,代码更干净。Java开发人员可以节省出重复构建,诸如hashCode和equals这样的方法以及各种业务对象模型的accessor和ToString等方法的大量时间。对于这些方法,它能够在编译源代码期间自动帮我们生成这些方法,并没有如反射那样降低程序的性能。
Lombok的基本使用示例
1.Val可以将变量申明是final类型。
public static void main (String[] args){
val setVar = new HashSet<String>();
val listsVar = new ArrayList<String>();
val mapVar = new HashMap<String, String>();
//=>上面代码相当于如下:
final Set<String> setVar2 = new HashSet<>();
final List<String> listsVar2 = new ArrayList<>();
final Map<String, String> maps2 = new HashMap<>();
}
2.@NonNull注解能够为方法或构造函数的参数提供非空检查。
public void notNullExample(@NonNull String string) {
//方法内的代码
}
//=>上面代码相当于如下:
public void notNullExample(String string) {
if (string != null) {
//方法内的代码相当于如下:
} else {
throw new NullPointerException("null");
}
}
3.@Cleanup注解能够自动释放资源。
public void jedisExample(String[] args) {
try {
@Cleanup Jedis jedis = redisService.getJedis();
} catch (Exception ex) {
logger.error(“Jedis异常:”,ex)
}
//=>上面代码相当于如下:
Jedis jedis= null;
try {
jedis = redisService.getJedis();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(“Jedis异常:”,ex)
} finally {
if (jedis != null) {
try {
jedis.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
4.@Getter/@Setter注解可以针对类的属性字段自动生成Get/Set方法。
public class OrderCreateDemoReq{
@Getter
@Setter
private String customerId;
@Setter
@Getter
private String poolId;
}
//上面请求Req类的代码相当于如下:
public class OrderCreateDemoReq{
private String customerId;
private String poolId;
public String getCustomerId(){
return customerId;
}
public String getPoolId(){
return poolId;
}
public void setCustomerId(String customerId){
this.customerId = customerId;
}
public void setPoolId(String poolId){
this.pool = pool;
}
}
5.@ToString注解,为使用该注解的类生成一个toString方法,默认的toString格式为:ClassName(fieldName= fieleValue ,fieldName1=fieleValue)。
@ToString(callSuper=true,exclude="someExcludedField")
public class Demo extends Bar {
private boolean someBoolean = true;
private String someStringField;
private float someExcludedField;
}
//上面代码相当于如下:
public class Demo extends Bar {
private boolean someBoolean = true;
private String someStringField;
private float someExcludedField;
@ Override
public String toString() {
return "Foo(super=" + super.toString() +
", someBoolean=" + someBoolean +
", someStringField=" + someStringField + ")";
}
}
6.@EqualsAndHashCode注解,为使用该注解的类自动生成equals和hashCode方法。
@EqualsAndHashCode(exclude = {"id"}, callSuper =true)
public class LombokDemo extends Demo{
private int id;
private String name;
private String gender;
}
//上面代码相当于如下:
public class LombokDemo extends Demo{
private int id;
private String name;
private String gender;
@Override
public boolean equals(final Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o == null)
return false;
if (o.getClass() != this.getClass())
return false;
if (!super.equals(o))
return false;
final LombokDemo other = (LombokDemo)o;
if (this.name == null ? other.name != null : !this.name.equals(other.name))
return false;
if (this.gender == null ? other.gender != null : !this.gender.equals(other.gender)) return false;
return true;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
final int PRIME = 31;
int result = 1;
result = result * PRIME + super.hashCode();
result = result * PRIME + (this.name == null ? 0 : this.name.hashCode());
result = result * PRIME + (this.gender == null ? 0 : this.gender.hashCode());
return result;
}
}
7.@NoArgsConstructor, @RequiredArgsConstructor, @AllArgsConstructor,这几个注解分别为类自动生成了无参构造器、指定参数的构造器和包含所有参数的构造器。
@RequiredArgsConstructor(staticName = "of")
@AllArgsConstructor(access = AccessLevel.PROTECTED)
public class ConstructorExample<T> {
private int x, y;
@NonNull private T description;
@NoArgsConstructor
public static class NoArgsExample {
@NonNull private String field;
}
}
//上面代码相当于如下:
public class ConstructorExample<T> {
private int x, y;
@NonNull private T description;
private ConstructorExample(T description) {
if (description == null) throw new NullPointerException("description");
this.description = description;
}
public static <T> ConstructorExample<T> of(T description) {
return new ConstructorExample<T>(description);
}
@java.beans.ConstructorProperties({"x", "y", "description"})
protected ConstructorExample(int x, int y, T description) {
if (description == null) throw new NullPointerException("description");
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.description = description;
}
public static class NoArgsExample {
@NonNull private String field;
public NoArgsExample() {
}
}
}
8.@Data注解作用比较全,其包含注解的集合 @ToString, @EqualsAndHashCode,所有字段的 @Getter和所有非final字段的 @Setter, @RequiredArgsConstructor。相当于以上几个注解的集合体。
9.@Builder注解提供了一种比较推崇的构建值对象的方式。
@Builder
public class BuilderExample {
private String name;
private int age;
@Singular private Set<String> occupations;
}
//上面代码相当于如下:
public class BuilderExample {
private String name;
private int age;
private Set<String> occupations;
BuilderExample(String name, int age, Set<String> occupations) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.occupations = occupations;
}
public static BuilderExampleBuilder builder() {
return new BuilderExampleBuilder();
}
public static class BuilderExampleBuilder {
private String name;
private int age;
private java.util.ArrayList<String> occupations;
BuilderExampleBuilder() {
}
public BuilderExampleBuilder name(String name) {
this.name = name;
return this;
}
public BuilderExampleBuilder age(int age) {
this.age = age;
return this;
}
public BuilderExampleBuilder occupation(String occupation) {
if (this.occupations == null) {
this.occupations = new java.util.ArrayList<String>();
}
this.occupations.add(occupation);
return this;
}
public BuilderExampleBuilder occupations(Collection<? extends String> occupations) {
if (this.occupations == null) {
this.occupations = new java.util.ArrayList<String>();
}
this.occupations.addAll(occupations);
return this;
}
public BuilderExampleBuilder clearOccupations() {
if (this.occupations != null) {
this.occupations.clear();
}
return this;
}
public BuilderExample build() {
Set<String> occupations = new HashSet<>();
return new BuilderExample(name, age, occupations);
}
@verride
public String toString() {
return "BuilderExample.BuilderExampleBuilder(name = " + this.name + ", age = " + this.age + ", occupations = " + this.occupations + ")";
}
}
}
10.@Synchronized注解类似Java中的Synchronized 关键字,但是可以隐藏同步锁。
public class SynchronizedExample {
private final Object readLock = new Object();
@Synchronized
public static void hello() {
System.out.println("world");
}
@Synchronized("readLock")
public void foo() {
System.out.println("bar");
}
//上面代码相当于如下:
public class SynchronizedExample {
private static final Object $LOCK = new Object[0];
private final Object readLock = new Object();
public static void hello() {
synchronized($LOCK) {
System.out.println("world");
}
}
public void foo() {
synchronized(readLock) {
System.out.println("bar");
}
}
}
Lombok背后的自定义注解原理
Lombok这款插件正是依靠可插件化的Java自定义注解处理API(JSR 269: Pluggable Annotation Processing API)来实现在Javac编译阶段利用“Annotation Processor”对自定义的注解进行预处理后生成真正在JVM上面执行的“Class文件”.其大致执行原理图如下:
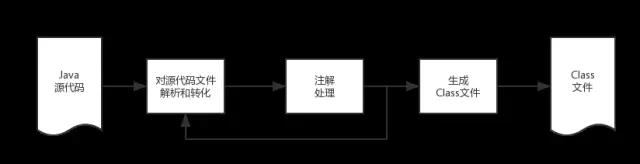
从上面的这个原理图上可以看出Annotation Processing是编译器在解析Java源代码和生成Class文件之间的一个步骤。其中Lombok插件具体的执行流程如下:

从上面的Lombok执行的流程图中可以看出,在Javac 解析成AST抽象语法树之后, Lombok 根据自己编写的注解处理器,动态地修改 AST,增加新的节点(即Lombok自定义注解所需要生成的代码),最终通过分析生成JVM可执行的字节码Class文件。使用Annotation Processing自定义注解是在编译阶段进行修改,而JDK的反射技术是在运行时动态修改,两者相比,反射虽然更加灵活一些但是带来的性能损耗更加大。Lombok认知的更多相关文章
- 3.lombok系列3:lombok的实验类特性
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/54powerman/article/details/72516755 lombok除了已经推荐使用的基本功能,还维护了一个创新型的注解,有些功能有违 ...
- %iowait和CPU使用率的正确认知
resources 理解 %IOWAIT (%WIO) LINUX系统的CPU使用率和LOAD Linux Performance Observability Tools How Linux CPU ...
- 【AI开发第一步】微软认知服务API应用
目录 介绍 API分类 使用‘视觉’API完成的Demo 点击直接看干货 介绍 从3月份Google家的阿尔法狗打败韩国围棋冠军选手李世石,到之后微软Build2016大会宣布的“智能机器人”战略.种 ...
- 记录一次bug解决过程:eclipse集成lombok插件
一 总结 eclipse集成插件lombok: 启动Spring Boot项目: sublime全局搜索关键字:ctrl + shift + F JDK8中的lambda表达式使用 二 BUG描述:集 ...
- lombok在IntelliJ IDEA下的使用
lombok是一款可以精减java代码.提升开发人员生产效率的辅助工具,利用注解在编译期自动生成setter/getter/toString()/constructor之类的代码.代码越少,意味着出b ...
- lombok 简化java代码注解
lombok 简化java代码注解 安装lombok插件 以intellij ide为例 File-->Setting-->Plugins-->搜索"lombok plug ...
- Lombok 安装、入门 - 消除冗长的 java 代码
lombok 提供了简单的注解的形式来帮助我们简化消除一些必须有但显得很臃肿的 java 代码. lombok 的官方网址:http://projectlombok.org/ lombok 安装1. ...
- lombok介绍
Lombok是一种JavaArchive(JAR)文件,可用来消除Java代码的冗长.在写代码时,可以通过这个插件消除各种getter和setter,toString等常用方法. lombok 注解: ...
- Lombok简化Java代码
导包:import lombok.Data; Lombok简化Java代码: 在Lombok中,生成构造方法的annotation一共有三个:@NoArgsConstructor, @Required ...
随机推荐
- Screen命令让Linux shell在后台运行
#screen ping ychack.com //挂置后台ping本站 #screen ping baidu.com //挂置后台ping百度 #screen -ls //列出进程 #screen ...
- 【转载】Git设置单个文件上传大小
git单个文件默认大小是50M,超过50M,会给出warning.大于100M会无法提交: 可以通过命令,修改单个文件默认大小(以设置500M以例): git config --global http ...
- Laradock 下安装Beast扩展
laradock/php-fpm/Dockfile ########################################################################## ...
- burpsuite下载安装及基本配置
jdk安装 根据电脑安装对应jdk版本 点此下载jdk 下载完成得到如下exe文件 配置Java环境变量 计算机右键-->属性-->高级系统设置-->环境变量 点击环境变量--> ...
- Java异常的限制
Java异常的限制 我在看JAVA编程思想,讲到异常的限制,看的代码和解释,非常的难看下去,直接写了他的代码. java编程思想关于异常限制的逻辑 它以棒球比赛为例子. 定义了Inning(一局比赛) ...
- HBase查询速度慢原因排查
问题:通过HBase访问服务在HBase中查询 ASSET_NORMAL 表速度很慢 如下,查询一条数据需要2.970s时间: 如下,统计总条数需要14.675s时间: HBase访问服务部署了3个节 ...
- Linux中{ }的用法
一.生成序列 格式:{#..#},按照ASCII表的顺序进行生成,如{a..c}表示a b c,也可以{c..a}倒叙的形式生成c b a # ..} # echo {z..a} z y x w v ...
- 关于C/C++的各种优化
一.常量 声明常量可以方便代码的修改,提高复用性. ; +; ; 同时,声明常量也可以减少重复运算,提高代码速度,例子如下: string s; cin>>s; ;i<len;i++ ...
- CF6
A A 不解释 #include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; namespace red{ inline int read() { int x= ...
- 内核MKDEV(MAJOR, MINOR)
版本:linux-2.6.24.4 宏: MKDEV(MAJOR, MINOR); 说明: 获取设备在设备表中的位置. MAJOR 主设备号 MINOR 次设备号 内核使用的版本号 ...
