RabbitMQ-learning
第一种模式=直连
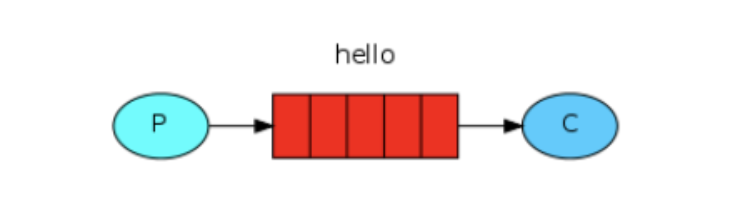
P:生产者,也就是要发送消息的程序
C:消费者:消息的接受者,会一直等待消息到来。
queue:消息队列,图中红色部分。类似一个邮箱,可以缓存消息;生产者向其中投递消息,消费者从其中取出消息。
producer:
package com.quan.rabbitmq.producer; import com.rabbitmq.client.Channel;
import com.rabbitmq.client.Connection;
import com.rabbitmq.client.ConnectionFactory; import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException; /**
* 直连模型:
* 生产者发送消息
* 消费者,等待消息到来消费
* 消息队列:可以缓存消息,生产者向其中投递消息,消费者从其中取出消息。
*
*/
public class RMQProducer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost("localhost");
connectionFactory.setPort(5672);
connectionFactory.setUsername("quan");
connectionFactory.setPassword("admin");
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost("quan"); Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); channel.queueDeclare("hello",true,false,false,null);
channel.basicPublish("","hello",null,"hello rabbit".getBytes()); channel.close();
connection.close();
} }
consumer:
package com.quan.rabbitmq.consumer; import com.rabbitmq.client.*; import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException; public class RMQConsumer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost("localhost");
connectionFactory.setPort(5672);
connectionFactory.setUsername("quan");
connectionFactory.setPassword("admin");
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost("quan");
//创建连接
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//通过连接创建通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); /**
* 参数1:声明通道对应的队列
* 参数2:指定是否持久化
* 参数3:指定是否独占对象
* 参数4:指定是否自动删除队列
* 参数5:对队列的额外设置
*/
channel.queueDeclare("hello",true,false,false,null);
channel.basicConsume("hello",true,new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println(new String(body));
}
}); } }
第二种模式=任务模型(work quene)

当消息处理比较耗时的时候,可能生产消息的速度会远远大于消息的消费速度。长此以往,消息就会堆积越来越多,无法及时处理。
此时就可以使用work 模型:让多个消费者绑定到一个队列,共同消费队列中的消息。队列中的消息一旦消费,就会消失,因此任务是不会被重复执行的。
P:生产者:任务的发布者
C1:消费者-1,领取任务并且完成任务,假设完成速度较慢
C2:消费者-2:领取任务并完成任务,假设完成速度快
P:
/**
* 直连模型:
* 生产者发送消息
* 消费者,等待消息到来消费
* 消息队列:可以缓存消息,生产者向其中投递消息,消费者从其中取出消息。
*
*/
public class RMQProducer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost("localhost");
connectionFactory.setPort(5672);
connectionFactory.setUsername("quan");
connectionFactory.setPassword("admin");
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost("quan"); Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection(); Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); channel.queueDeclare("hello",true,false,false,null);
for(int i =0 ;i<20;i++){
channel.basicPublish("","hello",null,(i+"=====>hello rabbit").getBytes());
} channel.close();
connection.close();
} }
C1
public class RMQConsumer21 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost("localhost");
connectionFactory.setPort(5672);
connectionFactory.setUsername("quan");
connectionFactory.setPassword("admin");
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost("quan");
//创建连接
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//通过连接创建通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
/**
* 参数1:声明通道对应的队列
* 参数2:指定是否持久化
* 参数3:指定是否独占对象
* 参数4:指定是否自动删除队列
* 参数5:对队列的额外设置
*/
channel.queueDeclare("hello",true,false,false,null);
channel.basicConsume("hello",true,new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("我是consumer1"+new String(body));
}
});
}
}
C2
public class RMQConsumer22 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost("localhost");
connectionFactory.setPort(5672);
connectionFactory.setUsername("quan");
connectionFactory.setPassword("admin");
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost("quan");
//创建连接
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//通过连接创建通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
/**
* 参数1:声明通道对应的队列
* 参数2:指定是否持久化
* 参数3:指定是否独占对象
* 参数4:指定是否自动删除队列
* 参数5:对队列的额外设置
*/
channel.queueDeclare("hello",true,false,false,null);
channel.basicConsume("hello",true,new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("我是consumer2"+new String(body));
}
});
}
}
re
当两个消费者都在监听通道中的消息的时候:
我们一旦发消息:
我是consumer2 0=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 2=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 4=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 6=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 8=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 10=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 12=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 14=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 16=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 18=====>hello rabbit @@@@@@@@@@@@@@ 我是consumer1 1=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer1 3=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer1 5=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer1 7=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer1 9=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer1 11=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer1 13=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer1 15=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer1 17=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer1 19=====>hello rabbit
默认情况下,RabbitMQ将按顺序将每个消息发送给下一个使用者。平均而言,每个消费者都会收到相同数量的消息。这种分发消息的方式称为循环。
消息确认机制:
public class RMQConsumer21 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, TimeoutException {
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory = new ConnectionFactory();
connectionFactory.setHost("localhost");
connectionFactory.setPort(5672);
connectionFactory.setUsername("quan");
connectionFactory.setPassword("admin");
connectionFactory.setVirtualHost("quan");
//创建连接
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//通过连接创建通道
final Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.queueDeclare("hello",true,false,false,null);
channel.basicQos(1);//一次只接受一条为确认的消息
//第二个参数:关闭自动确认消息
channel.basicConsume("hello",false,new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("我是consumer1 "+new String(body));
channel.basicAck(envelope.getDeliveryTag(),false);//手动确认消息
}
});
}
}
re:
我是consumer1 0=====>hello rabbit @@@@@@@@@@@ 我是consumer2 1=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 2=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 3=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 4=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 5=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 6=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 7=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 8=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 9=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 10=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 11=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 12=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 13=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 14=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 15=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 16=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 17=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 18=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 19=====>hello rabbit
第三种模式-广播
fanout 扇出===广播
消息发送流程:
- 可以有多个消费者
- 每个消费者有自己的queue(队列)
- 每个队列都要绑定到Exchange(交换机)
- 生产者发送的消息,只能发送到交换机,交换机来决定要发给哪个队列,生产者无法决定。
- 交换机把消息发送给绑定过的所有队列
- 队列的消费者都能拿到消息。实现一条消息被多个消费者消费

p;更新部分:
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
Channel channel = connection.createChannel();
channel.exchangeDeclare("logs","fanout");
for(int i =0 ;i<20;i++){
//第一个参数:交换机名字
//第二个参数:队列名字
//第三个参数:
//第四个参数:消息,是byte类型
channel.basicPublish("logs","",null,(i+"=====>hello rabbit").getBytes());
}
c1 c2 c3:这三个都是差不多的配置:
//绑定交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare("logs","fanout");
//创建临时队列
String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();
//将临时队列绑定交换机exchange
channel.queueBind(queue,"logs","");
//处理消息
channel.basicConsume(queue,true,new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("我是consumer1 "+new String(body)); }
});
re:
所有的消息,每个消费者都可以消费得到,
第四种模式-Routing-订阅模式中的-直连(direct)
在Fanout模式中,一条消息,会被所有订阅的队列都消费。但是,在某些场景下,我们希望不同的消息被不同的队列消费。
这时就要用到Direct类型的Exchange。
流程:
- 队列与交换机的绑定,不能是任意绑定了,而是要指定一个`RoutingKey`(路由key)
- 消息的发送方在 向 Exchange发送消息时,也必须指定消息的 `RoutingKey`。
- Exchange不再把消息交给每一个绑定的队列,而是根据消息的`Routing Key`进行判断,只有队列的`Routingkey`与消息的 `Routing key`完全一致,才会接收到消息
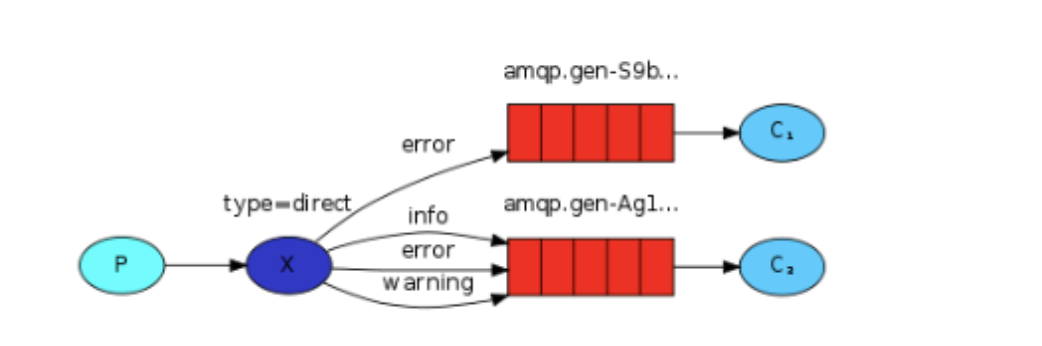
- P:生产者,向Exchange发送消息,发送消息时,会指定一个routing key。
- X:Exchange(交换机),接收生产者的消息,然后把消息递交给 与routing key完全匹配的队列
- C1:消费者,其所在队列指定了需要routing key 为 error 的消息
- C2:消费者,其所在队列指定了需要routing key 为 info、error、warning 的消息
情景:
c1 :error,info,debug
c2:error
c3:info
p:会每种key发一条消息:
p:改变rkey的值:
//声明交换机:参数1:交换机名称
//参数2:交换机类型:
channel.exchangeDeclare("logs1","direct");
String rkey = "debug";
//第一个参数:交换机名字
//第二个参数:队列名字/路由key
//第三个参数:
//第四个参数:消息,是byte类型
channel.basicPublish("logs1",rkey,null,(rkey+"消息=====>hello rabbit").getBytes());
channel.close();
connection.close();
}
c1:
//绑定交换机/参数2 交换机类型
channel.exchangeDeclare("logs1","direct");
//创建临时队列
String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();
//将临时队列绑定交换机exchange
//第一个参数:队列,第2个参数:交换机名字,第3个参数:路由key
channel.queueBind(queue,"logs1","error");
channel.queueBind(queue,"logs1","info");
channel.queueBind(queue,"logs1","debug");
//处理消息
channel.basicConsume(queue,true,new DefaultConsumer(channel){
@Override
public void handleDelivery(String consumerTag, Envelope envelope, AMQP.BasicProperties properties, byte[] body) throws IOException {
System.out.println("我是consumer1 "+new String(body)); }
}); }
c2:
//绑定交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare("logs1","direct");
//创建临时队列
String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();
//将临时队列绑定交换机exchange
//第一个参数:队列,第2个参数:交换机名字,第3个参数:路由key
channel.queueBind(queue,"logs1","error");
//处理消息
C3:
//创建连接
Connection connection = connectionFactory.newConnection();
//通过连接创建通道
Channel channel = connection.createChannel(); //绑定交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare("logs1","direct");
//创建临时队列
String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();
//将临时队列绑定交换机exchange
//第一个参数:队列,第2个参数:交换机名字,第3个参数:路由key
channel.queueBind(queue,"logs1","info");
//处理消息
p每个rkey发送一次消息后的结果:
我是consumer1 error消息=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer1 info消息=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer1 debug消息=====>hello rabbit 我是consumer2 error消息=====>hello rabbit 我是consumer3 info消息=====>hello rabbit
可以知道,这种类型的交换机是可以按需发送的。
Routing的订阅模式--topic:
Topic类型的Exchange与Direct相比,都是可以根据RoutingKey把消息路由到不同的队列。只不过Topic类型Exchange可以让队列
在绑定Routing key 的时候使用通配符!
这种模型Routingkey 一般都是由一个或多个单词组成,多个单词之间以”.”分割,例如: item.insert


p:
//声明交换机:参数1:交换机名称
//参数2:交换机类型:
channel.exchangeDeclare("topic1","topic");
String rkey = "user.debug.all";
//第一个参数:交换机名字
//第二个参数:队列名字/路由key
//第三个参数:
//第四个参数:消息,是byte类型
channel.basicPublish("topic1",rkey,null,(rkey+"消息=====>hello rabbit").getBytes());
c2:
//绑定交换机
channel.exchangeDeclare("topic1","topic");
//创建临时队列
String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();
//将临时队列绑定交换机exchange
//第一个参数:队列,第2个参数:交换机名字,第3个参数:路由key
channel.queueBind(queue,"topic1","user.#");
user.#可以匹配多个后面的单词:
c1:
//绑定交换机/参数2 交换机类型
channel.exchangeDeclare("topic1","topic");
//创建临时队列
String queue = channel.queueDeclare().getQueue();
//将临时队列绑定交换机exchange
//第一个参数:队列,第2个参数:交换机名字,第3个参数:路由key
channel.queueBind(queue,"topic1","user.*");
user.*只能接一个单词:
p发送了一次key为user.debug 和一次user.debug.all:
我是consumer1 user.debug消息=====>hello rabbit 我是consumer2 user.debug消息=====>hello rabbit
我是consumer2 user.debug.all消息=====>hello rabbit
RabbitMQ-learning的更多相关文章
- Scheduled Jobs with Custom Clock Processes in Java with Quartz and RabbitMQ
原文地址: https://devcenter.heroku.com/articles/scheduled-jobs-custom-clock-processes-java-quartz-rabbit ...
- NServiceBus+RabbitMQ开发分布式应用
前言 NServiceBus提供了8种传输管道组件,分别是Learning.MSMQ.Azure Service Bus.Azure Service Bus (Legacy).Azure S ...
- 消息队列——RabbitMQ学习笔记
消息队列--RabbitMQ学习笔记 1. 写在前面 昨天简单学习了一个消息队列项目--RabbitMQ,今天趁热打铁,将学到的东西记录下来. 学习的资料主要是官网给出的6个基本的消息发送/接收模型, ...
- RabbitMq应用二
在应用一中,基本的消息队列使用已经完成了,在实际项目中,一定会出现各种各样的需求和问题,rabbitmq内置的很多强大机制和功能会帮助我们解决很多的问题,下面就一个一个的一起学习一下. 消息响应机制 ...
- 【Machine Learning】KNN算法虹膜图片识别
K-近邻算法虹膜图片识别实战 作者:白宁超 2017年1月3日18:26:33 摘要:随着机器学习和深度学习的热潮,各种图书层出不穷.然而多数是基础理论知识介绍,缺乏实现的深入理解.本系列文章是作者结 ...
- 如何优雅的使用RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ无疑是目前最流行的消息队列之一,对各种语言环境的支持也很丰富,作为一个.NET developer有必要学习和了解这一工具.消息队列的使用场景大概有3种: 1.系统集成,分布式系统的设 ...
- RabbitMq应用一的补充(RabbitMQ的应用场景)
直接进入正题. 一.异步处理 场景:发送手机验证码,邮件 传统古老处理方式如下图 这个流程,全部在主线程完成,注册->入库->发送邮件->发送短信,由于都在主线程,所以要等待每一步完 ...
- RabbitMq应用一
RabbitMq应用一 RabbitMQ的具体概念,百度百科一下,我这里说一下我的理解,如果有少或者不对的地方,欢迎纠正和补充. 一个项目架构,小的时候,一般都是传统的单一网站系统,或者项目,三层架构 ...
- 【Machine Learning】Python开发工具:Anaconda+Sublime
Python开发工具:Anaconda+Sublime 作者:白宁超 2016年12月23日21:24:51 摘要:随着机器学习和深度学习的热潮,各种图书层出不穷.然而多数是基础理论知识介绍,缺乏实现 ...
- 【Machine Learning】机器学习及其基础概念简介
机器学习及其基础概念简介 作者:白宁超 2016年12月23日21:24:51 摘要:随着机器学习和深度学习的热潮,各种图书层出不穷.然而多数是基础理论知识介绍,缺乏实现的深入理解.本系列文章是作者结 ...
随机推荐
- 如何利用Smartbi做数据分析:2018内5月热销乘用车分析报告
在2018年第一季度热销乘用车分析报告中,SUV以总体销量15.4%的同比增长率让人不可小觑,Smartbi刚得到5月分析的数据就迫不及待的来看看是否热度不减,结果在5月这个所谓汽车销售淡季,轿车以9 ...
- git子模块的使用
1. 在项目中添加子模块 命令: git submodule add <url> 例子: git submodule add https://github.com/chaconinc/Db ...
- 【C# 线程】 延迟初始化
1. 简介 1.延迟初始化出现于.NET 4.0,主要用于提高性能,避免浪费计算,并减少程序内存要求.也可以称为,按需加载. 2.从net 4.0开始,C#开始支持延迟初始化,通过Lazy关键字,我们 ...
- Oracle PSU 简介
转至:http://blog.itpub.net/30327022/viewspace-2642815/ Oracle RAC创建完毕后,我们通常需要打上最新的PSU,因为里面是包含GI和DB的补丁集 ...
- IIS部署遇到问题(没有相关资源/权限不足无法读取配置文件)及解决方法
1:找不到web.config,如下图: 解决办法: 点击目录浏览--打开功能--启用(应用),再次浏览解决 2:再次预览出现别的错误500.19,权限不足,如下图: 解决办法:(右键编辑权限或者右上 ...
- git--撤销添加&放弃修改&代码冲突
git add . 后,撤销指定文件的add(还未提交): git reset HEAD 文件名 不保存本地改动,用远程代码覆盖: git reset --hard origin/dev 放弃工作区的 ...
- laravel 框架简易增删改查
参看网址:http://www.yan.com/mou/add 图书增加HTML页面 //图书增加路由 Route::get('mou/add','MouController@store'); //控 ...
- python的数据结构和基本语法
1.支持的数据类型 str(字符串类型).int(整型).flout(浮点型).bool(逻辑值).complex(复数[数学上的]).bytes(字节型).list(列表).tuple(元组[不可以 ...
- MySQL 导入数据时 2006-MySQLserver has gone away
MySQL 2006-MySQLserver has gone away MySQL 2006-MySQLserver has gone away 方式一(验证无误): 找到 mysql安装目录下的m ...
- 从MyIE2平滑升级到Maxthon的完美方案
经过几个Beta版本的测试MyIE2改名为Maxthon的新版浏览器终于发布了正式版本.喜欢MyIE2的朋友们也可以放心的将你的MyIE2升级为Maxthon了.以下是MyIE2平滑过渡到Mathxo ...
