SciTech-Mathmatics-Probability+Statistics-Population-Sampling-Types of Sampling Methods (With Examples)
Types of Sampling Methods (With Examples)
BY ZACH BOBBITTPOSTED ON SEPTEMBER 24, 2018


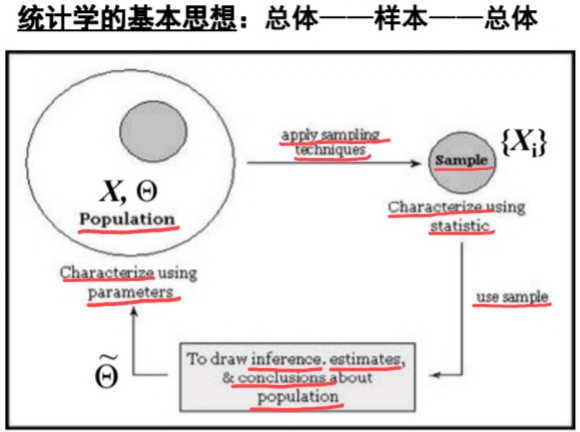
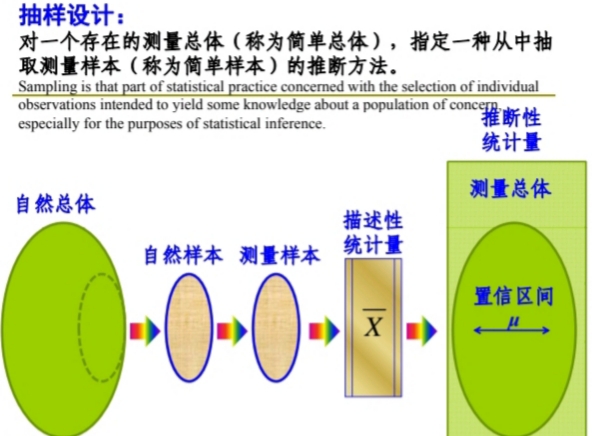
Researchers are often interested in answering questions about populations like:
- What is the average height of a certain species of plant?
- What is the average weight of a certain species of bird?
- What percentage of citizens in a certain city support a certain law?
the FIRST WAY to answer these questions is to go around and collect data on every single individual in the population of interest.
However, IF this is typically too costly and time-consuming which is why researchers instead take a sample of the population and use the data from the sample to draw conclusions about the population as a whole.
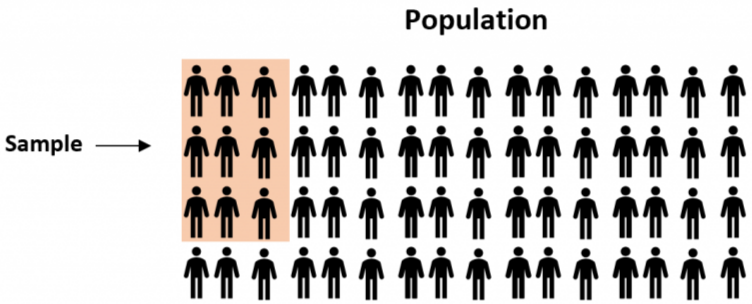
There are many different methods researchers can potentially use to obtain individuals to be in a sample. These are known as sampling methods.
In this post we share the most commonly used sampling methods in statistics, including the benefits and drawbacks of the various methods.
Probability Sampling Methods
The first class of sampling methods is known as probability sampling methods because every member in a population has an equal probability of being selected to be in the sample.
Simple random sample
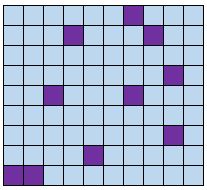
Definition: Every member of a population has an equal chance of being selected to be in the sample. Randomly select members through the use of a random number generator or some means of random selection.
Example: We put the names of every student in a class into a hat and randomly draw out names to get a sample of students.
Benefit : Simple random samples are usually representative of the population we're interested in since every member has an equal chance of being included in the sample.
Stratified random sample
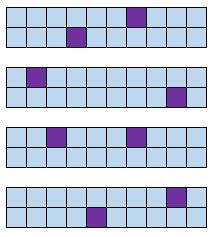
Definition: Split a population into groups. Randomly select some members from each group to be in the sample.
Example: Split up all students in a school according to their grade – freshman, sophomores, juniors, and seniors. Ask 50 students from each grade to complete a survey about the school lunches.
Benefit : Stratified random samples ensure that members from each group in the population are included in the survey.
Systematic random sample

Definition: Put every member of a population into some order. Choosing a random starting point and select every \(\large n\)th member to be in the sample.
Example: A teacher puts students in alphabetical order according to their last name, randomly chooses a starting point, and picks every 5th student to be in the sample.
Benefit : Systematic random samples are usually representative of the population we're interested in since every member has an equal chance of being included in the sample.
Cluster random sample
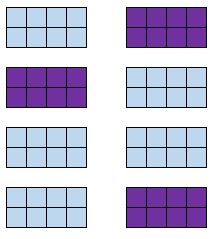
Definition: Split a population into clusters. Randomly select some of the clusters and include all members from those clusters in the sample.
Example: A company that gives whale watching tours wants to survey its customers. Out of ten tours they give one day, they randomly select four tours and ask every customer about their experience.
Benefit : Cluster random samples get every member from some of the groups, which is useful when each group is reflective of the population as a whole.
Non-probability Sampling Methods
Another class of sampling methods is known as non-probability sampling methods because not every member in a population has an equal probability of being selected to be in the sample.
This type of sampling method is sometimes used because it’s much cheaper and more convenient compared to probability sampling methods. It’s often used during exploratory analysis when researchers simply want to gain an initial understanding of a population.
However, the samples that result from these sampling methods cannot be used to draw inferences about the populations they came from because they typically aren’t representative samples.
Convenience sample
Definition: Choose members of a population that are readily available to be included in the sample.
Example: A researcher stands in front of a library during the day and polls people that happen to walk by.
Drawback: Location and time of day will affect the results. More than likely, the sample will suffer from undercoverage bias since certain people(e.g. those who work during the day) will not be represented as much in the sample.
Voluntary response sample
Definition: A researcher puts out a request for volunteers to be included in a study and members of a population voluntarily decide to be included in the sample or not.
Example: A radio host asks listeners to go online and take a survey on his website.
Drawback: People who voluntarily respond will likely have stronger opinions (positive or negative) than the rest of the population, which makes them an unrepresentative sample. Using this sampling method, the sample is likely to suffer from nonresponse bias – certain groups of people are simply less likely to provide responses.
Snowball sample
Definition: Researchers recruit initial subjects to be in a study and then ask those initial subjects to recruit additional subjects to be in the study. Using this approach, the sample size "snowballs" bigger and bigger as each additional subject recruits more subjects.
Example: Researchers are conducting a study of individuals with rare patterns, but it's difficult to find individuals who actually have the pattern. However, **if they can find just a few initial individuals to be in the study then they can ask them to recruit further individuals they may know through a private support group or through some other means.
Drawback: Sampling bias is likely to occur. Because initial subjects recruit additional subjects, it's likely that many of the subjects will share similar traits or characteristics that might be unrepresentative of the larger population under study. Thus, findings from the sample can't be extrapolated to the population.
Read more about snowballing sampling here.
Purposive sample
Definition: Researchers recruit individuals based on who they think will be most useful based on the purpose of their study.
Example: Researchers want to know about the opinions that individuals in a city have about **a potential new rock climbing gym being placed in the city square so they purposely seek out individuals that hang out at other rock climbing gyms around the city.
Drawback: The individuals in the sample are unlikely to be representative of the overall population. Thus, findings from the sample can't be extrapolated to the population.
SciTech-Mathmatics-Probability+Statistics-Population-Sampling-Types of Sampling Methods (With Examples)的更多相关文章
- Simple Random Sampling|representative sample|probability sampling|simple random sampling with replacement| simple random sampling without replacement|Random-Number Tables
1.2 Simple Random Sampling Census, :全部信息 Sampling: 抽样方式: representative sample:有偏向,研究者选择自己觉得有代表性的sam ...
- PRML读书会第十一章 Sampling Methods(MCMC, Markov Chain Monte Carlo,细致平稳条件,Metropolis-Hastings,Gibbs Sampling,Slice Sampling,Hamiltonian MCMC)
主讲人 网络上的尼采 (新浪微博: @Nietzsche_复杂网络机器学习) 网络上的尼采(813394698) 9:05:00 今天的主要内容:Markov Chain Monte Carlo,M ...
- Probability&Statistics 概率论与数理统计(1)
基本概念 样本空间: 随机试验E的所有可能结果组成的集合, 为E的样本空间, 记为S 随机事件: E的样本空间S的子集为E的随机事件, 简称事件, 由一个样本点组成的单点集, 称为基本事件 对立事件/ ...
- [Bayes] Hist & line: Reject Sampling and Importance Sampling
吻合度蛮高,但不光滑. > L= > K=/ > x=runif(L) > *x*(-x)^/K)) > hist(x[ind],probability=T, + xla ...
- SRS|Stratified sampling|系统抽样|Cluster sampling|multistage sampling|
生物统计学 总体和抽样 抽样方法: ========================================================= 简单随机抽样SRS:随机误差,系统误差 标准误, ...
- [Math Review] Statistics Basic: Sampling Distribution
Inferential Statistics Generalizing from a sample to a population that involves determining how far ...
- [Math Review] Statistics Basic: Estimation
Two Types of Estimation One of the major applications of statistics is estimating population paramet ...
- Sampling and Estimation
Sampling and Estimation Sampling Error Sampling error is the difference between a sample statistic(t ...
- Gibbs sampling
In statistics and in statistical physics, Gibbs sampling or a Gibbs sampler is aMarkov chain Monte C ...
- Create STATISTICS,UPDATE STATISTICS
该命令在一张表或者索引了的视图上更新查询优化统计数字信息. 默认情况下, 查询优化器已经更新了必要的用来提高查询计划的统计信息; 在某些情况下, 你可以通过使用UPDATE STATISTICS 命令 ...
随机推荐
- 全局搜索——Lucene.Net与盘古分词的实现思路
一.Lucene.Net 1.Lucene.Net介绍: Lucene.Net是一个C#开发的开源全文索引库(自带的有索引管理.分词.查询) Lucene.Net.Index 提供索引管理,词组排序. ...
- bat文件简短
bat文件 @echo off F: cd\pictures\projectStreet\FloatingShinyKnot-main node server.js cd\ bat静默运行(但会闪一下 ...
- Android去掉默认的标题栏
去掉默认的标题栏:在onCreate方法里添加supportRequestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE); @Override protected voi ...
- 1Panel + MaxKB 对接高德地图 MCP Server
一.场景说明: 通过 1Panel+MaxKB 两个开源工具实现高德地图(Amap) MCP 服务调用. 二.操作说明 步骤一:完成 1Panel 的安装部署 安装说明:在线安装 - 1Panel 文 ...
- codeup之有序插入
Description 有一个已排好序的数组,要求输入一个数后,按原来排序的规律将它插入到数组中. 假设数组长度为10,数组中前9个数(这9个数要求从键盘上输入,输入时要满足自小到大的输入顺序)已经按 ...
- Seata源码—8.Seata Saga模式的事务处理
大纲 1.Seata Saga案例简介 2.Seata Saga案例的状态机定义分析 3.Seata Saga分布式事务与状态机关系 4.Seata Saga案例的Dubbo服务调用配置分析 5.Se ...
- C#实现自己的MCP Client
市面上,有很多免费Client客户端. 虽然说,这些Client客户端可以满足我们大部分的需求,但是在实际企业业务场景中,免费的Client无法全部满足我们的需求. 下面我们用C# 实现MCP Cli ...
- SpringSecurity配置 1
spring security整合步骤 过滤器链 SpringSecurity的本质就是一个过滤器链,内部包含了提供各种功能的过滤器,基本案例中的过滤器链如下图所示: UsernamePassword ...
- linux 的 Docker 配置(版本24.04)
linux 的docker配置(版本24.04) 这里默认是server版本的, 个人感觉好用,资源消耗少 1.配置ssh连接 个人习惯用ssh连接使用 (如果失败,先配置下一步的换源) sudo a ...
- 使用Flask和OpenAI构建实时AI聊天应用
在当今AI技术迅速发展的时代,将AI能力集成到Web应用中已成为一种趋势.本文将分享我如何使用Flask框架和OpenAI API构建一个实时聊天应用,让用户可以与AI助手"Melon&qu ...
