Django Rest Framework用户访问频率限制
一. REST framework的请求生命周期
from app01 import views as app01_view urlpatterns = [
url(r'^limits/', api_view.LimitView.as_view()),
]
二. 实例代码
1. 代码
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework import exceptions
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework.throttling import SimpleRateThrottle class MySimpleRateThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
scope = "limit" def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
return self.get_ident(request) class LimitView(APIView):
authentication_classes = []
permission_classes = []
throttle_classes = [MySimpleRateThrottle, ] # 自定义分流类 def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
self.dispatch
return Response('控制访问频率示例') def throttled(self, request, wait): class MyThrottled(exceptions.Throttled):
default_detail = '请求被限制.'
extra_detail_singular = 'Expected available in {wait} second.'
extra_detail_plural = '还需要再等待{wait}' raise MyThrottled(wait)
2. 执行流程
def dispatch(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
`.dispatch()` is pretty much the same as Django's regular dispatch,
but with extra hooks for startup, finalize, and exception handling.
"""
self.args = args
self.kwargs = kwargs
# 1. 对request进行加工
# request封装了
"""
request,
parsers=self.get_parsers(),
authenticators=self.get_authenticators(),
negotiator=self.get_content_negotiator(),
parser_context=parser_context
"""
request = self.initialize_request(request, *args, **kwargs)
self.request = request
self.headers = self.default_response_headers # deprecate? try:
# 初始化request
# 确定request版本,用户认证,权限控制,用户访问频率限制
self.initial(request, *args, **kwargs) # Get the appropriate handler method
if request.method.lower() in self.http_method_names:
handler = getattr(self, request.method.lower(),
self.http_method_not_allowed)
else:
handler = self.http_method_not_allowed response = handler(request, *args, **kwargs) except Exception as exc:
response = self.handle_exception(exc)
# 6. 二次加工request
self.response = self.finalize_response(request, response, *args, **kwargs)
return self.response
dispatch
def initial(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Runs anything that needs to occur prior to calling the method handler.
"""
self.format_kwarg = self.get_format_suffix(**kwargs) # Perform content negotiation and store the accepted info on the request
neg = self.perform_content_negotiation(request)
request.accepted_renderer, request.accepted_media_type = neg # Determine the API version, if versioning is in use.
# 2. 确定request版本信息
version, scheme = self.determine_version(request, *args, **kwargs)
request.version, request.versioning_scheme = version, scheme # Ensure that the incoming request is permitted
# 3. 用户认证
self.perform_authentication(request)
# 4. 权限控制
self.check_permissions(request)
# 5. 用户访问频率限制
self.check_throttles(request)
initial
def check_throttles(self, request):
"""
Check if request should be throttled.
Raises an appropriate exception if the request is throttled.
"""
for throttle in self.get_throttles():
if not throttle.allow_request(request, self):
self.throttled(request, throttle.wait())
check_throttles
def get_throttles(self):
"""
Instantiates and returns the list of throttles that this view uses.
"""
return [throttle() for throttle in self.throttle_classes]
get_throttles
class APIView(View):
# The following policies may be set at either globally, or per-view.
renderer_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_RENDERER_CLASSES
parser_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_PARSER_CLASSES
authentication_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES
throttle_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES
permission_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES
content_negotiation_class = api_settings.DEFAULT_CONTENT_NEGOTIATION_CLASS
metadata_class = api_settings.DEFAULT_METADATA_CLASS
versioning_class = api_settings.DEFAULT_VERSIONING_CLASS
# Allow dependency injection of other settings to make testing easier.
settings = api_settings
schema = DefaultSchema()
throttle_classes
3. 执行throttle中allow_request方法
def allow_request(self, request, view):
"""
Implement the check to see if the request should be throttled. On success calls `throttle_success`.
On failure calls `throttle_failure`.
"""
if self.rate is None:
return True self.key = self.get_cache_key(request, view)
if self.key is None:
return True self.history = self.cache.get(self.key, [])
self.now = self.timer() # Drop any requests from the history which have now passed the
# throttle duration
while self.history and self.history[-1] <= self.now - self.duration:
self.history.pop()
if len(self.history) >= self.num_requests:
return self.throttle_failure()
return self.throttle_success()
自定义类继承SimpleRateThrottle
def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
"""
Should return a unique cache-key which can be used for throttling.
Must be overridden. May return `None` if the request should not be throttled.
"""
raise NotImplementedError('.get_cache_key() must be overridden')
get_cache_key
4. 处理报错异常
def throttled(self, request, wait):
"""
If request is throttled, determine what kind of exception to raise.
"""
raise exceptions.Throttled(wait)
throttled
class Throttled(APIException):
status_code = status.HTTP_429_TOO_MANY_REQUESTS
default_detail = _('Request was throttled.')
extra_detail_singular = 'Expected available in {wait} second.'
extra_detail_plural = 'Expected available in {wait} seconds.'
default_code = 'throttled' def __init__(self, wait=None, detail=None, code=None):
if detail is None:
detail = force_text(self.default_detail)
if wait is not None:
wait = math.ceil(wait)
detail = ' '.join((
detail,
force_text(ungettext(self.extra_detail_singular.format(wait=wait),
self.extra_detail_plural.format(wait=wait),
wait))))
self.wait = wait
super(Throttled, self).__init__(detail, code)
exceptions.Throttled
5. 重写throttled方法处理异常
def throttled(self, request, wait):
class MyThrottled(exceptions.Throttled):
default_detail = '请求被限制.'
extra_detail_singular = 'Expected available in {wait} second.'
extra_detail_plural = '还需要再等待{wait}'
raise MyThrottled(wait)
重写throttled方法
三. settings.py配置全局
1. 配置全局限流速度
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'UNAUTHENTICATED_USER': None,
'UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN': None,
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': [
],
'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES': [],
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES': {
'anon': '5/minute',
'user': '10/minute',
'limit': '2/minute' # 设置每分钟访问次数
}
}
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.filebased.FileBasedCache',
'LOCATION': 'cache',
}
}
settings.py
2. 访问2次
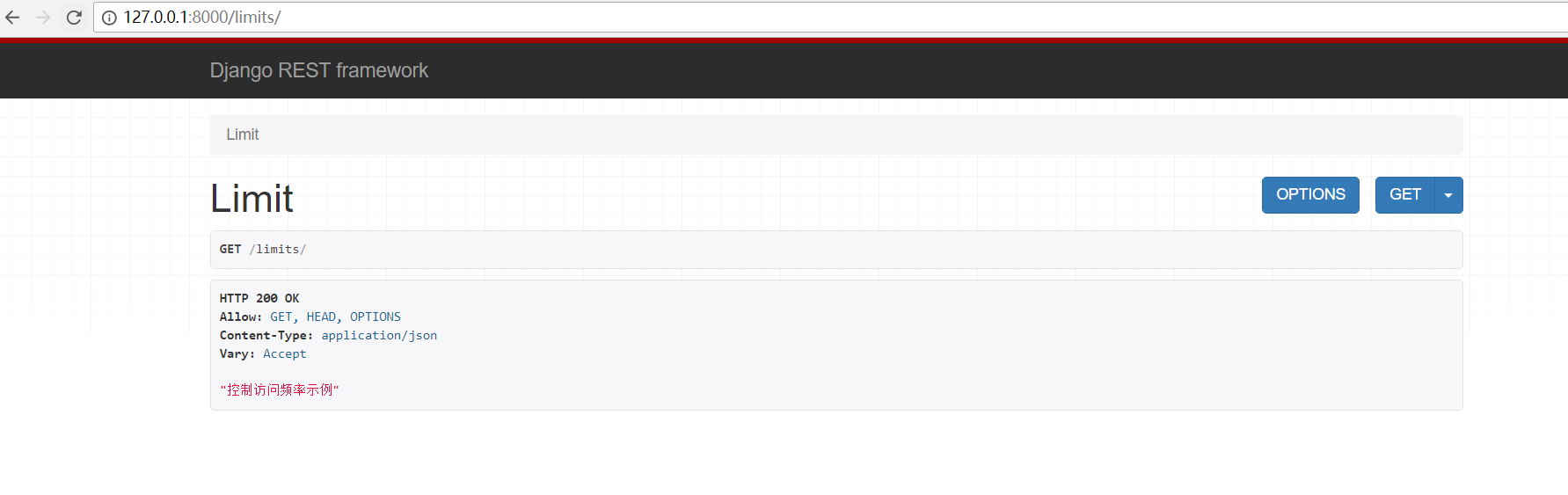
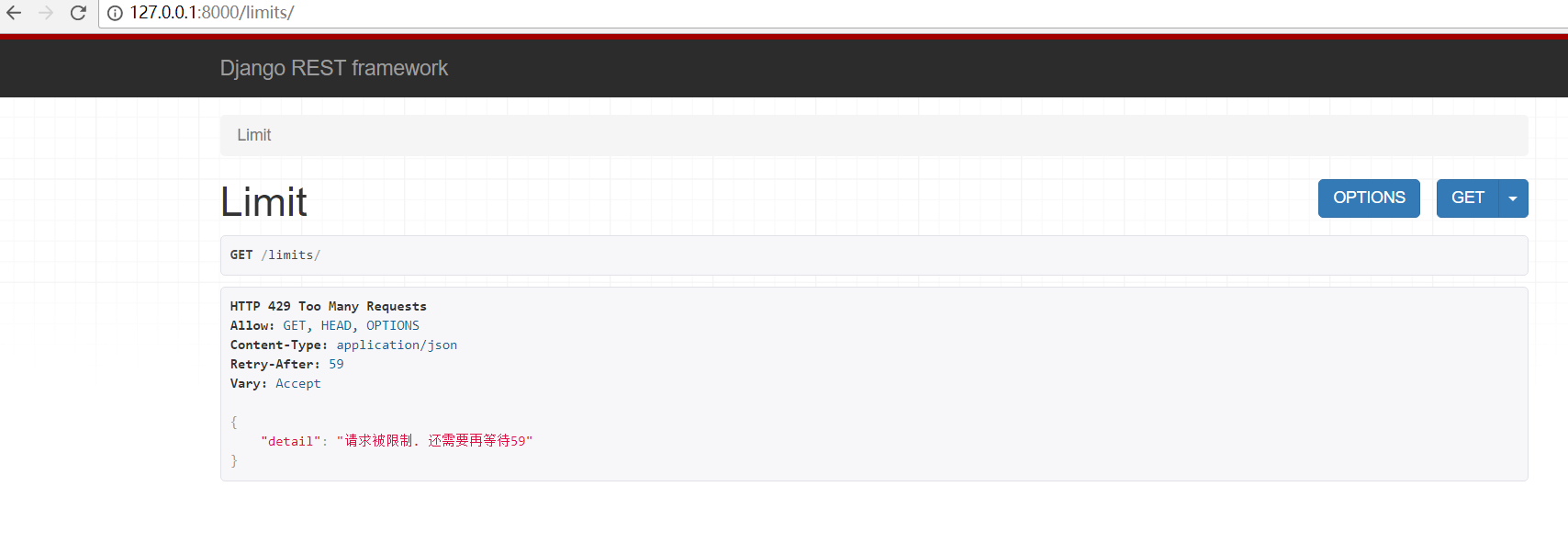
3. 超过次数,提示报错
Django Rest Framework用户访问频率限制的更多相关文章
- Django rest framework 限制访问频率(源码分析)
基于 http://www.cnblogs.com/ctztake/p/8419059.html 当用发出请求时 首先执行dispatch函数,当执行当第二部时: #2.处理版本信息 处理认证信息 处 ...
- Django中间件限制用户访问频率
原:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_38748717/article/details/79095399 一.定义限制访问频率的中间件 common/middleware.py ...
- django rest framework用户认证
django rest framework用户认证 进入rest framework的Apiview @classmethod def as_view(cls, **initkwargs): &quo ...
- Django REST framework 内置访问频率控制
对匿名用户采用 IP 控制访问频率,对登录用户采用 用户名 控制访问频率. from rest_framework.throttling import SimpleRateThrottle class ...
- Django Rest Framework 请求流程
用户请求到django,首先经过wsgi,中间件,然后到url路由系统,执行视图类中继承APIView执行as_view方法,在源码中可以看到VPIView继承了django的View类,通过supe ...
- Django REST framework 之 认证 权限 限制
认证是确定你是谁 权限是指你有没有访问这个接口的权限 限制主要是指限制你的访问频率 认证 REST framework 提供了一些开箱即用的身份验证方案,并且还允许你实现自定义方案. 接下类我们就自己 ...
- Django Rest Framework之用户频率/访问次数限制
内置接口代码基本结构 settings.py: REST_FRAMEWORK = { 'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES':['api.utils.mythrottle.UserThr ...
- Django REST framework 自定义(认证、权限、访问频率)组件
本篇随笔在 "Django REST framework 初识" 基础上扩展 一.认证组件 # models.py class Account(models.Model): &qu ...
- Django Rest Framework(认证、权限、限制访问频率)
阅读原文Django Rest Framework(认证.权限.限制访问频率) django_rest_framework doc django_redis cache doc
随机推荐
- 洛谷 P1505 [国家集训队]旅游 解题报告
P1505 [国家集训队]旅游 题目描述 \(\tt{Ray}\) 乐忠于旅游,这次他来到了\(T\)城.\(T\)城是一个水上城市,一共有 \(N\) 个景点,有些景点之间会用一座桥连接.为了方便游 ...
- UVA.136 Ugly Numbers (优先队列)
UVA.136 Ugly Numbers (优先队列) 题意分析 如果一个数字是2,3,5的倍数,那么他就叫做丑数,规定1也是丑数,现在求解第1500个丑数是多少. 既然某数字2,3,5倍均是丑数,且 ...
- JavaScript in 操作符
JavaScript的in操作符可以用来判断一个属性是否属于一个对象,也可以用来变量一个对象的属性 1. 判断属性属于对象 var mycar = {make: "Honda", ...
- ucenter通信实现同步登录、同步退出(详细)
首先,需要去官网下载一个ucenter的包.然后解压下来. 先把ucenter/ucenter这个文件夹复制到你的项目根目录下改名为uc_server;(这里只是我建议修改,以便于我下面写的配置); ...
- NYOJ 737DP
石子合并(一) 时间限制:1000 ms | 内存限制:65535 KB 难度:3 描述 有N堆石子排成一排,每堆石子有一定的数量.现要将N堆石子并成为一堆.合并的过程只能每次将相邻的 ...
- Web Audio API之手把手教你用web api处理声音信号:可视化音乐demo
1.Web Audio API 介绍 Web Audio API 提供了在Web上控制音频的一个非常有效通用的系统 ,这些通用系统通俗的讲就是我们可以利用Web Audio API提供的各种方法操作各 ...
- iPhoneX页面安全区域与内容重叠问题
转载自:https://www.cnblogs.com/lolDragon/p/7795174.html 1. iPhoneX的介绍 屏幕尺寸 我们熟知的iPhone系列开发尺寸概要如下: △ iP ...
- [LeetCode] Binary Tree Level Order Traversal 与 Binary Tree Zigzag Level Order Traversal,两种按层次遍历树的方式,分别两个队列,两个栈实现
Binary Tree Level Order Traversal Given a binary tree, return the level order traversal of its nodes ...
- LightOJ 1161 - Extreme GCD 容斥
题意:给你n个数[4,10000],问在其中任意选四个其GCD值为1的情况有几种. 思路:GCD为1的情况很简单 即各个数没有相同的质因数,所以求所有出现过的质因数次数再容斥一下-- 很可惜是错的,因 ...
- 【Dream Counting, 2006 Dec-数数的梦】数位dp
题意:给定两个数,问区间[A,B]中0~9分别出现了多少次.A,B<=10^18 题解:应该是最裸的数位dp吧..一开始没有记忆化tle了TAT 我们可以求出区间[0,B]的,再减去区间[0,A ...
