AStar寻路算法示例
概述
AStar算法是一种图形搜索算法,常用于寻路。他是以广度优先搜索为基础,集Dijkstra算法和最佳优先(best fit)于一身的一种算法。
示例1:4向

示例2:8向

思路
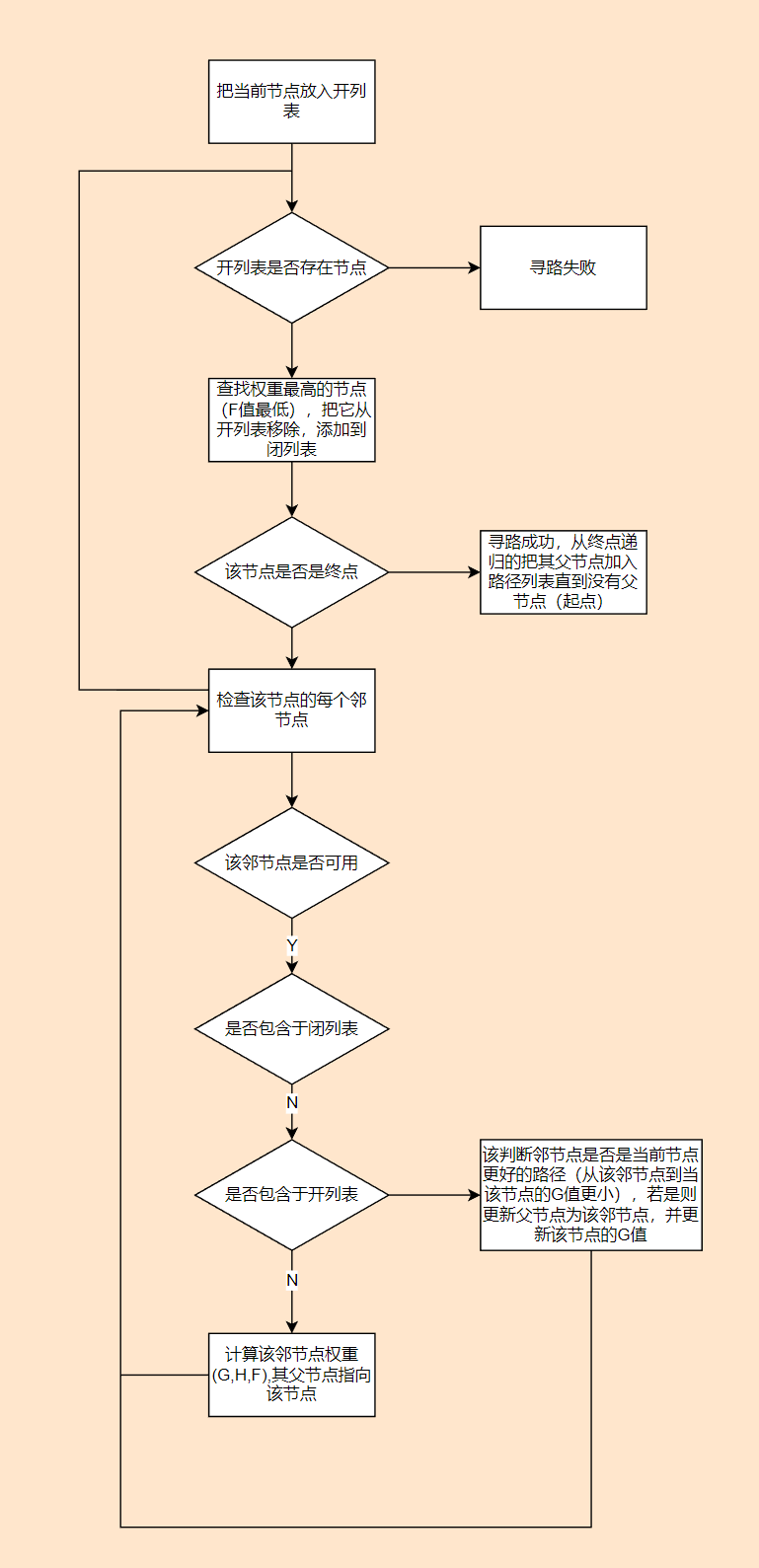
递归的通过估值函数找到最佳路径,估值函数与距离相关,也有可能与通过代价系数相关(例如平地系数为1,坡地系数为2),有三个参数:
- G:起点点到当前点的代价
- H: 当前点到终点的代价
- F: F = G + H 与最佳路径权重负相关的参数
代码示例
位置定义
public struct Vec2
{
public int x;
public int y;
public Vec2(int x, int y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public static Vec2 Zero
{
get
{
return new Vec2(0, 0);
}
}
public override bool Equals(object obj)
{
if (!(obj is Vec2))
return false;
var o = (Vec2)obj;
return x == o.x && y == o.y;
}
public override int GetHashCode()
{
return x.GetHashCode() + y.GetHashCode();
}
public static Vec2 operator +(Vec2 a, Vec2 b)
{
return new Vec2(a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y);
}
public static Vec2 operator *(Vec2 a, int n)
{
return new Vec2(a.x * n, a.y * n);
}
public static Vec2 operator *(int n, Vec2 a)
{
return new Vec2(a.x * n, a.y * n);
}
public static bool operator ==(Vec2 a, Vec2 b)
{
return a.x == b.x && a.y == b.y;
}
public static bool operator !=(Vec2 a, Vec2 b)
{
return !(a.x == b.x && a.y == b.y);
}
}
方向定义
public enum EDir
{
Up = 0,
Down = 1,
Left = 2,
Right = 3,
UpLeft = 4,
UpRight = 5,
DownLeft = 6,
DownRight = 7,
}
public abstract class CheckDirPol
{
abstract public Dictionary<EDir, Vec2> GetDir();
}
public class CheckDir4Pol : CheckDirPol
{
private Dictionary<EDir, Vec2> dirDict = new Dictionary<EDir, Vec2>
{
{EDir.Up, new Vec2(0, 1) },
{EDir.Down, new Vec2(0, -1) },
{EDir.Left, new Vec2(-1, 0) },
{EDir.Right, new Vec2(1, 0) },
};
override public Dictionary<EDir, Vec2> GetDir()
{
return dirDict;
}
}
public class CheckDir8Pol : CheckDirPol
{
private Dictionary<EDir, Vec2> dirDict = new Dictionary<EDir, Vec2>
{
{EDir.Up, new Vec2(0, 1) },
{EDir.Down, new Vec2(0, -1) },
{EDir.Left, new Vec2(-1, 0) },
{EDir.Right, new Vec2(1, 0) },
{EDir.UpLeft, new Vec2(-1, 1) },
{EDir.UpRight, new Vec2(1, 1) },
{EDir.DownLeft, new Vec2(-1, -1) },
{EDir.DownRight, new Vec2(1, -1) },
};
override public Dictionary<EDir, Vec2> GetDir()
{
return dirDict;
}
}
- 运用策略模式的技巧,以实现4向,8向搜索切换
估值函数
public abstract class EvaPol
{
abstract public float Calc(Vec2 a, Vec2 b);
}
public class MANEvaPol : EvaPol
{
override public float Calc(Vec2 a, Vec2 b)
{
return Mathf.Abs(a.x - b.x) + Mathf.Abs(a.y - b.y);
}
}
- 直接使用曼哈顿距离作为代价
节点定义
public class Node
{
public int id;
public Vec2 pos;
public float g;
public float h;
public float f;
public Vec2 prePos;
public bool hasPrePos;
public Node(Vec2 pos)
{
this.pos = pos;
}
public void SetPrePos(Vec2 pos)
{
prePos = pos;
hasPrePos = true;
}
}
算法上下文定义
Context context;
EvaPol disPol;
CheckDirPol checkDirPol;
public struct Context
{
public Vec2 end;
public Vec2 start;
public Node[,] nodes;
public List<Node> open;
public List<Node> close;
public int[,] map;
public List<Vec2> result;
public Vec2 size;
}
寻路算法
初始化
public void Init(Vec2 start, Vec2 end, int[,] map)
{
var x = map.GetLength(0);
var y = map.GetLength(1);
context = new Context()
{
start = start,
end = end,
open = new List<Node>(),
close = new List<Node>(),
map = map,
result = new List<Vec2>(),
size = new Vec2(x, y),
};
context.nodes = new Node[x, y];
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < x; j++)
context.nodes[i, j] = new Node(new Vec2(i, j));
disPol = new MANEvaPol();
//checkDirPol = new CheckDir4Pol();
checkDirPol = new CheckDir8Pol();
}
获取路径
public List<Vec2> GetResult()
{
return context.result;
}
寻路
寻路入口
public void FindPath()
{
var s = context.start;
var sn = context.nodes[s.x, s.y];
sn.g = 0;
sn.h = disPol.Calc(s, context.end);
sn.f = sn.g + sn.h;
context.open.Add(sn);
FindArrangement(sn);
}
递归函数
void FindArrangement(Node node)
{
context.close.Add(node);
context.open.Remove(node);
if (node.pos == context.end)
{
SetResult(node);
return;
}
CheckRound(node);
if (context.open.Count == 0)
return;
Node next = context.open[0];
for (int i = 1; i < context.open.Count; i++)
if (context.open[i].f < next.f)
next = context.open[i];
FindArrangement(next);
}
检查周围节点
void CheckRound(Node node)
{
var dirDict = checkDirPol.GetDir();
foreach (var pair in dirDict)
{
var dir = node.pos + pair.Value;
if (IsBlock(dir))
continue;
var dn = context.nodes[dir.x, dir.y];
if (context.close.Contains(dn))
continue;
if (context.open.Contains(dn))
TryOverridePath(node, dn);
else
{
dn.g = disPol.Calc(dn.pos, context.start);
dn.h = disPol.Calc(dn.pos, context.end);
dn.f = dn.g + dn.h;
dn.SetPrePos(node.pos);
context.open.Add(dn);
}
}
}
// 若是从邻节点到该节点路径更优,则替换更新
void TryOverridePath(Node a, Node b)
{
var g = a.g + disPol.Calc(a.pos, b.pos);
if (g < b.g)
{
b.g = g;
b.SetPrePos(a.pos);
}
}
bool IsBlock(Vec2 pos)
{
return !InMap(pos) || context.map[pos.x, pos.y] == 1;
}
bool InMap(Vec2 pos)
{
var x = pos.x;
var y = pos.y;
var size = context.size;
return x >= 0 && x < size.x && y >= 0 && y < size.y;
}
生成路径
void SetResult(Node node)
{
Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>();
while(node.hasPrePos)
{
q.Enqueue(node);
node = context.nodes[node.prePos.x, node.prePos.y];
}
while(q.Count > 0)
{
context.result.Add(q.Dequeue().pos);
}
}
完整代码
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
public struct Vec2
{
public int x;
public int y;
public Vec2(int x, int y)
{
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public static Vec2 Zero
{
get
{
return new Vec2(0, 0);
}
}
public override bool Equals(object obj)
{
if (!(obj is Vec2))
return false;
var o = (Vec2)obj;
return x == o.x && y == o.y;
}
public override int GetHashCode()
{
return x.GetHashCode() + y.GetHashCode();
}
public static Vec2 operator +(Vec2 a, Vec2 b)
{
return new Vec2(a.x + b.x, a.y + b.y);
}
public static Vec2 operator *(Vec2 a, int n)
{
return new Vec2(a.x * n, a.y * n);
}
public static Vec2 operator *(int n, Vec2 a)
{
return new Vec2(a.x * n, a.y * n);
}
public static bool operator ==(Vec2 a, Vec2 b)
{
return a.x == b.x && a.y == b.y;
}
public static bool operator !=(Vec2 a, Vec2 b)
{
return !(a.x == b.x && a.y == b.y);
}
}
public enum EDir
{
Up = 0,
Down = 1,
Left = 2,
Right = 3,
UpLeft = 4,
UpRight = 5,
DownLeft = 6,
DownRight = 7,
}
public class AstarFindPath
{
public class Node
{
public int id;
public Vec2 pos;
public float g;
public float h;
public float f;
public Vec2 prePos;
public bool hasPrePos;
public Node(Vec2 pos)
{
this.pos = pos;
}
public void SetPrePos(Vec2 pos)
{
prePos = pos;
hasPrePos = true;
}
}
public abstract class EvaPol
{
abstract public float Calc(Vec2 a, Vec2 b);
}
public class MANEvaPol : EvaPol
{
override public float Calc(Vec2 a, Vec2 b)
{
return Mathf.Abs(a.x - b.x) + Mathf.Abs(a.y - b.y);
}
}
public abstract class CheckDirPol
{
abstract public Dictionary<EDir, Vec2> GetDir();
}
public class CheckDir4Pol : CheckDirPol
{
private Dictionary<EDir, Vec2> dirDict = new Dictionary<EDir, Vec2>
{
{EDir.Up, new Vec2(0, 1) },
{EDir.Down, new Vec2(0, -1) },
{EDir.Left, new Vec2(-1, 0) },
{EDir.Right, new Vec2(1, 0) },
};
override public Dictionary<EDir, Vec2> GetDir()
{
return dirDict;
}
}
public class CheckDir8Pol : CheckDirPol
{
private Dictionary<EDir, Vec2> dirDict = new Dictionary<EDir, Vec2>
{
{EDir.Up, new Vec2(0, 1) },
{EDir.Down, new Vec2(0, -1) },
{EDir.Left, new Vec2(-1, 0) },
{EDir.Right, new Vec2(1, 0) },
{EDir.UpLeft, new Vec2(-1, 1) },
{EDir.UpRight, new Vec2(1, 1) },
{EDir.DownLeft, new Vec2(-1, -1) },
{EDir.DownRight, new Vec2(1, -1) },
};
override public Dictionary<EDir, Vec2> GetDir()
{
return dirDict;
}
}
public struct Context
{
public Vec2 end;
public Vec2 start;
public Node[,] nodes;
public List<Node> open;
public List<Node> close;
public int[,] map;
public List<Vec2> result;
public Vec2 size;
}
Context context;
EvaPol disPol;
CheckDirPol checkDirPol;
public void Init(Vec2 start, Vec2 end, int[,] map)
{
var x = map.GetLength(0);
var y = map.GetLength(1);
context = new Context()
{
start = start,
end = end,
open = new List<Node>(),
close = new List<Node>(),
map = map,
result = new List<Vec2>(),
size = new Vec2(x, y),
};
context.nodes = new Node[x, y];
for (int i = 0; i < x; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < x; j++)
context.nodes[i, j] = new Node(new Vec2(i, j));
disPol = new MANEvaPol();
//checkDirPol = new CheckDir4Pol();
checkDirPol = new CheckDir8Pol();
}
public void FindPath()
{
var s = context.start;
var sn = context.nodes[s.x, s.y];
sn.g = 0;
sn.h = disPol.Calc(s, context.end);
sn.f = sn.g + sn.h;
context.open.Add(sn);
FindArrangement(sn);
}
public List<Vec2> GetResult()
{
return context.result;
}
void FindArrangement(Node node)
{
context.close.Add(node);
context.open.Remove(node);
if (node.pos == context.end)
{
SetResult(node);
return;
}
CheckRound(node);
if (context.open.Count == 0)
return;
Node next = context.open[0];
for (int i = 1; i < context.open.Count; i++)
if (context.open[i].f < next.f)
next = context.open[i];
FindArrangement(next);
}
void SetResult(Node node)
{
Queue<Node> q = new Queue<Node>();
while(node.hasPrePos)
{
q.Enqueue(node);
node = context.nodes[node.prePos.x, node.prePos.y];
}
while(q.Count > 0)
{
context.result.Add(q.Dequeue().pos);
}
}
void CheckRound(Node node)
{
var dirDict = checkDirPol.GetDir();
foreach (var pair in dirDict)
{
var dir = node.pos + pair.Value;
if (IsBlock(dir))
continue;
var dn = context.nodes[dir.x, dir.y];
if (context.close.Contains(dn))
continue;
if (context.open.Contains(dn))
TryOverridePath(node, dn);
else
{
dn.g = disPol.Calc(dn.pos, context.start);
dn.h = disPol.Calc(dn.pos, context.end);
dn.f = dn.g + dn.h;
dn.SetPrePos(node.pos);
context.open.Add(dn);
}
}
}
void TryOverridePath(Node a, Node b)
{
var g = a.g + disPol.Calc(a.pos, b.pos);
if (g < b.g)
{
b.g = g;
b.SetPrePos(a.pos);
}
}
bool IsBlock(Vec2 pos)
{
return !InMap(pos) || context.map[pos.x, pos.y] == 1;
}
bool InMap(Vec2 pos)
{
var x = pos.x;
var y = pos.y;
var size = context.size;
return x >= 0 && x < size.x && y >= 0 && y < size.y;
}
}
AStar寻路算法示例的更多相关文章
- 算法:Astar寻路算法改进,双向A*寻路算法
早前写了一篇关于A*算法的文章:<算法:Astar寻路算法改进> 最近在写个js的UI框架,顺便实现了一个js版本的A*算法,与之前不同的是,该A*算法是个双向A*. 双向A*有什么好处呢 ...
- C#实现AStar寻路算法
AStar寻路算法是一种在一个静态路网中寻找最短路径的算法,也是在游戏开发中最常用到的寻路算法之一:最近刚好需要用到寻路算法,因此把自己的实现过程记录下来. 先直接上可视化之后的效果图,图中黑色方格代 ...
- 算法:Astar寻路算法改进
早前写了一篇<RCP:gef智能寻路算法(A star)> 出现了一点问题. 在AStar算法中,默认寻路起点和终点都是N x N的方格,但如果用在路由上,就会出现问题. 如果,需要连线的 ...
- 一个高效的A-star寻路算法(八方向)(
这种写法比较垃圾,表现在每次搜索一个点要遍历整个地图那么大的数组,如果地图为256*256,每次搜索都要执行65535次,如果遍历多个点就是n*65535,速度上实在是太垃圾了 简单说下思路,以后补充 ...
- javascript 实现 A-star 寻路算法
在游戏开发中,又一个很常见的需求,就是让一角色从A点走到B点,而我们期望所走的路是最短的,最容易想到的就是两点之间直线最短,我们可以通过勾股定理来求出两点之间的距离,但这个情况只能用于两点之间没有障碍 ...
- 对A-Star寻路算法的粗略研究
首先来看看完成后的效果: 其中灰色代表路障,绿色是起点和移动路径,红色代表终点 // = openArray[i+1].F) { minNode = openArray[i+1]; } } sta ...
- javascript的Astar版 寻路算法
去年做一个模仿保卫萝卜的塔防游戏的时候,自己写的,游戏框架用的是coco2d-html5 实现原理可以参考 http://www.cnblogs.com/technology/archive/2011 ...
- A*寻路算法的探寻与改良(三)
A*寻路算法的探寻与改良(三) by:田宇轩 第三分:这部分内容基于树.查找算法等对A*算法的执行效率进行了改良,想了解细 ...
- A星寻路算法入门(Unity实现)
最近简单学习了一下A星寻路算法,来记录一下.还是个萌新,如果写的不好,请谅解.Unity版本:2018.3.2f1 A星寻路算法是什么 游戏开发中往往有这样的需求,让玩家控制的角色自动寻路到目标地点, ...
- [转] A*寻路算法C++简单实现
参考文章: http://www.policyalmanac.org/games/aStarTutorial.htm 这是英文原文<A*入门>,最经典的讲解,有demo演示 http: ...
随机推荐
- 5N的多次方
N=eval(input(" 请输入一个数:")) for i in range (5): print(pow(N,i))
- 谣言检测——(PSA)《Probing Spurious Correlations in Popular Event-Based Rumor Detection Benchmarks》
论文信息 论文标题:Probing Spurious Correlations in Popular Event-Based Rumor Detection Benchmarks论文作者:Jiayin ...
- 计算机三大硬件和操作系统以及python解释器
今日分享内容概要 计算机五大组成部分详解 计算机三大核心硬件 操作系统 编程与编程语言 编程语言的发展历史 编程语言的分类 python解释器 python解释器多版本共存 分享详细 计算机五大组成部 ...
- Qt+ECharts开发笔记(五):ECharts的动态排序柱状图介绍、基础使用和Qt封装Demo
前言 上一篇的demo使用隐藏js代码的方式,实现了一个饼图的基本交互方式,并预留了Qt模块对外的基础接口. 本篇的demo实现了自动排序的柱状图,实现了一个自动排序柱状图的基本交互方式,即Qt ...
- Go_gin权限验证
权限管理 Casbin是用于Golang项目的功能强大且高效的开源访问控制库. 1. 特征 Casbin的作用: 以经典{subject, object, action}形式或您定义的自定义形式实施策 ...
- LcdTools如何实现PX01设置不同的画面不同的背光亮度
背光驱动分两种原理:恒压模式和恒流模式.恒压背光顾名思义提供恒定电压即可,这种屏正常来讲自带背光驱动电路,只需提供背光工作电压.背光使能和背光调光占空比控制.恒流背光指屏的背光只有纯灯串,需外部提供相 ...
- 【JavaWeb】学习笔记——JSP
概念 全称:Java Server Pages, Java服务端页面 描述:一种动态的网页技术,可以在其中定义HTML.JS.CSS等静态内容,以及Java代码的动态内容 说明:JSP = HTML ...
- Fidder 抓包工具
fiddler抓包原理 如上图本文一些 不重要 的鸡肋功能 自行百度 1. 安装与配置 1. 安装 安装地址https://www.telerik.com/download/fiddler可能有点慢 ...
- 云原生之旅 - 8)云原生时代的网关 Ingress Nginx
前言 当我们在Kubernetes部署的服务需要暴露给外部用户使用时,有三种选择:LoadBalancer,NodePort, Ingress. LoadBalancer类型得结合各个Cloud Pr ...
- ios手机键盘拉起之后页面不会回退的问题
在input输入框输入内容之后,点击完成,键盘下去了,可是页面没有回退回去,也就是页面会空出浏览器高度那一块,这个问题发现于ios手机中的微信浏览器.解决方案如下 <input type=&qu ...
