C - Building Fence
Long long ago, there is a famous farmer named John. He owns a big farm and many cows. There are two kinds of cows on his farm, one is Friesian, and another one is Ayrshire. Each cow has its own territory. In detail, the territory of Friesian is a circle, and of Ayrshire is a triangle. It is obvious that each cow doesn't want their territory violated by others, so the territories won't intersect.
Since the winter is falling, FJ has to build a fence to protect all his cows from hungry wolves, making the territory of cows in the fence. Due to the financial crisis, FJ is currently lack of money, he wants the total length of the fence minimized. So he comes to you, the greatest programmer ever for help. Please note that the part of fence don't have to be a straight line, it can be a curve if necessary.
Input
The input contains several test cases, terminated by EOF. The number of test cases does not exceed 20.
Each test case begins with two integers N and M(0 ≤ N, M ≤ 50, N + M > 0)which denotes the number of the Friesian and Ayrshire respectively. Then follows N + M lines, each line representing the territory of the cow. Each of the first N lines contains three integers X i, Y i, R i(1 ≤ R i ≤ 500),denotes the coordinates of the circle's centre and radius. Then each of the remaining M lines contains six integers X1 i, Y1 i, X2 i, Y2 i, X3 i, Y3 i, denotes the coordinates of the triangle vertices. The absolute value of the coordinates won't exceed 10000.
Output
For each test case, print a single line containing the minimal fence length. Your output should have an absolute error of at most 1e-3.
Sample Input
1 1
4 4 1
0 0 0 2 2 0
Sample Output
15.66692
Hint
Please see the sample picture for more details, the fence is highlighted with red.
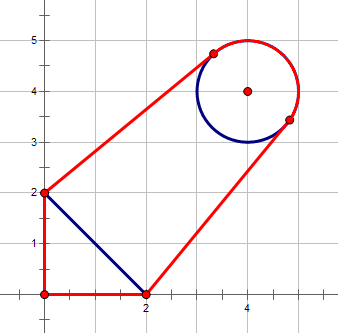
发现类似凸包,但是圆没法解决,做法是把圆拆开来就好了,拆成一千个点,然后套模板,求周长的话,可以直接求没两点距离,想要精确度高一点,可以在圆的点做个标记,是哪个圆,半径是多少,然后求的时候如果是同一个圆就算弧长
直接求距离的
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <iomanip>
#include<cmath>
#include<float.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#define sf scanf
#define pf printf
#define mm(x,b) memset((x),(b),sizeof(x))
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#define rep(i,a,n) for (int i=a;i<n;i++)
#define per(i,a,n) for (int i=a;i>=n;i--)
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef double db;
const ll mod=1e9+100;
const db e=exp(1);
const db eps=1e-8;
using namespace std;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
const int INF=0xfffffff;
struct Point
{
double x,y;
}p[150+50*2000],s[150+50*2000];
int top;
double direction(Point p1,Point p2,Point p3) {
double ans=(p3.x-p1.x)*(p2.y-p1.y)-(p2.x-p1.x)*(p3.y-p1.y);
return ans; }//点2和3,按哪个和点一的角度更小排,相同的话按哪个更近排
double dis(Point p1,Point p2) { return sqrt((p2.x-p1.x)*(p2.x-p1.x)+(p2.y-p1.y)*(p2.y-p1.y)); }
bool cmp(Point p1,Point p2)//极角排序
{
double temp=direction(p[0],p1,p2);
if(fabs(temp)<eps) temp=0;
if(temp<0)return true ;
if(temp==0&&dis(p[0],p1)<dis(p[0],p2))return true;
return false;
}
void Graham(int n)
{
int pos;
double minx,miny;
minx=miny=INF;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)//找最下面的基点
if(p[i].y<miny||(p[i].y==miny&&p[i].x<minx))
{
minx=p[i].x;
miny=p[i].y;
pos=i;
}
swap(p[0],p[pos]);
sort(p+1,p+n,cmp);
p[n]=p[0];
//sort(p+2,p+n,cmp1);
s[0]=p[0];s[1]=p[1];s[2]=p[2];
top=2;
for(int i=3;i<=n;i++)
{
while(direction(s[top-1],s[top],p[i])>=0&&top>=2)
top--;
s[++top]=p[i] ;
}
}
int main()
{
int n,m;
while(~sf("%d%d",&m,&n))
{
double x,y,r;
int ans=0;
while(m--)
{
sf("%lf%lf%lf",&x,&y,&r);
rep(i,0,2000)
{
p[ans].x=x+r*cos(2.0*pi*i/2000);
p[ans++].y=y+r*sin(2.0*pi*i/2000);
}
}
while(n--)
{
sf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf",&p[ans].x,&p[ans].y,&p[ans+1].x,&p[ans+1].y,&p[ans+2].x,&p[ans+2].y);
ans+=3;
}
Graham(ans);
double sum=0;
s[top]=s[0];
rep(i,0,top)
{
sum+=dis(s[i],s[i+1]);
}
pf("%.5lf\n",sum);
}
return 0;
}
求弧长的
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <iomanip>
#include<cmath>
#include<float.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#define sf scanf
#define pf printf
#define mm(x,b) memset((x),(b),sizeof(x))
#include<vector>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#define rep(i,a,n) for (int i=a;i<n;i++)
#define per(i,a,n) for (int i=a;i>=n;i--)
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef double db;
const ll mod=1e9+100;
const db e=exp(1);
const db eps=1e-8;
using namespace std;
const double pi=acos(-1.0);
const int INF=0xfffffff;
struct Point
{
double x,y,id,r;
}p[150+50*1002],s[150+50*1002];
int top;
double direction(Point p1,Point p2,Point p3) { double ans=(p3.x-p1.x)*(p2.y-p1.y)-(p2.x-p1.x)*(p3.y-p1.y);return ans; }//点2和3,按哪个和点一的角度更小排,相同的话按哪个更近排
double dis(Point p1,Point p2) { return sqrt((p2.x-p1.x)*(p2.x-p1.x)+(p2.y-p1.y)*(p2.y-p1.y)); }
bool cmp(Point p1,Point p2)//极角排序
{
double temp=direction(p[0],p1,p2);
if(fabs(temp)<eps) temp=0;
if(temp<0)return true ;
if(temp==0&&dis(p[0],p1)<dis(p[0],p2))return true;
return false;
}
void Graham(int n)
{
int pos;
double minx,miny;
minx=miny=INF;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)//找最下面的基点
if(p[i].y<miny||(p[i].y==miny&&p[i].x<minx))
{
minx=p[i].x;
miny=p[i].y;
pos=i;
}
swap(p[0],p[pos]);
sort(p+1,p+n,cmp);
p[n]=p[0];
s[0]=p[0];s[1]=p[1];s[2]=p[2];
top=2;
for(int i=3;i<=n;i++)
{
while(direction(s[top-1],s[top],p[i])>=0&&top>=2)
top--;
s[++top]=p[i] ;
}
}
int main()
{
int n,m;
while(~sf("%d%d",&m,&n))
{
double x,y,r;
int ans=0;
int ID=1;
while(m--)
{
sf("%lf%lf%lf",&x,&y,&r);
rep(i,0,1000)
{
p[ans].id=ID;
p[ans].r=r;
p[ans].x=x+r*cos(2.0*pi*i/1000);
p[ans++].y=y+r*sin(2.0*pi*i/1000);
}
ID++;
}
while(n--)
{
sf("%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf%lf",&p[ans].x,&p[ans].y,&p[ans+1].x,&p[ans+1].y,&p[ans+2].x,&p[ans+2].y);
p[ans].id=0;
p[ans+1].id=0;
p[ans+2].id=0;
ans+=3;
}
Graham(ans);
double sum=0;
rep(i,0,top)
if(s[i].id>0&&(s[i].id==s[(i+1)%top].id))
sum+=1.0*s[i].r*2*pi/1000.0;
else
sum+=dis(s[i],s[(i+1)%top]);
pf("%.5lf\n",sum);
}
return 0;
}
C - Building Fence的更多相关文章
- HDU 4667 Building Fence(2013多校7 1002题 计算几何,凸包,圆和三角形)
Building Fence Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65535/65535 K (Java/Others)To ...
- HDU 4667 Building Fence(求凸包的周长)
A - Building Fence Time Limit:1000MS Memory Limit:65535KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u ...
- HDU 4667 Building Fence
题意: 给n个圆和m个三角形,且保证互不相交,用一个篱笆把他们围起来,求最短的周长是多少. 做法:--水过... 把一个圆均匀的切割成500个点,然后求凸包. 注意:求完凸包,在求周长的时候记得要把圆 ...
- 4667 Building Fence 解题报告
题意:给n个圆和m个三角形,且保证互不相交,用一个篱笆把他们围起来,求最短的周长是多少. 解法1:在每个圆上均匀的取2000个点,求凸包周长就可以水过. 解法2:求出所有圆之间的外公切线的切点,以及过 ...
- [hdu4667]Building Fence 计算几何 瞎瘠薄搞
大致题意: 给出n个圆和m个三角形,求最小的的,能将所有图形覆盖的图形的周长. 正解为求所有三角形顶点与圆的切点以及圆和圆的切点构造凸包,再求路径. 因为要求结果误差<=1e-3 所以 我们可以 ...
- HDU 4667 Building Fence 计算几何 凸包+圆
1.三角形的所有端点 2.过所有三角形的端点对所有圆做切线,得到所有切点. 3.做任意两圆的外公切线,得到所有切点. 对上述所有点求凸包,标记每个点是三角形上的点还是某个圆上的点. 求完凸包后,因为所 ...
- hdu 4667 Building Fence < 计算几何模板>
//大白p263 #include <cmath> #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #include <string ...
- 【 2013 Multi-University Training Contest 7 】
HDU 4666 Hyperspace 曼哈顿距离:|x1-x2|+|y1-y2|. 最远曼哈顿距离,枚举x1与x2的关系以及y1与y2的关系,取最大值就是答案. #include<cstdio ...
- poj 1037 A decorative fence
题目链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=1037 Description Richard just finished building his new house. Now th ...
随机推荐
- STM32 F103 F407 F429 F767对比图
- 【Spark】榨干Spark性能-driver、exector内存突破256M
榨干Spark性能-driver.exector内存突破256M spark driver memory 256m_百度搜索 Spark executor.memory - CSDN博客 sparkd ...
- Google Maps瓦片(tile)地图文件下载(1-11层级)
整理硬盘时,发现一份去年下载的谷歌地图瓦片文件,整理并分享给大家. 地图来源:Google Maps(应该是国内谷歌地图) 采集时间:2017年6月 采集范围:0-6层级世界范围:7-11层级中国范围 ...
- art.template 循环里面分组。
后台提供给我们一个数组,我们要用模版实现上面的格式输出怎么版呢? 下面就是解决方案: <h2>循环4个一组</h2> <script type="text/ht ...
- Mac下打开多个eclipse
命令行执行: open -n /Eclipse所在路径/Eclipse.app
- 使用Git添加Tag的方法
简述作为版本管理工具,Git可以对某个版本打上标签(tag),表示本版本为发行版.在发布软件,以及使用CocoaPods创建依赖库等情况时,需要对其版本使用标签注释.故简单总结一下添加tag的方式. ...
- 逼格高又实用的Linux高级命令,开发运维都要懂!
在运维的坑里摸爬滚打好几年了,我还记得我刚开始的时候,我只会使用一些简单的命令,写脚本的时候,也是要多简单有多简单,所以有时候写出来的脚本又长又臭. 像一些高级点的命令,比如说 Xargs 命令.管道 ...
- centos7 mysql数据库安装和配置(转, 未验证)
一.系统环境 yum update升级以后的系统版本为 [root@yl-web yl]# cat /etc/redhat-release CentOS Linux release 7.1.1503 ...
- 【Windows】cmd条件判断
1.判断驱动器.文件或文件夹是否存在,用 if exist 语句: 2.判断某两个字符串是否相等,用 if "字符串1"=="字符串2" 语句: 3.判断某两个 ...
- rinetd 一个linux下的端口转发工具
inux下使用iptables实现端口转发,配置较为复杂,使用rinetd工具可以实现快速配置和修改端口转发. 例:本机ip:1.1.1.1 需要实现访问本机的8080端口,自动转发到2.2.2.2 ...
