codeforces 553 D Nudist Beach
题意大概是。给出一个图,保证每一个点至少有一条边以及随意两点间最多一条边。非常显然这个图有众多点集,若我们给每一个点定义一个权值,那每一个点集都有一个最小权值点,如今要求出一个点集,这个点集的最小权值点尽可能的大。
某个子集中。点的权值是这样算的。在该子集中这个点的度除以该点在图中的度。
乍看上去似乎无从下手。
能够显然知道的是。每一个点在图中的权值是非常easy算出来的,那我们尝试从图中进行删点。使得当前图的最小权值点的权值变大,显然能够知道要删除最小权值点。为什么呢?由于若删除次小权值点,若次小权值点跟最小权值点有连边,那最小权值点还是新图的最小权值点。若没有连边,那新图的最小权值点也依然未变。
所以仅仅有删除最小权值点才有可能改变新图的最小权值点,也仅仅有这样能让新图的最小权值发生改变。
那么到这里就十分明显了,仅仅要每次删除当前图的最小权值点。那么必定能够枚举出一个新图。这个新图的点构成的点集正是我们要的答案。
于是这个题就能够做了,我是直接做了两次删除,第一次得出最大最小权值是多少,第二次枚举到一个新图的最小权值等于最大最小权值。那么非常显然这个新图的子集就是答案。
维护一个小堆就好了,时间复杂度是2(n+m)log(n+m)
#include<map>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<bitset>
#include<climits>
#include<list>
#include<iomanip>
#include<stack>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
struct node
{
int no;
double val;
node(){}
node(int no,double val)
{
this->no=no;
this->val=val;
}
bool operator <(node one)const
{
return val>one.val;
}
};
priority_queue<node>q[2];
bool fb[100010],dl[100010];
vector<int>edge[100010];
int d[100010][2],dd[100010];
int main()
{
int n,m,k;
cin>>n>>m>>k;
int sum=k;
while(k--)
{
int t;
cin>>t;
fb[t]=1;
}
while(m--)
{
int a,b;
cin>>a>>b;
d[a][0]++;
d[b][0]++;
if(!fb[a])
d[b][1]++;
if(!fb[b])
d[a][1]++;
edge[a].push_back(b);
edge[b].push_back(a);
}
double mn=1e99;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(!fb[i])
{
q[0].push(node(i,double(d[i][1])/d[i][0]));
mn=min(mn,double(d[i][1])/d[i][0]);
}
q[1]=q[0];
int flag=0;
for(int i=0;i<2;i++)
{
memset(dl,0,sizeof(dl));
memset(dd,0,sizeof(dd));
if(i==1&&flag==0)
break;
while(q[i].size())
{
node t=q[i].top();
q[i].pop();
if(dl[t.no])
continue;
if(i==1)
{
if(t.no==flag)
break;
sum++;
}
dl[t.no]=1;
if(i==0&&t.val>mn)
{
mn=t.val;
flag=t.no;
}
for(int j=0;j<edge[t.no].size();j++)
{
int v=edge[t.no][j];
if(dl[v]||fb[v])
continue;
dd[v]++;
q[i].push(node(v,double(d[v][1]-dd[v])/d[v][0]));
}
}
}
cout<<n-sum<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(!fb[i]&&!dl[i])
cout<<i<<" ";
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Nudist Beach is planning a military operation to attack the Life Fibers. In this operation, they will attack and capture several cities which are currently under the control of the Life Fibers.
There are n cities, labeled from 1 to n,
and m bidirectional roads between them. Currently, there are Life Fibers in every city. In addition, there are k cities
that are fortresses of the Life Fibers that cannot be captured under any circumstances. So, the Nudist Beach can capture an arbitrary non-empty subset of cities with no fortresses.
After the operation, Nudist Beach will have to defend the captured cities from counterattack. If they capture a city and it is connected to many Life Fiber controlled cities, it will be easily defeated. So, Nudist Beach would like to capture a set of cities
such that for each captured city the ratio of Nudist Beach controlled neighbors among all neighbors of that city is as high as possible.
More formally, they would like to capture a non-empty set of cities S with no fortresses of Life Fibers. The strength of a city 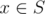 is
is
defined as (number of neighbors of x in S)
/ (total number of neighbors of x). Here, two cities are called neighbors if they are connnected with a road. The goal is to maximize
the strength of the weakest city in S.
Given a description of the graph, and the cities with fortresses, find a non-empty subset that maximizes the strength of the weakest city.
The first line of input contains three integers n, m, k (2 ≤ n ≤ 100 000, 1 ≤ m ≤ 100 000, 1 ≤ k ≤ n - 1).
The second line of input contains k integers, representing the cities with fortresses. These cities will all be distinct.
The next m lines contain the roads. The i-th
of these lines will have 2 integers ai, bi (1 ≤ ai, bi ≤ n, ai ≠ bi).
Every city will have at least one road adjacent to it.
There is no more than one road between each pair of the cities.
The first line should contain an integer r, denoting the size of an optimum set (1 ≤ r ≤ n - k).
The second line should contain r integers, denoting the cities in the set. Cities may follow in an arbitrary order. This line should
not contain any of the cities with fortresses.
If there are multiple possible answers, print any of them.
9 8 4
3 9 6 8
1 2
1 3
1 4
1 5
2 6
2 7
2 8
2 9
3
1 4 5
10 8 2
2 9
1 3
2 9
4 5
5 6
6 7
7 8
8 10
10 4
8
1 5 4 8 10 6 3 7
The first example case achieves a strength of 1/2. No other subset is strictly better.
The second example case achieves a strength of 1. Note that the subset doesn't necessarily have to be connected.
codeforces 553 D Nudist Beach的更多相关文章
- Codeforces 553D Nudist Beach(二分答案 + BFS)
题目链接 Nudist Beach 来源 Codeforces Round #309 (Div. 1) Problem D 题目大意: 给定一篇森林(共$n$个点),你可以在$n$个点中选择若干个构 ...
- Codeforces 553D Nudist Beach(图论,贪心)
Solution: 假设已经选了所有的点. 如果从中删掉一个点,那么其它所有点的分值只可能减少或者不变. 如果要使若干步删除后最小的分值变大,那么删掉的点集中肯定要包含当前分值最小的点. 所以每次删掉 ...
- codeforces 553D . Nudist Beach 二分
题目链接 有趣的题. 给一个图, n个点m条边. 有k个点不可选择. 现在让你选出一个非空的点集, 使得点集中strength最小的点的strength最大. strength的定义:一个点周围的点中 ...
- codeforces 553 A Kyoya and Colored Balls
这个题.比赛的时候一直在往dp的方向想,可是总有一个组合数学的部分没办法求, 纯粹组合数学撸,也想不到办法-- 事实上,非常显然.. 从后往前推,把第k种颜色放在最后一个,剩下的k球.还有C(剩余的位 ...
- Codeforces Round #309 (Div. 1)
A. Kyoya and Colored Balls 大意: 给定$k$种颜色的球, 第$i$种颜色有$c_i$个, 一个合法的排列方案满足最后一个第$i$种球的下一个球为第$i+1$种球, 求合法方 ...
- Codeforces 599C Day at the Beach(想法题,排序)
C. Day at the Beach One day Squidward, Spongebob and Patrick decided to go to the beach. Unfortunate ...
- Codeforces Round #332 (Div. 2) C. Day at the Beach 线段树
C. Day at the Beach Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/599/p ...
- Codeforces Round #326 (Div. 2) D. Duff in Beach dp
D. Duff in Beach Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/588/probl ...
- Codeforces Round #553 (Div. 2) D题
题目网址:http://codeforces.com/contest/1151/problem/D 题目大意:给出n组数对,(ai , bi),调整这n组数对的位置,最小化 ∑(ai*( i -1)+ ...
随机推荐
- Android 资源文件local.properties使用以及Gradle文件中的值、Manifests文件中的值
这篇也是因为Gradle存储密钥问题一路填坑总结的,期初连.properties创建都有疑问 因为当时是在Android下查看新建的properties一直没法看到 因为Gradle Scripts是 ...
- mysql-学习链接
http://www.cnblogs.com/lyhabc/p/3691555.html
- ASP.NET MVC下使用SWFUpload完成剪切头像功能
首先介绍SWFUpload组件 SWFUpload是一个客户端文件上传工具,最初由Vinterwebb.se开发,它通过整合Flash与JavaScript技术 为WEB开发者提供了一个具有丰富功能继 ...
- TOJ1840: Jack Straws 判断两线段相交+并查集
1840: Jack Straws Time Limit(Common/Java):1000MS/10000MS Memory Limit:65536KByteTotal Submit: 1 ...
- Java面试题之HashMap如何有效减少碰撞
1.扰动函数算法,促使元素位置分布均匀,减少碰撞几率: 2.使用final对象,并采用合适的equals方法和hashCode方法:
- vue 配合 element-ui使用搭建环境时候遇到的坑
在需要使用element-ui的时候,直接引入文件,发现会报错,解析不了css文件和字体,需要在webpack里面配置上css-loader和style-loader,最好的做法是把element-u ...
- vue 当中出现dom操作
在mounted当中进行dom相关操作 this.$refs
- 记录vim经常使用的几个命令
vi/vim 基本使用方法 vi编辑器是所有Unix及Linux系统下标准的编辑器. $ vim 1.txt 以vi打开一个文件就直接进入一般模式了(这是默认的模式).在这个模式中, 你可以使用上下左 ...
- springboot2.x整合redis实现缓存(附github链接)
本文代码已提交github: https://github.com/LCABC777/Springboot-redis(1)Springboot中使用redis操作的两种方式:lettuce和j ...
- vue报错之Duplicate keys detected: '0'. This may cause an update error.
昨天运行vue项目的时候,出现了[Vue warn]: Duplicate keys detected: '0'. This may cause an update error(错误,检测到重复的ke ...
