Android LinearLayout线性布局详解
为了更好地管理Android应用的用户界面里的各组件,Android提供了布局管理器。通过使用布局管理器,Android应用图形用户界面具有良好的平台无关性。推荐使用布局管理器来管理组件的分布、大小,而不是直接设置组件的位置和大小。可以使用布局管理器嵌套布局管理器,即也可作为一个UI组件来使用。
LinearLayout可以控制组件横向排列或者纵向排列,内容不会换行,超出屏幕部分将不会显示出来。
学习图解

LinearLayout 常用XML属性及方法
【属性一】orientation 设置子组件的排列方式(单选)
XML: android:orientation="horizontal"
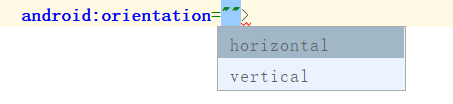
horizontal:横向排列
vertical:纵向排列
JAVA :linearLayout.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL);
LinearLayout.HORIZONTAL 横向排列

LinearLayout.VERTICAL 纵向排列
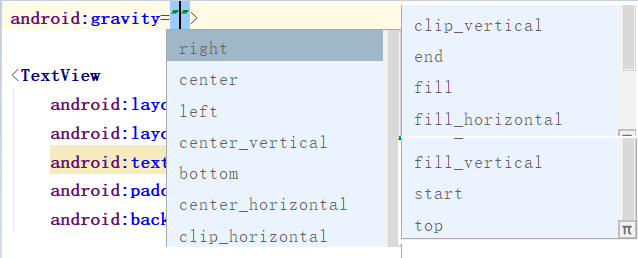
【属性二】gravity 设置子组件的对齐方式(多选)
XML: android:gravity="center"
JAVA :linearLayout.setGravity(Gravity.CENTER);
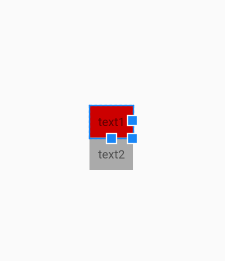
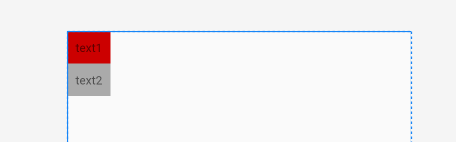
【属性三】baselineAligned 设置子元素基准线对弃,默认为true
基准线:
打开的英语练习本,那条红线就是基准线


XML: android:baselineAligned="false"

JAVA: linearLayout.setBaselineAligned(true);
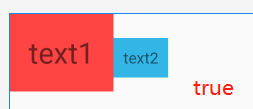
代码:true
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:baselineAligned="true"
android:orientation="horizontal"> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/holo_red_light"
android:padding="20dp"
android:text="text1"
android:textSize="30sp"> </TextView>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_light"
android:padding="10dp"
android:text="text2"
android:textSize="16sp"> </TextView>
</LinearLayout>
效果:

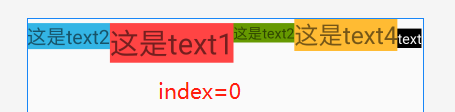
【搭配属性三】baselineAlignedChildIndex LinearLayout的基准线以他的第几个子元素为准,下标从0开始
一个LinearLayout 里面有很多 textview ,每一个 textview 都有自己的基准线,那么LinearLayout可能也是另一个LinearLayout的子元素,作为子元素 baselineAlignedChildIndex 就决定这他的一个基准线
XML:android:baselineAlignedChildIndex="0"
JAVA:linearLayout.setBaselineAlignedChildIndex(0);
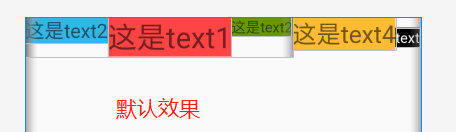
代码:⭐注意内部的LinearLayout,后面将在 第二个LinearLayout上添加 baselineAlignedChildIndex ,搭配 baselineAligned="false" 使用
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="horizontal"> <LinearLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:baselineAligned="false"
android:orientation="horizontal"> <TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_light"
android:text="这是text2"
android:textSize="20sp"> </TextView>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/holo_red_light"
android:text="这是text1"
android:textSize="30sp"> </TextView>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/holo_green_dark"
android:text="这是text2"
android:textSize="15sp"> </TextView>
</LinearLayout>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="这是text4"
android:textSize="25sp"
android:background="@android:color/holo_orange_light"
> </TextView>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="@android:color/black"
android:text="text"
android:textColor="@android:color/white"
android:textSize="15sp"> </TextView>
</LinearLayout>
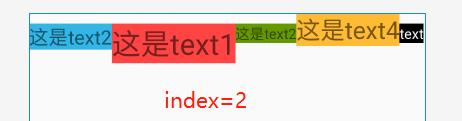
效果:

⭐ 总结
- 默认LinearLayout是没有基准线的,从图一和图三的对比可知。
- 下标从0开始三个子组件,最大index为2,超过2时布局将不显示
- 这个属性是用来决定当前LinearLayout的基准线时以哪个子组件为准的
Android LinearLayout线性布局详解的更多相关文章
- android:TableLayout表格布局详解
http://blog.csdn.net/justoneroad/article/details/6835915 这篇博文包括的内容:1.TableLayout简介2.TableLayout行列数的确 ...
- [置顶] Android系统五大布局详解Layout
我们知道Android系统应用程序一般是由多个Activity组成,而这些Activity以视图的形式展现在我们面前,视图都是由一个一个的组件构成的.组件就是我们常见的Button.TextEdit等 ...
- Android系统五大布局详解Layout
我们知道Android系统应用程序一般是由多个Activity组成,而这些Activity以视图的形式展现在我们面前, 视图都是由一个一个的组件构成的.组件就是我们常见的Button.TextEdit ...
- Android开发之线性布局详解(布局权重)
布局权重 线性布局支持给个别的子视图设定权重,通过android:layout_weight属性.就一个视图在屏幕上占多大的空间而言,这个属性给其设 定了一个重要的值.一个大的权重值,允许它扩大到填充 ...
- Android 之 TableLayout 布局详解
TableLayout简介 •简介 Tablelayout 类以行和列的形式对控件进行管理,每一行为一个 TableRow 对象,或一个 View 控件. 当为 TableRow 对象时,可在 Tab ...
- Android学习之基础知识六—Android四种布局详解
一.Android基本布局 布局是一种可以放置多个控件的容器,它可以按照一定规律调整内部控件的位置,而且布局内部除了可以放置控件外,还可以放置布局,实现多层布局嵌套.布局和控件.布局和布局之间的关系如 ...
- Android LinearLayout线性布局
LinearLayout是线性布局控件:要么横向排布,要么竖向排布 决定性属性:必须有的! android:orientation:vertical (垂直方向) .horizontal(水平方向) ...
- Android布局管理详解(1)—— LinearLayout 线性布局
Android的布局方式共有6种,分别是LinearLayout(线性布局).TableLayout(表格布局).FrameLayout(帧布局).RelativeLayout(相对布局).GridL ...
- Android开发重点难点1:RelativeLayout(相对布局)详解
前言 啦啦啦~博主又推出了一个新的系列啦~ 之前的Android开发系列主要以完成实验的过程为主,经常会综合许多知识来写,所以难免会有知识点的交杂,给人一种混乱的感觉. 所以博主推出“重点难点”系列, ...
随机推荐
- 【Android TimeCat】 解决cannot resolve symbol R
莫名其妙出现了,鬼知道怎么来的. 解决方法总结 1. 推荐 解决90%的情况: Build->Clean ProjectBuild->Rebuild Project 2. 不常见 Andr ...
- 数据库及MySQL概述
#什么是数据 用来描述事物的符号记录.可以是数字.文字.图形等,有多种形式,经过数字化之后存入计算机 #什么是数据库 数据库(Database)就是一个用来存放数据库的仓库,是按照一定的数据结构来组织 ...
- [面试专题]前端需要知道的web安全知识
前端需要知道的web安全知识 标签(空格分隔): 未分类 安全 [Doc] Crypto (加密) [Doc] TLS/SSL [Doc] HTTPS [Point] XSS [Point] CSRF ...
- 微信小程序最新授权方法,getUserInfo
20180511微信小程序正式关闭原先getUserInfo的逻辑 不再允许自动弹出授权框. 方法一: index.wxml(准备一个用于给用户授权的页面,我这里直接用了一个全屏按钮) <vie ...
- python之路-基本数据类型之list列表
1.概述 列表是python的基本数据类型之一,是一个可变的数据类型,用[]方括号表示,每一项元素使用逗号隔开,可以装大量的数据 #先来看看list列表的源码写了什么,方法:按ctrl+鼠标左键点li ...
- Yuchuan_Linux_C 编程之三 静态库的制作和使用
一.整体大纲 二.静态库的制作 1)命名规则 lib + 库的名字 + .a 例如:libyuchuan.a2)制作步骤: 1). 生成对应的.o文件 -- ...
- iview 踩坑之旅
公司重构管理系统,框架定了vue,UI在element和iview之间选,element样式被吐槽丑,于是选了iview,但是,,这个坑多啊... 废话少说,罗列了iview中容易出错或者懵逼的一些地 ...
- Git建立本地分支和远程分支的映射关系
git branch -vv:查看本地分支和远程分支的映射关系 在切换分支前,须本地建立新分支,例如:git branch release/v1.1 //本地建立release/v1.1分支成功后 ...
- 3DGIS与BIM集成集成技术及铁路桥梁可视化系统
3DGIS与BIM的集成技术 3DGIS与BIM的集成技术包括2部分:一是将Revit软件生成的BIM针对3DGIS的快速无损格式转换,这种转换包括几何信息(如形状.位置等信息)和属性信息(如建筑信息 ...
- win7下firefox和chrome升级到最新版之后页面打不开的解决办法
一.升级firefox到最新版后,页面崩溃,打开是空白页,连选项设置都打不开了. 最开始是我的firefox很久没升级,最近要要开始做开发,于是最让它自动升级.等升级到最新版本后,打开浏览器是结果显示 ...