重新认识 Spring IOC
spring IOC 剖析
再品IOC与DI
IOC(Inversion of Control)控制反转:所谓控制反转,就是把原先我们代码里面需要实现的对象创 建、依赖的代码,反转给容器来帮忙实现。那么必然的我们需要创建一个容器,同时需要一种描述来让 容器知道需要创建的对象与对象的关系。这个描述最具体表现就是我们所看到的配置文件。DI(Dependency Injection)依赖注入:就是指对象是被动接受依赖类而不是自己主动去找,换句话说就 是指对象不是从容器中查找它依赖的类,而是在容器实例化对象的时候主动将它依赖的类注入给它。
上面是 ioc 和 DI 的通俗理解,我们也可以用我们现有的知识来思考这两点的实现,其实两者主要还是依赖与反射机制来实现这些功能,那么我们为了提出一些关键问题,来跟着关键问题来看下具体的流程。
在
spring中对象之间的关系如何来表现
在我们配置文件中或者javaconfig中均又相应的方式来提现描述对象之间关系的文件或者信息存在哪里
可能存在于classpat、fileSystem、url或者context中,对于不同的存储位置和文件格式,其实的描述是不相同的,如何做到统一解析和声明
我们可以想一下,将这些外部的信息按照模型,进行转换,在内部维护一个统一的模型对象如何对这些信息进行不同的解析
根据各自的特性指定相应的策略来进行解析
IOC 容器的核心类
1. BeanFactory
在 spring 中 BeanFactory 是顶层的容器接口,我们可以看出来其实 spring 中容器的本质就是工厂, 他有非常多的实现类,我们这里把主要的核心类图展示: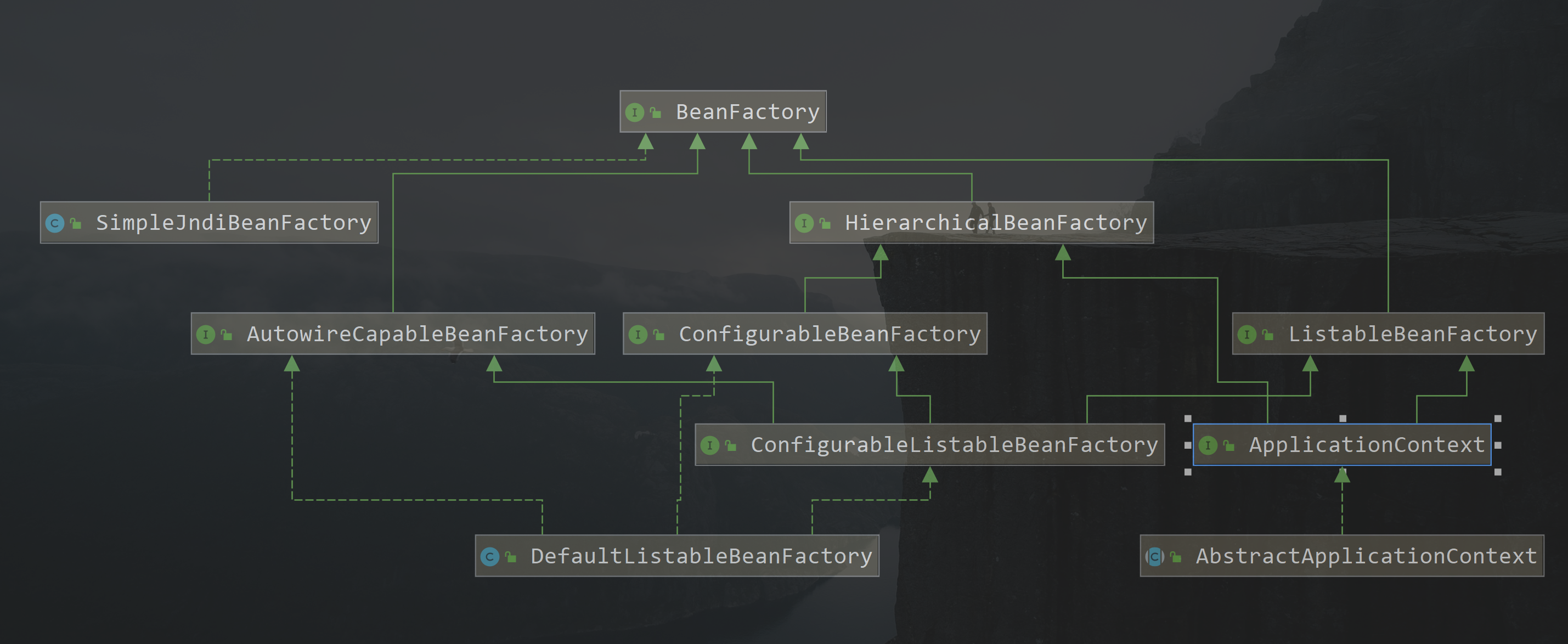
对上图做简单的说明:
BeanFactory 是顶层的容器接口,主要有三个子类接口
HierarchicalBeanFactory、AutowireCapableBeanFactory、ListableBeanFactory在继承的关系中我们可以看到都是接口和抽象类为主,多层次的封装,最终的实现类如
DefaultListableBeanFactory,还有类似AbstractApplicationContext的抽象子类,在spring中这些接口都有自己特定的使用场景,对每种场景中不同对象的创建传递到转化的过程中都进行了相应的控制限制,有很强的领域划分,职责单一可扩展性极强
public interface BeanFactory {
/**
* 主要勇于区分beanFactory与factoryBean,FactoryBean是spring内部生成对象的工厂即容器,
* 在我们通过过getBean获取对象时得到的是真实对象的代理对象,如果我们要获取产生对象代理的
* 工厂则需要加该前缀
*/
String FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX = "&";
/**
* 返回一个instance的实列 通过beanName
*/
Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException;
/**
* 通过BeanName与class类型来获取容器中的对象,多层限制校验
*/
<T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
/**
* 通过BeanName 同时指定相应的构造函数或者工厂方法的参数列表
*/
Object getBean(String name, Object... args) throws BeansException;
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType) throws BeansException;
<T> T getBean(Class<T> requiredType, Object... args) throws BeansException;
<T> ObjectProvider<T> getBeanProvider(Class<T> requiredType);
<T> ObjectProvider<T> getBeanProvider(ResolvableType requiredType);
/*
* 校验是否在IOC中存在
*/
boolean containsBean(String name);
/*
* 校验是单例或者原型模式
*/
boolean isSingleton(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isPrototype(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
/*
* 判断是IOC中bean的类型是否是typTomatch的类型
*/
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, ResolvableType typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
boolean isTypeMatch(String name, Class<?> typeToMatch) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
//获取指定bean的类型
@Nullable
Class<?> getType(String name) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
@Nullable
Class<?> getType(String name, boolean allowFactoryBeanInit) throws NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
// 获取bean的 别名
String[] getAliases(String name);
}
在spring中
BeanFactory定义了 容器的行为,但是并不会去实现这些,顶级接口制作了高度的抽象化处理,具体的容器的创建和运行们都是交给子类来实现,所以我们要知道IOC是如何运转的需要从spring中ico的实现子类来入门,如我们读取xml配置方式时的ClasspathXmlApplicationContext或者时在注解中使用的AnnotationConfigApplicationContext等,在这些具体的实现类中有容器初始化的具体流程在上面类图中
ApplicationContext类是非常重要的一个接口,这是spring提供的一个高级接口,也是我们以后接触最多的容器
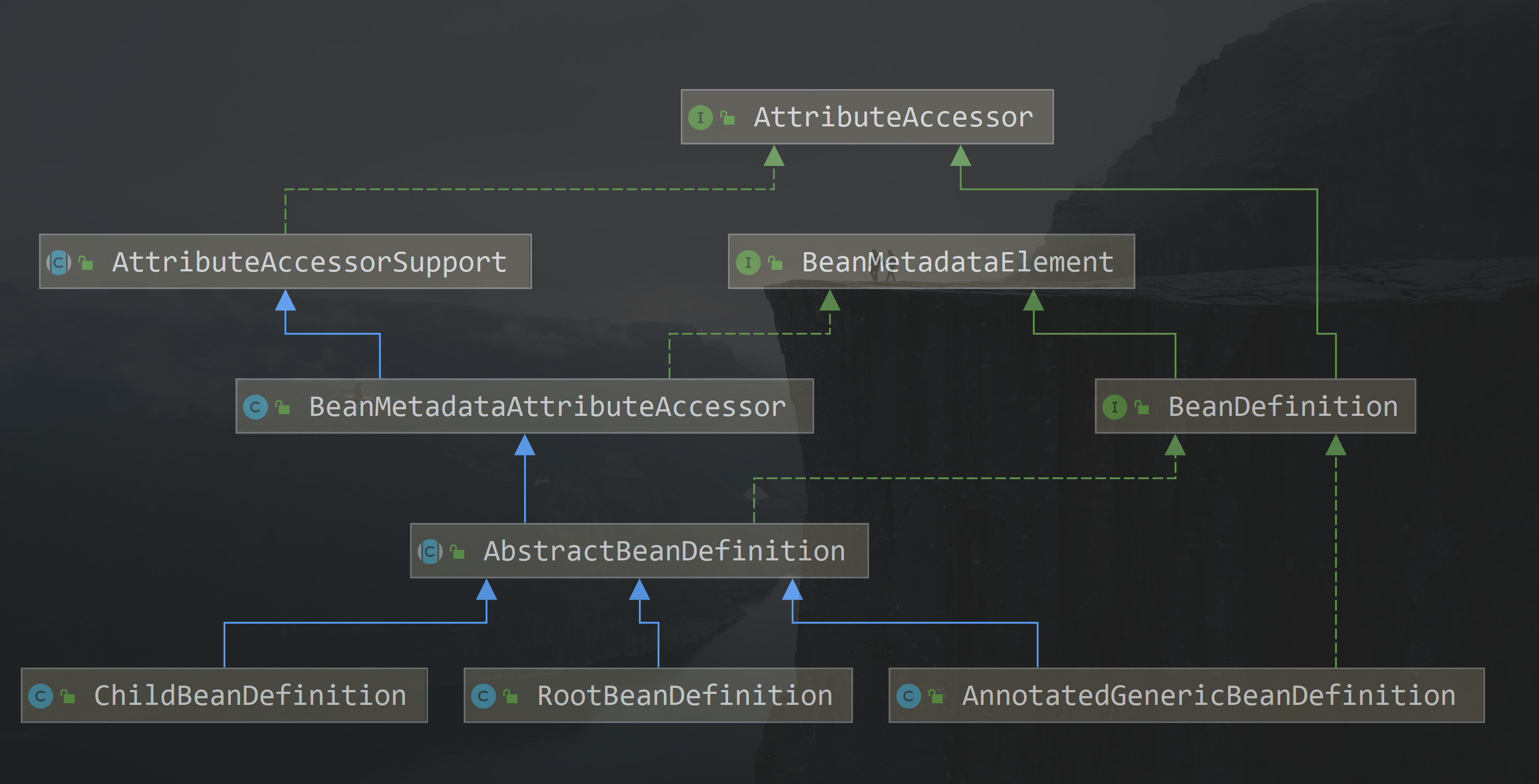
2. BeanDefinition
beandefinition 是spring中对对象关系,对象创建等一系列的定义模型,其本质其实是一个Map集合,其类图我们可以看一下:
3. BeanDefinitionReader
在我们创建初始化容器时,也就是bean工厂时,会根据这个工厂创建相应的 BeanDefinitionReader 对象,这个reader对象是一个资源解析器,这个解析的过程是复杂的在我们后边的解析中会具体来看各自的实现
4. ResourceLoader
所属包 org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader ,这是spring用来进行统一资源加载的顶级接口,里面定义行为,实现让具体的子类实现,类图我们可以看一下
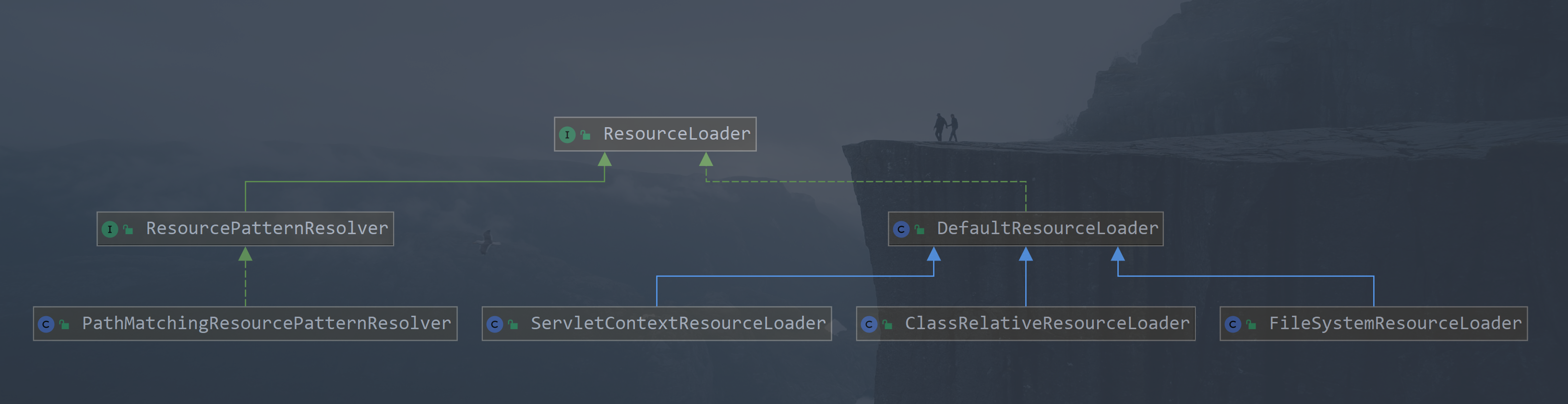
类图中展示的是 ResourceLoader 的核心实现, 在 spring 中容器也有实现该接口,关于统一资源加载的运转后期会专门说明
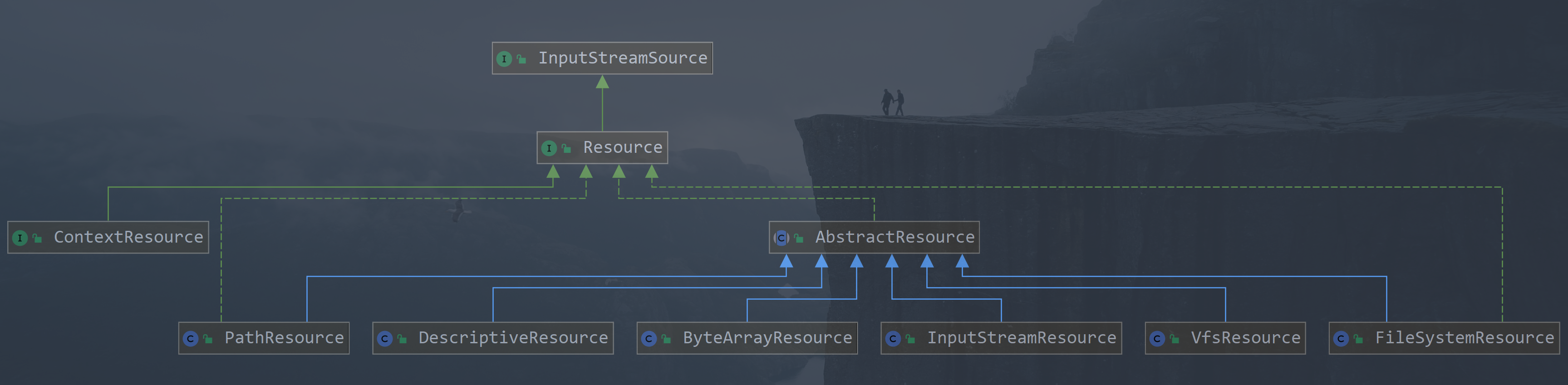
5. Resource
所属包 org.springframework.core.io.Resource , 该类是 spring 中资源加载的策略实现顶层接口,该类的每个实现类都是对某一种资源的访问策略,类图:
Web IOC 容器初识
我们在springMvc中很熟悉一个核心控制器 DispatcherServlet , 这个类做了一个集中分发和 web 容器初始的功能,首先我们来看一下类图
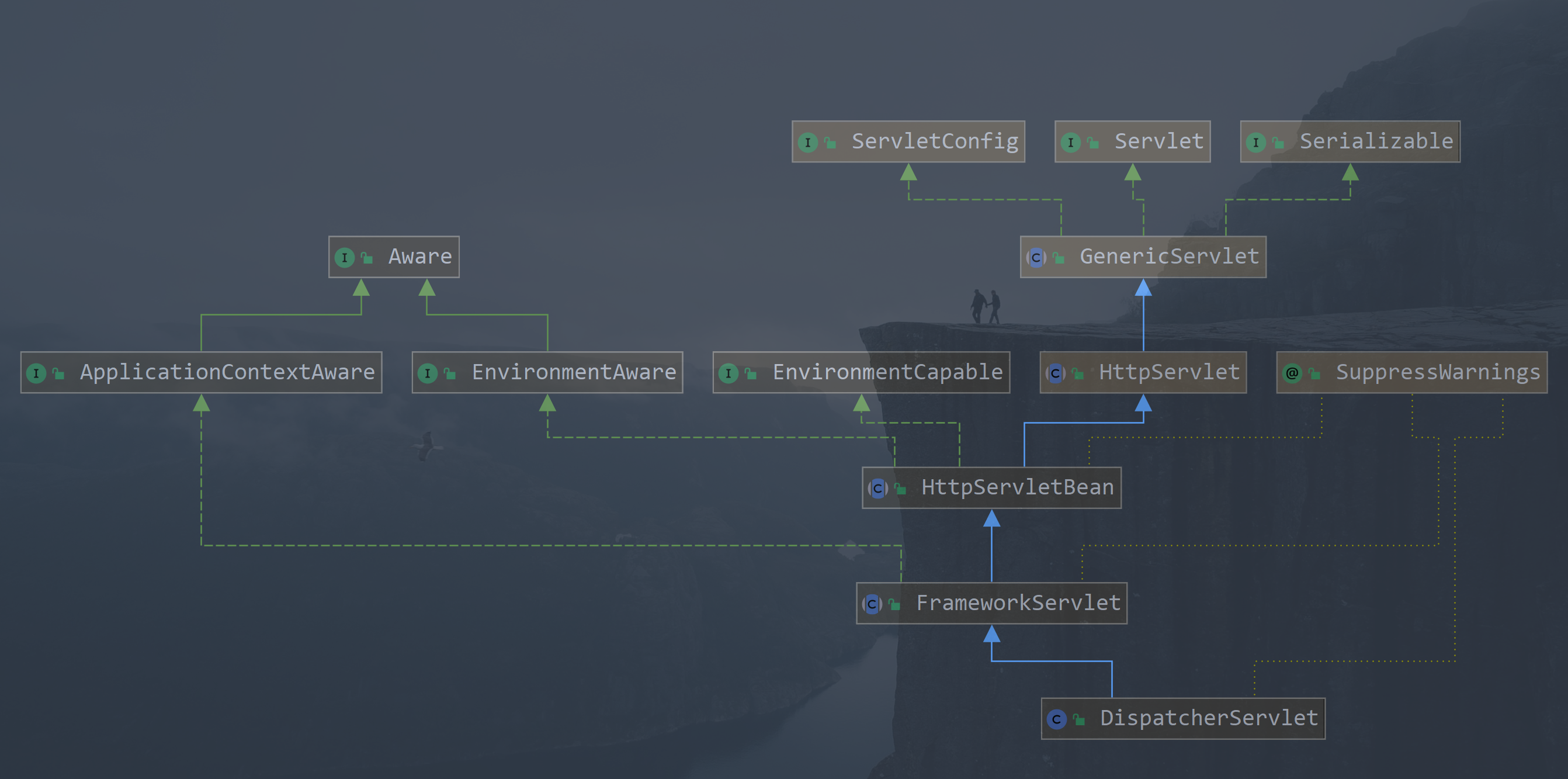
- 我们可以看到
DispatcherServlet继承了HttpServlet,我们熟悉HttpServlet是属于Servlet的 ,那么它必然有个init()的初始化方法,我们通过查看,可以看到在HttpServletBean中重写了init方法
/**
* 重写了init方法,对ServletContext初始化
* Map config parameters onto bean properties of this servlet, and
* invoke subclass initialization.
* @throws ServletException if bean properties are invalid (or required
* properties are missing), or if subclass initialization fails.
*/
@Override
public final void init() throws ServletException {
// Set bean properties from init parameters.
//读取初始化参数 如web.xml中 init-param
PropertyValues pvs = new ServletConfigPropertyValues(getServletConfig(), this.requiredProperties);
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
try {
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(this);
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = new ServletContextResourceLoader(getServletContext());
bw.registerCustomEditor(Resource.class, new ResourceEditor(resourceLoader, getEnvironment()));
initBeanWrapper(bw);
bw.setPropertyValues(pvs, true);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isErrorEnabled()) {
logger.error("Failed to set bean properties on servlet '" + getServletName() + "'", ex);
}
throw ex;
}
}
// Let subclasses do whatever initialization they like.
//初始化容器 是让子类FrameworkServlet具体实现的
initServletBean();
}
- 我们可以看到,
init方法中具体的容器实例方法FrameworkServlet来实现的,我们跟进去看一下initialServletBean的具体实现
/**
* Overridden method of {@link HttpServletBean}, invoked after any bean properties
* have been set. Creates this servlet's WebApplicationContext.
* 构建 web 上下文容器
*/
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring " + getClass().getSimpleName() + " '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Initializing Servlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
//容器初始化
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException | RuntimeException ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
String value = this.enableLoggingRequestDetails ?
"shown which may lead to unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data" :
"masked to prevent unsafe logging of potentially sensitive data";
logger.debug("enableLoggingRequestDetails='" + this.enableLoggingRequestDetails +
"': request parameters and headers will be " + value);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Completed initialization in " + (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime) + " ms");
}
}
- 我们看到
initWebApplicationContext()正是容器初始化的方法,我们继续跟进,我们现在是看容器初始化,其他暂时过掉,后面讲springmvc时在系统讲解
/**
* 初始化web容器 WebApplicationContext
* Initialize and publish the WebApplicationContext for this servlet.
* <p>Delegates to {@link #createWebApplicationContext} for actual creation
* of the context. Can be overridden in subclasses.
* @return the WebApplicationContext instance
* @see #FrameworkServlet(WebApplicationContext)
* @see #setContextClass
* @see #setContextConfigLocation
*/
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
//从ServletContext根容器中获取父容器 WebApplicationContext
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
//声明子容器
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
//构建父子容器的关系,这里判断当前容器是否有,
// 若存在则作为子容器来给他设置父容器rootcontext
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
// A context instance was injected at construction time -> use it
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> set
// the root application context (if any; may be null) as the parent
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
//判断子容器是否有引用,在ServletContext根容器中寻找,找到则赋值
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance was injected at construction time -> see if one
// has been registered in the servlet context. If one exists, it is assumed
// that the parent context (if any) has already been set and that the
// user has performed any initialization such as setting the context id
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
//若上面寻找也没找到,则这里进行容器的赋值 构建一个容器,但是这个容器并没有初始化 只是建立了引用
if (wac == null) {
// No context instance is defined for this servlet -> create a local one
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
//这里触发onRefresh方法进行容器真真初始化
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
// Either the context is not a ConfigurableApplicationContext with refresh
// support or the context injected at construction time had already been
// refreshed -> trigger initial onRefresh manually here.
synchronized (this.onRefreshMonitor) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// Publish the context as a servlet context attribute.
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
}
return wac;
}
- 我们看到真真初始化容器的方法
onRefresh()方法, 跟进找到DispatcherServlet中的实现类,其中又调用了initStrategies()方法,继续进入
/**
* This implementation calls {@link #initStrategies}.
*/
@Override
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
initStrategies(context);
}
/**
* 初始化容器,进行springmvc的9大组件初始化
* Initialize the strategy objects that this servlet uses.
* <p>May be overridden in subclasses in order to initialize further strategy objects.
*/
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
//多文件上传组件
initMultipartResolver(context);
//国际化组件,也就是本地语言环境
initLocaleResolver(context);
//初始化主题模板处理器
initThemeResolver(context);
//初始化HandMapping映射
initHandlerMappings(context);
//初始化HandlerAdapters参数适配器
initHandlerAdapters(context);
//初始化一场拦截组件
initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
//初始化视图预处理解析器,
initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
//初始化视图解析器
initViewResolvers(context);
//初始化FlashMap
initFlashMapManager(context);
}
IOC容器初始化
IOC容器的初始化有多种方式,可以是配置文件也可以为 Javaconfig 的方式,常见的如 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext
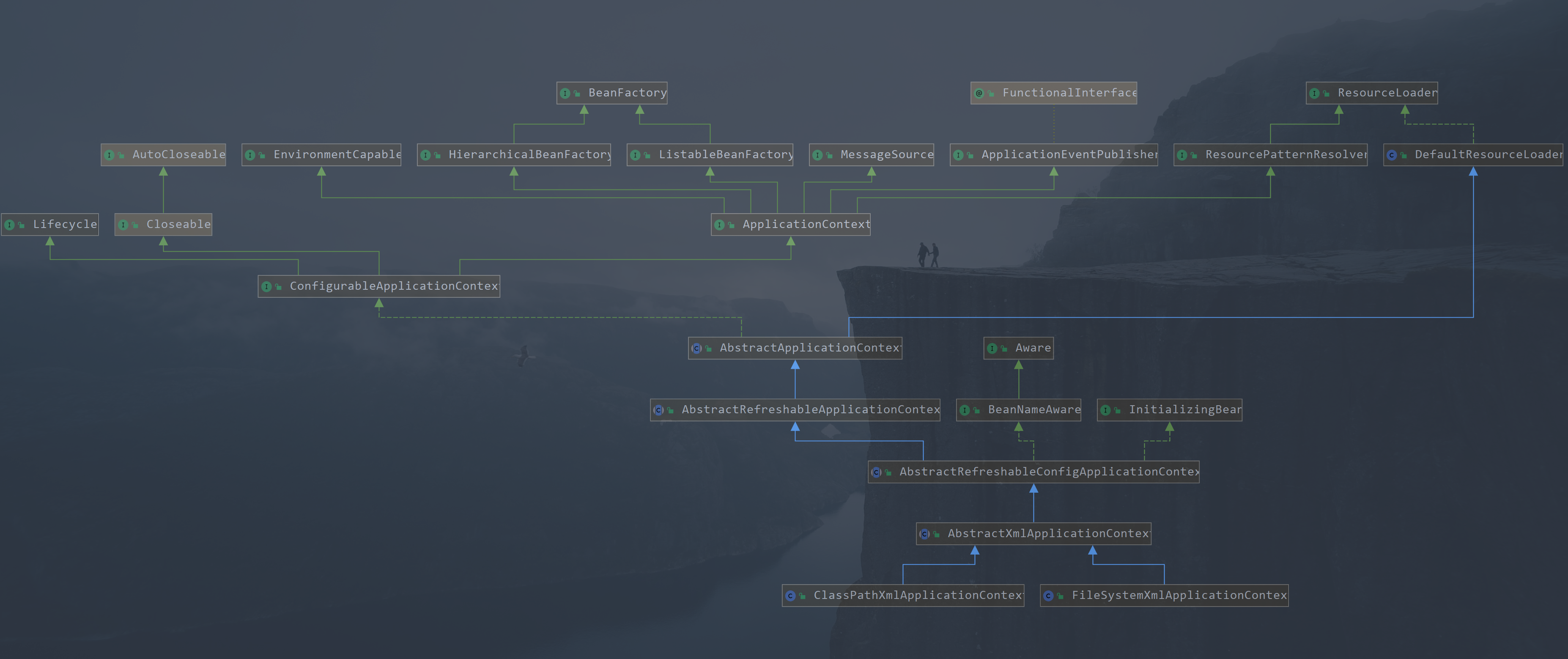
- IOC中主要过程可以概述为_定位_、加载、注册 三个基本过程,我们常见的容器都是
ApplicationContext,ResourceLoader是所有资源加载的基类,我们可以发现所有的IOC容器都是继承了BeanFactory,这也说明了所有的容器本质上都是一个bean工厂 - 我们可以通过下面的代码获取容器
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(CONTEXT_WILDCARD);
那么在这个创建容器的内部具体是如何构建加载容器的,我们可以进入看一下
//调用的构造函数
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation) throws BeansException {
this(new String[] {configLocation}, true, null);
}
这里有调用的一个构造函数,这个才是真真执行的过程,我们发现内部执行力 refresh() 方法
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
//调用父类的构造函数进行资源加载设置
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
- 大家可以自己看一下,其实像
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext、FileSystemXmlApplicationContext、XmlWebApplicationContext这些类都调用了refresh()方法,这个方法是他们父类AbstractApplicationContext实现的 ,这里应用的了装饰器模式策略模式
本文由AnonyStar 发布,可转载但需声明原文出处。
仰慕「优雅编码的艺术」 坚信熟能生巧,努力改变人生
欢迎关注微信公账号 :coder简码 获取更多优质文章
更多文章关注笔者博客 :IT简码
重新认识 Spring IOC的更多相关文章
- 【初探Spring】------Spring IOC(三):初始化过程---Resource定位
我们知道Spring的IoC起到了一个容器的作用,其中装得都是各种各样的Bean.同时在我们刚刚开始学习Spring的时候都是通过xml文件来定义Bean,Spring会某种方式加载这些xml文件,然 ...
- 【初探Spring】------Spring IOC(一)
IOC:Inversion of Control(控制反转).IOC它所体现的并不是一种技术,而是一种思想,一种将设计好的对象交给容器来管理的思想.IOC的核心思想就体现在控制.反转这两个词上面,要理 ...
- spring ioc
spring ioc是spring的核心之一,也是spring体系的基础,那么spring ioc所依赖的底层技术是什么的?反射,以前我们开发程序的时候对象之间的相互调用需要用new来实现,现在所有的 ...
- Spring IoC源码解析——Bean的创建和初始化
Spring介绍 Spring(http://spring.io/)是一个轻量级的Java 开发框架,同时也是轻量级的IoC和AOP的容器框架,主要是针对JavaBean的生命周期进行管理的轻量级容器 ...
- spring笔记6 spring IOC的中级知识
1,spring ioc的整体流程,xml配置 spring ioc初始化的流程结合上图 步骤编号 完成的工作 1 spring容器读取配置文件,解析称注册表 2 根据注册表,找到相应的bean实现类 ...
- 谈谈对Spring IOC的理解(转)
学习过Spring框架的人一定都会听过Spring的IoC(控制反转) .DI(依赖注入)这两个概念,对于初学Spring的人来说,总觉得IoC .DI这两个概念是模糊不清的,是很难理解的,今天和大家 ...
- 自己动手编写spring IOC源码
前言:对于spring IOC概念不是很了解的朋友可以阅读我上一篇博客--轻松理解spring IOC(这两篇博客也是由于我的个人原因导致现在才发布,惭愧啊).通过这篇博客的理解之后,相信大家会对sp ...
- spring ioc 源码解析
什么是ioc? 通俗的解释是:(spring)框架中,完成对象的创建和注入的容器. springIOC体系结构: spring IOC的创建是典型的工厂模式,这一系列的bean工厂如上所示. 其核心是 ...
- Spring:源码解读Spring IOC原理
Spring IOC设计原理解析:本文乃学习整理参考而来 一. 什么是Ioc/DI? 二. Spring IOC体系结构 (1) BeanFactory (2) BeanDefinition 三. I ...
- 谈谈对Spring IOC的理解
学习过Spring框架的人一定都会听过Spring的IoC(控制反转) .DI(依赖注入)这两个概念,对于初学Spring的人来说,总觉得IoC .DI这两个概念是模糊不清的,是很难理解的,今天和大家 ...
随机推荐
- Array(数组)对象-->join() 方法
1.定义和用法 join() 方法把数组中的所有元素用指定的参数作为分隔符拼接成一个字符串. 语法: array.join(separator) 举例: var arr = [1,2,3,4,5]; ...
- 分享一本Java并发编程的免费好书
最近当当的大促销又开始了,估计很多人脑子一热,又花钱囤了不少技术书吧. 在我看来大部分程序员买技术书的用途(以下排名按用途从大到小): 让领导.同事看见,你看我多爱学习: 给自己一个心理安慰,我还没废 ...
- STC15W串口通信的一些梳理
由于控制串口1进行通信移植到串口3出现了阻力,因此很有必要对串口通信进行更进一步的梳理>>>> 一 STC15W串口对应引脚: 由此我们得到四个串口引脚分别为:串口1:P3 . ...
- PostgreSQL中RECURSIVE递归查询使用总结
RECURSIVE 前言 CTE or WITH 在WITH中使用数据修改语句 WITH使用注意事项 RECURSIVE 递归查询的过程 拆解下执行的过程 1.执行非递归部分 2.执行递归部分,如果是 ...
- alg-最长回文字符串
class Solution { public: std::string longestPalindrome(const std::string& s) { if (s.empty()) { ...
- Cilium架构 (Cilium 2)
Cilium架构 译自:http://docs.cilium.io/en/stable/architecture/ 本文档描述了Cilium的架构.它通过记录BPF数据路径(datapath)的钩子来 ...
- DataGridView编辑状态自动提交
在使用bindingSource.bindingNavigator+DataGridView修改时会发现,当你需要保存修改过后的内容,必须将光标指向另外一行,DataGridView才会将编辑过后的数 ...
- L5语言模型与数据集
本次实验使用的数据下载: jaychou_lyrics.txt 链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1LJSrkpV84YF61OPmjIHGIw 提取码:dj53 语言模型 一段自 ...
- Java中StringBuffer类
StringBuffer: 线程安全的可变字符串. StringBuffer和String的区别?前者长度和内容可变,后者不可变.如果使用前者做字符串的拼接,不会浪费太多的资源. StringBuff ...
- Flutter Weekly Issue 53
插件 left-scroll-actions A useful left scroll actions widget like WeChat.一款仿微信效果的 Flutter 左滑菜单插件.现在支持i ...
