Intro to Machine Learning
本节主要用于机器学习入门,介绍两个简单的分类模型:
决策树和随机森林
不涉及内部原理,仅仅介绍基础的调用方法
1. How Models Work
以简单的决策树为例
This step of capturing patterns from data is called fitting or training the model
The data used to train the data is called the trainning data
After the model has been fit, you can apply it to new data to predict prices of additional homes
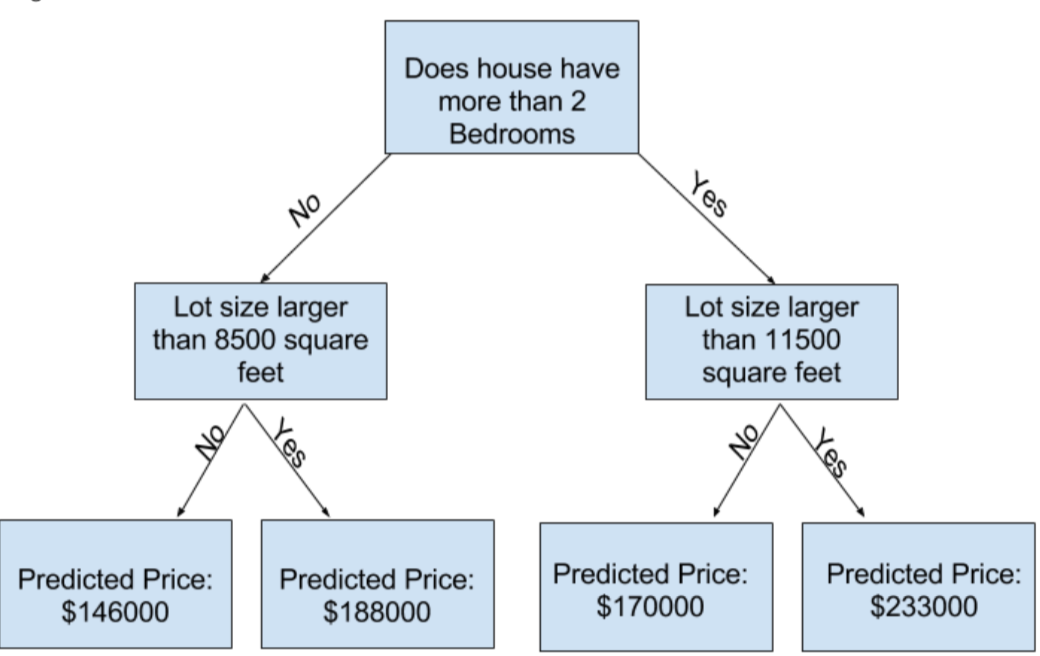
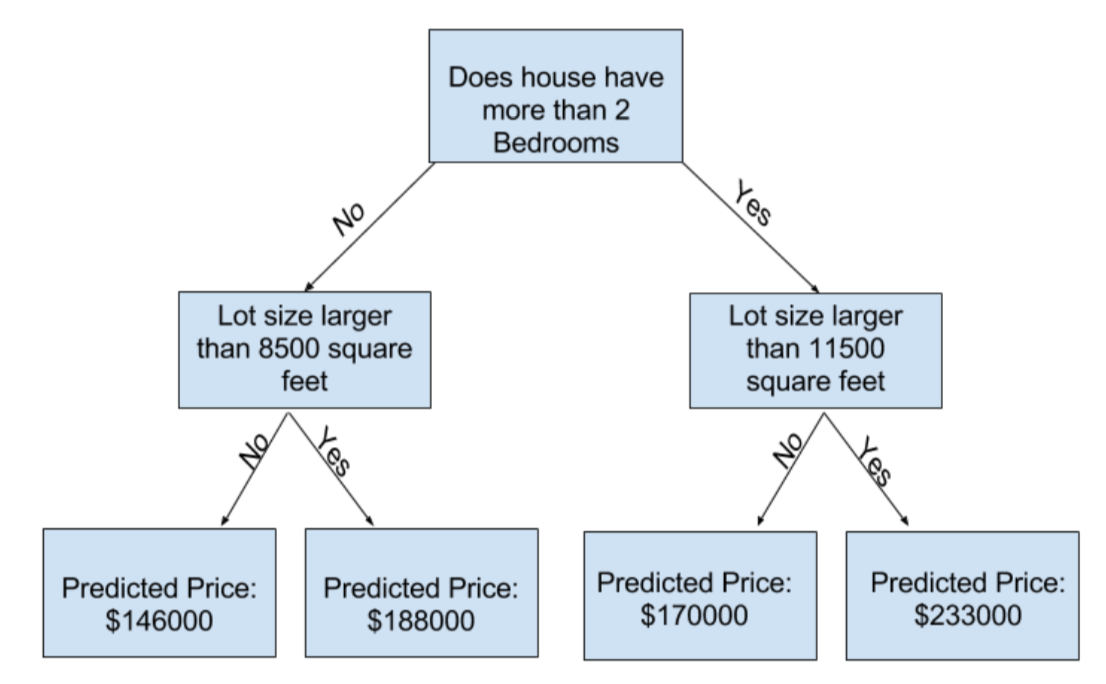
2.Basic Data Exploration
使用pandas中的describle()来探究数据:
melbourne_file_path = '../input/melbourne-housing-snapshot/melb_data.csv'
melbourne_data = pd.read_csv(melbourne_file_path)
melbourne.describe()
output:
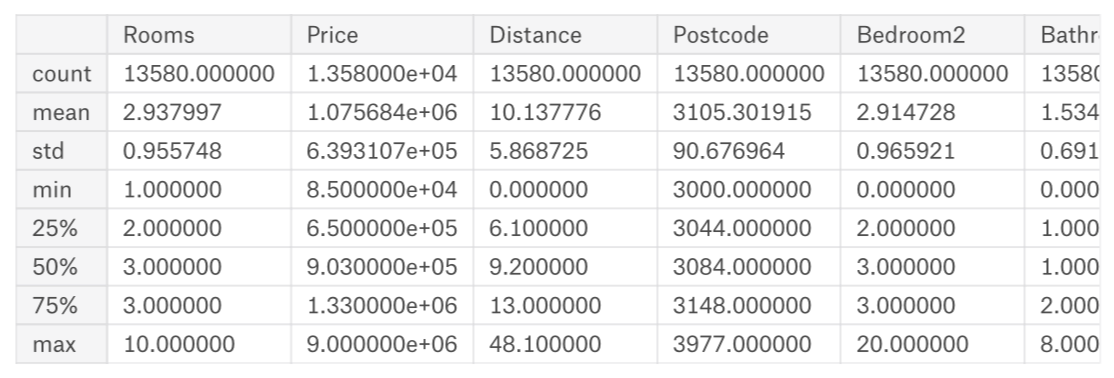
注:数值含义
count: 非缺失值的数量
mean: 平均值
std: 标准偏差,它度量值在数值上的分布情况
min、25%、50%、75%、max: 将每一列按照从lowest到highest排序,最小值是min, 1/4位置上,大于25%而小于50%是25%
3.Your First Machine Learning Model
- Selecting Data for Modeling
import pandas as pd
melbourne_file_path = ' ../input/melbourne-housing-snapshot/melb_data.csv'
melbourne_data = pd.read_csv(melbourne_file_path)
- Selecting The Prediction Target
方法:使用dot-notation来挑选prediction target
- Choosing "Features"
melbourne_features = ['Rooms', 'Bathroom', 'Landsize', 'Lattitude', 'Longtitude']
X = melbourne_data[melbourne_features]
查看数据是否加载正确:
X.head()
探究数据基本特性:
- Building Your Model
我们使用scikit-learn来创造模型,scikit-learn教程如下:
具体的原理可以根据需要自己探究
https://scikit-learn.org/stable/supervised_learning.html#supervised-learning
构建模型步骤:
- Define:
What type of model will it be? A decision tree? Some other type of model? Some other parameters of the model type are specified too.
- Fit:
Capture patterns from provided data. This is the heart of modeling
- Predict:
Just what it sounds like
- Evaluate:
Determine how accurate the model's predictions are
实现:
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
melbourne_mode = DecisionTreeRegressor(random_state=1)
melbourne_mode.fit(X , y)
打印出开始几行:
print (X.head())
预测后的价格如下:
print (melbourne_mode.predict(X.head())
4.Model Validation
由于预测的价格和真实的价格会有差距,而差距多少,我们需要衡量
使用Mean Absolute Error
error= actual-predicted
在实际过程中,我们要将数据分成两份,一份用于训练,叫做training data, 一份用于验证叫validataion data
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
train_X, val_X, train_y, val_y = train_test_split(X, y, random_state=0)
melbourne_model = DecisionTreeRegressor()
melbourne_model.fit(train_X, train_y)
val_predictions = melbourne_model.predict(val_X)
print(mean_absolute_error(val_y, val_predictions))
5.Underfitting and Overfitting
- overfitting: A model matches the data almost perfectly, but does poorly in validation and other new data.
- underfitting: When a model fails to capture important distinctions and patterns in the data, so it performs poorly even in training data.
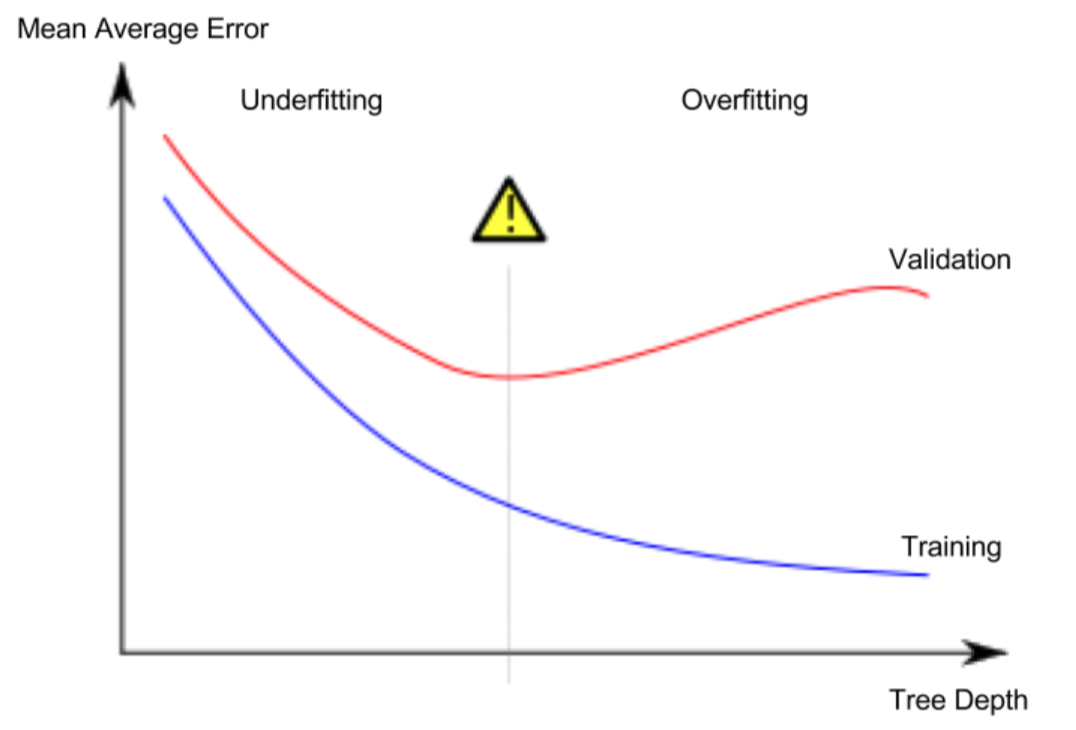
The more leaves we allow the model to make, the more we move from the underfitting area in the above graph to overfitting area.
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error
from sklearn.tree import DecsionTreeRegressor
def get_ame(max_leaf_nodes, train_X, val_X, train_y, val_y):
model = DecisionTreeRegressor(max_leaf_nodes = max_leaf_nodes, random_state = 0)
model.fit(train_X, train_y)
preds_val = model.predict(val_X)
mae = mean_absolute_error(val_y, preds_val)
return(mae)
我可以使用循环比较选择最合适的max_leaf_nodes
for max_leaf_nodes in [5,50,500,5000]:
my_ame = get_ame(max_leaf_nodes, train_X, val_X, train_y, val_y)
print(max_leaf_nodes, my_ame)

最后可以发现,当max leaf nodes 为 500时,MAE最小, 接下来我们换另外一种模型
6.Random Forests
The random forest uses many trees, and it makes a prediction by averaging the predictions of each component tree. It generally has much better predictive accuracy than a single decision tree and it works well with default parameters.
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error
forest_model = RandomForestRegressor(random_state=1)
forest_model.fit(train_X,train_y)
melb_preds = forest_model.predict(val_X)
print(mean_absolute_error(val_y, melb_preds))
可以发现最后的误差,相对于决策树小。
one of the best features of Random Forest models is that they generally work reasonably even without this tuning.

7.Machine Learning Competitions
- Build a Random Forest model with all of your data
- Read in the "test" data, which doesn't include values for the target. Predict home values in the test data with your Random Forest model.
- Submit those predictions to the competition and see your score.
- Optionally, come back to see if you can improve your model by adding features or changing your model. Then you can resubmit to see how that stacks up on the competition leaderboard.
Intro to Machine Learning的更多相关文章
- 【机器学习Machine Learning】资料大全
昨天总结了深度学习的资料,今天把机器学习的资料也总结一下(友情提示:有些网站需要"科学上网"^_^) 推荐几本好书: 1.Pattern Recognition and Machi ...
- 机器学习(Machine Learning)&深度学习(Deep Learning)资料【转】
转自:机器学习(Machine Learning)&深度学习(Deep Learning)资料 <Brief History of Machine Learning> 介绍:这是一 ...
- How do I learn machine learning?
https://www.quora.com/How-do-I-learn-machine-learning-1?redirected_qid=6578644 How Can I Learn X? ...
- 机器学习(Machine Learning)与深度学习(Deep Learning)资料汇总
<Brief History of Machine Learning> 介绍:这是一篇介绍机器学习历史的文章,介绍很全面,从感知机.神经网络.决策树.SVM.Adaboost到随机森林.D ...
- Easy machine learning pipelines with pipelearner: intro and call for contributors
@drsimonj here to introduce pipelearner – a package I'm developing to make it easy to create machine ...
- How do I learn mathematics for machine learning?
https://www.quora.com/How-do-I-learn-mathematics-for-machine-learning How do I learn mathematics f ...
- 机器学习案例学习【每周一例】之 Titanic: Machine Learning from Disaster
下面一文章就总结几点关键: 1.要学会观察,尤其是输入数据的特征提取时,看各输入数据和输出的关系,用绘图看! 2.训练后,看测试数据和训练数据误差,确定是否过拟合还是欠拟合: 3.欠拟合的话,说明模 ...
- 【Machine Learning】KNN算法虹膜图片识别
K-近邻算法虹膜图片识别实战 作者:白宁超 2017年1月3日18:26:33 摘要:随着机器学习和深度学习的热潮,各种图书层出不穷.然而多数是基础理论知识介绍,缺乏实现的深入理解.本系列文章是作者结 ...
- 【Machine Learning】Python开发工具:Anaconda+Sublime
Python开发工具:Anaconda+Sublime 作者:白宁超 2016年12月23日21:24:51 摘要:随着机器学习和深度学习的热潮,各种图书层出不穷.然而多数是基础理论知识介绍,缺乏实现 ...
随机推荐
- Asp.Net Core WebAPI+PostgreSQL部署在Docker中
PostgreSQL是一个功能强大的开源数据库系统.它支持了大多数的SQL:2008标准的数据类型,包括整型.数值值.布尔型.字节型.字符型.日期型.时间间隔型和时间型,它也支持存储二进制的大对像, ...
- 使用rpm安装指定版本的docker(1.12.6)
一.原因 如果系统是Centos7.3,直接使用yum install docker安装的docker版本是1.13.1,导致在创建容器的会报错,错误如下: 所以为了防止安装高版本的docker引发的 ...
- Node.js爬虫实战 - 爬你喜欢的
前言 今天没有什么前言,就是想分享些关于爬虫的技术,任性.来吧,各位客官,里边请... 开篇第一问:爬虫是什么嘞? 首先咱们说哈,爬虫不是"虫子",姑凉们不要害怕. 爬虫 - 一种 ...
- 洛谷 P1120 小木棍
题意简述 给出n个数,求最小的l,使n个数可分成若干组,每组和都为l. 题解思路 暴力搜索+剪枝 代码 #include <cstdio> #include <cstdlib> ...
- 调用百度翻译 API 来翻译网站信息
之前说过jquery.i18n.js 来做网站的中英翻译,前提就得做一套中文内容,一套英文内容来解决,好处是中英翻译可以准确无误,本篇文章我们来看一下调用百度翻译的 API 来进行网站的翻译,但是翻译 ...
- (三十二)c#Winform自定义控件-表格
前提 入行已经7,8年了,一直想做一套漂亮点的自定义控件,于是就有了本系列文章. 开源地址:https://gitee.com/kwwwvagaa/net_winform_custom_control ...
- RN 性能优化
按需加载: 导出模块使用属性getter动态require 使用Import语句导入模块,会自动执行所加载的模块.如果你有一个公共组件供业务方使用,例如:common.js import A from ...
- nginx单机1w并发优化
目录 ab工具 整体优化思路 具体的优化思路 编写脚本完成并发优化配置 性能统计工具 tips 总结 ab工具 ab -c 10000 -n 200000 http://localhost/index ...
- 为什么操作DOM会影响WEB应用的性能?
面试官经常会问你:"平时工作中,你怎么优化自己应用的性能?" 你回答如下:"我平时遵循以下几条原则来优化我的项目.以提高性能,主要有:" a. 减少DOM操作的 ...
- 存储型XSS的发现经历和一点绕过思路
再次骚扰 某SRC提现额度竟然最低是两千,而已经有750的我不甘心呐,这不得把这2000拿出来嘛. 之后我就疯狂的挖这个站,偶然发现了一个之前没挖出来的点,还有个存储型XSS! 刚开始来到这个之前挖过 ...
