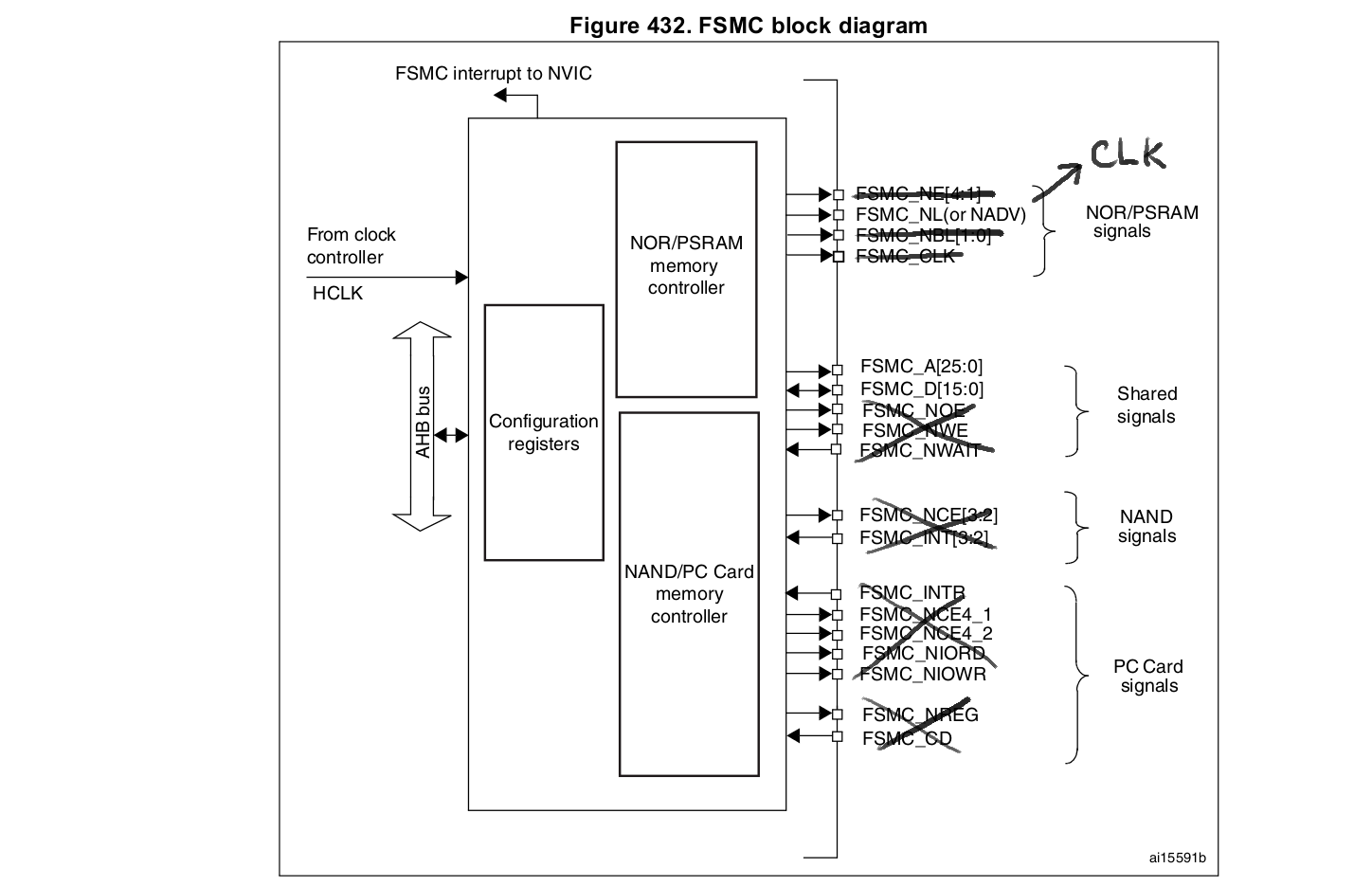
STM32F4: Generating parallel signals with the FSMC
STM32F4: Generating parallel signals with the FSMC
The goal: The memory controller can be used to generate a "generic" 16-bit parallel data stream with clock. Address generation will be disregarded, as well as other control signals dedicated to memory chips.
It must be noted that the STM32F40x and STM32F41x have the FSMC (static memories), while theSTM32F42x and STM32F43x have the FMC (static and dynamic memories). The differences between the two concern the support of SDRAM (dynamic RAM), address and data write FIFOs (both data and address, instead of data only for FSMC, and 16-word long instead of 2-word long only for FSMC), and the 32-bit wide data bus for FMC (See [1]).
Set pins (1st attempt)
Only data bus FSMC_D[15:0] and clock FSMC_CLK will be used (set as alternate function). The other pins are set as standard GPIOs (general purpose output).
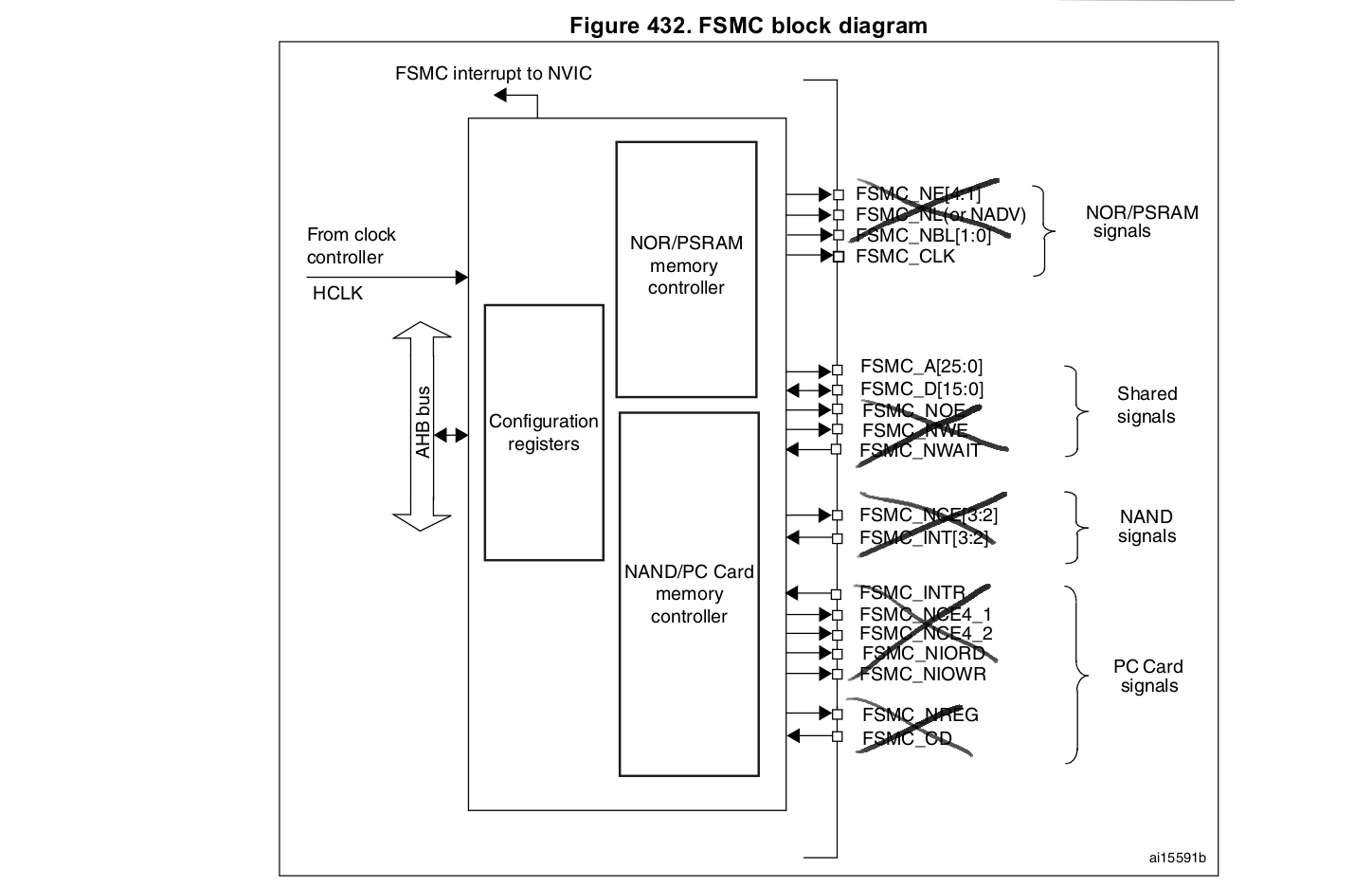
FSMC is alternate function 12 according to the datasheet (See "Table 9. Alternate function mapping" in [2]).
/* PD: 0, 1, 3, 8, 9, 10, 14, 15 -> alternate function (0b10) */
GPIOD->MODER = 0xA56A559A;
GPIOD->AFR[] = 0xCCCCCCCC; /* FSMC = AF12 (0xC) */
GPIOD->AFR[] = 0xCCCCCCCC;
/* PE: 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 -> alternate function (0b10) */
GPIOE->MODER = 0xAAAA9555;
GPIOE->AFR[] = 0xCCCCCCCC;
GPIOE->AFR[] = 0xCCCCCCCC;
FSMC setup/init (1st attempt)
Be careful of the the wicked register map documentation of the FSMC block:
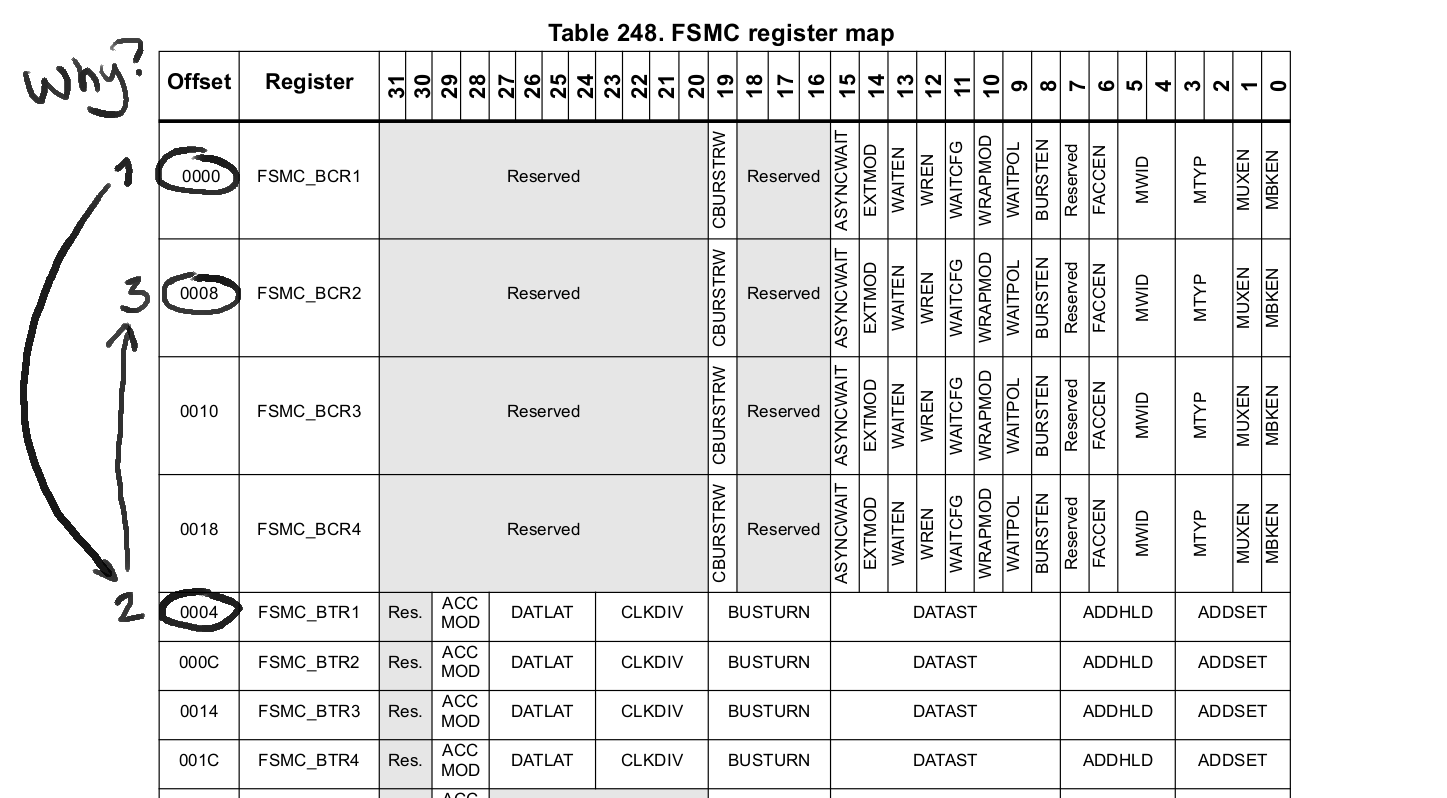
This is very misleading, since all other table are ordered as found in memory, but not here.
/* PSRAM, synchronous (burst), non-multiplexed */
/* control register */
FSMC_Bank1->BTCR[] = FSMC_BCR1_CBURSTRW | FSMC_BCR1_WAITPOL | FSMC_BCR1_BURSTEN | FSMC_BCR1_MWID_0 | FSMC_BCR1_WREN | FSMC_BCR1_MTYP_0 /* PSRAM */ | FSMC_BCR1_MBKEN;
/* timing register */
FSMC_Bank1->BTCR[] = FSMC_BTR1_CLKDIV_1 /* div 3 */ ;
It is noticable that the timing are all set to 0, except the clock.
Result (1st attempt)
The code writing to the FSMC is using an array and simulate a sequencial memory request, in order to take advantage of the burst mode.
volatile uint16_t* fsmc = (uint16_t*)0x60000000;
for(uint32_t i=; i<(sizeof(bitstream_bin)/); i++) {
uint16_t w = ((uint16_t*)bitstream_bin)[i];
fsmc[i] = w;
}
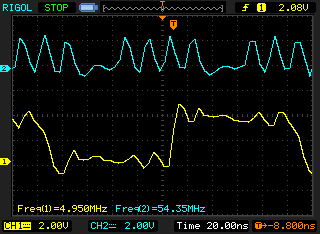
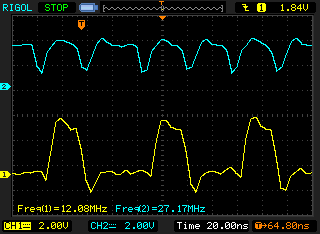
The clock is ~54MHz, but the maximum clock is HCLK/2 = 168/2=84MHz. Unfortunately, my oscilloscope is too slow for this.
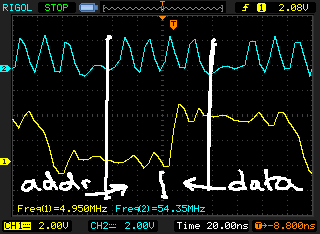
At least, 4 clock cycles are required to write one data. Data latency (DATLAT lowest value is 2). There is one cyle to give the address, two cyle of latency, one cyle for give the data.
At max FSMC speed (~84MHz), after dividing the clock by 4, the 16-bit parallel transmission would only be ~20MHz.

Bursts are possible up to 32 bits (two 16-bit data words). When using this feature, two data words are send for each address, hence more data is sent, but the clock is hard to use: 3 ticks for the (empty) address, 1 tick for the first data, 1 tick for the second data (5 cycles for 2 data, ~30MHz max).
Set pins (2nd attempt)
/* PD: 0, 1, 8, 9, 10, 14, 15 -> alternate function (0b10) */
GPIOD->MODER = 0xA56A555A;
GPIOD->AFR[] = 0xCCCCCCCC; /* FSMC = AF12 (0xC) */
GPIOD->AFR[] = 0xCCCCCCCC;
/* PE: 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15 -> alternate function (0b10) */
GPIOE->MODER = 0xAAAA9555;
GPIOE->AFR[] = 0xCCCCCCCC;
GPIOE->AFR[] = 0xCCCCCCCC;
/* PB: 7 -> AF */
GPIOB->MODER = 0x55551555;
GPIOB->AFR[] = 0xCCCCCCCC;
GPIOB->AFR[] = 0xCCCCCCCC;
FSMC setup/init (2nd attempt)
/* NOR flash, asynchronous, multiplexed */
/* control register */
FSMC_Bank1->BTCR[] = FSMC_BCR1_WREN | FSMC_BCR1_FACCEN | FSMC_BCR1_MWID_0 /* 16-bit */ | FSMC_BCR1_MTYP_1 /* NOR flash */ | FSMC_BCR1_MUXEN | FSMC_BCR1_MBKEN;
/* timing register */
FSMC_Bank1->BTCR[] = FSMC_BTR1_CLKDIV_0 | FSMC_BTR1_DATAST_0 | FSMC_BTR1_ADDHLD_0 | FSMC_BTR1_ADDSET_1;
Result (2nd attempt)
We want to use the NADV signal as a new clock CLK.
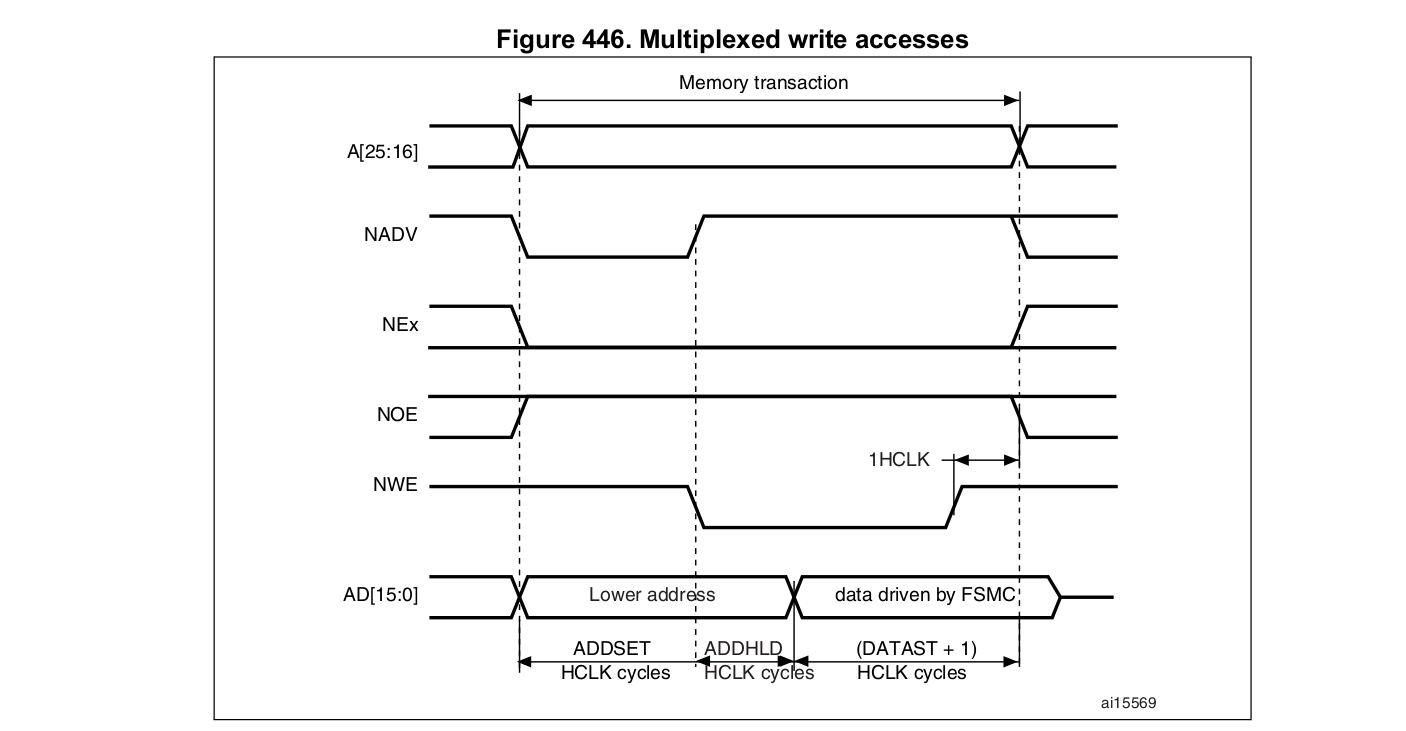
volatile uint16_t* fsmc = (uint16_t*)0x60000000;
uint16_t w[] = {
0xFFFF, 0x0000, 0xFFFF, 0x0000,
0xFFFF, 0x0000, 0xFFFF, 0x0000}; for(uint32_t i=;i<;i++) {
fsmc[] = w[i];
}
We write to the same address in order to force a new memory transaction and cycle NADV.
The problem is that the data bus is updated after the positive edge of the NADV "clock". This issue can be overcome by multiplexing the address and data bus and put the data value as address. The ADDSET value is also increased in order to have a more balanced clock (ADDSET=3).
for(uint32_t i=;i<;i++) {
uint16_t v = w[i];
fsmc[v] = v;
}
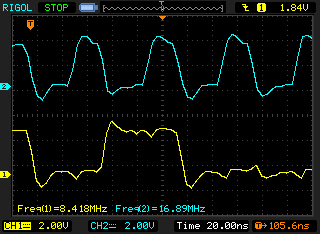
Unfortately, the overall clock speed decreased because the address "trick".
Conclusion
A "nice looking" 16-bit parallel signal with clock can be generated at approx. 16MHz using the memory controller (FSMC) in asynchronous NOR Flash mode. 20MHz can be achieved with an external clock divider (div 4) in synchronous PSRAM mode. If the clock edge can be aligned with the data edge, 27MHz is possible from SRAM.
Note: the FMC (Flexible Memory Controller, also supporting SDRAM) in SDRAM mode can generate a synchronous burst of one data per clock. In this case, 84MHz is possible in theory. I haven't the hardware to test it.
STM32F4: Generating parallel signals with the FSMC的更多相关文章
- STM32F4: GENERATING A SINE WAVE
http://amarkham.com/?p=49
- Flexible implementation of a system management mode (SMM) in a processor
A system management mode (SMM) of operating a processor includes only a basic set of hardwired hooks ...
- PMP用语集
AC actual cost 实际成本 ACWP actual cost of work performed 已完工作实际成本 BAC budget at completion 完工预算 BCWP b ...
- 论文翻译:2021_DeepFilterNet: A Low Complexity Speech Enhancement Framework for Full-Band Audio based on Deep Filtering
论文地址:DeepFilterNet:基于深度滤波的全频带音频低复杂度语音增强框架 论文代码:https://github.com/ Rikorose/DeepFilterNet 引用:Schröte ...
- STM32F4—fsmc的配置步骤
0:开启GPIO时钟和FSMC时钟 1:配置GPIO 2:配置片选控制寄存器 3:配置片选时序寄存器 4:配置写入时序寄存器 GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStructure;/ ...
- STM32F4 SPI with DMA
STM32F4 SPI with DMA A few people have requested code, so I thought I’d post the code showing how I’ ...
- Generating Complex Procedural Terrains Using GPU
前言:感慨于居然不用tesselation也可以产生这么复杂的地形,当然致命的那个关于不能有洞的缺陷还是没有办法,但是这个赶脚生成的已经足够好了,再加上其它模型估 计效果还是比较震撼的.总之好文共分享 ...
- GNU Parallel Tutorial
GNU Parallel Tutorial Prerequisites Input sources A single input source Multiple input sources Linki ...
- Massively parallel supercomputer
A novel massively parallel supercomputer of hundreds of teraOPS-scale includes node architectures ba ...
随机推荐
- Android利用LocalSocket实现Java端进程与C端进程之间的IPC
Android是建立在Linux之上的OS,在涉及到安全.网络协议.文件加密等功能时,往往需要通过C语言调用底层API来实现,而如何发出指令让C端执行我们想要的功能,并且在执行之后有返回结果呢,这就需 ...
- HDU 2056 龟兔赛跑 (DP)
题意:见题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2059 解题报告:以前一直没看出来这题是个DP题,知道是DP题就简单了 .首先要把起点和终点看成 ...
- 第14月第1天 uialterview 键盘 uibutton圆角
1. 在IOS 8之后 当UIAlertView 和keyboard 同时出现时,会出现键盘闪现的情况 所以就修正UIAlertView http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_ ...
- Spark笔记之使用UDAF(User Defined Aggregate Function)
一.UDAF简介 先解释一下什么是UDAF(User Defined Aggregate Function),即用户定义的聚合函数,聚合函数和普通函数的区别是什么呢,普通函数是接受一行输入产生一个输出 ...
- Ubuntu下mysql使用
1. 从网上安装 sudo apt-get install mysql-server.装完已经自动配置好环境变量,可以直接使用mysql的命令. 注:建议将/etc/apt/source.list中的 ...
- java采用zip方式实现String的压缩和解压缩CompressStringUtil类
CompressStringUtil类:不多说,直接贴代码: /** * 压缩 * * @param paramString * @return */ public static final byte ...
- InnoDB Lock浅谈
数据库使用锁是为了支持更好的并发,提供数据的完整性和一致性.InnoDB是一个支持行锁的存储引擎,锁的类型有:共享锁(S).排他锁(X).意向共享(IS).意向排他(IX).为了提供更好的并发,Inn ...
- csu 1982:小M的移动硬盘(双向链表)
Description 最近小M买了一个移动硬盘来储存自己电脑里不常用的文件.但是他把这些文件一股脑丢进移动硬盘后,觉得这些文件似乎没有被很好地归类,这样以后找起来岂不是会非常麻烦? 小M最终决定要把 ...
- 《Photoshop智能手机APP界面设计》学习笔记-转
第一章 APP用户界面基础 1.1 手机UI设计相关基本概念 1.1.1 什么是UI设计 UI(User's Interface)即用户界面,它不仅仅是美化界面,还需要研究用户,让界面变得更友好.简洁 ...
- .NetCore中结合ExceptionLess的处理对Polly再次封装
/// <summary> /// Polly封装 liyouming /// </summary> public class PollyServicesFactory { p ...
