Paper Reading - Learning to Evaluate Image Captioning ( CVPR 2018 ) ★
Link of the Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.06422
Innovations:
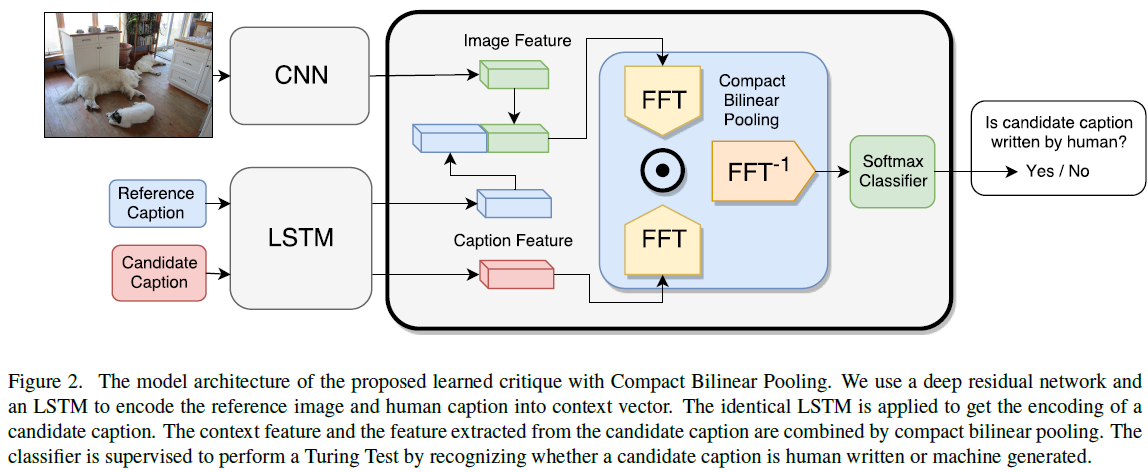
- The authors propose a novel learning based discriminative evaluation metric that is directly trained to distinguish between human and machine-generated captions. They train an automatic critique to distinguish generated captions from human-written ones, and then score candidate captions by how successful they are in fooling the critique. Formally, given a critique parametrized by Θ, a reference image i, and a generated caption c, the score is defined as the probability for the caption of being human-written, as assigned by the critique: scoreΘ(c, i) = P(c is human written | i, Θ). More generally, the reference image represents the context in which the generated caption is evaluated. To provide further information about the relevance and salience of the image content, a reference caption can additionally be supplied to the context. Let C(i) denotes the context of image i, then reference caption c could be included as part of context, i.e. c∈C(i). The score with context becomes scoreΘ(c, i) = P(c is human written | C(i), Θ).
- To systematically create pathological sentences, the authors define several transformations to generate unnatural sentences that might get high scores in an evaluation metric. Their proposed data augmentation scheme uses these transformations to generate large number of negative examples. Formally, a transformation Τ takes an image-caption dataset and generates a new one: Τ({(c, i) ∈ D}; γ) = {(c1', i1'), ..., (cn', in')}, where i, ii' are images, c, ci' are captions, D is a list of caption-image tuples representing the original dataset, and γ is a hyper-parameter that controls the strength of the transformation. Specifically, authors define following three transformations to generate pathological image-captions pairs:
- Random Captions ( RC ): To ensure the metric pays attention to the image content, they randomly sample human written captions from other images in the training set: TRC(D; γ) = {(c', i) | (c, i), (c', i') ∈ D, i'∈Nγ(i)}, where Nγ(i) represents the set of images that are top γ percent nearest neighbors to image i.
- Word Permutation ( WP ): To make sure that their metric pays attention to sentence structure, authors randomly permute at least 2 words in the reference caption: TWP(D; γ) = {(c', i) | (c, i) ∈ D, c' ∈ Pγ(c) \ {c}}, where Pγ(c) represents all sentences generated by permuting γ percent of words in caption c.
- Random Word ( RW ): To explore rare words authors replace from 2 to all words of the reference caption with random words from the vocabulary: TRW(D; γ) = {(c', i) | (c, i) ∈ D, c' ∈ Wγ(c) \ {c}}, where Wγ(c) represents all sentences generated by randomly replacing γ percent words from caption c.

- The authors propose a systematic approach to measure the robustness of an evaluation metric to a given pathological transformation.
General Points:
- Commonly used evaluation metrics for Image Captioning: BLEU, METEOR, ROUGE, CIDEr, SPICE. These metrics face two challenges. Firstly, many metrics fail to correlate well with human judgments. Metrics based on measuring word overlap between candidate and reference captions find it difficult to capture semantic meaning of a sentence, therefore often lead to bad correlation with human judgments. Secondly, each evaluation metric has its well-known blind spot, and rule-based metrics are often inflexible to be responsive to new pathological cases.
- Compact Bilinear Pooling ( CBP ) has been demonstrated in Multimodal compact bilinear pooling for visual question answering and visual grounding to be very effective in combining heterogeneous information of image and text.
Paper Reading - Learning to Evaluate Image Captioning ( CVPR 2018 ) ★的更多相关文章
- Paper Reading - Convolutional Image Captioning ( CVPR 2018 )
Link of the Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.09151 Motivation: LSTM units are complex and inherentl ...
- Paper Reading - Learning like a Child: Fast Novel Visual Concept Learning from Sentence Descriptions of Images ( ICCV 2015 )
Link of the Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1504.06692.pdf Innovations: The authors propose the Novel V ...
- Paper Reading: Stereo DSO
开篇第一篇就写一个paper reading吧,用markdown+vim写东西切换中英文挺麻烦的,有些就偷懒都用英文写了. Stereo DSO: Large-Scale Direct Sparse ...
- 读paper笔记[Learning to rank]
读paper笔记[Learning to rank] by Jiawang 选读paper: [1] Ranking by calibrated AdaBoost, R. Busa-Fekete, B ...
- 在矩池云上复现 CVPR 2018 LearningToCompare_FSL 环境
这是 CVPR 2018 的一篇少样本学习论文:Learning to Compare: Relation Network for Few-Shot Learning 源码地址:https://git ...
- 爬取CVPR 2018过程中遇到的坑
爬取 CVPR 2018 过程中遇到的坑 使用语言及模块 语言: Python 3.6.6 模块: re requests lxml bs4 过程 一开始都挺顺利的,先获取到所有文章的链接再逐个爬取获 ...
- Paper Reading - Convolutional Sequence to Sequence Learning ( CoRR 2017 ) ★
Link of the Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.03122 Motivation: Compared to recurrent layers, convol ...
- Paper Reading - Deep Captioning with Multimodal Recurrent Neural Networks ( m-RNN ) ( ICLR 2015 ) ★
Link of the Paper: https://arxiv.org/pdf/1412.6632.pdf Main Points: The authors propose a multimodal ...
- Paper Reading - Deep Visual-Semantic Alignments for Generating Image Descriptions ( CVPR 2015 )
Link of the Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.2306 Main Points: An Alignment Model: Convolutional Ne ...
随机推荐
- 启动tomcat的时候为啥你启动的是8,启动起来的确实其他的Tomcat
如果发现,是启动tomcat的时候为啥你启动的是8,启动起来的确实其他的Tomcat ,你可以去看看你的环境变量,是不是配了一个tomcat,
- Struts2+Spring+Hibernate整合开发(Maven多模块搭建)
Struts2+Spring+Hibernate整合开发(Maven多模块搭建) 0.项目结构 Struts2:web层 Spring:对象的容器 Hibernate:数据库持久化操作 1.父模块导入 ...
- 安装 vue-devtools
1. github下载 vue-devtools: git clone https://github.com/vuejs/vue-devtools 2. node install 安装包 3. vi ...
- MYSQL小函数大用途之-------FIND_IN_SET
没有前言和解释,直接看怎么用 当前我所知道两种用法: 第一种:和like的作用有点相似,但用这个函数会比like更准确的查到你想要的数据. 前提是当前的字段满足俩个要求: 类型为字符型. 储存格式为- ...
- 【NXP开发板应用—智能插排】3.驱动GPIO点亮外接LED
[前言] 首先感谢深圳市米尔科技有限公司举办的这次活动并予以本人参加这次活动的机会,以往接触过嵌入式,但那都是皮毛,最多刷个系统之类的,可以说对于嵌入式系统开发这件事情是相当非常陌生的,这次活动为我提 ...
- macos 安装 brew
ruby -e "$(curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Homebrew/install/master/install)" ...
- c语言数据结构(一)
第一章 绪论 一.数据与数据结构 数据:所有能被输入到计算机中,且被计算机处理的符号的集合计算机操作的对象的总称.是计算机处理的信息的某种特定的符号表示形式. 数据元素:数据中的一个“个体”,数据 ...
- 20145234黄斐《信息安全系统设计基础》第八周(Linux下vim相关命令)
Linux下vim相关命令 在编辑程序时经常使用vim,所以记住一些常用的指令还是很有必要的 文件命令 vim file 打开单个文件vim file vim file1 file2 file3 .. ...
- SVN的使用——下载、安装
今天我们来学习一下如何使用SVN(Subversion) 既然要使用SVN那么我们就先来认识一下SVN.SVN的全名是Subversion,它是一个自由,开源的版本控制系统.在Subversion管理 ...
- iOS 库 开发小结
1.基本用法 定义类,导出头文件,注意头文件,库文件的search path 2.加载资源 - 使用主工程的文件,耦合性太强 - 封装到NSBundle中 NSBundle可以封装xib storyb ...
