最大流应用(Maximum Flow Application)
1. 二分图匹配(Bipartite Matching)
1.1 匹配(Matching)
Def. Given an undirected graph \(G = (V, E)\), subset of edges \(M ⊆ E\) is a matching if each node appears in at most one edge in \(M\).
定义. 给定一个无向图\(G = (V, E)\), 如果一个边的集合\(M \subseteq E\)并且每个顶点最多只出现在一条\(M\)中的边中, 则称\(M\)是一个匹配.
Max matching problem. Given a graph \(G\), find a max-cardinality matching.
最大匹配问题. 给定一个无向图\(G\), 找到一个集合元素最多的匹配.
1.2 二分图匹配(Bipartite matching)
Def. A graph G is bipartite if the nodes can be partitioned into two subsets \(L\) and \(R\) such that every edge connects a node in \(L\) with a node in \(R\).
Bipartite matching problem. Given a bipartite graph \(G = (L ∪ R, E)\), find a max cardinality matching.
max-flow formulation. Create digraph \(G' = (L ∪ R ∪ \set{s, t}, E')\):
- Direct all edges from \(L\) to \(R\), and assign infinite (or unit) capacity.
- Add unit-capacity edges from \(s\) to each node in \(L\).
- Add unit-capacity edges from each node in \(R\) to \(t\).
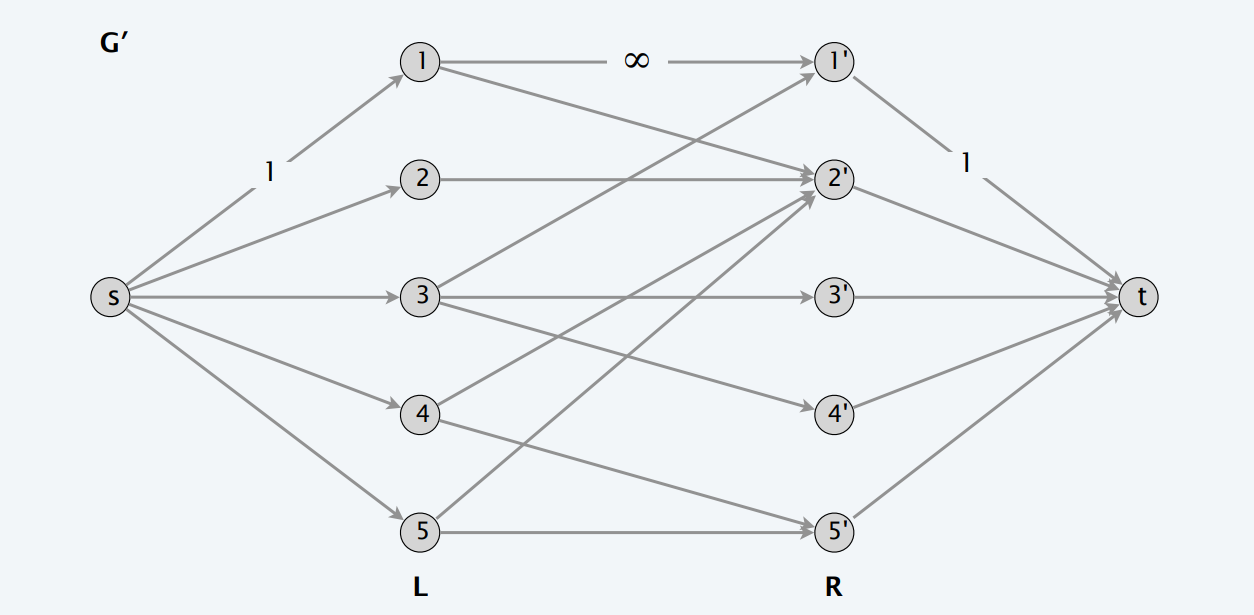
Theorem. 1–1 correspondence between matchings of cardinality \(k\) in \(G\) and integral flows of value \(k\) in \(G'\).
1.3 二分图完美匹配(Perfect matchings in bipartite graphs)
Def. Given a graph \(G = (V, E)\), a subset of edges \(M ⊆ E\) is a perfect matching if each node appears in exactly one edge in \(M\).
Notation. Let \(S\) be a subset of nodes, and let \(N(S)\) be the set of nodes adjacent to nodes in \(S\).
Observation. If a bipartite graph \(G = (L ∪ R, E)\) has a perfect matching, then \(|N(S)|\geq|S|\) for all subsets \(S \subseteq L\).
Theorem. [Frobenius 1917, Hall 1935] Let \(G = (L ∪ R, E)\) be a bipartite graph with \(|L| = |R|\). Then, graph G has a perfect matching iff \(|N(S)|\geq|S|\) for all subsets \(S \subseteq L\).
2. 不相交路径(Edge-disjoint Paths)
2.1 有向图中的不相交路径(Edge-disjoint Paths in Directed Graphs
2.1.1 问题描述(Problem Description)
Def. Two paths are edge-disjoint if they have no edge in common.
定义. 如果两个路径没有公共边, 则认为他们是不相交路径
Edge-disjoint paths problem. Given a digraph \(G = (V, E)\) and two nodes \(s\) and \(t\), find the max number of edge-disjoint \(s↝t\) paths.
不想交路径问题 给定一个有向图\(G = (V, E)\)和两个节点\(s\), \(t\), 找到其间不相交路径的最大数目.
2.1.2 解法(Solution)
Max-flow formulation. Assign unit capacity to every edge, and define it as \(G^\prime\)
Integral flow theorem. If each edge in a flow network has integral capacity, then there exists an integral maximal flow.
1–1 correspondence Theorem. 1–1 correspondence between k edge-disjoint \(s↝t\) paths in \(G\) and integral flows of value \(k\) in \(G'\).
- Integral flow theorem. \(\Rightarrow\) there exists a max flow \(f^*\) in \(G^\prime\) that is integral.
- 1–1 correspondence Theorem. \(\Rightarrow\) \(f^*\) corresponds to max number of edge-disjoint \(s↝t\) paths in \(G\).
2.1.3 补充(Addition)
Menger's Theorem. The max number of edge-disjoint \(s↝t\) paths equals the min number of edges whose removal disconnects \(t\) from \(s\).
2.2 无向图中的不相交路径(Edge-disjoint Paths in Undirected Graphs)
2.2.1 问题描述(Problem Description)
Given a graph \(G = (V, E)\) and two nodes \(s\) and \(t\), find the max number of edge-disjoint \(s↝t\) paths.
2.2.2 解法(Solution)
Max-flow formulation. Replace each edge with two antiparallel edges and assign unit capacity to every edge.
Observation. Two paths \(P1\) and \(P2\) may be edge-disjoint in the digraph but not edge-disjoint in the undirected graph
Lemma. In any flow network, there exists a maximum flow \(f\) in which for each pair of antiparallel edges \(e\) and \(e'\) : either \(f(e) = 0\) or \(f (e') = 0\) or both. Moreover, integrality theorem still holds.
Theorem. Max number of edge-disjoint \(s↝t\) paths = value of max flow.
3. 最大流问题扩展(Extensions to Max Flow)
3.1 多源点多汇点(Multiple sources and sinks)
Def. Given a digraph \(G = (V, E)\) with edge capacities \(c(e) ≥ 0\) and multiple source nodes and multiple sink nodes, find max flow that can be sent from the source nodes to the sink nodes.
max-flow formulation. Define new digraph as \(G'\):
- Add a new source node \(s\) and sink node \(t\).
- For each original source node \(s_i\) add edge \((s, s_i)\) with capacity \(\infty\).
- For each original sink node \(t_j\), add edge \((t_j, t)\) with capacity \(\infty\).
Claim. 1–1 correspondence between flows in \(G\) and \(G'\).
3.2 循环(Circulation)
3.2.1 供给需求循环(Circulation with supplies and demands)
Def. Given a digraph \(G = (V, E)\) with edge capacities \(c(e) ≥ 0\) and node demands \(d(v)\), a circulation is a function \(f(e)\) that satisfies:
- For each \(e\in E\): \(0\leq f(e)\leq c(e)\)
- For each \(v\in V\): \(\textstyle \sum_{e \space in \space to \space v}f(e) - \sum_{e \space out \space of \space v}f(e)=d(v)\)
max-flow formulation. Define new digraph as \(G'\):
- Add new source \(s\) and sink \(t\).
- For each \(v\) with \(d(v) < 0\), add \(edge (s, v)\) with capacity \(−d(v)\).
- For each \(v\) with \(d(v) > 0\), add \(edge (v, t)\) with capacity \(d(v)\).
Claim. \(G\) has circulation iff \(G'\) has max flow of value \(\displaystyle D = \sum_{v:d(v)>0}d(v) = \sum_{v:d(v)<0}-d(v)\)
3.2.2 带下界的供给需求循环(Circulation with supplies, demands, and lower bounds
Def. Given a digraph \(G = (V, E)\) with edge capacities \(c(e) ≥ 0\), lower bounds ℓ(e) ≥ 0, and node demands \(d(v)\), a circulation is a function \(f(e)\) that satisfies:
- For each \(e\in E\): \(\mathscr l(e)\leq f(e)\leq c(e)\)
- For each \(v\in V\): \(\textstyle \sum_{\text{e in to v}}f(e) - \sum_{\text{e out of v}}f(e)=d(v)\)
Max-flow formulation. Model lower bounds as circulation with demands.
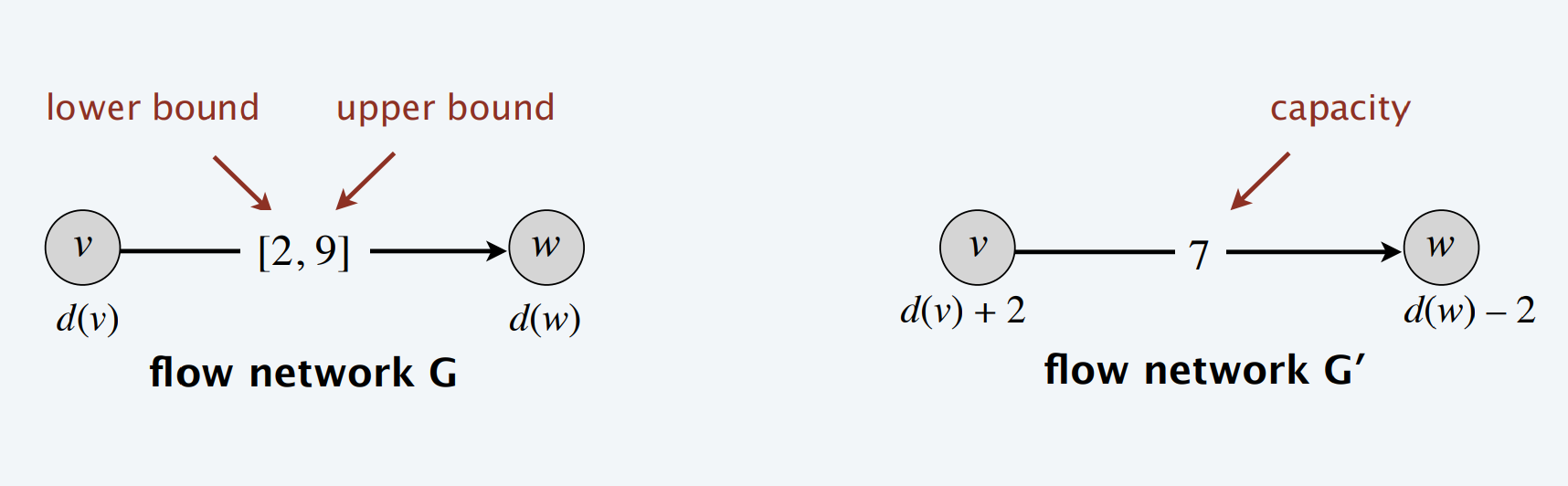
Theorem. There exists a circulation in \(G\) iff there exists a circulation in \(G'\).
Moreover, if all demands, capacities, and lower bounds in \(G\) are integers, then there exists a circulation in \(G\) that is integer-valued.
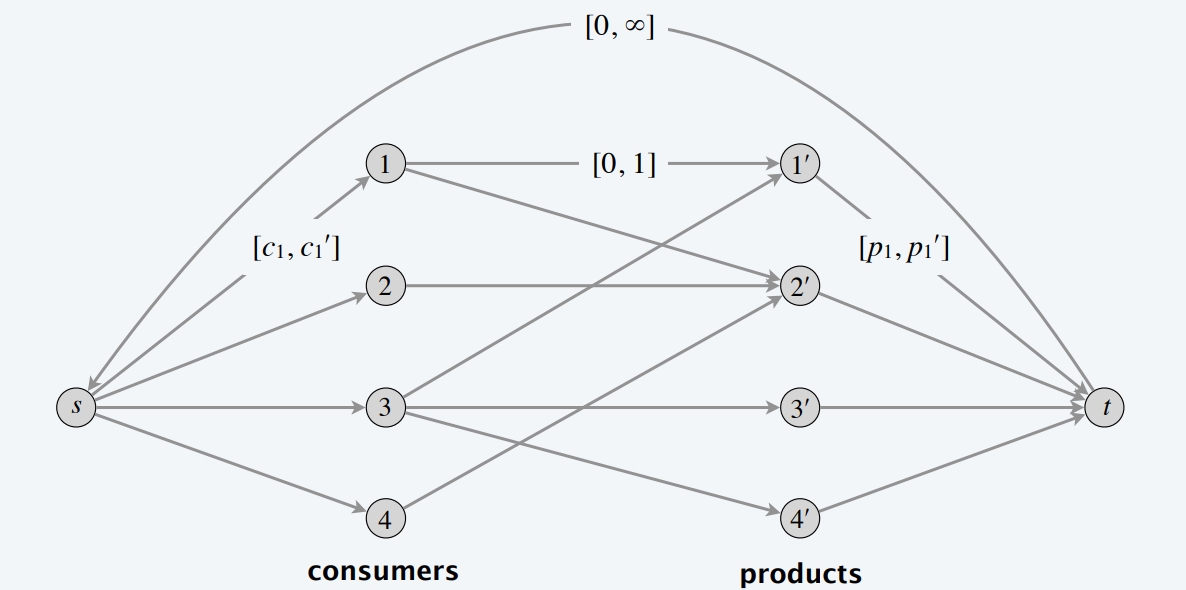
4. 调查设计问题(Survey Design)
4.1 问题描述(Problem Description)
- Design survey asking \(n_1\) consumers about \(n_2\) products.
- Can survey consumer \(i\) about product \(j\) only if they own it.
- Ask consumer \(i\) between \(c_i\) and \(c_i'\) questions.
- Ask between \(p_j\) and \(p_j'\) consumers about product \(j\).
Goal. Design a survey that meets these specs, if possible.
4.2 解法(Solution)
Max-flow formulation. Model as a circulation problem with lower bounds (all supplies and demands are 0):
- Add edge \((i, j)\) if consumer \(i\) owns product \(j\).
- Add edge from s to consumer \(j\).
- Add edge from product \(i\) to \(t\).
- Add edge from \(t\) to \(s\).
- All demands = 0.
Integer circulation \(\Leftrightarrow\) feasible survey design.
最大流应用(Maximum Flow Application)的更多相关文章
- [Algorithm] Maximum Flow
Ref MIT: lecture-13-incremental-improvement-max-flow-min-cut/ Ford Fulkerson algorithm for finding m ...
- 前端必须了解的布局常识:普通流(normal flow)
目录 一.概述 二.块级元素和内联元素 常见的块级元素 BFC 常见的行内元素 IFC 三.哪些情况会脱离普通流 浮动 绝对定位 固定定位 display:none 四.总结 五.参考资料 一.概述 ...
- [转载]Maximum Flow: Augmenting Path Algorithms Comparison
https://www.topcoder.com/community/data-science/data-science-tutorials/maximum-flow-augmenting-path- ...
- 网络流--最大流--HDU 3549 Flow Problem
题目链接 Problem Description Network flow is a well-known difficult problem for ACMers. Given a graph, y ...
- SPOJ 4110 Fast Maximum Flow (最大流模板)
题目大意: 无向图,求最大流. 算法讨论: Dinic可过.终于我的常数还是太大.以后要注意下了. #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> # ...
- [图论]最大流问题(Maximum flow)的定义
首先定义网络(network)N =(V,E), V表示顶点(Vertices)集合, E表示边(Edges)集合. s,t是V中的两个顶点,分别表示网络N中的源点(source)和汇点(sink). ...
- Dynamics CRM2016 业务流程之Task Flow(一)
Task Flow 属于CRM移动端的特性,如果在项目实施中用不到CRM自带的APP或者对自APP不感冒的,那就没有往下看的必要了,移步吧. 该功能默认是不开启的,需要我们去系统设置中开启它,打勾,选 ...
- Maximum Flow and Minimum Cut
最大流最小割 Introduction Mincut Problem 最小割问题,输入是带权有向图,有一个源点 s(source)和一个汇点 t(target),边的权重在这里称作容量(capacit ...
- Maximum Flow Exhaustion of Paths Algorithm
参考youtube上的视频: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sxyCzzUuXLo 笔记: 只要是那条路上为0后,就不会再走那条路. 所以没有S->U->W ...
- Dynamics CRM2016 业务流程之Task Flow(二)
接上篇,Page页设置完后,按照业务流程管理也可以继续设置Insert page after branch 或者 Add branch,我这里选择后者,并设置了条件,如果Pipeline Phase ...
随机推荐
- 问题:配置apache的相关配置文件报错:Invalid command 'Order' (已解决)
1. 问题描述 在虚拟文件httpd-vhosts.conf里面,directory里加入Order allow,deny,重启apache,出现Invalid command 'Order', pe ...
- 杭电OJ--1003题C++实现
#include<iostream>using namespace std;int a[100000];void solve(int k,int n,int t);int main(){ ...
- OPENGL入门的小知识点
记录一下看到的知识点. 大部分知识点来自于https://learnopengl-cn.github.io/ 1.什么是OpenGL 一般它被认为是一个API,包含了一系列可以操作图形.图像的函数.然 ...
- Linux 使用vsftpd服务传输文件
文件传输协议 FTP是一种在互联网中进行文件传输的协议,基于客户端/服务器模式,默认使用20.21号端口,其中端口20(数据端口)用于进行数据传输,端口21(命令端口)用于接受客户端发出的相关FTP命 ...
- Jenkins启动失败的七个问题
1.jdk版本和路径问题(注意第6个问题) which java vim /etc/init.d/jenkins 2.用户名问题 查看/etc/sysconfig/jenkins的JENKINS_US ...
- spring session + redis实现共享session
一.代码 1.pom.xml <!--spring session--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boo ...
- python+scrcpy实现将安卓设备录屏并保存到pc本地
一)scrcpy下载及安装 参考链接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/80264357 二)python+scrcpy实现将安卓设备录屏并保存到pc本地 示例代码: impo ...
- Python openpyxl【包】
介绍 Excel是我们日常工作中经常用到的办公软件,在处理数据和表格方面有着优异的性能,那么能不能用python来操作Excel呢? 答案是肯定的,openpyxl是一个第三方库,可以处理xlsx格式 ...
- Tesstwo9.1.0配置步骤
一,配置步骤 环境:Tesstwo9.1.0+Android10(华为)+Android11(模拟器) 1.查看tess-two的最新版本(GitHub - rmtheis/tess-two: For ...
- JS计算加减乘除出现多位小数的解决方法
function add(arg1, arg2){ let decima1, decima2, differ, m; try { decima1 = arg1.toString().split('.' ...
