ADADELTA: AN ADAPTIVE LEARNING RATE METHOD
引
这篇论文比较短,先看了这篇,本来应该先把ADAGRAD看了的。普通的基于梯度下降的方法,普遍依赖于步长,起始点的选择,所以,受ADAGRAD的启发,作者提出了一种ADADELTA的方法。
\]
其中\(g_t=\frac{\partial f(x_t)}{\partial x_t}\),所以下一步迭代就是:
\]
主要内容
ADAGRAD方法:
\]
也就是,步长与之前所有的梯度有关,显然这个步长是会逐渐减少的。但是这个缺点也很明显,如果起始点的梯度很大,那么就会导致后续步长很小,而一开始的梯度很小,就会导致后续步长很大,产生振荡,有些怪怪的。
而ADADELTA希望只关心一部分的梯度,比如
\]
但是这么做,每次迭代都必须记录\(k\)个梯度,这显得不怎么效率,于是,作者相处了一个法子:
\]
可以看到,对于\(g_1\),\(t+1\)步之后其影响为:\(\rho^t(1-\rho) g_1\),对整个迭代造成的影响是一个等比序列:
\]
最后趋向于:
\]
这么做就俩劝其美啦。
记:
\]
其中\(\epsilon\)是为了让除法有意义而添加的小量。
所以
\]
这还不是最终版本,另一个启发决定了\(\eta\)的选择。
我们知道,很多问题是有实际含义的,\(x\)可能是有单位的,比如是米,天等,所以,一个很自然的期望是,\(\Delta x\)的单位和\(x\)是保持一致的。但是:
\]
也就是说\(\Delta x\)的步长单位和梯度单位是一致的,就像是\(l=vt\),\(\Delta t\)的步长单位是\(m/s\),是时间单位的倒数。
而利用二阶导数迭代步长就符合单位一致(如Newton方法):
\]
其中\(H\)为Hessian矩阵。
又注意到:
\]
于是,完全体的ADADELTA方法变为如下:
\]
分子式\(t-1\)的原因式\(\Delta x_t\)压根不知道,所木有办法,就将就一下。
算法
完整的算法如下:
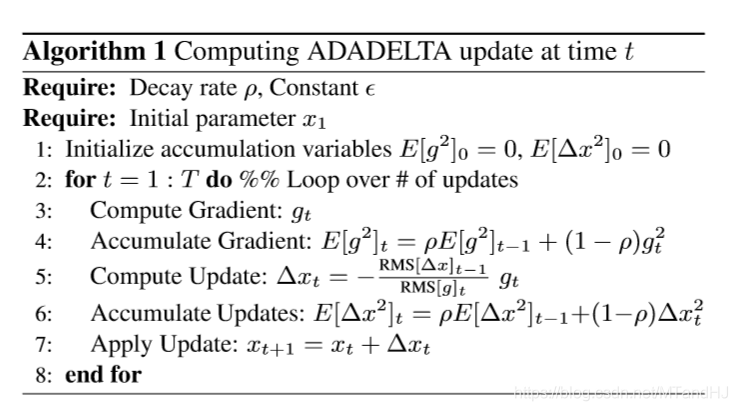
需要注意一点的是,在实际实验中,我们设置\(E[\Delta x^2]_0=1\)而不是如算法中所说的0。因为,如果设置为0,那么意味着第一步只进行相当微小的迭代,所以之后也都是微小的迭代。或许作者是将\(\epsilon\)设置为\(1\)?而不是一个小量?
ADADELTA 代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
这次用比较怪一点的方式来写,首先,创建一个类,用来存放函数\(f\)和梯度\(g\)
class ADADELTA:
def __init__(self, function, gradient, rho=0.7):
assert hasattr(function, "__call__"), "Invalid function"
assert hasattr(gradient, "__call__"), "Invalid gradient"
assert 0 < rho < 1, "Invalid rho"
self.__function = function
self.__gradient = gradient
self.rho = rho
self.acc_gradient = 0 #初始化accumulate gradient
self.acc_updates = 1 #初始化accumulate updates
self.progress = []
@property
def function(self):
return self.__function
@property
def gradient(self):
return self.__gradient
def reset(self):
self.acc_gradient = 0 #初始化accumulate gradient
self.acc_updates = 1 #初始化accumulate updates
self.progress = []
计算累计梯度
\]
def accumulate_gradient(self, gt):
self.acc_gradient = self.rho * self.acc_gradient \
+ (1 - self.rho) * gt ** 2
return self.acc_gradient
ADADELTA.accumulate_gradient = accumulate_gradient
更新\(E[\Delta x]_t\)
\]
def accumulate_updates(self, deltax):
self.acc_updates = self.rho * self.acc_updates \
+ (1 - self.rho) * deltax ** 2
return self.acc_updates
ADADELTA.accumulate_updates = accumulate_updates
计算更新步长:
\]
def step(self, x, smoothingterm=1e-8):
gt = self.gradient(x)
self.accumulate_gradient(gt)
RMS_gt = np.sqrt(self.acc_gradient + smoothingterm)
RMS_up = np.sqrt(self.acc_updates + smoothingterm)
deltax = -RMS_up / RMS_gt * gt
self.accumulate_updates(deltax)
return x + deltax
ADADELTA.step = step
进行t步
def process(self, startx, t, smoothingterm=1e-8):
x = startx
for i in range(t):
self.progress.append(x)
x = self.step(x, smoothingterm)
return self.progress
ADADELTA.process = process
可视化
def plot(self):
x = np.arange(1, len(self.progress) + 1)
y = np.array([
self.function(item) for item in self.progress
])
fig, ax = plt.subplots(constrained_layout=True)
ax.plot(x, y)
ax.set_xlabel("steps")
ax.set_ylabel("value of function")
ax.set_title("value with steps")
plt.show()
ADADELTA.plot = plot
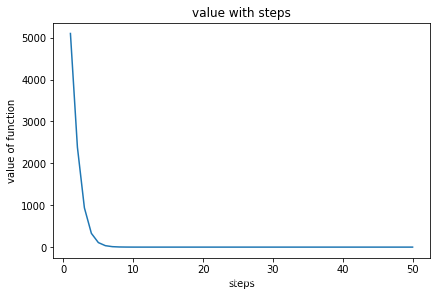
def function(x):
return x[0] ** 2 + 50 * x[1] ** 2
def gradient(x):
return 2 * x[0] + 100 * x[1]
test = ADADELTA(function, gradient, 0.9)
test.reset()
startx = np.array([10, 10])
test.process(startx, 50)
test.plot()
ADADELTA: AN ADAPTIVE LEARNING RATE METHOD的更多相关文章
- Deep Learning 32: 自己写的keras的一个callbacks函数,解决keras中不能在每个epoch实时显示学习速率learning rate的问题
一.问题: keras中不能在每个epoch实时显示学习速率learning rate,从而方便调试,实际上也是为了调试解决这个问题:Deep Learning 31: 不同版本的keras,对同样的 ...
- Keras 自适应Learning Rate (LearningRateScheduler)
When training deep neural networks, it is often useful to reduce learning rate as the training progr ...
- Dynamic learning rate in training - 培训中的动态学习率
I'm using keras 2.1.* and want to change the learning rate during training. I know about the schedul ...
- mxnet设置动态学习率(learning rate)
https://blog.csdn.net/xiaotao_1/article/details/78874336 如果learning rate很大,算法会在局部最优点附近来回跳动,不会收敛: 如果l ...
- 学习率(Learning rate)的理解以及如何调整学习率
1. 什么是学习率(Learning rate)? 学习率(Learning rate)作为监督学习以及深度学习中重要的超参,其决定着目标函数能否收敛到局部最小值以及何时收敛到最小值.合适的学习率 ...
- 跟我学算法-吴恩达老师(mini-batchsize,指数加权平均,Momentum 梯度下降法,RMS prop, Adam 优化算法, Learning rate decay)
1.mini-batch size 表示每次都只筛选一部分作为训练的样本,进行训练,遍历一次样本的次数为(样本数/单次样本数目) 当mini-batch size 的数量通常介于1,m 之间 当 ...
- learning rate warmup实现
def noam_scheme(global_step, num_warmup_steps, num_train_steps, init_lr, warmup=True): ""& ...
- pytorch learning rate decay
关于learning rate decay的问题,pytorch 0.2以上的版本已经提供了torch.optim.lr_scheduler的一些函数来解决这个问题. 我在迭代的时候使用的是下面的方法 ...
- machine learning (5)---learning rate
degugging:make sure gradient descent is working correctly cost function(J(θ)) of Number of iteration ...
随机推荐
- JavaScript小数、百分数的转换
百分数转化为小数 function toPoint(percent){ var str=percent.replace("%",""); str= str/10 ...
- 【leetcode】15. 3 Sum 双指针 压缩搜索空间
Given an integer array nums, return all the triplets [nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]] such that i != j, i ...
- Linux服务器---xopps
XOOPS XOOPS是一款用php制作的开源网站管理系统,可用于构建各种网络站点. 1.下载XOOPS软件(https://xoops.org/) 2.将XOOPS软件中的htdocs文件夹拷贝到a ...
- Can a C++ class have an object of self type?
A class declaration can contain static object of self type,it can also have pointer to self type,but ...
- spring boot @EnableWebMvc禁用springMvc自动配置原理。
说明: 在spring boot中如果定义了自己的java配置文件,并且在文件上使用了@EnableWebMvc 注解,那么sprig boot 的默认配置就会失效.如默认的静态文件配置路径:&quo ...
- 01 - Vue3 UI Framework - 开始
写在前面 一年多没写过博客了,工作.生活逐渐磨平了棱角. 写代码容易,写博客难,坚持写高水平的技术博客更难. 技术控决定慢慢拾起这份坚持,用作技术学习的阶段性总结. 返回阅读列表点击 这里 开始 大前 ...
- SimpleCursorAdapter 原理和实例
SimpleCursorAdapter 1. 原理参见下面代码注释 Cursor cursor = dbHelper.fetchAllCountries(); //cursor中存储需要加载到list ...
- 微前端框架 qiankun 技术分析
我们在single-spa 技术分析 基本实现了一个微前端框架需要具备的各种功能,但是又实现的不够彻底,遗留了很多问题需要解决.虽然官方提供了很多样例和最佳实践,但是总显得过于单薄,总给人一种&quo ...
- MemoryCache 如何清除全部缓存?
最近有个需求需要定时清理服务器上所有的缓存.本来以为很简单的调用一下 MemoryCache.Clear 方法就完事了.谁知道 MemoryCache 类以及 IMemoryCache 扩展方法都没有 ...
- ss命令用来显示处于活动状态的套接字信息。
ss命令用来显示处于活动状态的套接字信息.ss命令可以用来获取socket统计信息,它可以显示和netstat类似的内容.但ss的优势在于它能够显示更多更详细的有关TCP和连接状态的信息,而且比net ...
