Sending e-mail with Spring MVC---reference
reference from:http://www.codejava.net/frameworks/spring/sending-e-mail-with-spring-mvc
Table of contents:
1.Spring framework’s support for e-mail
3.Creating e-mail sending form
4.Configuring SMTP server settings and Spring MVC
5.Creating Spring MVC controller class
6.Creating result page and error page
8.Download Eclipse project/WAR file
This tutorial provides a sample spring MVC application that allows user sending an e-mail message by filling a web form. The e-mail form looks like following screenshot:
In this tutorial, you are supposed to familiar with Java EE development as well as developing Spring MVC-based applications.
1. Spring framework’s support for e-mail
Based on JavaMail, Spring framework provides high-level abstraction API which greatly simplifies e-mail sending process. Let’s take a brief look at this API in the following class diagram:
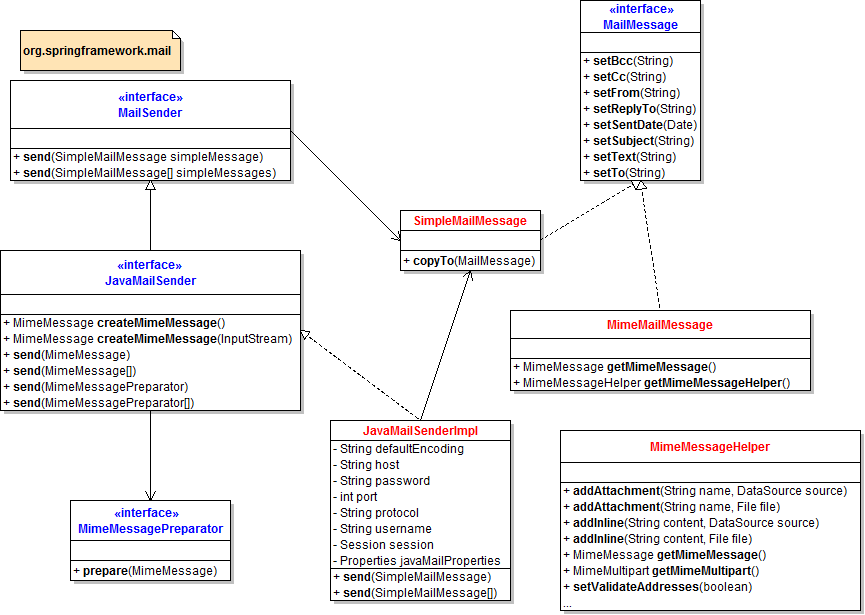
To send e-mail messages, we can use an implementation of interface MailSender – the JavaMailSenderImpl class which is built upon on JavaMail. It’s convenient to configure this implementation as a bean in Spring’s context:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
<bean id="mailSender" class="org.springframework.mail.javamail.JavaMailSenderImpl"> <!-- SMTP settings --> <property name="host" value="SMTP_HOST" /> <property name="port" value="SMTP_PORT" /> <property name="username" value="USER_NAME" /> <property name="password" value="PASSWORD" /> <property name="javaMailProperties"> <!-- additional properties specific to JavaMail --> <props> <prop key="mail.transport.protocol">smtp</prop> <prop key="mail.smtp.auth">true</prop> <prop key="mail.smtp.starttls.enable">true</prop> </props> </property></bean> |
This bean holds properties for SMTP and JavaMail and can be injected to a business/service class which needs to send an e-mail, for example:
|
1
|
mailSender.send(email); |
In which email is an object of a type that implements MailMessage interface, such as SimpleMailMessage class. We can construct the email object as follows:
|
1
2
3
4
|
SimpleMailMessage email = new SimpleMailMessage();email.setTo(toAddress);email.setSubject(subject);email.setText(body); |
That’s for a simple mail message (plain text). In case if we want to send HTML e-mail or attach files to the e-mail, we can useMimeMailMessage class with the help of MimeMessagePreparator class and MimeMessageHelper class. For example, sending an e-mail in HTML format with an attachment:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
mailSender.send(new MimeMessagePreparator() { public void prepare(MimeMessage mimeMessage) throws MessagingException { MimeMessageHelper message = new MimeMessageHelper(mimeMessage, true, "UTF-8"); message.setFrom(fromEmail); message.setTo(toEmail); message.setSubject("A file for you"); message.setText("<b>See the attached</b>", true); message.addAttachment("CoolStuff.doc", new File("CoolStuff.doc")); }}); |
The following table summarizes the interfaces and classes provided in org.springframework.mail package:
|
org.springframework.mail |
|
Click on a link in the table to see API documentation for the corresponding interface/class.
2. Required jar files
The application requires the following jar files copied to its WEB-INF\lib directory:
|
Required jar files |
|
|
mail.jar |
|
|
spring-beans-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar spring-context-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar spring-context-support-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar spring-core-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar spring-expression-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar spring-web-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar spring-webmvc-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar |
|
|
commons-logging-1.1.1.jar |
|
NOTE: Click on a hyperlink in the table above to download the corresponding software.
The sample application we are going to build contains the following key files:
- EmailForm.jsp: displays an e-mail form.
- Result.jsp: shows successful message after the e-mail has been sent.
- Error.jsp: shows error message in case of an exception is thrown.
- SendEmailController.java: the Spring controller class that takes input from e-mail form, calls Spring’s mailSender to send the e-mail, and redirects user to either successful page or error page.
- spring-mvc.xml: Spring’s context configuration file. Here we will configure SMTP server settings and various properties for JavaMail.
- web.xml: web deployment descriptor file.
3. Creating e-mail sending form
Create a JSP file called EmailForm.jsp with the following HTML code:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%><!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"><title>Email with Spring MVC</title></head><body> <center> <h1>Sending e-mail with Spring MVC</h1> <form method="post" action="sendEmail.do"> <table border="0" width="80%"> <tr> <td>To:</td> <td><input type="text" name="recipient" size="65" /></td> </tr> <tr> <td>Subject:</td> <td><input type="text" name="subject" size="65" /></td> </tr> <tr> <td>Message:</td> <td><textarea cols="50" rows="10" name="message"></textarea></td> </tr> <tr> <td colspan="2" align="center"> <input type="submit" value="Send E-mail" /> </td> </tr> </table> </form> </center></body></html> |
This is a simple form with three fields: To, Subject and Message – which are necessary attributes for a simple outgoing e-mail message. On submitting this form, the action named “sendEmail.do” will be called, as specified by the form’s action attribute. We will implement a Spring controller class for handling this action in the next section.
4. Configuring SMTP server settings and Spring MVC
Create a Spring context configuration file called spring-mvc.xml with the following XML code:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="net.codejava.spring" /> <bean id="mailSender" class="org.springframework.mail.javamail.JavaMailSenderImpl"> <property name="host" value="smtp.gmail.com" /> <property name="port" value="587" /> <property name="username" value="youremail" /> <property name="password" value="yourpassword" /> <property name="javaMailProperties"> <props> <prop key="mail.transport.protocol">smtp</prop> <prop key="mail.smtp.auth">true</prop> <prop key="mail.smtp.starttls.enable">true</prop> </props> </property> </bean> <bean id="viewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <property name="prefix" value="/" /> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp" /> </bean> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleMappingExceptionResolver"> <property name="exceptionMappings"> <props> <prop key="java.lang.Exception">Error</prop> </props> </property> </bean> </beans> |
This configuration is pretty straightforward:
- <context:component-scan ... />: tells Spring to scan the package net.codejava.spring for initializing components which are annotated by Spring annotations (It’s a Spring controller class, in case of this application).
- Bean mailSender: this is the important part because it declares a Spring bean for e-mail implementation – theJavaMailSenderImpl class and configures SMTP server settings, which is for a Gmail account in this case. This bean will be injected to a Spring controller class which will be covered in the next section.
- Bean viewResolver: maps logical view names to real JSP file names.
- Bean SimpleMappingExceptionResolver: maps all exceptions of type java.lang.Exception to be handled byError.jsp page.
The web deployment descriptor file (web.xml) is configured as follows:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0"> <display-name>EmailSpringMVC</display-name> <servlet> <servlet-name>SpringController</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/spring-mvc.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>SpringController</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>EmailForm.jsp</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list></web-app> |
It declares Spring controller servlet with its context configuration file (/WEB-INF/spring-mvc.xml). The controller is configured to handle all requests whose URL end with pattern: *.do. And the default page when accessing the application is the email form (EmailForm.jsp).
5. Creating Spring MVC controller class
In order to handle submission from the e-mail form, we need to create a Spring controller class as follows:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
package net.codejava.spring;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.mail.SimpleMailMessage;import org.springframework.mail.javamail.JavaMailSender;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;@Controller@RequestMapping("/sendEmail.do")public class SendEmailController { @Autowired private JavaMailSender mailSender; @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST) public String doSendEmail(HttpServletRequest request) { // takes input from e-mail form String recipientAddress = request.getParameter("recipient"); String subject = request.getParameter("subject"); String message = request.getParameter("message"); // prints debug info System.out.println("To: " + recipientAddress); System.out.println("Subject: " + subject); System.out.println("Message: " + message); // creates a simple e-mail object SimpleMailMessage email = new SimpleMailMessage(); email.setTo(recipientAddress); email.setSubject(subject); email.setText(message); // sends the e-mail mailSender.send(email); // forwards to the view named "Result" return "Result"; }} |
This controller class is quite simple. It is declared as a Spring MVC controller by the annotation @Controller, and is mapped to the e-mail form’s action by the @RequestMapping annotation. We inject the mailSender bean declared in spring-mvc.xml file into this controller through the private field also named mailSender. The injection is done automatically by Spring as we use the @Autowired annotation.
The method doSendEmail()is responsible for capturing input from e-mail form, creating a SimpleMailMessage object and sending the e-mail by invoking the send() method on the mailSender bean. The e-mail is in plain text format. Finally, it returns a view named “Result” which causes Spring to use the viewResolver to find and load appropriate JSP file (Result.jsp).
6. Creating result page and error page
Code the Result.jsp file as follows:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%><!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"><title>Send e-mail result</title></head><body> <center> <h2>Thank you, your email has been sent.</h2> </center></body></html> |
And code the Error.jsp as follows:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%><!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"><title>Error</title></head><body> <center> <h2>Sorry, the email was not sent because of the following error:</h2> <h3>${exception.message}</h3> </center></body></html> |
As we can see, the result page simply tells the user that the e-mail has been sent, while the error page displays an error message if any exception thrown during the process of sending e-mail.
7. Run the application
So far we have created all the key pieces of the application. Let’s deploy it on a servlet container like Tomcat, and access the application by typing the following URL into browser’s address bar (your host name and port number maybe different, depending on server configuration):
http://localhost:8080/EmailSpringMVC
The e-mail form is displayed, type in required information:
Hit Send E-mail button, it may take a while for the e-mail to be sent. A successful message comes from the result page in case everything is going well:
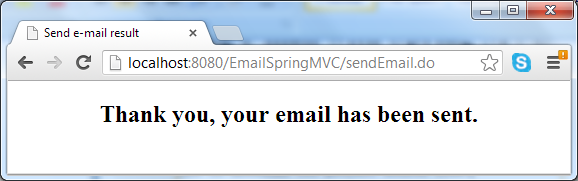
In case of error (such as network failure or the SMTP server could not be reached), the error page displays:
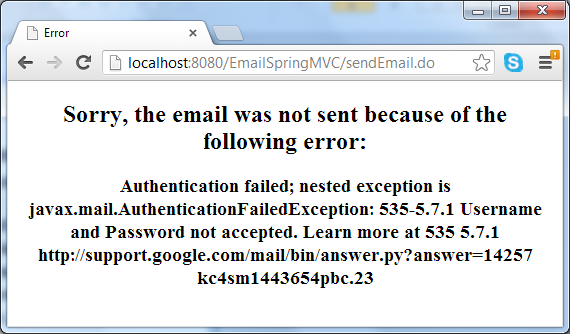
You can download the sample application as an Eclipse project or deployable WAR file in the attachment section, and remember to update SMTP settings to match your e-mail account.
Sending e-mail with Spring MVC---reference的更多相关文章
- Spring MVC Hello World Example(转)
Spring 3 You may interest at this Spring 3 MVC hello world example. In Spring MVC web application, i ...
- Spring Boot Reference Guide
Spring Boot Reference Guide Authors Phillip Webb, Dave Syer, Josh Long, Stéphane Nicoll, Rob Winch, ...
- Spring MVC Hibernate MySQL Integration(集成) CRUD Example Tutorial【摘】
Spring MVC Hibernate MySQL Integration(集成) CRUD Example Tutorial We learned how to integrate Spring ...
- 我是如何进行Spring MVC文档翻译项目的环境搭建、项目管理及自动化构建工作的
感兴趣的同学可以关注这个翻译项目 . 我的博客原文 和 我的Github 前段时间翻译的Spring MVC官方文档完成了第一稿,相关的文章和仓库可以点击以下链接.这篇文章,主要是总结一下这个翻译项目 ...
- Spring MVC 框架的架包分析,功能作用,优点
由于刚搭建完一个MVC框架,决定分享一下我搭建过程中学习到的一些东西.我觉得不管你是个初级程序员还是高级程序员抑或是软件架构师,在学习和了解一个框架的时候,首先都应该知道的是这个框架的原理和与其有关j ...
- spring mvc 快速入门
---------- 转自尚学堂 高淇 --------- Spring MVC 背景介绍 Spring 框架提供了构建 Web 应用程序的全功能 MVC 模块.使用 Spring 可插入的 MVC ...
- (转载)spring mvc DispatcherServlet详解之一---处理请求深入解析
要深入理解spring mvc的工作流程,就需要先了解spring mvc的架构: 从上图可以看到 前端控制器DispatcherServlet在其中起着主导作用,理解了DispatcherServl ...
- Spring MVC 学习总结(二)——控制器定义与@RequestMapping详解
一.控制器定义 控制器提供访问应用程序的行为,通常通过服务接口定义或注解定义两种方法实现. 控制器解析用户的请求并将其转换为一个模型.在Spring MVC中一个控制器可以包含多个Action(动作. ...
- Spring MVC学习笔记——Welcome
参考: http://blog.csdn.net/hehexiaoyou/article/details/23747617 http://www.codingyun.com/article/47.ht ...
- Spring MVC Integration,Spring Security
http://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/4.2.0.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#authorize-reque ...
随机推荐
- 今天,安装了一个GANGLIA玩玩,以后再测试NAGIOS吧。
说不定以后派得上用场呢.. 还有,NGINX也要学,不能老是凭站IIS,APACHE混饭吃吧,现在它都这么流行了..新浪,网易,腾讯.
- [QuickX]xcode运行Quick-cocos2d-x项目时自动更新lua资源文件
1.项目设置 build settings ->build options ->Scan all source files and Includes = YES 2.加入script (1 ...
- 透过表象看本质!?之二——除了最小p乘,还有PCA
如图1所示,最小p乘法求得是,而真实值到拟合曲线的距离为.那么,对应的是什么样的数据分析呢? 图1 最小p乘法的使用的误差是.真实值到拟合曲线的距离为 假如存在拟合曲线,设直线方程为.真实值到该曲线的 ...
- 一起啃PRML - 1.2 Probability Theory 概率论
一起啃PRML - 1.2 Probability Theory @copyright 转载请注明出处 http://www.cnblogs.com/chxer/ A key concept in t ...
- 通过新的 Azure 媒体服务资源管理器工具管理媒体工作流
Xavier Pouyat Azure 媒体服务高级项目经理 几个月前,一家广播公司找到了我,希望我向他们提供一种图形界面工具,好让他们使用 Azure媒体服务来上传.管理资产并对资产进行编 ...
- android layout 属性大全
第一类:属性值为true可false android:layout_centerHrizontal 水平居中 android:layout_centerVertical 垂直居中 android:la ...
- 如何将数据库中已有表导入到powerDesigner生成pdm文件
1.create new PDM: 2.select database menu; 3.click Reverse Engineer database :4.then choose your scr ...
- HDU-2975 Billboard
Billboard Time Limit : 20000/8000ms (Java/Other) Memory Limit : 32768/32768K (Java/Other) Total Su ...
- js 获取 sktime时间
效果图如下: HTML代码: <html> <head> <script> //------------------------------------------ ...
- PHP配置图文教程
组合解释:lamp,其英文译为灯,可以方便记忆.其实每个字母代表的是一个英文缩写.l-->Linux,a-->Apache,m-->MySql,p-->PHP 由于以上资源都是 ...
