TensorFlow从入门到理解(五):你的第一个循环神经网络RNN(回归例子)
运行代码:
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt BATCH_START = 0
TIME_STEPS = 20
BATCH_SIZE = 50
INPUT_SIZE = 1
OUTPUT_SIZE = 1
CELL_SIZE = 10
LR = 0.006 def get_batch():
global BATCH_START, TIME_STEPS
# xs shape (50batch, 20steps)
xs = np.arange(BATCH_START, BATCH_START+TIME_STEPS*BATCH_SIZE).reshape((BATCH_SIZE, TIME_STEPS)) / (10*np.pi)
seq = np.sin(xs)
res = np.cos(xs)
BATCH_START += TIME_STEPS
# plt.plot(xs[0, :], res[0, :], 'r', xs[0, :], seq[0, :], 'b--')
# plt.show()
# returned seq, res and xs: shape (batch, step, input)
return [seq[:, :, np.newaxis], res[:, :, np.newaxis], xs] class LSTMRNN(object):
def __init__(self, n_steps, input_size, output_size, cell_size, batch_size):
self.n_steps = n_steps
self.input_size = input_size
self.output_size = output_size
self.cell_size = cell_size
self.batch_size = batch_size
with tf.name_scope('inputs'):
self.xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_steps, input_size], name='xs')
self.ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, n_steps, output_size], name='ys')
with tf.variable_scope('in_hidden'):
self.add_input_layer()
with tf.variable_scope('LSTM_cell'):
self.add_cell()
with tf.variable_scope('out_hidden'):
self.add_output_layer()
with tf.name_scope('cost'):
self.compute_cost()
with tf.name_scope('train'):
self.train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(LR).minimize(self.cost) def add_input_layer(self,):
l_in_x = tf.reshape(self.xs, [-1, self.input_size], name='2_2D') # (batch*n_step, in_size)
# Ws (in_size, cell_size)
Ws_in = self._weight_variable([self.input_size, self.cell_size])
# bs (cell_size, )
bs_in = self._bias_variable([self.cell_size,])
# l_in_y = (batch * n_steps, cell_size)
with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'):
l_in_y = tf.matmul(l_in_x, Ws_in) + bs_in
# reshape l_in_y ==> (batch, n_steps, cell_size)
self.l_in_y = tf.reshape(l_in_y, [-1, self.n_steps, self.cell_size], name='2_3D') def add_cell(self):
lstm_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell(self.cell_size, forget_bias=1.0, state_is_tuple=True)
with tf.name_scope('initial_state'):
self.cell_init_state = lstm_cell.zero_state(self.batch_size, dtype=tf.float32)
self.cell_outputs, self.cell_final_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(
lstm_cell, self.l_in_y, initial_state=self.cell_init_state, time_major=False) def add_output_layer(self):
# shape = (batch * steps, cell_size)
l_out_x = tf.reshape(self.cell_outputs, [-1, self.cell_size], name='2_2D')
Ws_out = self._weight_variable([self.cell_size, self.output_size])
bs_out = self._bias_variable([self.output_size, ])
# shape = (batch * steps, output_size)
with tf.name_scope('Wx_plus_b'):
self.pred = tf.matmul(l_out_x, Ws_out) + bs_out def compute_cost(self):
losses = tf.contrib.legacy_seq2seq.sequence_loss_by_example(
[tf.reshape(self.pred, [-1], name='reshape_pred')],
[tf.reshape(self.ys, [-1], name='reshape_target')],
[tf.ones([self.batch_size * self.n_steps], dtype=tf.float32)],
average_across_timesteps=True,
softmax_loss_function=self.ms_error,
name='losses'
)
with tf.name_scope('average_cost'):
self.cost = tf.div(
tf.reduce_sum(losses, name='losses_sum'),
self.batch_size,
name='average_cost')
tf.summary.scalar('cost', self.cost) @staticmethod
def ms_error(labels, logits):
return tf.square(tf.subtract(labels, logits)) def _weight_variable(self, shape, name='weights'):
initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(mean=0., stddev=1.,)
return tf.get_variable(shape=shape, initializer=initializer, name=name) def _bias_variable(self, shape, name='biases'):
initializer = tf.constant_initializer(0.1)
return tf.get_variable(name=name, shape=shape, initializer=initializer) if __name__ == '__main__':
model = LSTMRNN(TIME_STEPS, INPUT_SIZE, OUTPUT_SIZE, CELL_SIZE, BATCH_SIZE)
sess = tf.Session()
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("logs", sess.graph)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init)
# relocate to the local dir and run this line to view it on Chrome (http://0.0.0.0:6006/):
# $ tensorboard --logdir='logs' plt.ion()
plt.show()
for i in range(200):
seq, res, xs = get_batch()
if i == 0:
feed_dict = {
model.xs: seq,
model.ys: res,
# create initial state
}
else:
feed_dict = {
model.xs: seq,
model.ys: res,
model.cell_init_state: state # use last state as the initial state for this run
} _, cost, state, pred = sess.run(
[model.train_op, model.cost, model.cell_final_state, model.pred],
feed_dict=feed_dict) # plotting
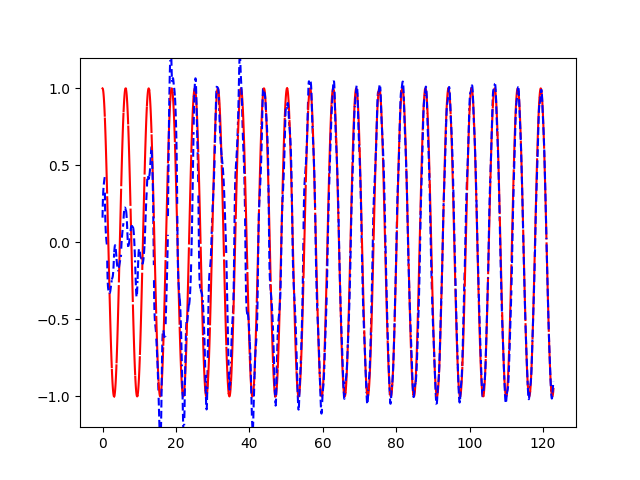
plt.plot(xs[0, :], res[0].flatten(), 'r', xs[0, :], pred.flatten()[:TIME_STEPS], 'b--')
plt.ylim((-1.2, 1.2))
plt.draw()
plt.pause(0.3) if i % 20 == 0:
print('cost: ', round(cost, 4))
result = sess.run(merged, feed_dict)
writer.add_summary(result, i)
运行结果:
TensorFlow从入门到理解(五):你的第一个循环神经网络RNN(回归例子)的更多相关文章
- TensorFlow从入门到理解(四):你的第一个循环神经网络RNN(分类例子)
运行代码: import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data # set rando ...
- TensorFlow从入门到理解
一.<莫烦Python>学习笔记: TensorFlow从入门到理解(一):搭建开发环境[基于Ubuntu18.04] TensorFlow从入门到理解(二):你的第一个神经网络 Tens ...
- 通过keras例子理解LSTM 循环神经网络(RNN)
博文的翻译和实践: Understanding Stateful LSTM Recurrent Neural Networks in Python with Keras 正文 一个强大而流行的循环神经 ...
- 基于TensorFlow的循环神经网络(RNN)
RNN适用场景 循环神经网络(Recurrent Neural Network)适合处理和预测时序数据 RNN的特点 RNN的隐藏层之间的节点是有连接的,他的输入是输入层的输出向量.extend(上一 ...
- TensorFlow从入门到理解(六):可视化梯度下降
运行代码: import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from mpl_toolkits.m ...
- TensorFlow从入门到理解(三):你的第一个卷积神经网络(CNN)
运行代码: from __future__ import print_function import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutoria ...
- TensorFlow从入门到理解(二):你的第一个神经网络
运行代码: from __future__ import print_function import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import matplo ...
- TensorFlow从入门到理解(一):搭建开发环境【基于Ubuntu18.04】
*注:教程及本文章皆使用Python3+语言,执行.py文件都是用终端(如果使用Python2+和IDE都会和本文描述有点不符) 一.安装,测试,卸载 TensorFlow官网介绍得很全面,很完美了, ...
- 循环神经网络-RNN入门
首先学习RNN需要一定的基础,即熟悉普通的前馈神经网络,特别是BP神经网络,最好能够手推. 所谓前馈,并不是说信号不能反向传递,而是网络在拓扑结构上不存在回路和环路. 而RNN最大的不同就是存在环路. ...
随机推荐
- 第三篇-以LinearLayout进行Android界面设计
一.新建一个项目 选择empty activity,此时项目里面没有main.java的文件. 二.手动创建java文件 Project那儿选择android模式,在app/java/com....一 ...
- 第二篇:用Android Studio编写Hello World
将Android Studio的环境搭建好后,第一个写Hello World测试程序.Android Studio v3.2.1. 一.新建工程 点击Start a new Android Studi ...
- golang与vscode的安装与配置
一.golang的下载与安装 以下都是win10的安装与配置 go语言官方下载地址:https://golang.org/dl/ 找到适合你系统的版本下载 傻瓜式安装开始... 二.golang环境变 ...
- 2019阿里校招测评题,光明小学完全图最短路径问题(python实现)
题目:光明小学的小朋友们要举行一年一度的接力跑大赛了,但是小朋友们却遇到了一个难题:设计接力跑大赛的线路,你能帮助他们完成这项工作么?光明小学可以抽象成一张有N个节点的图,每两点间都有一条道路相连.光 ...
- Day5--Python--字典
字典1.什么是字典 dict. 以{}表示,每一项用逗号隔开,内部元素用key:value的形式来保存数据 {'jj':'林俊杰','jay':'周杰伦'} 查询效率非常高,通过key来查找元素 内部 ...
- Go语言(IDEA下+Eclipse下)Hello World
第一步,去下载Go环境 然后安装即可. IDEA 先安装GO插件: ..点击Browse... ..搜索GO ..点击安装,安装完之后重启 ..重启完之后,New~(IDEA已经自动识别出系统中安装的 ...
- 洛谷 P2622 关灯问题II(状压DP入门题)
传送门 https://www.cnblogs.com/violet-acmer/p/9852294.html 题解: 相关变量解释: int n,m; ];//a[i][j] : 第i个开关对第j个 ...
- 退回win7后无法上网 的解决方法
如果网卡驱动没问题的话,那你是不是装了360安全卫士,如果装了你打开网络和共享中心———更改适配器设置————右键本地连接———属性————把360局域网防护驱动程序前面的对勾去掉然后确定,一般就能解 ...
- 【清北学堂2018-刷题冲刺】Contest 4
Task 1:序列 [问题描述] 小H原本有一个由连续的正整数组成的序列,如{4,5,6}或{10,11,12,13,14,15,16},但是她最近睡眠不足,只能记得其中的一些数字.她想知道,她最少 ...
- (基础) 平方和与立方和 hdu2007
平方和与立方和 链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2007 Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) ...
