【转载】XGBoost调参
- General Parameters: Guide the overall functioning
- Booster Parameters: Guide the individual booster (tree/regression) at each step
- Learning Task Parameters: Guide the optimization performed
general parameters
- booster [default=gbtree](基分类器类型)
- Select the type of model to run at each iteration. It has 2 options:
- gbtree: tree-based models
- gblinear: linear models
- Select the type of model to run at each iteration. It has 2 options:
- silent [default=0]:
- Silent mode is activated if set to 1, i.e. no running messages will be printed.
- It’s generally good to keep it 0 as the messages might help in understanding the model.
- nthread [default to maximum number of threads available if not set]
- This is used for parallel processing and number of cores in the system should be entered
- If you wish to run on all cores, value should not be entered and algorithm will detect automatically
booster parameters
Though there are 2 types of boosters, I’ll consider only tree booster here because it always outperforms the linear booster and thus the later is rarely used.
- eta [default=0.3](学习率,非常重要的参数)
- Analogous to learning rate in GBM
- Makes the model more robust by shrinking the weights on each step
- Typical final values to be used: 0.01-0.2
- min_child_weight [default=1](控制过拟合,如果太大会导致欠拟合)
- Defines the minimum sum of weights of all observations required in a child.(叶子节点中实例数 * 叶子节点的score)
- This is similar to min_child_leaf in GBM but not exactly. This refers to min “sum of weights” of observations while GBM has min “number of observations”.
- Used to control over-fitting. Higher values prevent a model from learning relations which might be highly specific to the particular sample selected for a tree.
- Too high values can lead to under-fitting hence, it should be tuned using CV.
- max_depth [default=6](最大深度,一般增加特征,深度变小)
- The maximum depth of a tree, same as GBM.
- Used to control over-fitting as higher depth will allow model to learn relations very specific to a particular sample.
- Should be tuned using CV.
- Typical values: 3-10
- max_leaf_nodes
- The maximum number of terminal nodes or leaves in a tree.
- Can be defined in place of max_depth. Since binary trees are created, a depth of ‘n’ would produce a maximum of 2^n leaves.
- If this is defined, GBM will ignore max_depth.
- gamma [default=0](分裂所需的最小损失减少值)
- A node is split only when the resulting split gives a positive reduction in the loss function. Gamma specifies the minimum loss reduction required to make a split.
- Makes the algorithm conservative. The values can vary depending on the loss function and should be tuned.
- max_delta_step [default=0]
- In maximum delta step we allow each tree’s weight estimation to be. If the value is set to 0, it means there is no constraint. If it is set to a positive value, it can help making the update step more conservative.
- Usually this parameter is not needed, but it might help in logistic regression when class is extremely imbalanced.
- This is generally not used but you can explore further if you wish.
- subsample [default=1](样本采样的比例,防止过拟合)
- Same as the subsample of GBM. Denotes the fraction of observations to be randomly samples for each tree.
- Lower values make the algorithm more conservative and prevents overfitting but too small values might lead to under-fitting.
- Typical values: 0.5-1
- colsample_bytree [default=1](特征采样的比例,防止过拟合)
- Similar to max_features in GBM. Denotes the fraction of columns to be randomly samples for each tree.
- Typical values: 0.5-1
- colsample_bylevel [default=1]
- Denotes the subsample ratio of columns for each split, in each level.
- I don’t use this often because subsample and colsample_bytree will do the job for you. but you can explore further if you feel so.
- lambda [default=1](L2正则化系数)
- L2 regularization term on weights (正则化系数)(analogous to Ridge regression)
- This used to handle the regularization part of XGBoost. Though many data scientists don’t use it often, it should be explored to reduce overfitting.
- alpha [default=0](L1正则化系数)
- L1 regularization term on weight (analogous to Lasso regression)
- Can be used in case of very high dimensionality so that the algorithm runs faster when implemented
- scale_pos_weight [default=1](正例的权重,如果使用对数损失,默认1即可)
- A value greater than 0 should be used in case of high class imbalance as it helps in faster convergence.
learning task parameters
These parameters are used to define the optimization objective the metric to be calculated at each step.
- objective [default=reg:linear](损失函数)
- This defines the loss function to be minimized. Mostly used values are:
- binary:logistic –logistic regression for binary classification, returns predicted probability (not class)
- multi:softmax –multiclass classification using the softmax objective, returns predicted class (not probabilities)
- you also need to set an additional num_class (number of classes) parameter defining the number of unique classes
- multi:softprob –same as softmax, but returns predicted probability of each data point belonging to each class.
- This defines the loss function to be minimized. Mostly used values are:
- eval_metric [ default according to objective ]
- The metric to be used for validation data.
- The default values are rmse for regression and error for classification.
- Typical values are:
- rmse – root mean square error
- mae – mean absolute error
- logloss – negative log-likelihood
- error – Binary classification error rate (0.5 threshold)
- merror – Multiclass classification error rate
- mlogloss – Multiclass logloss
- auc: Area under the curve
- seed [default=0](随机数种子,可指定多个不同的种子,训练不同的模型,然后ensemble)
- The random number seed.
- Can be used for generating reproducible results and also for parameter tuning.
General Approach for Parameter Tuning
- Choose a relatively high learning rate. Generally a learning rate of 0.1 works but somewhere between 0.05 to 0.3 should work for different problems. Determine the optimum number of trees for this learning rate. XGBoost has a very useful function called as “cv” which performs cross-validation at each boosting iteration and thus returns the optimum number of trees required.
- Tune tree-specific parameters ( max_depth, min_child_weight, gamma, subsample, colsample_bytree) for decided learning rate and number of trees. Note that we can choose different parameters to define a tree and I’ll take up an example here.
- Tune regularization parameters (lambda, alpha) for xgboost which can help reduce model complexity and enhance performance.
- Lower the learning rate and decide the optimal parameters .
先初始化一个比较大的学习率,然后利用xgboost自带的cv调整树的数目,其次调整树相关的参数,包括深度、最小孩子节点权重等,最后调整学习率
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import xgboost as xgb
from xgboost.sklearn import XGBClassifier
from sklearn import cross_validation, metrics
from sklearn.grid_search import GridSearchCV '''
xgb is the direct xgboost library.
XGBClassifier is an sklearn wrapper for XGBoost.This allows us to use sklearn's Grid Search with
parallel processing .
''' train = pd.read_csv("train_modified.csv")
target = "Disbursed"
IDcol = "ID" def modelfit(alg, dtrain, predictors, useTrainCV = True, cv_folds = 5, early_stopping_rounds = 50):
if useTrainCV:
xgb_param = alg.get_xgb_params()
xgtrain = xgb.DMatrix(dtrain[predictors].values, label = dtrain[target].values)
cvresult = xgb.cv(xgb_param, xgtrain, num_boost_round = alg.get_params()['n_estimators'],
nfold = cv_folds, metrics = 'auc', early_stopping_rounds = early_stopping_rounds)
alg.set_params(n_estimators = cvresult.shape[0])alg.fit(dtrain[predictors], dtrain[</span><span style="color: #800000">'</span><span style="color: #800000">Disbursed</span><span style="color: #800000">'</span>], eval_metric = <span style="color: #800000">'</span><span style="color: #800000">auc</span><span style="color: #800000">'</span><span style="color: #000000">) dtrain_predictions </span>=<span style="color: #000000"> alg.predict(dtrain[predictors])
dtrain_predprob </span>= alg.predict_proba(dtrain[predictors])[:,1<span style="color: #000000">] </span><span style="color: #0000ff">print</span> <span style="color: #800000">"</span><span style="color: #800000">\nModel Report</span><span style="color: #800000">"</span>
<span style="color: #0000ff">print</span> <span style="color: #800000">"</span><span style="color: #800000">Accuracy : %.4g</span><span style="color: #800000">"</span> % metrics.accuracy_score(dtrain[<span style="color: #800000">'</span><span style="color: #800000">Disbursed</span><span style="color: #800000">'</span><span style="color: #000000">].values, dtrain_predictions)
</span><span style="color: #0000ff">print</span> <span style="color: #800000">"</span><span style="color: #800000">AUC Score (Train): %f</span><span style="color: #800000">"</span> % metrics.roc_auc_score(dtrain[<span style="color: #800000">'</span><span style="color: #800000">Disbursed</span><span style="color: #800000">'</span><span style="color: #000000">], dtrain_predprob)
predictors = [x for x in train.columns if x not in [target, IDcol]]
xgb1 = XGBClassifier(learning_rate = 0.1, n_estimators = 1000, max_depth = 5, min_child_weight = 1, gamma = 0, subsample = 0.8,
colsample_bytree = 0.8, objective = 'binary:logistic', nthread = 4, scale_pos_weight = 1, seed = 27)
modelfit(xgb1, train, predictors)
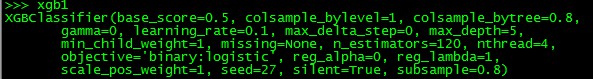
由上图可知,在给定learning_rate = 0.1的情况下,n_estimators = 120是最佳的树的个数
参考:
https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2016/03/complete-guide-parameter-tuning-xgboost-with-codes-python/
http://xgboost.readthedocs.io/en/latest/parameter.html#general-parameters
https://github.com/dmlc/xgboost/tree/master/demo/guide-python
http://xgboost.readthedocs.io/en/latest/python/python_api.html
【转载】XGBoost调参的更多相关文章
- Xgboost调参总结
一.参数速查 参数分为三类: 通用参数:宏观函数控制. Booster参数:控制每一步的booster(tree/regression). 学习目标参数:控制训练目标的表现. 二.回归 from xg ...
- xgboost 调参参考
XGBoost的参数 XGBoost的作者把所有的参数分成了三类: 1.通用参数:宏观函数控制. 2.Booster参数:控制每一步的booster(tree/regression). 3.学习目标参 ...
- 机器学习--Xgboost调参
Xgboost参数 'booster':'gbtree', 'objective': 'multi:softmax', 多分类的问题 'num_class':10, 类别数,与 multisoftma ...
- xgboost 调参 !
https://jessesw.com/XG-Boost/ http://blog.csdn.net/u010414589/article/details/51153310
- xgboost调参
The overall parameters have been divided into 3 categories by XGBoost authors: General Parameters: G ...
- xgboost调参过程
from http://blog.csdn.net/han_xiaoyang/article/details/52665396
- xgboost使用调参
欢迎关注博主主页,学习python视频资源 https://blog.csdn.net/q383700092/article/details/53763328 调参后结果非常理想 from sklea ...
- XGBoost和LightGBM的参数以及调参
一.XGBoost参数解释 XGBoost的参数一共分为三类: 通用参数:宏观函数控制. Booster参数:控制每一步的booster(tree/regression).booster参数一般可以调 ...
- LightGBM 调参方法(具体操作)
sklearn实战-乳腺癌细胞数据挖掘(博主亲自录制视频) https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005269003& ...
随机推荐
- mysql远程表/视图-应用
Date :20140213Auth: Jin参考http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_757b0e130101erl5.htmlhttp://dev.mysql.com/do ...
- HDU 2389 Rain on your Parade(二分匹配,Hopcroft-Carp算法)
Rain on your Parade Time Limit: 6000/3000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 655350/165535 K (Java/Ot ...
- MathType中带上下标字符不对其
如图,上面的好看,下面的就不好看的. 上面的图使用下图下面的形式,下面的图是用的是上面的形式. 如图可以看出,右侧的更好. 比如UiTVj这样的,需要分别都用下面的形式,不能UiT用上面的,Vj直接输 ...
- Microsoft office(2)多级标题的设置
在Microsoft office中要达到下面的标题结构: 1.首先将文字准备好: 2.将“绪论”,“无线...介绍”等章节标题分别选中 :段落-->大纲级别-->1级 3.同样的,“研究 ...
- 万里长征第二步——django个人博客(第七步 ——上传文件)
在项目目录下新建一个 ‘uploads’文件夹以保存上传的文件 配置setting.py文件 MEDIA_URL = '/uploads/' MEDIA_ROOT = os.path.join(BAS ...
- C#程序输出信息到调试窗口的几种方式
网站项目: System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine("aaa"); 控制项目:Console.WriteLine("bbb"); ...
- 一起talk GDB吧(第五回:GDB查看信息)
各位看官们.大家好,上一回中我们说的是GDB的调用栈调试功能,而且说了怎样使用GDB进行查看调用 栈.这一回中,我们继续介绍GDB的调试功能:查看信息.当然了.我们也会介绍怎样使用GDB查看程序 执行 ...
- 【转】go语言的字节序
原文:http://lihaoquan.me/2016/11/5/golang-byteorder.html 这个人的博客写的不错,品质也比较高. 我应该也要有这种精神,这种态度.深入到计算机的世界中 ...
- DevExpress.Build.v14.2
DevExpress.Build.v14.2 using Microsoft.Build.AppxPackage; using Microsoft.Build.Framework; using Sys ...
- 在Lucene或Solr中实现高亮的策略
一:功能背景 近期要做个高亮的搜索需求,曾经也搞过.所以没啥难度.仅仅只是原来用的是Lucene,如今要换成Solr而已,在Lucene4.x的时候,散仙在曾经的文章中也分析过怎样在搜索的时候实现高亮 ...
