异常处理(try...catch...final 和 throw , throws)
1.传统(弱语言)处理异常方式
原理:利用判断来控制异常出现
publicclass Test01 {
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入第一个数:");
intnum1 = 0;
if(sc.hasNextInt()) {
num1 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入第二个数:");
intnum2 = 0;
if(sc.hasNextInt()) {
num2 = sc.nextInt();
if(0 == num2) {
System.out.println("除数不能为0!");
}else {
intr = num1 / num2;
System.out.println("num1/num2 = "+r);
}
}else {
System.out.println("第二个数输入不是数字");
}
}else {
System.out.println("第一个数输入不是数字!");
}
}
}
这样做的缺点:
【1】通过判断处理异常影响执行效率。
【2】判断逻辑和业务逻辑交织在一起,不利于后期维护。
2.异常
异常是所有异常类的直接或间接父类。
异常是指在运行过程中发生了不正常的情况,这是它就会中断程序。
异常处理机制:指java中异常处理机制为程序提供处理异常的能力,从而使程序不中断的运行。
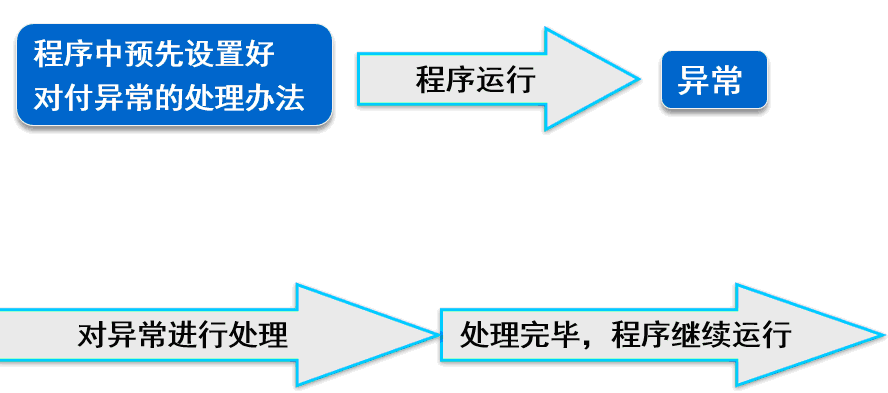
3.异常处理
异常处理的关键字有:try...catch 和 try...catch...finally
1)try...catch
解释:try— 把有可能产生异常的代码放到try代码块中,catch—负责捕获异常并匹配异常再处理异常。
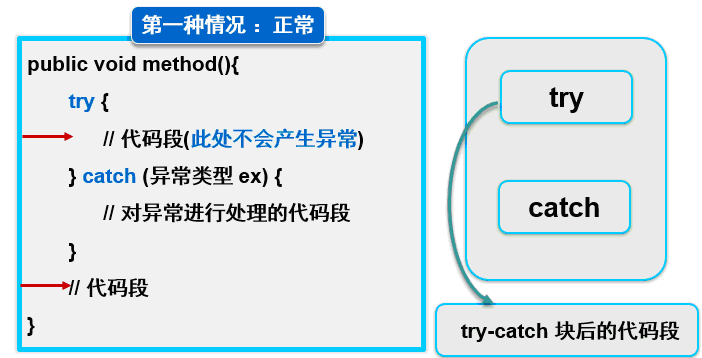
【1】正常执行,没有遇到异常
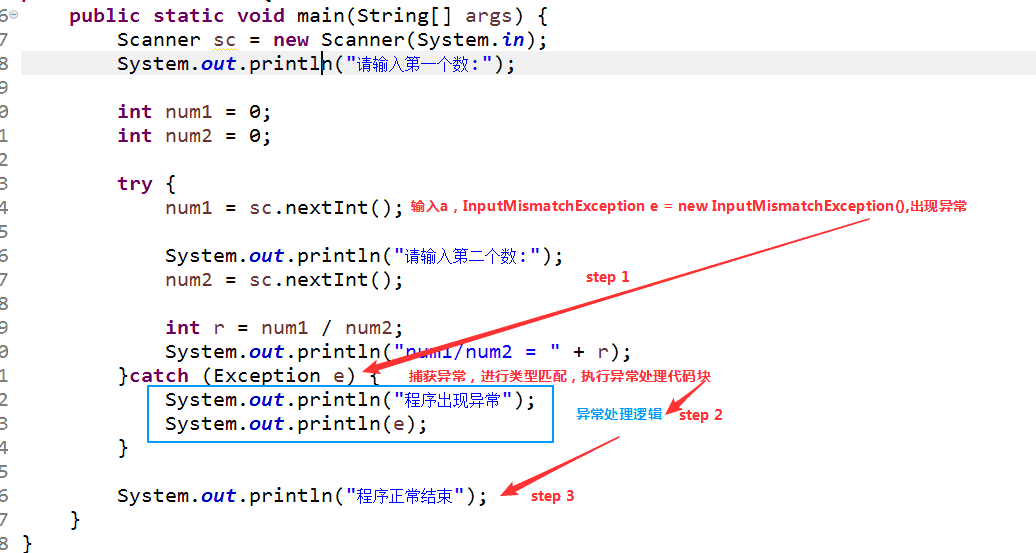
【2】出现异常,异常处理,正常结束。(红字是处理异常步骤)
异常常见方法:
prinStackTrace:打印异常的执行堆栈信息(在控制台中异常堆栈信息输出位置不固定)
java.util.InputMismatchException
at java.util.Scanner.throwFor(Scanner.java:864)
at java.util.Scanner.next(Scanner.java:1485)
at java.util.Scanner.nextInt(Scanner.java:2117)
at java.util.Scanner.nextInt(Scanner.java:2076)
at cn.sxt02.exception02.Test01.main(Test01.java:14)
一般,异常的堆栈信息很多,开发者只需要看懂
——第一行:异常简单的信息(异常类型,异常描述等)
——最后一行:异常出现的位置(如上的Test01.java:14)
getMessage:返回异常的描述信息
packagecn.sxt02.exception02;
importjava.util.Scanner;
publicclass Test01 {
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入第一个数:"); intnum1 = 0;
intnum2 = 0; try {
num1 = sc.nextInt(); System.out.println("请输入第二个数:");
num2 = sc.nextInt(); intr = num1 / num2;
System.out.println("num1/num2 = " + r);
}catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("程序出现异常");
// 打印异常的信息
// System.out.println(e.toString()); // 打印异常堆栈信息
e.printStackTrace(); // 返回异常的描述信息,如果没有信息,返回null(InputMismatchException没有描述信息)
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
} System.out.println("程序正常结束");
}
【3】异常类型不匹配
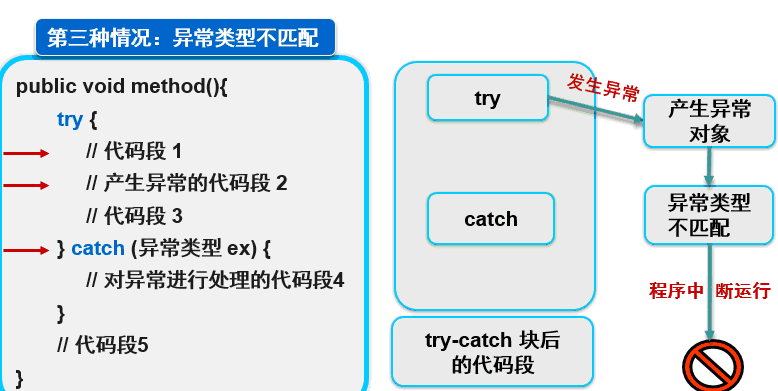
【4】多重catch
publicclass Test03 {
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入第一个数:");
intnum1 = 0;
intnum2 = 0;
try {
num1 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入第二个数:");
num2 = sc.nextInt();
intr = num1 / num2;
System.out.println("num1/num2 = " + r);
}catch (ArithmeticExceptione) {
System.out.println("数学计算异常:"+e.getMessage());
}catch(InputMismatchExceptione) {
System.out.println("输入不匹配异常:"+e.getMessage());
}catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("发送异常:"+e.getMessage());
}
System.out.println("程序正常结束");
}
}
2)try...catch...finally
解读:把有可能产生异常的代码放到try的代码块中,catch捕捉异常并匹配异常再处理异常,finally块用于收尾工作
(如关闭数据库,关闭文件,释放内存等资源)
注:finally :无论是否发生异常,finally都将执行,常用于收尾工作
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入第一个数:");
intnum1 = 0;
intnum2 = 0;
try {
num1 = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("请输入第二个数:");
num2 = sc.nextInt();
intr = num1 / num2;
System.out.println("num1/num2 = " + r);
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("程序出现异常");
} finally {
System.out.println("不管是否出现异常,finally都执行");
}
System.out.println("程序正常结束");
}
特殊情况:
【1】finally不执行的情况
System.exit(0)正常退出jvm,程序结束,不会执行finally
【2】catch可以省略,变成try...finally形式
4.return
当return存在于try...catch...finally时的执行顺序(return始终在最后)
packagecn.sxt02.exception03; /**
* 存在return的情况
*/
publicclass Test02 { publicstaticintdiv(inta, intb) { try {
intr = a / b;
returnr; } catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("出现异常"); return 0; } finally {
System.out.println("我是finally");
} } publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) { intr = Test02.div(10, 0);
System.out.println("r=" + r);
System.out.println("程序正常结束");
}
}
5.异常的分类
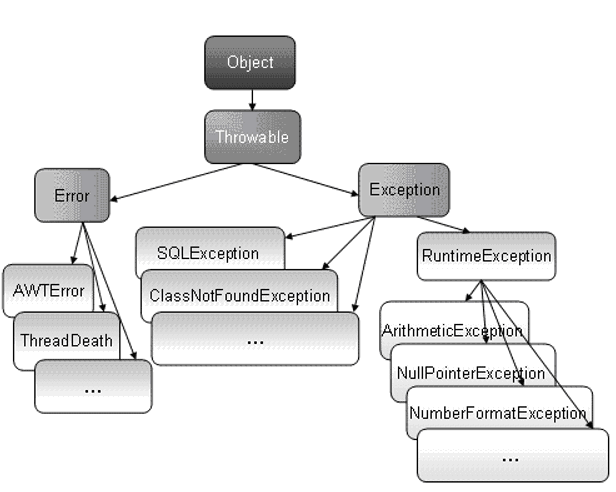
Throwable类是 Java 语言中所有错误(Error)或异常(Exception)的父类,只有当对象是此类(或其子类之一)的实例时,才能通过 Java 虚拟机或者 Java throw 语句抛出。
Error 类表示错误类。仅靠程序本身无法恢复的严重错误。如jvm内存耗尽、jvm崩溃等。
Exception类表示异常类,可以通过java 异常处理机制处理。
Exception根据是否处理分为两种情况。
RuntimeException:运行时异常。不要求程序必须做出处理。是所有运行时异常的父类。
CheckedException:检查时异常。要求程序必须处理,不处理编译不通过。
publicclass Test01 {
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) {
// 运行时异常
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// runtime exception
intr = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("r = "+ r);
// 检查时异常
SimpleDateFormatdf = newSimpleDateFormat();
try {
Date date = df.parse("2019");
} catch (ParseExceptione) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
常见的运行时异常
ArithmeticException:数学计算异常。如除数为0
InputMismatchException:输入不匹配异常。
ArrayIndexOutofBoundsException:数组下标越界异常。
NullPointException:空指针异常,对象没有初始化就使用时,jvm就会抛出该异常。
IllegalArgumentException:非法参数异常。
ClassCastException:强制类型转化异常。
NumberFormatException:数字格式化异常。如把“abc”格式化为数字。
常见的检查时异常:
ClassNotFoundException:类没有被发现异常。
SQLException:数据库相关异常
IOException:IO操作异常
ParseException:解析错误异常
FileNotFoundException:文件未发现异常。
运行时异常和检查时异常的区别:
运行时异常:包括RuntimeException及其所有子类。不要求程序必须对它们作出处理,比如InputMismatchException、 ArithmeticException、NullPointerException等。即使没有使用try-catch或throws进行处理,仍旧可以进行
编译和运行。如果运行时发生异常,会输出异常的堆栈信息并中止程序执行。
检查时异常:Checked异常(非运行时异常):除了运行时异常外的其他异常类都是Checked异常。程序必须捕获或者
声明抛出这种异常,否则出现编译错误,无法通过编译。处理方式包括两种:通过try-catch捕获异常,
通过throws声明抛出异常从而交给上一级调用方法处理
6.声明异常
1)throws关键字
解读:当一个方法可能存在异常,而此时自身又无法更好的处理,可以交给外界处理。此时用throws声明并抛出异常。
publicclass Test01 {
publicstaticintdiv(inta, intb) throws ArithmeticException{
intr = 0;
r = a / b;
returnr;
}
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) {
try {
Test01.div(10, 0);
} catch (ArithmeticExceptione) {
System.out.println("除数不能为0");
}
}
}
注:开发者可以根据需求声明检查时异常 (Exception或者非运行时异常及其子类) 和运行时异常(RuntimeException或其子类)
如果抛出异常后,调用处不知道如何处理异常,可以选择继续声明异常(抛出异常),这个过程叫做异常上抛。
publicclass Test01 {
publicstaticintdiv(inta, intb) throws Exception{
intr = 0;
r = a / b;
returnr;
}
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//【1】调用处知道如何处理!
/*
try {
Test01.div(10, 0);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
*/
// 【2】调用处也不知道如何处理
Test01.div(10, 0);
}
}
2)声明异常和重载的关系
声明异常和重载没有任何关系
publicclass Test01 {
publicstaticintdiv(inta, intb) throws Exception{
intr = 0;
r = a / b;
returnr;
}
publicstaticintdiv(inta, intb) {
intr = 0;
r = a / b;
returnr;
}
}
注:方法重载:
【1】方法名相同
【2】参数列表不同(个数,类型,不同类型的顺序不同)
【3】和返回值,修饰符,声明异常无关
3)声明异常和重写的关系
声明异常和方法重写有关系,关系如下
[1]父类方法声明了异常(检测时或运行时),子类可以不声明任何异常。
publicclass Father {
publicvoidshowInfo() throws Exception{
}
}
publicclass Son extendsFather{
@Override
publicvoidshowInfo(){
}
}
理解:父类方法抛出异常,子类在重写过程中把该异常处理掉了,所以子类方法不用声明异常。
[2] 父类方法声明没有声明任何异常(检测时或运行时),子类也不声明异常或者声明运行时异常。
publicclass Father {
publicvoidshowInfo(){
}
}
publicclass Son extendsFather{
@Override
publicvoidshowInfo() throws Exception{
}
}
[3]父类声明了异常(检测时或运行时),子类声明完全一样的异常。
publicclass Father {
publicvoidshowInfo() throwsException{
}
}
publicclass Son extendsFather{
@Override
publicvoidshowInfo() throwsException {
}
}
7.手动抛出异常
1)throw
除了系统自动抛出异常外,有些问题需要开发者手动抛出异常。使用关键字throw
packagecn.sxt02.exception06;
publicclass Student {
private String name;
private String gender;
public String getName() {
returnname;
}
publicvoidsetName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getGender() {
returngender;
}
publicvoidsetGender(String gender) throws Exception{
if(gender.equals("男") || gender.equals("女")) {
this.gender = gender;
}else {
thrownew Exception("性别不合法!");
}
}
publicStudent(String name, String gender) {
super();
this.name = name;
this.gender = gender;
}
publicStudent() {
super();
}
}
publicclass Test01 {
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args){
Student stu = newStudent();
stu.setName("二狗");
try {
stu.setGender("xxx");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}
2)自定义异常
理解:如果开发者需要手动抛出的异常在系统不存在,可以自定义异常。
注意:如果要自定义异常,首先要确定异常类型,如果异常是运行时异常,必须继承RuntimeException或其子类;如果异常是检查时异常,必须继承Exception或其子类。
——异常的命名方式,参考系统命名方式,以Exception结尾。
publicclassAgeExceptionextendsException{
publicAgeException() {
super();
}
publicAgeException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}
异常处理(try...catch...final 和 throw , throws)的更多相关文章
- Java基础学习总结(86)——Java异常处理机制Exception抛出异常时throw和throws用法详解
什么时运行时异常?什么是非运行时异常? 通俗的讲: 运行时异常:就是编译通过,运行时就崩了,比如数组越界. 非运行时异常:就是编译不通过,这时就得必须去处理了.不然就没法运行了. 全面的讲: Thro ...
- Java 异常处理 try catch finally throws throw 的使用和解读(一)
//最近的一个内部表决系统开发过程中,//发现对异常处理还存在一些模棱两可的地方,//所以想着整理一下//主要涉及到://1.try catch finally throws throw 的使用和解读 ...
- java异常处理之throw, throws,try和catch
转自 http://blog.csdn.net/zhouyong80/article/details/1907799 程序运行过程中可能会出现异常情况,比如被0除.对负数计算平方根等,还有可能会出现 ...
- Java基础-异常处理机制 及异常处理的五个关键字:try/catch/finally/throw /throws
笔记: /** 异常处理机制: 抓抛模型 * 1."抛", 一旦抛出,程序终止! printStackTrace()显示异常路径! * 2."抓", 抓住异常 ...
- Java throw throws try...catch区别
java里的异常多种多样,这是一种非常有用的机制,它能帮助我们处理那些我们未知的错误,在java里,关于异常的有throw throws,还有一个try catch 程序块.接下来我们挨个看看这几个的 ...
- java:异常机制(try,catch,finally,throw,throws,自定义异常)
* String类中的格式化字符串的方法: * public static String format(String format, Object... args):使用指定的格式字符串和参数返回一个 ...
- T-SQL编程中的异常处理-异常捕获(catch)与抛出异常(throw)
本文出处: http://www.cnblogs.com/wy123/p/6743515.html T-SQL编程与应用程序一样,都有异常处理机制,比如异常的捕获与异常的抛出,本文简单介绍异常捕获与异 ...
- C++异常处理解析: 异常的引发(throw), 捕获(try catch)、异常安全
前言: C++的异常处理机制是用于将运行时错误检测和错误处理功能分离的一 种机制(符合高内聚低耦合的软件工程设计要求), 这里主要总结一下C++异常处理的基础知识, 包括基本的如何引发异常(使用th ...
- 顺平讲try catch finally throw throws(精华)
try catch finally 有点像if else语句 还有像javascript的服务器执行成功后的回调函数,success:function(){ 进行处理 }; throws的意思是将异 ...
随机推荐
- [android] 轮播图-滑动图片标题焦点
谷歌提供的v4包,ViewPager 在布局文件中,先添加<android.support.v4.view.ViewPager/>控件,这个只是轮播的区域 在布局文件中,布置标题描述部分 ...
- LinkedBlockQueue生产消费源码解析
LinkedBlockQueue自JDK1.5以后提供的一种阻塞队列,遵循生产者消费者模式,实现了BlockQueue接口,如图 从它的名字可以了解到它是采用链表的方式实现了阻塞队列,并且定义了“节点 ...
- Spring Security(三)
Spring Security(三) 个性化用户认证流程 自定义登录页面 在配置类中指定登录页面和接收登录的 url @Configuration public class BrowserSecuri ...
- 畅通工程(hdu1232)并查集
畅通工程 Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) Total Submi ...
- Service 动态更新 UI
http://blog.csdn.net/u013724061/article/details/38642049 最终效果: 动态显示当前时间和电量 思路: 首先在Activity里用内部类定义两种广 ...
- ThinkPHP5微信扫码支付
1.把微信官网下载的demo放在根目录/vendor/目录下,这里我的是/vendor/wxpay_pc目录 2.把cert里面的文件替换成自己项目的证书(登陆微信商户平台,账户中心,API安全下载) ...
- Bootstrap4响应式布局之栅格系统
前面说了Bootstrap4的下载和简单使用,现在我们接着往下学习,Bootstrap4的响应式布局主要依靠栅格系统来实现的.面老K先来讲解一下Bootstrap4的栅格系统,让你能够更快的了解Boo ...
- idea 提交 Push rejected: Push to origin/master was rejected
idea中,发布项目到码云上,当时按照这样的流程添加Git,然后push,提示:push to origin/master war rejected". 解决方案如下: 1.切换到自己项目所 ...
- h5向上翻页图标晃动动画,css固定h5向上翻页图标在页面上
//html结构<div class='upImg'><div> //css .upImg { background-image: url(../images/01.png); ...
- 解决跨域问题之anywhere
anywhere搭建服务,ionic PC端和手机端可以通过网址来查看网页效果.解决跨域问题 大家都知道编写完HTML代码后,可以直接在pc端的浏览器查看,但现在手机端越来越广泛了,想跟在pc端查看网 ...
