【极角排序、扫描线】UVa 1606 - Amphiphilic Carbon Molecules(两亲性分子)
Shanghai Hypercomputers, the world's largest computer chip manufacturer, has invented a new class of nanoparticles called Amphiphilic Carbon Molecules (ACMs). ACMs are semiconductors. It means that they can be either conductors or insulators of electrons, and thus possess a property that is very important for the computer chip industry. They are also amphiphilic molecules, which means parts of them are hydrophilic while other parts of them are hydrophobic. Hydrophilic ACMs are soluble in polar solvents (for example, water) but are insoluble in nonpolar solvents (for example, acetone). Hydrophobic ACMs, on the contrary, are soluble in acetone but insoluble in water. Semiconductor ACMs dissolved in either water or acetone can be used in the computer chip manufacturing process.
As a materials engineer at Shanghai Hypercomputers, your job is to prepare ACM solutions from ACM particles. You go to your factory everyday at 8 am and find a batch of ACM particles on your workbench. You prepare the ACM solutions by dripping some water, as well as some acetone, into those particles and watch the ACMs dissolve in the solvents. You always want to prepare unmixed solutions, so you first separate the ACM particles by placing an Insulating Carbon Partition Card (ICPC) perpendicular to your workbench. The ICPC is long enough to completely separate the particles. You then drip water on one side of the ICPC and acetone on the other side. The ICPC helps you obtain hydrophilic ACMs dissolved in water on one side and hydrophobic ACMs dissolved in acetone on the other side. If you happen to put the ICPC on top of some ACM particles, those ACMs will be right at the border between the water solution and the acetone solution, and they will be dissolved. Fig.1 shows your working situation.
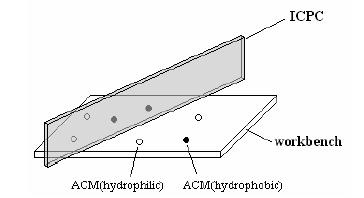
Your daily job is very easy and boring, so your supervisor makes it a little bit more challenging by asking you to dissolve as much ACMs into solution as possible. You know you have to be very careful about where to put the ICPC since hydrophilic ACMs on the acetone side, or hydrophobic ACMs on the water side, will not dissolve. As an experienced engineer, you also know that sometimes it can be very difficult to find the best position for the ICPC, so you decide to write a program to help you. You have asked your supervisor to buy a special digital camera and have it installed above your workbench, so that your program can obtain the exact positions and species (hydrophilic or hydrophobic) of each ACM particle in a 2D pictures taken by the camera. The ICPC you put on your workbench will appear as a line in the 2D pictures.
Input
There will be no more than 10 test cases. Each case starts with a line containing an integer N, which is the number of ACM particles in the test case. N lines then follow. Each line contains three integers x, y, r, where (x, y) is the position of the ACM particle in the 2D picture and r can be 0 or 1, standing for the hydrophilic or hydrophobic type ACM respectively. The absolute value of x, y will be no larger than 10000. You may assume that N is no more than 1000. N = 0 signifies the end of the input and need not be processed. Fig.2 shows the positions of ACM particles and the best ICPC position for the last test case in the sample input.
Output
For each test case, output a line containing a single integer, which is the maximum number of dissolved ACM particles.
Sample Input
3
0 0 0
0 1 0
2 2 1
4
0 0 0
0 4 0
4 0 0
1 2 1
7
-1 0 0
1 2 1
2 3 0
2 1 1
0 3 1
1 4 0
-1 2 0
0 【题意】 给定平面上的n个点,分别为黑色和白色,现在需要放置一条隔板,使得隔板一侧的白点数目加上另一侧的黑点总数最大。隔板上的点可以看做是在任意一侧; 【分析】 贪心策略:假设隔板一定经过至少两个点; 方法:①暴力枚举--先枚举两个点,然后输出两侧黑白点的个数。复杂度O(n^3).90%会TLE...;
②先找一个基准点,让隔板绕该点旋转。每当隔板扫过一个点就动态修改两侧的点数。在此之前,需对所有点相对于基准点(即将基准点看做(0,0))进行极角排序。复杂度O(n^2*logn);
【NOTE】 极角排序:通俗的说,就是根据坐标系内每一个点与x轴所成的角,逆时针比较,。按照角度从小到大的方式排序。用到的函数是atan2(y, x);
扫描线:这个概念也比较好理解。注意动态维护的时候细节问题(代码中会有详解,当然只针对自己这种第一次接触看不懂人家代码的菜)。
小技巧:因题目要求求两侧不同颜色的点数和,可以预处理将黑点做中心对称。这样原本位于两侧的黑白点的点就会分布在同一侧内了(真心巧妙。。。);
【代码】
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = ;
struct Node
{
int x, y;
double rad;
int col;
bool operator < (const Node& a) const
{
return rad < a.rad;
}
}node[maxn], tnode[maxn];
int Cross(Node a, Node b)
{
return (a.x*b.y - b.x*a.y) >= ;
}
int main()
{
//freopen("out.txt", "w", stdout) ;
int n, ans, cnt = ;
while(scanf("%d", &n) && n)
{
ans = ;
for(int i = ; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d%d", &node[i].x, &node[i].y, &node[i].col);
}
if(n <= ) {printf("%d\n", n); continue;}
cnt = ;
for(int basicp = ; basicp < n; basicp++) //基准点
{
for(int i = ; i < n; i++) //各点相对于基准点的坐标
{
if(i == basicp) continue;
tnode[cnt].x = node[i].x-node[basicp].x;
tnode[cnt].y = node[i].y-node[basicp].y;
if(node[i].col) {tnode[cnt].x = -tnode[cnt].x; tnode[cnt].y = -tnode[cnt].y;} //对黑点中心对称
tnode[cnt].rad = atan2(tnode[cnt].y, tnode[cnt].x); //求极角
cnt++;
}
sort(tnode, tnode+cnt); //极角排序。几何意义为由x轴正半轴逆时针旋转;
int l = , r = ; //l, r:求tnode[l~r]之间的点
int sum = ; //注意这个sum = 2;
while(l < cnt)
{
if(r == l) //主要针对初始情况
{
r=(r+)%cnt; sum++;
}
while(l != r&&Cross(tnode[l],tnode[r])) //Cross(tnode[l],tnode[r]) 叉积:若小于0则两点的夹角大于180度。跳出循环
{
r=(r+)%cnt; sum++;
}
sum--; //sum-1主要是为了在枚举新的起点时减去老的起点。而初始sum=2也是为了符合这一条件
l++; //枚举新的起点
ans=max(ans,sum);
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
return ;
}
【总结】 看代码很明显又是看了别人的。希望能长个教训吧,以后遇到类似的题自己能独立写出来、
【极角排序、扫描线】UVa 1606 - Amphiphilic Carbon Molecules(两亲性分子)的更多相关文章
- UVA 1606 Amphiphilic Carbon Molecules 两亲性分子 (极角排序或叉积,扫描法)
任意线可以贪心移动到两点上.直接枚举O(n^3),会TLE. 所以采取扫描法,选基准点,然后根据极角或者两两做叉积比较进行排排序,然后扫一遍就好了.旋转的时候在O(1)时间推出下一种情况,总复杂度为O ...
- uva 1606 amphiphilic carbon molecules【把缩写写出来,有惊喜】(滑动窗口)——yhx
Shanghai Hypercomputers, the world's largest computer chip manufacturer, has invented a new classof ...
- UVA - 1606 Amphiphilic Carbon Molecules 极角扫描法
题目:点击查看题目 思路:这道题的解决思路是极角扫描法.极角扫描法的思想主要是先选择一个点作为基准点,然后求出各点对于该点的相对坐标,同时求出该坐标系下的极角,按照极角对点进行排序.然后选取点与基准点 ...
- UVA - 1606 Amphiphilic Carbon Molecules (计算几何,扫描法)
平面上给你一些具有黑或白颜色的点,让你设置一个隔板,使得隔板一侧的黑点加上另一侧的白点数最多.隔板上的点可视作任意一侧. 易知一定存在一个隔板穿过两个点且最优,因此可以先固定以一个点为原点,将其他点中 ...
- UVa 1606 Amphiphilic Carbon Molecules (扫描法+极角排序)
题意:平面上有 n 个点,每个点不是黑的就是白的,现在要放一个隔板,把它们分成两部分,使得一侧的白点数加上另一侧的黑点数最多. 析:这个题很容易想到的就是暴力,不妨假设隔板至少经过两个点,即使不经过也 ...
- UVa 1606 - Amphiphilic Carbon Molecules
链接: https://uva.onlinejudge.org/index.php?option=com_onlinejudge&Itemid=8&page=show_problem& ...
- UVA - 1606 Amphiphilic Carbon Molecules(两亲性分子)(扫描法)
题意:平面上有n(n <= 1000)个点,每个点为白点或者黑点.现在需放置一条隔板,使得隔板一侧的白点数加上另一侧的黑点数总数最大.隔板上的点可以看做是在任意一侧. 分析:枚举每个基准点i,将 ...
- 【UVa】1606 Amphiphilic Carbon Molecules(计算几何)
题目 题目 分析 跟着lrj学的,理解了,然而不是很熟,还是发上来供以后复习 代码 #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; ; stru ...
- POJ 2280 Amphiphilic Carbon Molecules 极角排序 + 扫描线
从TLE的暴力枚举 到 13313MS的扫描线 再到 1297MS的简化后的扫描线,简直感觉要爽翻啦.然后满怀欣喜的去HDU交了一下,直接又回到了TLE.....泪流满面 虽说HDU的时限是2000 ...
随机推荐
- POJ 1287 Networking (最小生成树)
Networking 题目链接: http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vjudge/contest/124434#problem/B Description You are assigned ...
- mysql数据库中查询时间
项目中要对数据按时间处理,在数据库中,时间处理的格式如 2014-12-09 06:30:17 时间查询出来如下所示: 现在要查询具体有哪天的数据,应用substring函数,SQL如下: ) as ...
- C#类、静态类、静态变量,初始化执行顺序
执行顺序: 类的静态变量 ↓ 类的静态构造函数 ↓ 类的普通变量 ↓ 基类的静态变量 ↓ 基类的静态构造函数 ↓ 基类的普通变量 ↓ 基类的构造函数 ↓ 类的构造函数
- Educational Codeforces Round 5 - C. The Labyrinth (dfs联通块操作)
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/616/problem/C 题意就是 给你一个n行m列的图,让你求’*‘这个元素上下左右相连的连续的’.‘有多少(本身也算一个), ...
- windows 花式装系统
目录 一.安装系统前准备 准备U盘 准备好一个制作启动盘的软件 准备系统镜像 二.接下来先制作启动盘(以微PE为例) 三.插上u盘,调BIOS(BIOS即基本输入输出系统) 四.进入PE 五.开始安装 ...
- C#文件后缀名详解
C#文件后缀名详解 .sln:解决方案文件,为解决方案资源管理器提供显示管理文件的图形接口所需的信息. .csproj:项目文件,创建应用程序所需的引用.数据连接.文件夹和文件的信息. .aspx:W ...
- xmlBean学习二
由上一遍的准备工作完成后,可以很简单的就进行对xml文件的操作, package com; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; impor ...
- PL/pgSQL的RETURN QUERY例子
我的例子: 数据准备: create table custinfo(custid integer,callingcnt integer); ,),(,),(,); 函数生成: CREATE OR RE ...
- Cocos2d-x中由sprite来驱动Box2D的body运动(用来制作平台游戏中多变的机关)
好久都没写文章了,就来一篇吧.这种方法是在制作<胖鸟大冒险>时用到的.<胖鸟大冒险>中使用Box2D来进行物理模拟和碰撞检測,因此对每一个机关须要创建一个b2body.然后&l ...
- UOJ #148. 【NOIP2015】跳石头 二分
#148. [NOIP2015]跳石头 Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://uoj.ac/problem/148 Descripti ...
