Android自定义控件之自定义ViewGroup实现标签云
前言:
前面几篇讲了自定义控件绘制原理Android自定义控件之基本原理(一),自定义属性Android自定义控件之自定义属性(二),自定义组合控件Android自定义控件之自定义组合控件(三),常言道:“好记性不如烂笔头,光说不练假把式!!!”,作为一名学渣就是因为没有遵循这句名言才沦落于此,所以要谨遵教诲,注重理论与实践相结合,今天通过自定义ViewGroup来实现一下项目中用到的标签云。
自定义控件相关文章地址:
需求背景:
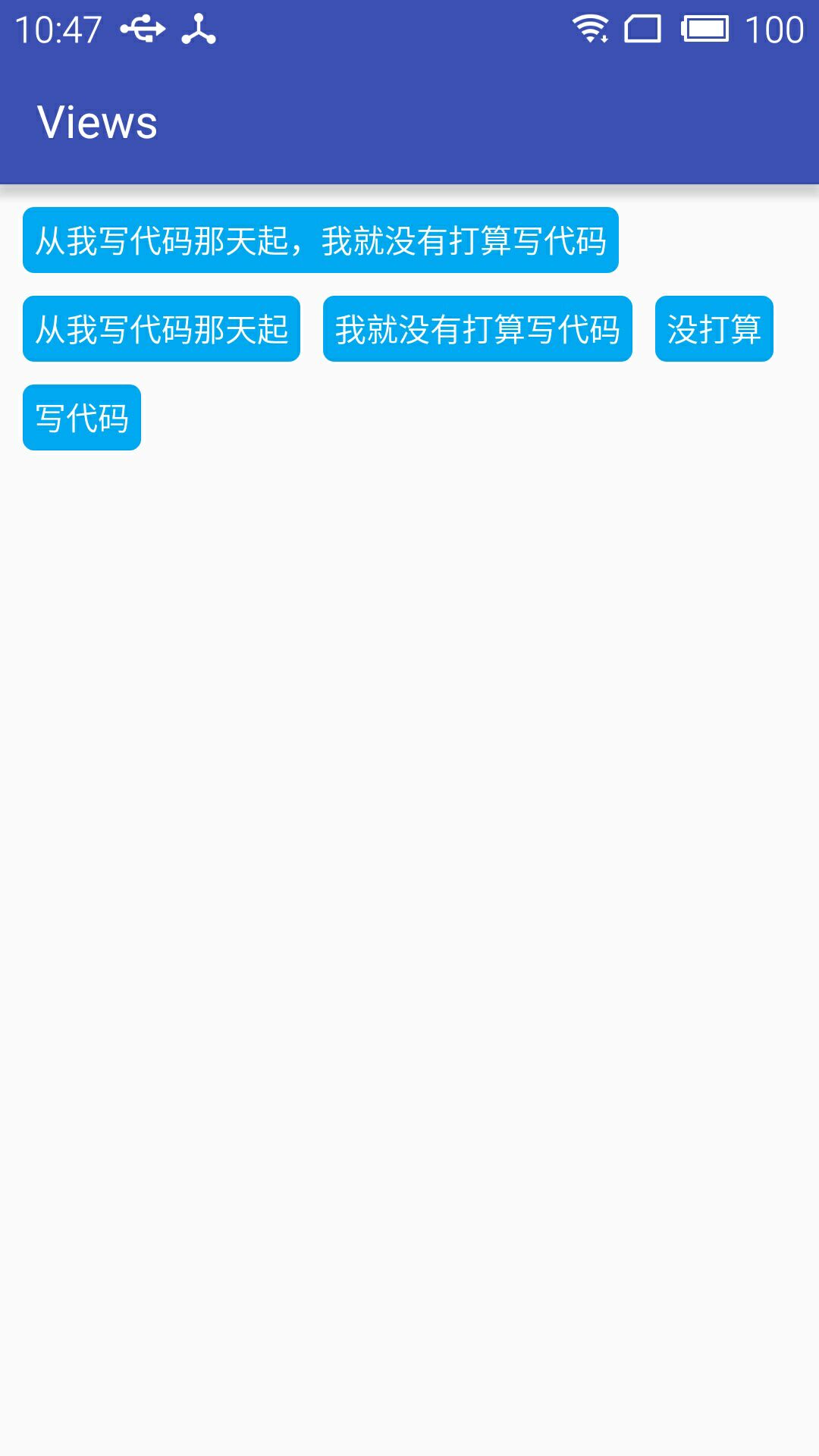
公司需要实现一个知识点的标签显示,每个标签的长度未知,如下图所示

基本绘制流程:
绘制原理这里不再介绍大致介绍下绘制流程
- 构造函数获取自定义属性
- onMeasure()方法,测量子控件的大小
- onLayout()方法,对子控件进行布局
1.)自定义属性
<declare-styleable name="TagsLayout">
<attr name="tagVerticalSpace" format="dimension" />
<attr name="tagHorizontalSpace" format="dimension" />
</declare-styleable>
2.)构造函数中获取自定义属性值
private int childHorizontalSpace;
private int childVerticalSpace; public TagsLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
TypedArray attrArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.TagsLayout);
if (attrArray != null) {
childHorizontalSpace = attrArray.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.TagsLayout_tagHorizontalSpace, 0);
childVerticalSpace = attrArray.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.TagsLayout_tagVerticalSpace, 0);
attrArray.recycle();
}
}
3.)onMeasure函数测量子控件大小,然后设置当前控件大小
@Override
protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
return new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
} /**
* 负责设置子控件的测量模式和大小 根据所有子控件设置自己的宽和高
*/
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 获得它的父容器为它设置的测量模式和大小
int sizeWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int sizeHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int modeWidth = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int modeHeight = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
// 如果是warp_content情况下,记录宽和高
int width = 0;
int height = 0;
/**
* 记录每一行的宽度,width不断取最大宽度
*/
int lineWidth = 0;
/**
* 每一行的高度,累加至height
*/
int lineHeight = 0; int count = getChildCount();
int left = getPaddingLeft();
int top = getPaddingTop();
// 遍历每个子元素
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getVisibility() == GONE)
continue;
// 测量每一个child的宽和高
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 得到child的lp
ViewGroup.LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
// 当前子空间实际占据的宽度
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + childHorizontalSpace;
// 当前子空间实际占据的高度
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + childVerticalSpace; if (lp != null && lp instanceof MarginLayoutParams) {
MarginLayoutParams params = (MarginLayoutParams) lp;
childWidth += params.leftMargin + params.rightMargin;
childHeight += params.topMargin + params.bottomMargin;
} /**
* 如果加入当前child,则超出最大宽度,则的到目前最大宽度给width,类加height 然后开启新行
*/
if (lineWidth + childWidth > sizeWidth - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight()) {
width = Math.max(lineWidth, childWidth);// 取最大的
lineWidth = childWidth; // 重新开启新行,开始记录
// 叠加当前高度,
height += lineHeight;
// 开启记录下一行的高度
lineHeight = childHeight;
child.setTag(new Location(left, top + height, childWidth + left - childHorizontalSpace, height + child.getMeasuredHeight() + top));
} else {// 否则累加值lineWidth,lineHeight取最大高度
child.setTag(new Location(lineWidth + left, top + height, lineWidth + childWidth - childHorizontalSpace + left, height + child.getMeasuredHeight() + top));
lineWidth += childWidth;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight);
}
}
width = Math.max(width, lineWidth) + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight();
height += lineHeight;
sizeHeight += getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom();
height += getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom();
setMeasuredDimension((modeWidth == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) ? sizeWidth : width, (modeHeight == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) ? sizeHeight : height);
}
通过遍历所有子控件调用measureChild函数获取每个子控件的大小,然后通过宽度叠加判断是否换行,叠加控件的高度,同时记录下当前子控件的坐标,这里记录坐标引用了自己写的一个内部类Location.java
/**
* 记录子控件的坐标
*/
public class Location {
public Location(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
this.left = left;
this.top = top;
this.right = right;
this.bottom = bottom;
} public int left;
public int top;
public int right;
public int bottom; }
4.)onLayout函数对所有子控件重新布局
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int count = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getVisibility() == GONE)
continue;
Location location = (Location) child.getTag();
child.layout(location.left, location.top, location.right, location.bottom);
}
}
这里直接遍历所有子控件调用子控件的layout函数进行布局。
如何使用:
1.布局问自己中直接引用
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:lee="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"> <com.whoislcj.views.TagsLayout
android:id="@+id/image_layout"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="10dp"
lee:tagHorizontalSpace="10dp"
lee:tagVerticalSpace="10dp" /> </LinearLayout>
2.)代码添加标签
TagsLayout imageViewGroup = (TagsLayout) findViewById(R.id.image_layout);
ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams lp = new ViewGroup.MarginLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
String[] string={"从我写代码那天起,我就没有打算写代码","从我写代码那天起","我就没有打算写代码","没打算","写代码"};
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
TextView textView = new TextView(this);
textView.setText(string[i]);
textView.setTextColor(Color.WHITE);
textView.setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.round_square_blue);
imageViewGroup.addView(textView, lp);
}
具体效果
3.)最后附上TagsLayout全部代码
public class TagsLayout extends ViewGroup {
private int childHorizontalSpace;
private int childVerticalSpace;
public TagsLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
TypedArray attrArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.TagsLayout);
if (attrArray != null) {
childHorizontalSpace = attrArray.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.TagsLayout_tagHorizontalSpace, 0);
childVerticalSpace = attrArray.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.TagsLayout_tagVerticalSpace, 0);
attrArray.recycle();
}
}
/**
* 负责设置子控件的测量模式和大小 根据所有子控件设置自己的宽和高
*/
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 获得它的父容器为它设置的测量模式和大小
int sizeWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int sizeHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int modeWidth = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int modeHeight = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
// 如果是warp_content情况下,记录宽和高
int width = 0;
int height = 0;
/**
* 记录每一行的宽度,width不断取最大宽度
*/
int lineWidth = 0;
/**
* 每一行的高度,累加至height
*/
int lineHeight = 0;
int count = getChildCount();
int left = getPaddingLeft();
int top = getPaddingTop();
// 遍历每个子元素
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getVisibility() == GONE)
continue;
// 测量每一个child的宽和高
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 得到child的lp
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
// 当前子空间实际占据的宽度
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin + childHorizontalSpace;
// 当前子空间实际占据的高度
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin + childVerticalSpace;
/**
* 如果加入当前child,则超出最大宽度,则的到目前最大宽度给width,类加height 然后开启新行
*/
if (lineWidth + childWidth > sizeWidth - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight()) {
width = Math.max(lineWidth, childWidth);// 取最大的
lineWidth = childWidth; // 重新开启新行,开始记录
// 叠加当前高度,
height += lineHeight;
// 开启记录下一行的高度
lineHeight = childHeight;
child.setTag(new Location(left, top + height, childWidth + left - childHorizontalSpace, height + child.getMeasuredHeight() + top));
} else {// 否则累加值lineWidth,lineHeight取最大高度
child.setTag(new Location(lineWidth + left, top + height, lineWidth + childWidth - childHorizontalSpace + left, height + child.getMeasuredHeight() + top));
lineWidth += childWidth;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight);
}
}
width = Math.max(width, lineWidth) + getPaddingLeft() + getPaddingRight();
height += lineHeight;
sizeHeight += getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom();
height += getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom();
setMeasuredDimension((modeWidth == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) ? sizeWidth : width, (modeHeight == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) ? sizeHeight : height);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
int count = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
if (child.getVisibility() == GONE)
continue;
Location location = (Location) child.getTag();
child.layout(location.left, location.top, location.right, location.bottom);
}
}
/**
* 记录子控件的坐标
*/
public class Location {
public Location(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
this.left = left;
this.top = top;
this.right = right;
this.bottom = bottom;
}
public int left;
public int top;
public int right;
public int bottom;
}
}
TagsLayout.java
总结:
至此有关简单的自定义控件已经介绍的差不多了,项目中很复杂的控件现在涉及的比较少,以后用到之后再做记录。
Android自定义控件之自定义ViewGroup实现标签云的更多相关文章
- Android自定义控件之自定义组合控件
前言: 前两篇介绍了自定义控件的基础原理Android自定义控件之基本原理(一).自定义属性Android自定义控件之自定义属性(二).今天重点介绍一下如何通过自定义组合控件来提高布局的复用,降低开发 ...
- Android自定义控件之自定义组合控件(三)
前言: 前两篇介绍了自定义控件的基础原理Android自定义控件之基本原理(一).自定义属性Android自定义控件之自定义属性(二).今天重点介绍一下如何通过自定义组合控件来提高布局的复用,降低开发 ...
- Android 自定义控件之继承ViewGroup创建新容器
欢迎大家来学习本节内容,前几节我们已经学习了其他几种自定义控件,分别是Andriod 自定义控件之音频条及 Andriod 自定义控件之创建可以复用的组合控件还没有学习的同学请先去学习下,因为本节将使 ...
- android自定义控件(3)-自定义当前按钮属性
那么还是针对我们之前写的自定义控件:开关按钮为例来说,在之前的基础上,我们来看看有哪些属性是可以自定义的:按钮的背景图片,按钮的滑块图片,和按钮的状态(是开还是关),实际上都应该是可以在xml文件中直 ...
- android自定义控件(4)-自定义水波纹效果
一.实现单击出现水波纹单圈效果: 照例来说,还是一个自定义控件,观察这个效果,发现应该需要重写onTouchEvent和onDraw方法,通过在onTouchEvent中获取触摸的坐标,然后以这个坐标 ...
- android自定义控件(五) 自定义组合控件
转自http://www.cnblogs.com/hdjjun/archive/2011/10/12/2209467.html 代码为自己编写 目标:实现textview和ImageButton组合, ...
- 老猪带你玩转android自定义控件二——自定义索引栏listview
带索引栏的listview,在android开发非常普遍,方便用户进行字母索引,就像微信通讯录这样: 今天,我们就从零到一实现这个具有索引栏的listview. 怎么实现这个控件了,我们应当梳理出一个 ...
- 玩转android自定义控件二——自定义索引栏listview
带索引栏的listview,在android开发非常普遍,方便用户进行字母索引,就像微信通讯录这样: 今天,我们就从零到一实现这个具有索引栏的listview. 怎么实现这个控件了,我们应当梳理出一个 ...
- Android动画效果之自定义ViewGroup添加布局动画
前言: 前面几篇文章介绍了补间动画.逐帧动画.属性动画,大部分都是针对View来实现的动画,那么该如何为了一个ViewGroup添加动画呢?今天结合自定义ViewGroup来学习一下布局动画.本文将通 ...
随机推荐
- RecyclerView使用大全
RecylerView介绍 RecylerView是support-v7包中的新组件,是一个强大的滑动组件,与经典的ListView相比,同样拥有item回收复用的功能,这一点从它的名字recyler ...
- JavaScript中fn()和return fn()
看博客时,注意到return的重要性 参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/raoyunxiao/p/5644032.html 看似反常的例子: var i = 0; function ...
- 微软Azure 经典模式下创建内部负载均衡(ILB)
微软Azure 经典模式下创建内部负载均衡(ILB) 使用之前一定要注意自己的Azure的模式,老版的为cloud service模式,新版为ARM模式(资源组模式) 本文适用于cloud servi ...
- SQL Server-聚焦APPLY运算符(二十七)
前言 其实有些新的特性在SQL Server早就已经出现过,但是若非系统的去学习数据库你会发现在实际项目中别人的SQL其实是比较复杂的,其实利用新的SQL Server语法会更加方便和简洁,从本节开始 ...
- .net Elasticsearch 学习入门笔记
一. es安装相关1.elasticsearch安装 运行http://localhost:9200/2.head插件3.bigdesk插件安装(安装细节百度:windows elasticsear ...
- C++随笔:从Hello World 探秘CoreCLR的内部(1)
紧接着上次的问题,上次的问题其实很简单,就是HelloWorld.exe运行失败,而本文的目的,就是成功调试HelloWorld这个控制台应用程序. 通过我的寻找,其实是一个名为TryRun的文件出了 ...
- Create a Team in RHEL7
SOLUTION VERIFIED September 13 2016 KB2620131 Environment Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7 NetworkManager ...
- MSYS2——Windows平台下模拟linux环境的搭建
最近从MSYS1.0迁移到了MSYS2.0,简单讲,MSYS2.0功能更强大,其环境模拟更加符合linux.虽然本身来自cygwin,但其集成了pacman软件管理工具,很有linux范,并且可以直接 ...
- [数据结构]——二叉树(Binary Tree)、二叉搜索树(Binary Search Tree)及其衍生算法
二叉树(Binary Tree)是最简单的树形数据结构,然而却十分精妙.其衍生出各种算法,以致于占据了数据结构的半壁江山.STL中大名顶顶的关联容器--集合(set).映射(map)便是使用二叉树实现 ...
- SharePonit 2010 更改另存为列表模板的语言类型
从朋友处得来一个列表模板:AccessApplicationSharePoint.stp 将其通过:网站操作----网站设置----列表模板,上传进去.然后去创建列表,发现找不到此模板. 根据多年老司 ...