pwnable.kr memcpy之write up
// compiled with : gcc -o memcpy memcpy.c -m32 -lm
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <math.h> unsigned long long rdtsc(){
asm("rdtsc");
} char* slow_memcpy(char* dest, const char* src, size_t len){
int i;
for (i=; i<len; i++) {
dest[i] = src[i];
}
return dest;
} char* fast_memcpy(char* dest, const char* src, size_t len){
size_t i;
// 64-byte block fast copy
if(len >= ){
i = len / ;
len &= (-);
while(i-- > ){
__asm__ __volatile__ (
"movdqa (%0), %%xmm0\n"
"movdqa 16(%0), %%xmm1\n"
"movdqa 32(%0), %%xmm2\n"
"movdqa 48(%0), %%xmm3\n"
"movntps %%xmm0, (%1)\n"
"movntps %%xmm1, 16(%1)\n"
"movntps %%xmm2, 32(%1)\n"
"movntps %%xmm3, 48(%1)\n"
::"r"(src),"r"(dest):"memory");
dest += ;
src += ;
}
} // byte-to-byte slow copy
if(len) slow_memcpy(dest, src, len);
return dest;
} int main(void){ setvbuf(stdout, , _IONBF, );
setvbuf(stdin, , _IOLBF, ); printf("Hey, I have a boring assignment for CS class.. :(\n");
printf("The assignment is simple.\n"); printf("-----------------------------------------------------\n");
printf("- What is the best implementation of memcpy? -\n");
printf("- 1. implement your own slow/fast version of memcpy -\n");
printf("- 2. compare them with various size of data -\n");
printf("- 3. conclude your experiment and submit report -\n");
printf("-----------------------------------------------------\n"); printf("This time, just help me out with my experiment and get flag\n");
printf("No fancy hacking, I promise :D\n"); unsigned long long t1, t2;
int e;
char* src;
char* dest;
unsigned int low, high;
unsigned int size;
// allocate memory
char* cache1 = mmap(, 0x4000, , MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -, );
char* cache2 = mmap(, 0x4000, , MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -, );
src = mmap(, 0x2000, , MAP_PRIVATE|MAP_ANONYMOUS, -, ); size_t sizes[];
int i=; // setup experiment parameters
for(e=; e<; e++){ // 2^13 = 8K
low = pow(,e-);
high = pow(,e);
printf("specify the memcpy amount between %d ~ %d : ", low, high);
scanf("%d", &size);
if( size < low || size > high ){
printf("don't mess with the experiment.\n");
exit();
}
sizes[i++] = size;
} sleep();
printf("ok, lets run the experiment with your configuration\n");
sleep(); // run experiment
for(i=; i<; i++){
size = sizes[i];
printf("experiment %d : memcpy with buffer size %d\n", i+, size);
dest = malloc( size ); memcpy(cache1, cache2, 0x4000); // to eliminate cache effect
t1 = rdtsc();
slow_memcpy(dest, src, size); // byte-to-byte memcpy
t2 = rdtsc();
printf("ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : %llu\n", t2-t1); memcpy(cache1, cache2, 0x4000); // to eliminate cache effect
t1 = rdtsc();
fast_memcpy(dest, src, size); // block-to-block memcpy
t2 = rdtsc();
printf("ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : %llu\n", t2-t1);
printf("\n");
} printf("thanks for helping my experiment!\n");
printf("flag : ----- erased in this source code -----\n");
return ;
}
分析源码:
size_t sizes[];
int i=; // setup experiment parameters
for(e=; e<; e++){ // 2^13 = 8K
low = pow(,e-);
high = pow(,e);
printf("specify the memcpy amount between %d ~ %d : ", low, high);
scanf("%d", &size);
if( size < low || size > high ){
printf("don't mess with the experiment.\n");
exit();
}
sizes[i++] = size;
}
从上代码中分析得到,需要输入2的n次幂和2的n+1次幂之间
// run experiment
for(i=; i<; i++){
size = sizes[i];
printf("experiment %d : memcpy with buffer size %d\n", i+, size);
dest = malloc( size );
这段代码分析得到,输入size后malloc分配空间,分配的空间大小就是我们输入的size大小。
memcpy(cache1, cache2, 0x4000); // to eliminate cache effect
t1 = rdtsc();
slow_memcpy(dest, src, size); // byte-to-byte memcpy
t2 = rdtsc();
printf("ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : %llu\n", t2-t1); memcpy(cache1, cache2, 0x4000); // to eliminate cache effect
t1 = rdtsc();
fast_memcpy(dest, src, size); // block-to-block memcpy
t2 = rdtsc();
printf("ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : %llu\n", t2-t1);
printf("\n");
}
分配空间后,分别用slow_memcpy和fast_memcpy两种方式,对堆块内的数据向另外一个内存地址拷贝,并比较二者时间。那么分析一下slow_memcpy和fast_memcpy:
char* slow_memcpy(char* dest, const char* src, size_t len){
int i;
for (i=; i<len; i++) {
dest[i] = src[i];
}
return dest;
}
char* fast_memcpy(char* dest, const char* src, size_t len){
size_t i;
// 64-byte block fast copy
if(len >= 64){
i = len / 64;
len &= (64-1);
while(i-- > 0){
__asm__ __volatile__ (
"movdqa (%0), %%xmm0\n"
"movdqa 16(%0), %%xmm1\n"
"movdqa 32(%0), %%xmm2\n"
"movdqa 48(%0), %%xmm3\n"
"movntps %%xmm0, (%1)\n"
"movntps %%xmm1, 16(%1)\n"
"movntps %%xmm2, 32(%1)\n"
"movntps %%xmm3, 48(%1)\n"
::"r"(src),"r"(dest):"memory");
dest += 64;
src += 64;
}
}
slow_memcpy是循环赋值,fast_memcpy是用asm汇编指令movdqa进行拷贝。拷贝结束后输入flag。
根据提示生成可执行程序,然后执行程序看一下:
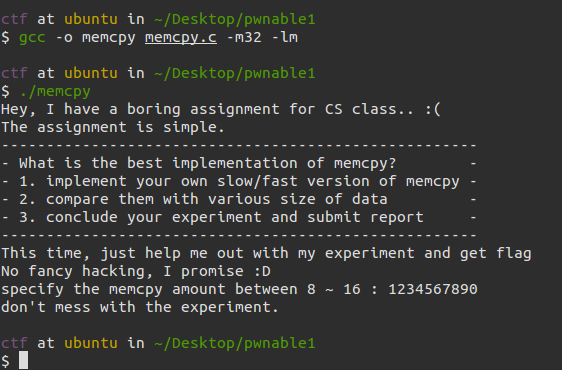
那么我们运行程序来看一下:
随便输入发现出错了:
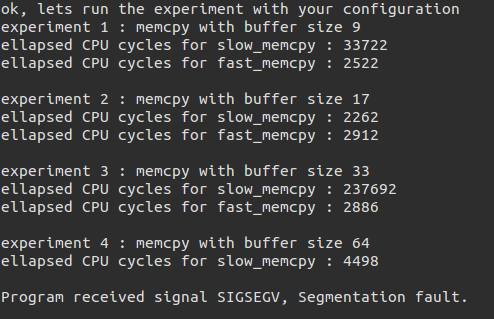
我们用gdb来看,发现了出错的位置:

出错的位置,也就是movntps的执行出了问题,百度了一下movntps的用法:
假设用户申请的堆块大小是a的话,malloc(a)分配的堆块大小为 8*(int((a+4)/8)+1)。
因此假设第一个malloc分配地址是16字节对齐的,则每次请求大小为16字节对齐的数据块即可成功运行结束。可以用脚本来算一下:
# coidng = utf-8
while(1):
a = raw_input()
a = int(a)
if ((a+4)%16>=9) or ((a+4)%16==0):
print a," is true"
else:
print a," is false"
根据脚本算出来的数,我们输入得到flag:
memcpy@ubuntu:~$ ls
memcpy.c readme
memcpy@ubuntu:~$ cat readme
the compiled binary of "memcpy.c" source code (with real flag) will be executed under memcpy_pwn privilege if you connect to port 9022.
execute the binary by connecting to daemon(nc 0 9022). memcpy@ubuntu:~$ nc o 9022
nc: getaddrinfo: Name or service not known
memcpy@ubuntu:~$ nc 0 9022
Hey, I have a boring assignment for CS class.. :(
The assignment is simple.
-----------------------------------------------------
- What is the best implementation of memcpy? -
- 1. implement your own slow/fast version of memcpy -
- 2. compare them with various size of data -
- 3. conclude your experiment and submit report -
-----------------------------------------------------
This time, just help me out with my experiment and get flag
No fancy hacking, I promise :D
specify the memcpy amount between 8 ~ 16 : 9
specify the memcpy amount between 16 ~ 32 : 21
specify the memcpy amount between 32 ~ 64 : 40
specify the memcpy amount between 64 ~ 128 : 70
specify the memcpy amount between 128 ~ 256 : 135
specify the memcpy amount between 256 ~ 512 : 265
specify the memcpy amount between 512 ~ 1024 : 520
specify the memcpy amount between 1024 ~ 2048 : 1030
specify the memcpy amount between 2048 ~ 4096 : 2055
specify the memcpy amount between 4096 ~ 8192 : 5210
ok, lets run the experiment with your configuration
experiment 1 : memcpy with buffer size 9
ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : 1497
ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : 438 experiment 2 : memcpy with buffer size 21
ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : 384
ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : 411 experiment 3 : memcpy with buffer size 40
ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : 636
ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : 672 experiment 4 : memcpy with buffer size 70
ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : 1134
ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : 288 experiment 5 : memcpy with buffer size 135
ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : 1938
ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : 237 experiment 6 : memcpy with buffer size 265
ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : 3633
ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : 291 experiment 7 : memcpy with buffer size 520
ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : 7287
ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : 342 experiment 8 : memcpy with buffer size 1030
ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : 13860
ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : 441 experiment 9 : memcpy with buffer size 2055
ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : 27561
ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : 984 experiment 10 : memcpy with buffer size 5210
ellapsed CPU cycles for slow_memcpy : 72930
ellapsed CPU cycles for fast_memcpy : 2628 thanks for helping my experiment!
flag : 1_w4nn4_br34K_th3_m3m0ry_4lignm3nt
pwnable.kr memcpy之write up的更多相关文章
- 【pwnable.kr】 memcpy
pwnable的新一题,和堆分配相关. http://pwnable.kr/bin/memcpy.c ssh memcpy@pwnable.kr -p2222 (pw:guest) 我觉得主要考察的是 ...
- pwnable.kr simple login writeup
这道题是pwnable.kr Rookiss部分的simple login,需要我们去覆盖程序的ebp,eip,esp去改变程序的执行流程 主要逻辑是输入一个字符串,base64解码后看是否与题目 ...
- 【pwnable.kr】 asm
一道写shellcode的题目, #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <stdlib.h> #inclu ...
- pwnable.kr之simple Login
pwnable.kr之simple Login 懒了几天,一边看malloc.c的源码,一边看华庭的PDF.今天佛系做题,到pwnable.kr上打开了simple Login这道题,但是这道题个人觉 ...
- pwnable.kr的passcode
前段时间找到一个练习pwn的网站,pwnable.kr 这里记录其中的passcode的做题过程,给自己加深印象. 废话不多说了,看一下题目, 看到题目,就ssh连接进去,就看到三个文件如下 看了一下 ...
- pwnable.kr bof之write up
这一题与前两题不同,用到了静态调试工具ida 首先题中给出了源码: #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <st ...
- pwnable.kr col之write up
Daddy told me about cool MD5 hash collision today. I wanna do something like that too! ssh col@pwnab ...
- pwnable.kr brainfuck之write up
I made a simple brain-fuck language emulation program written in C. The [ ] commands are not impleme ...
- pwnable.kr login之write up
main函数如下: auth函数如下: 程序的流程如下: 输入Authenticate值,并base64解码,将解码的值代入md5_auth函数中 mad5_auth()生成其MD5值并与f87cd6 ...
随机推荐
- 【Android Developers Training】 13. 支持不同平台版本
注:本文翻译自Google官方的Android Developers Training文档,译者技术一般,由于喜爱安卓而产生了翻译的念头,纯属个人兴趣爱好. 原文链接:http://developer ...
- JS实现全选、不选、反选
思路:1.获取元素.2.用for循环历遍数组,把checkbox的checked设置为true即实现全选,把checkbox的checked设置为false即实现不选.3.通过if判断,如果check ...
- jquery.jqprint-0.3.js打印table表格遇到的坑
在谷歌控制台输入window.print();可以调起当前整个页面的打印预览,那么要想打印页面某块区域内容怎么办呢? 我找到了jqprint插件,其原理是运用iframe 元素创建另外一个文档的内联框 ...
- js实现两个输入框中的数字相乘并自动将结果显示在第三个输入框
<script type="text/javascript"> function cal(ida,idb,idc) { var numa=Number(document ...
- AT&T汇编helloworld
摘自:http://blog.163.com/guixl_001/blog/static/417641042012112102642703/ 代码: #hello.s .data # 数据段声明 ms ...
- input的文件上传图片
<img id="headIMG" src="img/header_default.jpg"/> <input type="file ...
- 掌握好这23个Linux命令常用项
运维工程师(Operations)在国内又称为运维开发工程师(Devops),在国外称为 SRE(SiteReliability Engineering).负责维护并确保整个服务的高可用性,同时不断优 ...
- 如何共享数据?- 每天5分钟玩转 Docker 容器技术(41)
数据共享是 volume 的关键特性,本节我们详细讨论通过 volume 如何在容器与 host 之间,容器与容器之间共享数据. 容器与 host 共享数据 我们有两种类型的 data volume, ...
- POJ 1986 Distance Queries / UESTC 256 Distance Queries / CJOJ 1129 【USACO】距离咨询(最近公共祖先)
POJ 1986 Distance Queries / UESTC 256 Distance Queries / CJOJ 1129 [USACO]距离咨询(最近公共祖先) Description F ...
- JVM学习(1)——通过实例总结Java虚拟机的运行机制-转载http://www.cnblogs.com/kubixuesheng/p/5199200.html
JVM系类的文章全部转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/kubixuesheng/p/5199200.html 特别在此声明.那位博主写的真的很好 ,感谢!! 俗话说,自己写的代码, ...
