Project 03- STM32F4xx PID controller
Project 03- STM32F4xx PID controller
CMSIS files from ARM provides ARM Math functions.
There are also PID controller functions in different formats for f32, q31 and q7.
This tutorial/project will talk about how to implement PID controller on STM32F4xx using PID functions from ARM.
PID Controller
Fast about PID controller.
PID stands for Proportional-Integral-Derivative controller.
This is a control loop feedback mechanism widely used in industrial control systems.
It calculates the error between measured value and the desired setpoint value.
According to the error, it then calculates output value to minimize this error.
I will not go step-by-step on how PID works. More you can look on the sites below:
ARM PID library
ARM company provides 3 different PID controller functions:
- f32: float
- q31: integer
- q7: char
For each of the three types, you have three functions:
- f32
- arm_pid_init_f32
- arm_pid_reset_f32
- arm_pid_f32
- q31
- arm_pid_init_q31
- arm_pid_reset_q31
- arm_pid_q31
- q7
- arm_pid_init_q7
- arm_pid_reset_q7
- arm_pid_q7
There are also ARM PID structure, where you pass PID parameters.
More in project example below.
If you need additional info about these functions, you have detailed manual here.
PID Sample project
In the project, 2 DS18B20 temperature sensors are used.
They are configured in 12bit resolution, so delay between 2 calculations is about ~750ms.
If you read about PID controller, you realize that you cannot calculate PID controller results every x microcontroller,
because it has integral part which is used to sum all the errors in period.
More calculations you have, more integral error you have.
We have one device connected as “reference” temperature.
Second sensor is placed near DC FAN,
so when DC fan is turned ON, it is cooling the second DS18B20.
The goal is, that both temperatures are the same.
In my case, it was about 23°C on the reference sensor.
Then, I touched the second DS18B20 near DC fan and I heated them. DC fan was turned on.
Everything is displayed via USART to computer.
FAN is controlled via 1kHz PWM output.
According to the error between both sensors, more error, more duty cycle to DC fan.
This is just a sample project, so PID parameters are not set optimal.
For every project you have to set parameters for specific project.
This example successfully works on all STM32F4xx development board such as Discovery and Nucleo.
In the example, 1 PID controller is used.
If you need to control more than just one thing,
you can add additional ARM PID instances and
you can use more than just one PID controller at a time.
Pinout
- Both DS18B20 sensors are connected to the same pin: PA6
- DC fan PWM pin (controlled via transistor): PA5
- USART output: PB6, 115200baud
Example
/**
* Keil project for DS18B20 & ARM PID example
*
* Before you start, select your target, on the right of the "Load" button
*
* @author Tilen Majerle
* @email tilen@majerle.eu
* @website http://stm32f4-discovery.com
* @ide Keil uVision 5
* @packs STM32F4xx Keil packs version 2.2.0 or greater required
* @stdperiph STM32F4xx Standard peripheral drivers version 1.4.0 or greater required
*
* Additional defines in "Options for Target" > "C/C++" > "Defines"
* - ARM_MATH_CM4
* - __FPU_PRESENT = 1
*/
/* Include core modules */
#include "stm32f4xx.h"
/* Include my libraries here */
#include "defines.h"
#include "tm_stm32f4_delay.h"
#include "tm_stm32f4_onewire.h"
#include "tm_stm32f4_ds18b20.h"
#include "tm_stm32f4_disco.h"
#include "tm_stm32f4_usart.h"
#include "tm_stm32f4_pwm.h"
#include <stdio.h> /* Include ARM math */
#include "arm_math.h" /* How many sensors we are expecting on 1wire bus? */
#define EXPECTING_SENSORS 2 #define TEMP_CURRENT temps[1] /* Temperature we actually have */
#define TEMP_WANT temps[0] /* Temperature we want to have */ /* Choose PID parameters */
#define PID_PARAM_KP 100 /* Proporcional */
#define PID_PARAM_KI 0.025 /* Integral */
#define PID_PARAM_KD 20 /* Derivative */ int main(void) {
/* Timer data for PWM */
TM_PWM_TIM_t TIM_Data;
char buf[];
uint8_t devices, i, count;
/* DS18B20 devices ID */
uint8_t device[EXPECTING_SENSORS][];
/* Temperatures from 2 sensors */
float temps[EXPECTING_SENSORS];
/* PID error */
float pid_error;
/* Duty cycle for PWM */
float duty = ;
/* ARM PID Instance, float_32 format */
arm_pid_instance_f32 PID;
/* One wire instance */
TM_OneWire_t OneWire; /* Set PID parameters */
/* Set this for your needs */
PID.Kp = PID_PARAM_KP; /* Proporcional */
PID.Ki = PID_PARAM_KI; /* Integral */
PID.Kd = PID_PARAM_KD; /* Derivative */ /* Initialize PID system, float32_t format */
arm_pid_init_f32(&PID, ); /* Initialize system */
SystemInit(); /* Initialize delay */
TM_DELAY_Init(); /* Initialize Leds */
TM_DISCO_LedInit(); /* Initialize USART1, TX: PB6, 115200 baud */
TM_USART_Init(USART1, TM_USART_PinsPack_2, ); /* Initialize TIM2, 1kHz frequency */
TM_PWM_InitTimer(TIM2, &TIM_Data, ); /* Initialize TIM2, Channel 1, PinsPack 2 = PA5 */
TM_PWM_InitChannel(&TIM_Data, TM_PWM_Channel_1, TM_PWM_PinsPack_2); /* Set default duty cycle */
TM_PWM_SetChannelPercent(&TIM_Data, TM_PWM_Channel_1, duty); /* Initialize OneWire, pin PA6 */
TM_OneWire_Init(&OneWire, GPIOA, GPIO_PIN_6); /* Checks for any device on 1-wire */
count = ;
devices = TM_OneWire_First(&OneWire);
while (devices) {
/* Get full ROM value, 8 bytes, give location of first byte where to save */
TM_OneWire_GetFullROM(&OneWire, device[count]);
/* Increase count for devices */
count++;
/* Get next device */
devices = TM_OneWire_Next(&OneWire);
} /* We need 2 devices */
if (count != ) {
TM_USART_Puts(USART1, "We expect 2 devices on 1-wire. Quiting!\n"); /* While */
while ();
} /* Go through all connected devices and set resolution to 12bits */
for (i = ; i < count; i++) {
TM_DS18B20_SetResolution(&OneWire, &device[i][], TM_DS18B20_Resolution_12bits);
} /* Start temperature conversion on all devices */
TM_DS18B20_StartAll(&OneWire); while () {
/* If all sensors are done with conversion */
/* This will happen about every 750ms, because DS18B20 needs ~750ms for conversion in 12bit resolution mode */
if (TM_DS18B20_AllDone(&OneWire)) {
/* Read temperature 1, reference temperature */
TM_DS18B20_Read(&OneWire, device[], &TEMP_WANT); /* Read temperature 2, actual temperature */
TM_DS18B20_Read(&OneWire, device[], &TEMP_CURRENT); /* Start new temperature conversion on all devices */
TM_DS18B20_StartAll(&OneWire); /* Set LEDs according to the which temperature is higher */
if (TEMP_CURRENT > TEMP_WANT) {
TM_DISCO_LedOn(LED_GREEN);
TM_DISCO_LedOff(LED_RED);
} else if (TEMP_CURRENT < TEMP_WANT) {
TM_DISCO_LedOn(LED_RED);
TM_DISCO_LedOff(LED_GREEN);
} else {
TM_DISCO_LedOff(LED_ALL);
} /* Calculate error */
pid_error = TEMP_CURRENT - TEMP_WANT; /* Calculate PID here, argument is error */
/* Output data will be returned, we will use it as duty cycle parameter */
duty = arm_pid_f32(&PID, pid_error); /* Check overflow, duty cycle in percent */
if (duty > ) {
duty = ;
} else if (duty < ) {
duty = ;
} /* Set PWM duty cycle for DC FAN to cool down sensor for "TEMP_CURRENT" */
TM_PWM_SetChannelPercent(&TIM_Data, TM_PWM_Channel_1, duty); /* Format string */
sprintf(buf, "Expected: %2.3f C\nActual: %2.3f C\nError: %2.3f C\nDuty cycle: %3.2f %%\n----\n", TEMP_WANT, TEMP_CURRENT, pid_error, duty); /* Send to USART */
TM_USART_Puts(USART1, buf);
}
}
}
2 PID controller
2.1 Description
The proportional-integral-derivative or PID controller is commonly used in the industry.
It is a feedback loop controller that manages the process command with a view to reducing the error
between the desired set point and the measured process variable.
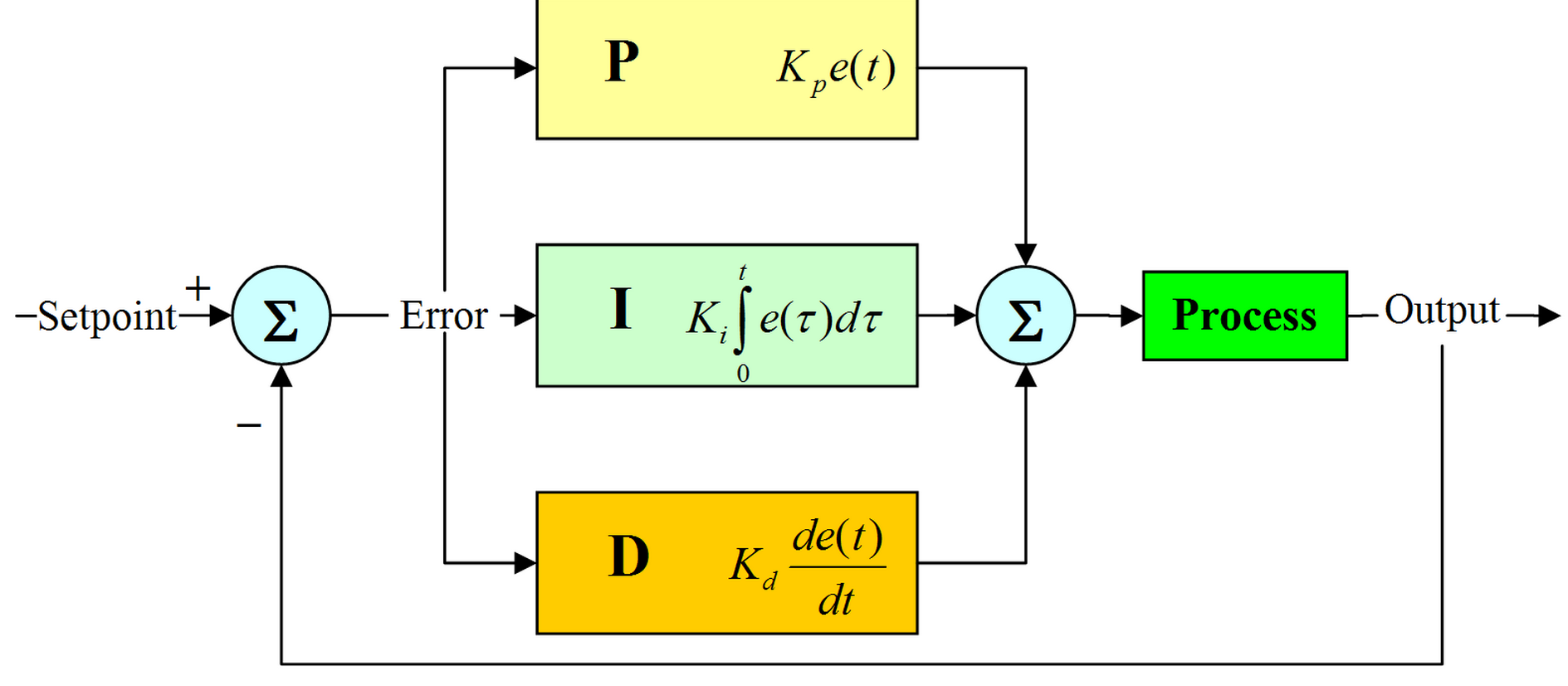
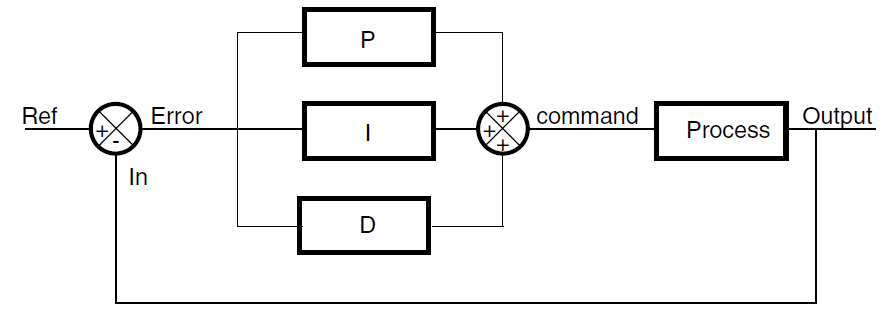
The following block diagram shows the parallel structure of a PID controller.
This is the structure implemented in this DSP library.
Figure 1. Block diagram of PID controller
DSP library functions
The DSP library provides three PID functions:
● DoPID: a PID core loop coded in C (the error is computed outside the function)
● DoFullPID: a full PID controller coded in C (with error computing)
● PID_stm32: an optimized PID core loop written in assembly
Project 03- STM32F4xx PID controller的更多相关文章
- SpringMVC学习03(控制器Controller)
3.控制器Controller 3.1 控制器Controller 控制器复杂提供访问应用程序的行为,通常通过接口定义或注解定义两种方法实现. 控制器负责解析用户的请求并将其转换为一个模型. 在Spr ...
- 《Symfony 5全面开发》教程03、使用Controller创建第一个页面
我们使用Phpstorm打开我们的项目目录,展开项目目录文件夹. Symfony项目其实也是composer项目,如果你新拿到一个Symfony项目, 你可以在控制台中使用composer insta ...
- PID控制器(比例-积分-微分控制器)- II
Table of Contents Practical Process Control Proven Methods and Best Practices for Automatic PID Cont ...
- Be a Smart Project Manager
The key to being a smart project manager is to remember how you are going to manage your project, to ...
- 增量与位置PID
转载:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_408540af0100b17n.html http://bbs.ednchina.com/BLOG_ARTICLE_211739. ...
- MATLAB-离散系统的数字PID控制仿真
%PID Controller clear all; close all; ts=0.001; %采样时间=0.001s sys=tf(,]); %建立被控对象传递函数 dsys=c2d(sys,t ...
- PID算法(c 语言)(转)
PID算法(c 语言)(来自老外) #include <stdio.h> #include<math.h> //定义PID 的结构体 struct _pid { int pv; ...
- PID算法(c 语言)(来自老外)
#include <stdio.h> #include<math.h> //定义PID 的结构体 struct _pid { int pv; // integer that c ...
- PID控制器(比例-积分-微分控制器)- IV
调节/测量放大电路电路图:PID控制电路图 如图是PlD控制电路,即比例(P).积分(I).微分(D)控制电路. A1构成的比例电路与环路增益有关,调节RP1,可使反相器的增益在0·5一∞范围内变化; ...
随机推荐
- python的一个小原理
在许多语言当中,类似于a.b()这样的调用方法是一个整体,但在Python中,它其实是两部分:获取属性a.b,调用().所以也可以写成: c = a.b c() 2.关于继承 class a: num ...
- mac安装ocr
mac安装Tesserocr 安装 Imagemagick 和 Tesseract 库: brew install imagemagick brew install tesseract --all-l ...
- C#使用redis学习笔记
1.官网:http://redis.io/(英) http://www.redis.cn/(中) 2.下载:https://github.com/dmajkic/redis/downloads(Wi ...
- 洛谷 2257 - YY的GCD
莫比乌斯反演半模板题 很容易可以得到 \[Ans = \sum\limits_{p \in prime} \sum\limits_{d = 1}^{\min (\left\lfloor\frac{a} ...
- net MongoDB安装
Mongo服务器端下载链接:https://www.mongodb.com/download-center?jmp=nav 客户端查看工具Mongovue工具下载链接:http://pan.baidu ...
- 深入理解java虚拟机-01 走进java
第一章是对java的产生,历史的整体介绍 java的使用很广泛,安装jdk的时候会看到一句广告语runs in 10 billions machines.使用java的设备多达几十亿台 1.概述 优点 ...
- CEF 中的那些坑
CEF (Chromium Embedded Framework) 的大名也听说很久了,最近因为客户的需求,简单地研究了一下.结果遇到了一个接一个的坑,且慢慢道来.比之前用QtWebkit的坑还要多和 ...
- .NetCore中的程序通过Docker在CentOS中部署
基础说明 安装Docker过程就略过了 创建一个Asp.Net Core程序 启用Docker支持,会生成Dockerfile文件,接下来看下这个文件,当然不同的版本生成的具体可能不一致 FROM m ...
- Codeforces Round #380 Div.2 F - Financiers Game
F - Financiers Game 这种两人博弈一般都可以用两个dp写, 一个dp描述第一个人的最优态, 第二个dp描述第二个人的最优态,难点在于优化空间... 我感觉这个空间开得有点玄学.. d ...
- oracle用户名小写时,利用sqlplus连接
[oracle@upright92 ~]$ sqlplus / as sysdba SQL*Plus: Release 11.2.0.4.0 Production on Tue May 22 10:3 ...
