DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.12
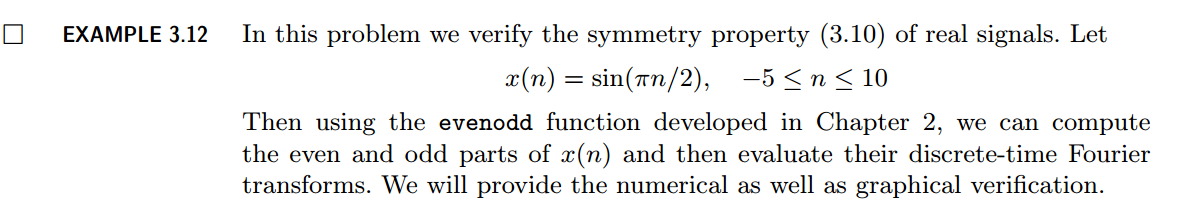
用到的性质
代码:
n = -5:10; x = sin(pi*n/2);
k = -100:100; w = (pi/100)*k; % freqency between -pi and +pi , [0,pi] axis divided into 101 points.
X = x * (exp(-j*pi/100)) .^ (n'*k); % DTFT of x % signal decomposition
[xe,xo,m] = evenodd(x,n); % even and odd parts
XE = xe * (exp(-j*pi/100)) .^ (m'*k); % DTFT of xe
XO = xo * (exp(-j*pi/100)) .^ (m'*k); % DTFT of xo magXE = abs(XE); angXE = angle(XE); realXE = real(XE); imagXE = imag(XE);
magXO = abs(XO); angXO = angle(XO); realXO = real(XO); imagXO = imag(XO);
magX = abs(X); angX = angle(X); realX = real(X); imagX = imag(X); %verification
XR = real(X); % real part of X
error1 = max(abs(XE-XR)); % Difference
XI = imag(X); % imag part of X
error2 = max(abs(XO-j*XI)); % Difference figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'x sequence')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
stem(n,x); title('x sequence'); xlabel('n'); ylabel('x(n)'); grid on; figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'xe & xo sequence')
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,1,1); stem(m,xe); title('xe sequence '); xlabel('m'); ylabel('xe(m)'); grid on;
subplot(2,1,2); stem(m,xo); title('xo sequence '); xlabel('m'); ylabel('xo(m)'); grid on; %% --------------------------------------------------------------------
%% START X's mag ang real imag
%% --------------------------------------------------------------------
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'X its Magnitude and Angle, Real and Imaginary Part');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,magX); grid on; axis([-1,1,0,9]);
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |X|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, angX/pi); grid on; axis([-1,1,-1,1]);
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w/pi, realX); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w/pi, imagX); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary');
%% -------------------------------------------------------------------
%% END X's mag ang real imag
%% ------------------------------------------------------------------- %% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% START XE's mag ang real imag
%% --------------------------------------------------------------
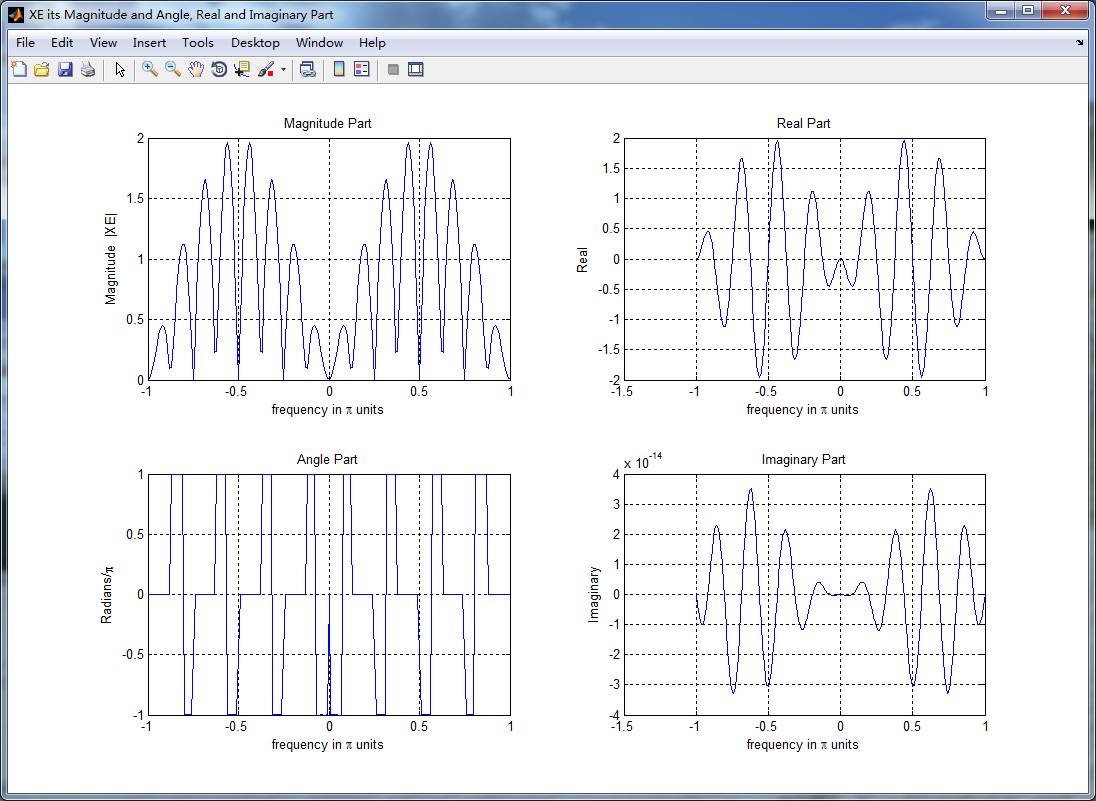
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'XE its Magnitude and Angle, Real and Imaginary Part');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,magXE); grid on; axis([-1,1,0,2]);
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |XE|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, angXE/pi); grid on; axis([-1,1,-1,1]);
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w/pi, realXE); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w/pi, imagXE); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary'); %% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% END XE's mag ang real imag
%% -------------------------------------------------------------- %% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% START XO's mag ang real imag
%% --------------------------------------------------------------
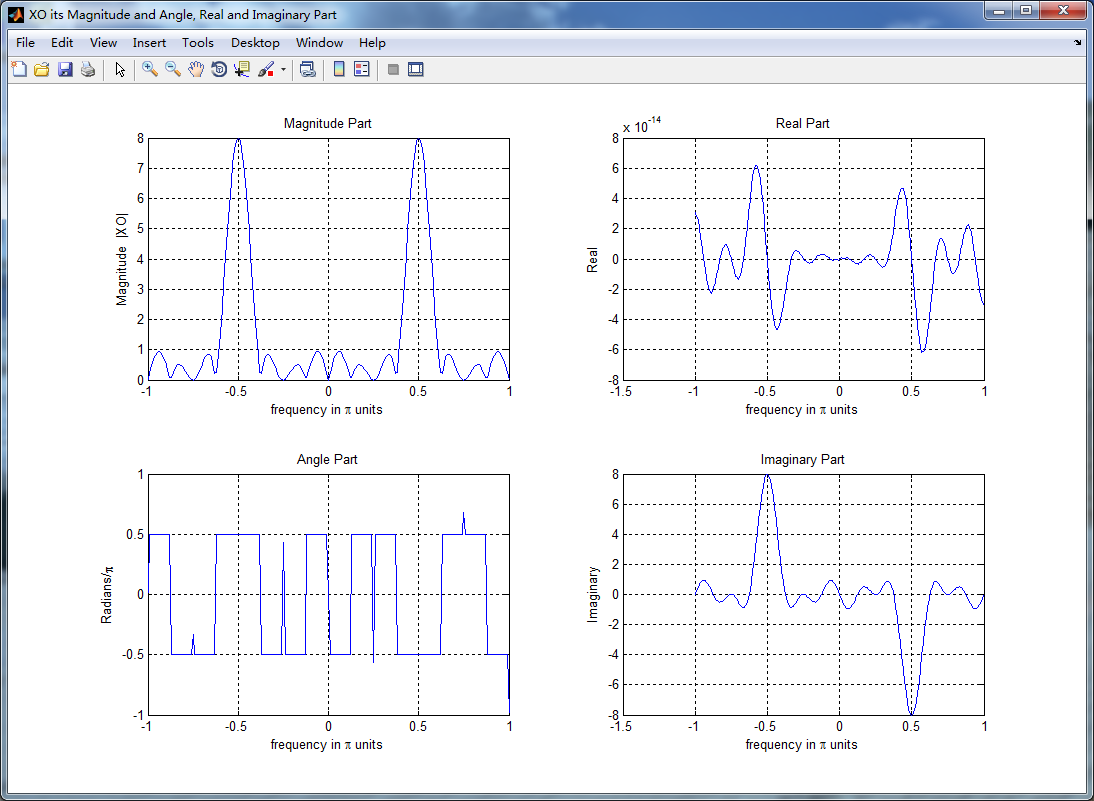
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'XO its Magnitude and Angle, Real and Imaginary Part');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,magXO); grid on; axis([-1,1,0,8]);
title('Magnitude Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Magnitude |XO|');
subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi, angXO/pi); grid on; axis([-1,1,-1,1]);
title('Angle Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Radians/\pi'); subplot('2,2,2'); plot(w/pi, realXO); grid on;
title('Real Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Real');
subplot('2,2,4'); plot(w/pi, imagXO); grid on;
title('Imaginary Part');
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Imaginary'); %% --------------------------------------------------------------
%% END XO's mag ang real imag
%% -------------------------------------------------------------- %% ----------------------------------------------------------------
%% START Graphical verification
%% ----------------------------------------------------------------
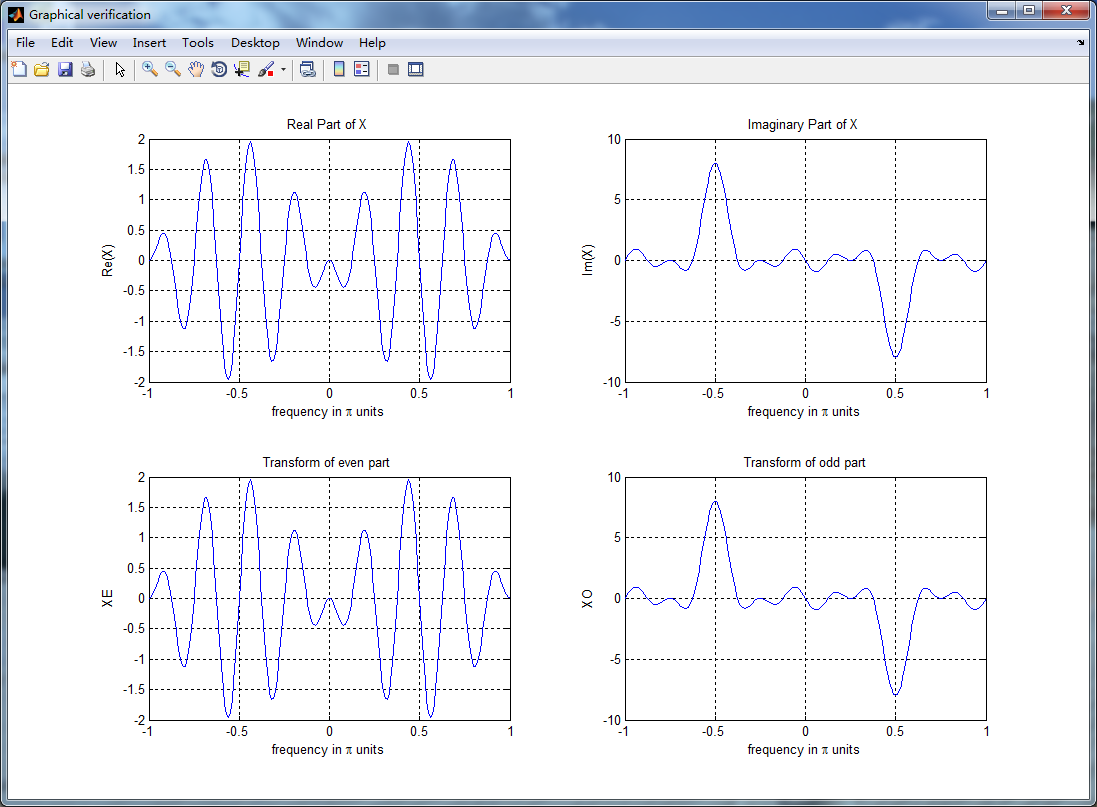
figure('NumberTitle', 'off', 'Name', 'Graphical verification');
set(gcf,'Color','white');
subplot(2,2,1); plot(w/pi,XR); grid on; axis([-1,1,-2,2]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Re(X)'); title('Real Part of X ');
subplot(2,2,2); plot(w/pi,XI); grid on; axis([-1,1,-10,10]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('Im(X)'); title('Imaginary Part of X '); subplot(2,2,3); plot(w/pi,realXE); grid on; axis([-1,1,-2,2]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('XE'); title('Transform of even part ');
subplot(2,2,4); plot(w/pi,imagXO); grid on; axis([-1,1,-10,10]);
xlabel('frequency in \pi units'); ylabel('XO'); title('Transform of odd part'); %% ----------------------------------------------------------------
%% END Graphical verification
%% ----------------------------------------------------------------
运行结果:



DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.12的更多相关文章
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.21
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) % Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*a ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.19
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Discrete-time Signa ...
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.18
代码: % Analog Signal Dt = 0.00005; t = -0.005:Dt:0.005; xa = exp(-1000*abs(t)); % Continuous-time Fou ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.23
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x1(n) : Ts = 0.0002 Ts = 0.0002; n = -25:1:25; nTs = n*Ts; x1 = exp(-1000 ...
- DSP using MATLAB示例Example3.16
代码: b = [0.0181, 0.0543, 0.0543, 0.0181]; % filter coefficient array b a = [1.0000, -1.7600, 1.1829, ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.11
用到的性质 上代码: n = -5:10; x = rand(1,length(n)); k = -100:100; w = (pi/100)*k; % freqency between -pi an ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例 Example3.10
用到的性质 上代码: n = -5:10; x = rand(1,length(n)) + j * rand(1,length(n)); k = -100:100; w = (pi/100)*k; % ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.22
代码: % Discrete-time Signal x2(n) Ts = 0.001; n = -5:1:5; nTs = n*Ts; Fs = 1/Ts; x = exp(-1000*abs(nT ...
- DSP using MATLAB 示例Example3.17
随机推荐
- LAMP 之 mysql 安装
搞了成日 = = 呢个野.... 大部分东西写在 印象笔记 中....不过呢个野特别繁琐,所以记录落黎(小白一枚,大家见谅) 总结下,唔系好容易唔记得 >W< (可能唔会甘完整,我将我自认 ...
- 为什么使用<!DOCTYPE HTML>
不管是刚接触前端,还是你已经"精通"web前端开发的内容,你应该知道在你写html的时候需要定义文档类型:你知道如果没有它,浏览器在渲染页面的时候会使用怪异模式:你知道各个浏览器在 ...
- JavaScript高级程序设计学习笔记--变量、作用域和内存问题
传递参数 function setName(obj){ obj.name="Nicholas"; obj=new object(); obj.name="Greg&quo ...
- 【leetcode】Swap Nodes in Pairs (middle)
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head. For example,Given 1->2-&g ...
- 【XLL API 函数】xlGetName
以字符串格式返回 DLL 文件的长文件名. 原型 Excel12(xlGetName, LPXLOPER12 pxRes, 0); 参数 这个函数没有参数 属性值和返回值 返回文件名和路径 实例 \S ...
- IOS- 02 零碎知识总结
1.UIView,UIViewController,UIWindow和CALayer UIView是什么,做什么:UIView是用来显示内容的,可以处理用户事件 CALayer是什么,做什么:CALa ...
- jquery this 与javascript的this
<div class="list"> <table> <thead> <tr> <th width="110&quo ...
- 启动Eclipse弹出:Failed to load JavaHL Library 错误框的解决办法
一.问题背景描述: eclipse安装完svn插件以后,在启动时出现:Failed to load JavaHL Library. These are the errors that were en ...
- grep(Global Regular Expression Print)
.grep -iwr --color 'hellp' /home/weblogic/demo 或者 grep -iw --color 'hellp' /home/weblogic/demo/* (-i ...
- React Native实例之房产搜索APP
React Native 开发越来越火了,web app也是未来的潮流, 现在react native已经可以完成一些最基本的功能. 通过开发一些简单的应用, 可以更加熟练的掌握 RN 的知识. 在学 ...
