SpringBoot集成Spring Security(4)——自定义表单登录
通过前面三篇文章,你应该大致了解了 Spring Security 的流程。你应该发现了,真正的 login 请求是由 Spring Security 帮我们处理的,那么我们如何实现自定义表单登录呢,比如添加一个验证码…
源码地址:https://github.com/jitwxs/blog_sample
文章目录
一、添加验证码
1.1 验证码 Servlet
1.2 修改 login.html
1.3 添加匿名访问 Url
二、AJAX 验证
三、过滤器验证
3.1 编写验证码过滤器
3.2 注入过滤器
3.3 运行程序
四、Spring Security 验证
4.1 WebAuthenticationDetails
4.2 AuthenticationDetailsSource
4.3 AuthenticationProvider
4.4 运行程序
首先在上一篇文章的基础上,添加验证码功能。
一、添加验证码
验证码的 Servlet 代码,大家无需关心其内部实现,我也是百度直接捞了一个,直接复制即可。
1.1 验证码 Servlet
/**
* @author jitwxs
* @date 2018/3/29 20:35
*/
public class VerifyServlet extends HttpServlet { private static final long serialVersionUID = -5051097528828603895L; /**
* 验证码图片的宽度。
*/
private int width = 100; /**
* 验证码图片的高度。
*/
private int height = 30; /**
* 验证码字符个数
*/
private int codeCount = 4; /**
* 字体高度
*/
private int fontHeight; /**
* 干扰线数量
*/
private int interLine = 16; /**
* 第一个字符的x轴值,因为后面的字符坐标依次递增,所以它们的x轴值是codeX的倍数
*/
private int codeX; /**
* codeY ,验证字符的y轴值,因为并行所以值一样
*/
private int codeY; /**
* codeSequence 表示字符允许出现的序列值
*/
char[] codeSequence = { 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I', 'J',
'K', 'L', 'M', 'N', 'O', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'W',
'X', 'Y', 'Z', '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9' }; /**
* 初始化验证图片属性
*/
@Override
public void init() throws ServletException {
// 从web.xml中获取初始信息
// 宽度
String strWidth = this.getInitParameter("width");
// 高度
String strHeight = this.getInitParameter("height");
// 字符个数
String strCodeCount = this.getInitParameter("codeCount");
// 将配置的信息转换成数值
try {
if (strWidth != null && strWidth.length() != 0) {
width = Integer.parseInt(strWidth);
}
if (strHeight != null && strHeight.length() != 0) {
height = Integer.parseInt(strHeight);
}
if (strCodeCount != null && strCodeCount.length() != 0) {
codeCount = Integer.parseInt(strCodeCount);
}
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//width-4 除去左右多余的位置,使验证码更加集中显示,减得越多越集中。
//codeCount+1 //等比分配显示的宽度,包括左右两边的空格
codeX = (width-4) / (codeCount+1);
//height - 10 集中显示验证码
fontHeight = height - 10;
codeY = height - 7;
} /**
* @param request
* @param response
* @throws ServletException
* @throws java.io.IOException
*/
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, java.io.IOException {
// 定义图像buffer
BufferedImage buffImg = new BufferedImage(width, height, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
Graphics2D gd = buffImg.createGraphics();
// 创建一个随机数生成器类
Random random = new Random();
// 将图像填充为白色
gd.setColor(Color.LIGHT_GRAY);
gd.fillRect(0, 0, width, height);
// 创建字体,字体的大小应该根据图片的高度来定。
Font font = new Font("Times New Roman", Font.PLAIN, fontHeight);
// 设置字体。
gd.setFont(font);
// 画边框。
gd.setColor(Color.BLACK);
gd.drawRect(0, 0, width - 1, height - 1);
// 随机产生16条干扰线,使图象中的认证码不易被其它程序探测到。
gd.setColor(Color.gray);
for (int i = 0; i < interLine; i++) {
int x = random.nextInt(width);
int y = random.nextInt(height);
int xl = random.nextInt(12);
int yl = random.nextInt(12);
gd.drawLine(x, y, x + xl, y + yl);
}
// randomCode用于保存随机产生的验证码,以便用户登录后进行验证。
StringBuffer randomCode = new StringBuffer();
int red = 0, green = 0, blue = 0;
// 随机产生codeCount数字的验证码。
for (int i = 0; i < codeCount; i++) {
// 得到随机产生的验证码数字。
String strRand = String.valueOf(codeSequence[random.nextInt(36)]);
// 产生随机的颜色分量来构造颜色值,这样输出的每位数字的颜色值都将不同。
red = random.nextInt(255);
green = random.nextInt(255);
blue = random.nextInt(255);
// 用随机产生的颜色将验证码绘制到图像中。
gd.setColor(new Color(red,green,blue));
gd.drawString(strRand, (i + 1) * codeX, codeY);
// 将产生的四个随机数组合在一起。
randomCode.append(strRand);
}
// 将四位数字的验证码保存到Session中。
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
session.setAttribute("validateCode", randomCode.toString());
// 禁止图像缓存。
response.setHeader("Pragma", "no-cache");
response.setHeader("Cache-Control", "no-cache");
response.setDateHeader("Expires", 0); response.setContentType("image/jpeg");
// 将图像输出到Servlet输出流中。
ServletOutputStream sos = response.getOutputStream();
ImageIO.write(buffImg, "jpeg", sos);
sos.close();
}
}
然后在 Application 中注入该 Servlet:
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
} /**
* 注入验证码servlet
*/
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean indexServletRegistration() {
ServletRegistrationBean registration = new ServletRegistrationBean(new VerifyServlet());
registration.addUrlMappings("/getVerifyCode");
return registration;
}
}
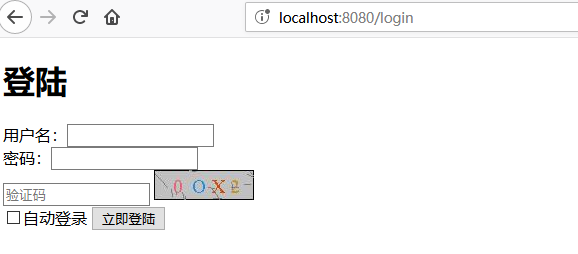
1.2 修改 login.html
在原本的 Login 页面基础上加上验证码字段:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>登陆</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>登陆</h1>
<form method="post" action="/login">
<div>
用户名:<input type="text" name="username">
</div>
<div>
密码:<input type="password" name="password">
</div>
<div>
<input type="text" class="form-control" name="verifyCode" required="required" placeholder="验证码">
<img src="getVerifyCode" title="看不清,请点我" onclick="refresh(this)" onmouseover="mouseover(this)" />
</div>
<div>
<label><input type="checkbox" name="remember-me"/>自动登录</label>
<button type="submit">立即登陆</button>
</div>
</form>
<script>
function refresh(obj) { obj.src = "getVerifyCode?" + Math.random(); } function mouseover(obj) { obj.style.cursor = "pointer"; }
</script>
</body>
</html>
1.3 添加匿名访问 Url
不要忘记在 WebSecurityConfig 中允许该 Url 的匿名访问,不然没有登录是没有办法访问的:
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
// 如果有允许匿名的url,填在下面
.antMatchers("/getVerifyCode").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
// 设置登陆页
.formLogin().loginPage("/login")
// 设置登陆成功页
.defaultSuccessUrl("/").permitAll()
// 登录失败Url
.failureUrl("/login/error")
// 自定义登陆用户名和密码参数,默认为username和password
// .usernameParameter("username")
// .passwordParameter("password")
.and()
.logout().permitAll()
// 自动登录
.and().rememberMe()
.tokenRepository(persistentTokenRepository())
// 有效时间:单位s
.tokenValiditySeconds(60)
.userDetailsService(userDetailsService); // 关闭CSRF跨域
http.csrf().disable();
}
这样验证码就加好了,运行下程序:
下面才算是这篇文章真正的部分。我们如何才能实现验证码验证呢,思考一下,应该有以下几种实现方式:
- 登录表单提交前发送 AJAX 验证验证码
- 使用自定义过滤器(Filter),在 Spring security 校验前验证验证码合法性
- 和用户名、密码一起发送到后台,在 Spring security 中进行验证
二、AJAX 验证
使用 AJAX 方式验证和我们 Spring Security 框架就没有任何关系了,其实就是表单提交前先发个 HTTP 请求验证验证码,本篇不再赘述。
三、过滤器验证
使用过滤器的思路是:在 Spring Security 处理登录验证请求前,验证验证码,如果正确,放行;如果不正确,调到异常。
3.1 编写验证码过滤器
自定义一个过滤器,实现 OncePerRequestFilter (该 Filter 保证每次请求一定会过滤),在 isProtectedUrl() 方法中拦截了 POST 方式的 /login 请求。
在逻辑处理中从 request 中取出验证码,并进行验证,如果验证成功,放行;验证失败,手动生成异常。
注:这里的异常设置在上一篇已经说过了:SpringBoot集成Spring Security(3)——异常处理
public class VerifyFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
private static final PathMatcher pathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher();
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException {
if(isProtectedUrl(request)) {
String verifyCode = request.getParameter("verifyCode");
if(!validateVerify(verifyCode)) {
//手动设置异常
request.getSession().setAttribute("SPRING_SECURITY_LAST_EXCEPTION",new DisabledException("验证码输入错误"));
// 转发到错误Url
request.getRequestDispatcher("/login/error").forward(request,response);
} else {
filterChain.doFilter(request,response);
}
} else {
filterChain.doFilter(request,response);
}
}
private boolean validateVerify(String inputVerify) {
//获取当前线程绑定的request对象
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest();
// 不分区大小写
// 这个validateCode是在servlet中存入session的名字
String validateCode = ((String) request.getSession().getAttribute("validateCode")).toLowerCase();
inputVerify = inputVerify.toLowerCase();
System.out.println("验证码:" + validateCode + "用户输入:" + inputVerify);
return validateCode.equals(inputVerify);
}
// 拦截 /login的POST请求
private boolean isProtectedUrl(HttpServletRequest request) {
return "POST".equals(request.getMethod()) && pathMatcher.match("/login", request.getServletPath());
}
}
3.2 注入过滤器
修改 WebSecurityConfig 的 configure 方法,添加一个 addFilterBefore() ,具有两个参数,作用是在参数二之前执行参数一设置的过滤器。
Spring Security 对于用户名/密码登录方式是通过 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 处理的,我们在它之前执行验证码过滤器即可。
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
// 如果有允许匿名的url,填在下面
.antMatchers("/getVerifyCode").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
// 设置登陆页
.formLogin().loginPage("/login")
// 设置登陆成功页
.defaultSuccessUrl("/").permitAll()
// 登录失败Url
.failureUrl("/login/error")
// 自定义登陆用户名和密码参数,默认为username和password
// .usernameParameter("username")
// .passwordParameter("password")
.and()
.addFilterBefore(new VerifyFilter(),UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class)
.logout().permitAll()
// 自动登录
.and().rememberMe()
.tokenRepository(persistentTokenRepository())
// 有效时间:单位s
.tokenValiditySeconds(60)
.userDetailsService(userDetailsService); // 关闭CSRF跨域
http.csrf().disable();
}
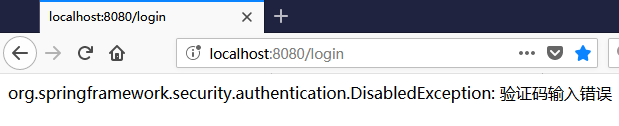
3.3 运行程序
现在来测试下,当验证码错误后:
四、Spring Security 验证
使用过滤器就已经实现了验证码功能,但其实它和 AJAX 验证差别不大。
- AJAX 是在提交前发一个请求,请求返回成功就提交,否则不提交;
- 过滤器是先验证验证码,验证成功就让 Spring Security 验证用户名和密码;验证失败,则产生异常·。
如果我们要做的需求是用户登录是需要多个验证字段,不单单是用户名和密码,那么使用过滤器会让逻辑变得复杂,这时候可以考虑自定义 Spring Security 的验证逻辑了…
4.1 WebAuthenticationDetails
我们知道 Spring security 默认只会处理用户名和密码信息。这时候就要请出我们的主角——WebAuthenticationDetails。
WebAuthenticationDetails: 该类提供了获取用户登录时携带的额外信息的功能,默认提供了 remoteAddress 与 sessionId 信息。
我们需要实现自定义的 WebAuthenticationDetails,并在其中加入我们的验证码:
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.WebAuthenticationDetails; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; /**
* 获取用户登录时携带的额外信息
* @author jitwxs
* @since 2018/5/9 11:15
*/
public class CustomWebAuthenticationDetails extends WebAuthenticationDetails {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 6975601077710753878L;
private final String verifyCode; public CustomWebAuthenticationDetails(HttpServletRequest request) {
super(request);
// verifyCode为页面中验证码的name
verifyCode = request.getParameter("verifyCode");
} public String getVerifyCode() {
return this.verifyCode;
} @Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(super.toString()).append("; VerifyCode: ").append(this.getVerifyCode());
return sb.toString();
}
}
在这个方法中,我们将前台 form 表单中的 verifyCode 获取到,并通过 get 方法方便被调用。
4.2 AuthenticationDetailsSource
自定义了WebAuthenticationDetails,我i们还需要将其放入 AuthenticationDetailsSource 中来替换原本的 WebAuthenticationDetails ,因此还得实现自定义 AuthenticationDetailsSource :
import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationDetailsSource;
import org.springframework.security.web.authentication.WebAuthenticationDetails;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; /**
* 该接口用于在Spring Security登录过程中对用户的登录信息的详细信息进行填充
* @author jitwxs
* @since 2018/5/9 11:18
*/
@Component
public class CustomAuthenticationDetailsSource implements AuthenticationDetailsSource<HttpServletRequest, WebAuthenticationDetails> {
@Override
public WebAuthenticationDetails buildDetails(HttpServletRequest request) {
return new CustomWebAuthenticationDetails(request);
}
}
该类内容将原本的 WebAuthenticationDetails 替换为了我们的 CustomWebAuthenticationDetails。
然后我们将 CustomAuthenticationDetailsSource 注入Spring Security中,替换掉默认的 AuthenticationDetailsSource。
修改 WebSecurityConfig,首先注入 CustomAuthenticationDetailsSource ,然后在config()中使用 authenticationDetailsSource(authenticationDetailsSource)方法来指定它。
@Autowired
private AuthenticationDetailsSource<HttpServletRequest, WebAuthenticationDetails> authenticationDetailsSource; @Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.authorizeRequests()
// 如果有允许匿名的url,填在下面
.antMatchers("/getVerifyCode").permitAll()
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
// 设置登陆页
.formLogin().loginPage("/login")
// 设置登陆成功页
.defaultSuccessUrl("/").permitAll()
// 登录失败Url
.failureUrl("/login/error")
// 自定义登陆用户名和密码参数,默认为username和password
// .usernameParameter("username")
// .passwordParameter("password")
// 指定authenticationDetailsSource
.authenticationDetailsSource(authenticationDetailsSource)
.and()
.logout().permitAll()
// 自动登录
.and().rememberMe()
.tokenRepository(persistentTokenRepository())
// 有效时间:单位s
.tokenValiditySeconds(60)
.userDetailsService(userDetailsService); // 关闭CSRF跨域
http.csrf().disable();
}
4.3 AuthenticationProvider
至此我们通过自定义WebAuthenticationDetails和AuthenticationDetailsSource将验证码和用户名、密码一起带入了Spring Security中,下面我们需要将它取出来。
这里需要我们自定义AuthenticationProvider,需要注意的是,如果是我们自己实现AuthenticationProvider,那么我们就需要自己做密码校验了。
@Component
public class CustomAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {
@Autowired
private CustomUserDetailsService customUserDetailsService; @Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
// 获取用户输入的用户名和密码
String inputName = authentication.getName();
String inputPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString(); CustomWebAuthenticationDetails details = (CustomWebAuthenticationDetails) authentication.getDetails(); String verifyCode = details.getVerifyCode();
if(!validateVerify(verifyCode)) {
throw new DisabledException("验证码输入错误");
} // userDetails为数据库中查询到的用户信息
UserDetails userDetails = customUserDetailsService.loadUserByUsername(inputName); // 如果是自定义AuthenticationProvider,需要手动密码校验
if(!userDetails.getPassword().equals(inputPassword)) {
throw new BadCredentialsException("密码错误");
} return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(inputName, inputPassword, userDetails.getAuthorities());
} private boolean validateVerify(String inputVerify) {
//获取当前线程绑定的request对象
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest();
// 不分区大小写
// 这个validateCode是在servlet中存入session的名字
String validateCode = ((String) request.getSession().getAttribute("validateCode")).toLowerCase();
inputVerify = inputVerify.toLowerCase(); System.out.println("验证码:" + validateCode + "用户输入:" + inputVerify); return validateCode.equals(inputVerify);
} @Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
// 这里不要忘记,和UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken比较
return authentication.equals(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class);
}
}
不要忘记在 WebSecurityConfig 注入进去:
@Autowired
private CustomAuthenticationProvider customAuthenticationProvider; @Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.authenticationProvider(customAuthenticationProvider);
auth.userDetailsService(userDetailsService).passwordEncoder(new PasswordEncoder() {
@Override
public String encode(CharSequence charSequence) {
return charSequence.toString();
} @Override
public boolean matches(CharSequence charSequence, String s) {
return s.equals(charSequence.toString());
}
});
}
4.4 运行程序
是不是比较复杂,为了实现该需求自定义了 WebAuthenticationDetails、AuthenticationDetailsSource、AuthenticationProvider,让我们运行一下程序,当输入错误验证码时:
五、SpringSecurity加密方法
源码大致理解:
public class BCryptPasswordEncoder implements PasswordEncoder
public interface PasswordEncoder {
String encode(CharSequence var1);
boolean matches(CharSequence var1, String var2);
}
第一个方法是加密方法,可以将明文密码加密成Bcrypt算法的密码。每次加密都会根据不同的盐生成不同的密文(同一明文,每次生成的密码都不一样),因而需要用第二种方法来比对密码正确与否。
第二个方法用于比对密码,第一个参数为明文密码,第二个参数为加密后的密文,如果匹配则返回true,如果不匹配则返回false。
CustomAuthenticationProvider 修改如下:
@Component
public class CustomAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {
@Autowired
private CustomUserDetailsService customUserDetailsService; @Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
// 获取用户输入的用户名和密码
String inputName = authentication.getName();
String inputPassword = authentication.getCredentials().toString(); CustomWebAuthenticationDetails details = (CustomWebAuthenticationDetails) authentication.getDetails(); String verifyCode = details.getVerifyCode();
if(!validateVerify(verifyCode)) {
throw new DisabledException("验证码输入错误");
} // userDetails为数据库中查询到的用户信息
UserDetails userDetails = customUserDetailsService.loadUserByUsername(inputName);
//加密
BCryptPasswordEncoder encoder = new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
// 如果是自定义AuthenticationProvider,需要手动密码校验
if(!encoder.matches(inputPassword,userDetails.getPassword()) {
throw new BadCredentialsException("密码错误");
} return new UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken(inputName, inputPassword, userDetails.getAuthorities());
} private boolean validateVerify(String inputVerify) {
//获取当前线程绑定的request对象
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest();
// 不分区大小写
// 这个validateCode是在servlet中存入session的名字
String validateCode = ((String) request.getSession().getAttribute("validateCode")).toLowerCase();
inputVerify = inputVerify.toLowerCase(); System.out.println("验证码:" + validateCode + "用户输入:" + inputVerify); return validateCode.equals(inputVerify);
} @Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
// 这里不要忘记,和UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken比较
return authentication.equals(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken.class);
}
}
---------------------
作者:Jitwxs
来源:CSDN
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/yuanlaijike/article/details/80253922
SpringBoot集成Spring Security(4)——自定义表单登录的更多相关文章
- spring security 之自定义表单登录源码跟踪
上一节我们跟踪了security的默认登录页的源码,可以参考这里:https://www.cnblogs.com/process-h/p/15522267.html 这节我们来看看如何自定义单表认 ...
- SpringBoot集成Spring Security(2)——自动登录
在上一章:SpringBoot集成Spring Security(1)——入门程序中,我们实现了入门程序,本篇为该程序加上自动登录的功能. 文章目录 一.修改login.html二.两种实现方式 2. ...
- SpringBoot集成Spring Security入门体验
一.前言 Spring Security 和 Apache Shiro 都是安全框架,为Java应用程序提供身份认证和授权. 二者区别 Spring Security:重量级安全框架 Apache S ...
- SpringBoot集成Spring Security(5)——权限控制
在第一篇中,我们说过,用户<–>角色<–>权限三层中,暂时不考虑权限,在这一篇,是时候把它完成了. 为了方便演示,这里的权限只是对角色赋予权限,也就是说同一个角色的用户,权限是 ...
- SpringBoot集成Spring Security(7)——认证流程
文章目录 一.认证流程 二.多个请求共享认证信息 三.获取用户认证信息 在前面的六章中,介绍了 Spring Security 的基础使用,在继续深入向下的学习前,有必要理解清楚 Spring Sec ...
- SpringBoot集成Spring Security(6)——登录管理
文章目录 一.自定义认证成功.失败处理 1.1 CustomAuthenticationSuccessHandler 1.2 CustomAuthenticationFailureHandler 1. ...
- SpringSecurity 自定义表单登录
SpringSecurity 自定义表单登录 本篇主要讲解 在SpringSecurity中 如何 自定义表单登录 , SpringSecurity默认提供了一个表单登录,但是实际项目里肯定无法使用的 ...
- SpringBoot集成Spring Security
1.Spring Security介绍 Spring security,是一个强大的和高度可定制的身份验证和访问控制框架.它是确保基于Spring的应用程序的标准 --来自官方参考手册 Spring ...
- springboot集成spring security(一)
一,添加pom依赖 <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId& ...
随机推荐
- 截图自动添加水印图片工具 pickpick设置中文语言
推荐一款截图工具,主要是可以截图自动带水印,效果不错 最近发现我的不少文章被转载的到处都是.乱七八糟,这个功能后续准备做个水印用起来,感觉不错 主角介绍 首先介绍下主角 PickPick
- 【题解】Norma [COCI2014] [SP22343]
[题解]Norma [COCI2014] [SP22343] 传送门:\(\text{Norma [COCI2014]}\) \(\text{[SP22343]}\) [题目描述] 给定一个整数 \( ...
- Asp.Net Mvc日志处理
/// <summary> /// 日志处理帮助类 /// </summary> public class LogHelper { private static Queue&l ...
- “金九银十”已过,总结我的天猫、蚂蚁、头条面试经历(Java岗)
跳槽时时刻刻都在发生,但是我建议大家跳槽之前,先想清楚为什么要跳槽.切不可跟风,看到同事一个个都走了,自己也盲目的开始面试起来(期间也没有准备充分),到底是因为技术原因(影响自己的发展,偏移自己规划的 ...
- deepin可视化程序打不开问题排查方法
anyconnect是一个VPN软件,在deepin系统下安装完成之后,并不能够直接使用,点击启动图标之后没有反应. 要想分析问题,必须从命令行入手,错误会打印在控制台. 如何根据一个图标来找到一个程 ...
- 汇编指令之JMP,CALL,RET(修改EIP的值!!!)
简单介绍了,JMP指令按市面上的意思来说是跳转到指定地址,但我这里不这么说,JMP, CALL, RET三个指令均为修改EIP值的指令,EAX, ECX, EBX, EDX, ESP, EBP, ES ...
- 8.InfluxDB-InfluxQL基础语法教程--ORDER BY子句
本文翻译自官网,官网地址:(https://docs.influxdata.com/influxdb/v1.7/query_language/data_exploration/) 在InfluxDB中 ...
- 数据挖掘--OPTICS
OPTICS是基于DBSCAN算法的缺陷提出来的一个算法. 核心思想:为每个数据对象计算出一个顺序值(ordering).这些值代表了数据对象的基于密度的族结构,位于同一个族的数据对象具有相近的顺序值 ...
- Windows出现“引用账户被锁定,且暂时无法登录”解决方法
1. 问题描述如下: i. 远程桌面登录时,出现提示必须修改密码才能登录,是因为密码过期所导致的,如下图: ii. 当我们登录Windows控制台(基于OpenStack平台的虚拟机)进行修改密码时, ...
- Django Windows+IIS+wfastcgi 环境下部署
教程基于 Windows 10专业版 + Python3.6 + IIS + wfastcgi 之上部署Django2.2的,同样适用于Windows server2012服务器和Windows7及以 ...