Linked List Cycle I&&II——快慢指针(II还没有完全理解)
Linked List Cycle I
Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it.
Follow up:
Can you solve it without using extra space?
该问题是经典面试问题,其标准解法是用两个指针,一快一慢,如果在快的指针能够追上慢的指针,则有环,否则无环。为了熟悉一下Python,用Python又写了一遍。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
if(head==NULL||head->next==NULL)
return false;
ListNode *flag1=head;
ListNode *flag2=head;
while()
{
if(flag1->next==NULL)
return false;
else
flag1=flag1->next;
if(flag2->next==NULL)
return false;
else
flag2=flag2->next;
if(flag2->next==NULL)
return false;
else
flag2=flag2->next;
if(flag1==flag2)
return true; }
}
};
Python版本:
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None class Solution:
# @param head, a ListNode
# @return a boolean
def hasCycle(self, head):
if head==None or head.next==None:
return False
flag1=head
flag2=head
while True:
flag1=flag1.next
if flag1.next==None:
return False
flag2=flag2.next
if flag2.next==None:
return False
flag2=flag2.next
if flag2.next==None:
return False
if flag1==flag2:
return True
Linked List Cycle II
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
Note: Do not modify the linked list.
Follow up:
Can you solve it without using extra space?
感觉又是一道数学题,没想了,直接看的人家是怎么做的。
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/x1957/p/3406448.html
比I麻烦点的就是找到循环开始点TAT
I只是判断是否循环。要求不使用额外空间(不然hash就可以了
按I的思路,我们又慢指针S和快指针F。。。F走两步,S走一步。。。若有环,必定相遇。
画个图(很丑勿喷
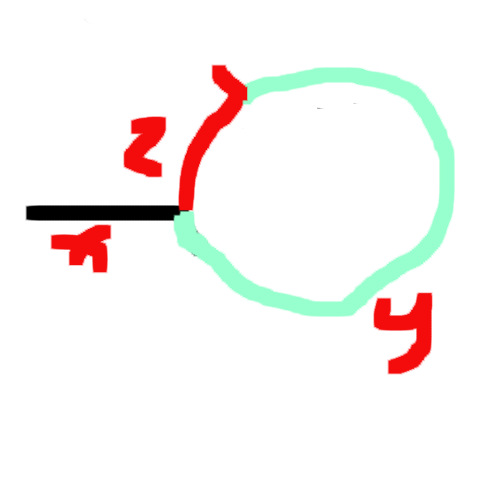
假设在红色凸起的地方相遇了。
F走的路程应该是S的两倍
S = x + y
F = x + y + z + y = x + 2y + z
2*S = F
2x+2y = x + 2y + z
得到x = z
也就是从head到环开始的路程 = 从相遇到环开始的路程
那么。。。只要S和F相遇了,我们拿一个从头开始走,一个从相遇的地方开始走
两个都走一步,那么再次相遇必定是环的开始节点!
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
// IMPORTANT: Please reset any member data you declared, as
// the same Solution instance will be reused for each test case.
if(head == NULL) return NULL;
ListNode* S = head;
ListNode* F = head; while(F != NULL){
if(F) F = F -> next;
if(F) F = F -> next;
if(S) S = S -> next;
if(F != NULL && F == S){
S = head;
while(S != F){
S = S -> next;
F = F -> next;
}
return S;
}
}
return NULL;
}
};
关于此题,网上看到一个更好的解释,解释如下:
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/sysucph/article/details/15378043
对于判断链表是否有环,方法很简单,用两个指针,一开始都指向头结点,一个是快指针,一次走两步,一个是慢指针,一次只走一步,当两个指针重合时表示存在环了。
证明:假设链表有环,环的长度为N,慢指针在起始位置,快指针在位置k(位置从0开始计数),那么快指针只要比慢指针多走经过N-k步,就可以追上慢指针了(因为之前已经多走了k步,在多走N-K步则一共多走了一圈,刚好相遇)。。。,因为每一次快指针都比慢指针多走一步,所以一定可以在有限的步数追上慢指针。
现在的问题是如何求出环的起始位置,我们先给出结论:当快指针和慢指针重合的时候,把一个指针重新指向头指针,两个指针现在速度一样,一次走一步,那么当两个指针值相同时,所在的指针就是我们要找的起始位置。
证明内容来自一个国外的网站:http://umairsaeed.com/2011/06/23/finding-the-start-of-a-loop-in-a-circular-linked-list/
要证明上面这个结论,我们先证明一个结论,假设慢指针Slow停在环的起始位置时,快指针Fast停在第k个位置,那么两个指针相遇时会停在从起始位置倒数第k个位置,也就是n-k这个位置
从Slow停在环的起始位置,假设最终停在n-x相遇。
因为Fast只要再比Slow多走n-k步,就可以追上Slow,而每一次操作Fast都比Slow多走一步,因为只需要再走n-k步就可以追上Slow,此时Slow停在n-k这个位置。
这意味着,如果Slow从环的起始位置,Fast从环的第k个位置开始,最终两个指针会在n-k这个位置相遇(n为环的长度)
假设一开始Fast和Slow从开始位置开始遍历这个链表。
令m = 3,表示经过三步,Slow结点到达环的起始位置,此时Fast在环的第m个位置,因为Fast比Slow多走了m步
根据刚才的结论,当Slow停在起始位置,Fast停在m位置,两个链表最后会在n-m位置相遇
此时把Slow移到头结点位置,两个结点都是要经过m步,才刚刚好到达环的起始位置。
这里好起来好像m小于环的长度l,才成立。其实是一样的。
假设m = t*l+k
这就是说,环最终停在n-k这个位置了。还需要k步就可以到达环的起始结点。而把Slow结点重新设置为头结点,则需要t*l+k步才第一次到达环的起始结点,
但是注意了,多走了k*l步,Fast结点还是会停在环的起始位置的。
得证!!!
和室友大神lyc交流,大神的想了一会,秒了= =!
大神的解释是这样的:假设环的长度为l,从开始到两个指针第一次相遇总共走了m步,那么Fast指针走了2*m步,Slow指针走了m步,Fast比 Slow多走了m步,Fast比Slow多走了x圈,那么有x*l==m,l是m的一个因子,再走m步,两个指针每次走一步,Fast移到开头位 置,Slow走了m步停在第一次相遇位置,Fast因为也是每次走一步,所以也会停在相遇位置,而且可以看出来,一旦Fast进入环,Fast和Slow 结点就保持相对静止了。。。碉堡了。。春哥
Linked List Cycle I&&II——快慢指针(II还没有完全理解)的更多相关文章
- [LeetCode题解]142. 环形链表 II | 快慢指针
解题思路 本题是在141. 环形链表基础上的拓展,如果存在环,要找出环的入口. 如何判断是否存在环,我们知道通过快慢指针,如果相遇就表示有环.那么如何找到入口呢? 如下图所示的链表: 当 fast 与 ...
- 【算法分析】如何理解快慢指针?判断linked list中是否有环、找到环的起始节点位置。以Leetcode 141. Linked List Cycle, 142. Linked List Cycle II 为例Python实现
引入 快慢指针经常用于链表(linked list)中环(Cycle)相关的问题.LeetCode中对应题目分别是: 141. Linked List Cycle 判断linked list中是否有环 ...
- Linked List Cycle && Linked List Cycle II
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null. Note ...
- LeetCode: Linked List Cycle II 解题报告
Linked List Cycle II Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cyc ...
- LeetCode142:Linked List Cycle II
题目: Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null. ...
- leetcode 141. Linked List Cycle 、 142. Linked List Cycle II
判断链表有环,环的入口结点,环的长度 1.判断有环: 快慢指针,一个移动一次,一个移动两次 2.环的入口结点: 相遇的结点不一定是入口节点,所以y表示入口节点到相遇节点的距离 n是环的个数 w + n ...
- 【LeetCode】142. Linked List Cycle II (2 solutions)
Linked List Cycle II Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cyc ...
- LeetCode141 Linked List Cycle. LeetCode142 Linked List Cycle II
链表相关题 141. Linked List Cycle Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it. Follow up:Can y ...
- [算法][LeetCode]Linked List Cycle & Linked List Cycle II——单链表中的环
题目要求 Linked List Cycle Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it. Follow up: Can you so ...
随机推荐
- 2-17作业 数据库和shell综合练习
1. 使用shell把“12306用户名和密码库-不要使用记事本打开会卡死-解压后可使用word或ultraedit打开.rar”中的所有记录成生sql语句,然后把sql导入数据库,成一个uPwd_1 ...
- java使用POI操作XWPFDocument中的XWPFParagraph(段落)对象的属性略解
我用的是office word 2016版 创建文本对象 XWPFDocument docxDocument = new XWPFDocument(); 创建段落对象 XWPFParagraph pa ...
- Nginx的配置文件简介及在Nginx中配置基于不同ip的虚拟主机
Nginx的配置文件简介及在Nginx中配置基于不同ip的虚拟主机: #user nobody; worker_processes 1; #error_log logs/error.log; #err ...
- [POI2007] ZAP-Queries (莫比乌斯反演)
[POI2007] ZAP-Queries 题目描述 Byteasar the Cryptographer works on breaking the code of BSA (Byteotian S ...
- 转ajax的jsonp的文章
转:http://justcoding.iteye.com/blog/1366102/ Js是不能跨域请求.出于安全考虑,js设计时不可以跨域. 什么是跨域: 1.域名不同时. 2.域名相同,端口不同 ...
- linux shell脚本攻略笔记
前一阵子系统学习了下<linux shell脚本攻略>这本书.在此记录下自己的学习笔记 1. 输出颜色字符 echo -e "\e[1:41m" 1表示背景色 2 ...
- SDRAM初始化
DDR配置过程比较复杂,基本上是按照DDR控制器的时序要求来做的,其中很多参数要结合DDR芯片本身的参数来定,还有些参数是时序参数,要去详细计算.所以DDR配置非常繁琐.细致.专业.所以我们对DDR初 ...
- 杭电多校第七场-J-Sequence
题目描述 Let us define a sequence as belowYour job is simple, for each task, you should output Fn module ...
- 51Nod 1133 不重叠的线段 | 典型贪心
Input示例 3 1 5 2 3 3 6 Output示例 2 题意:给出n条一维线段,求不重合的最多线段数. 解析:这个是典型的贪心算法的区间问题. 贪心策略:每次取尽可能短的区间,而且保证相互之 ...
- 【hdu5217-括号序列】线段树
题意:给一串括号,有2个操作,1.翻转某个括号.2.查询某段区间内化简后第k个括号是在原序列中的位置.1 ≤ N,Q ≤ 200000. 题解: 可以知道,化简后的序列一定是)))((((这种形式的. ...




