9. Complex Vectors and Matrices
9.1 Real versus Complex
- R= line of all real numbers (\(-\infty < x < \infty\)) \(\longleftrightarrow\) C=plane of all complex numbers \(z=x+iy\)
- |x| = absolute value of x \(\longleftrightarrow\) \(|z| = \sqrt{x^2+y^2} = r\) = absolute value (or modulus) of z
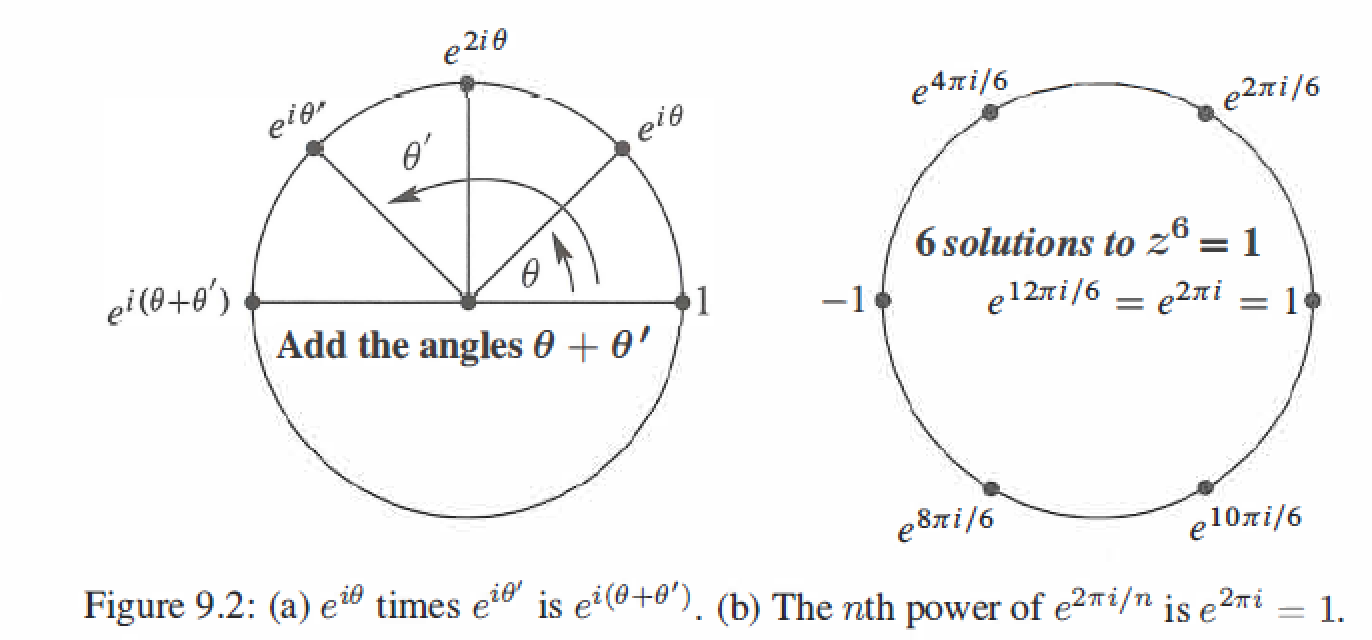
- 1 and -1 solve \(x^2=1\) \(\longleftrightarrow\) \(z=1,w,...,w^{n-1}\) solve \(z^n=1\) where \(w = e^{2\pi i/n}\)
- \(R^n\) : vectors with n real components \(\longleftrightarrow\) \(C^n\): vectors with n complex components
- length : \(||x||^2 = x_1^2 + \cdots + x_n^2\) \(\longleftrightarrow\) \(||z||^2 = |z_1|^2 + \cdots + |z_n|^2\)
- transpose : \(A_{ij}^T = A_{ji}\) \(\longleftrightarrow\) conjugate transpose \(A_{ij}^H = \overline{A_{ji}}\)
- dot/inner product : \(x^Ty = x_1y_1 + \cdots + x_ny_n\) \(\longleftrightarrow\) dot/inner product : \(u^Hv = \overline{u_1}v_1 + \cdots + \overline{u_n}v_n\)
- reason for \(A^T\) : \((Ax)^Ty = x^T(A^Ty)\) \(\longleftrightarrow\) reason for \(A^H\): \((Au)^Hv = u^H(A^Hv)\)
- orthgonality : \(x^Ty = 0\) \(\longleftrightarrow\) orthgonality : \(u^Hv = 0\)
- symmetric matrices: \(S=S^T\) \(\longleftrightarrow\) Hermitian matrices: \(S=S^H\)
- skew-symmetric matrices : \(K^T = K^{-1}\) \(\longleftrightarrow\) skew-Hermitian matrices : \(K^H = -K\)
- orthgonal matrices : \(Q^T = Q^{-1}\) \(\longleftrightarrow\) unitary matrices : \(U^H = U^{-1}\)
- orthonormal matrices : \(Q^TQ = I\) \(\longleftrightarrow\) orthonormal matrices : \(U^HU = I\)
- \(S = Q\Lambda Q^{-1} = Q\Lambda Q^T\) \(\longleftrightarrow\) \(S = U\Lambda U^{-1} = U\Lambda U^H\)
- \((Qx)^T(Qy)= x^Ty\) and \(||Qx|| = ||x||\) \(\longleftrightarrow\) \((Ux)^H(Uy)= x^Hy\) and \(||Uz|| = ||z||\)
9.2 Complex Numbers
Complex numbers correspond to points in a plane. Real numbers go along the x axis.Pure imaginary numbers are on the y axis. The complex number \(a+bi\) is at the point with coordinates (a, b).

Keys:
Add : \((a + bi) + (c + di) = (a+c)+(b+d)i\)
Multiply : \((a+bi)(a-bi)=a^2+b^2\)
Eigenvalues \(\lambda\) 和 \(\overline{\lambda}\) : If \(Ax=\lambda x\) and A is real then \(A\overline{x}=\overline{\lambda}\overline{x}\)
Euler's Formula : \(e^{i\theta}= cos\theta + isin\theta\)
Polar Form : The number \(z=a+ib\) is also \(z=rcos\theta + irsin\theta = re^{i\theta} \ \ with \ \ r = |z| = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2}\)
Powers: The nth power of \(z=r(cos\theta+isin\theta)\) is \(z^n=r^n(cos(n\theta)+isin(n\theta))\)
The nth roots of 1 : Set \(w=e^{2\pi i/n}\), the nth powers of \(1,w,w^2,...,w^{n-1}\) all equal 1, they solve the equation \(z^n=1\)
9.3 Hermitian and Unitary Matrices
When we transpose a complex vector z or matrix A , also take the complex conjugate too.
With \(z_j = a_j + i b_j\):
conjugate transpose : \(\overline{z}^T=[\overline{z_1} \cdots \overline{z_n}] = [a_1 - ib_1 \cdots a_n - ib_n]\)
length squared : \([\overline{z_1} \cdots \overline{z_n}] \left[ \begin{matrix} z_1 \\ \vdots \\ z_n\end{matrix}\right]= |z_1|^2 + \cdots + |z_n|^2 \longleftrightarrow \overline{z}^Tz=z^Hz = ||z||^2\) (\(z^H\) is z Hermitian)
Inner product : \(u^{H}v = [\overline{u_1} \cdots \overline{u_n}] \left[ \begin{matrix} v_1 \\ \vdots \\ v_n\end{matrix}\right]= \overline{u_1}v_1 + \cdots + \overline{u_n}v_n\)
Hermitian Matrix
Among complex matrices, with Hermitian matrices : \(S=S^H, s_{ij} = \overline{s_{ji}}\)
S^H = \left[ \begin{matrix} 2&3+3(-i) \\ 3-3(-i)&5 \end{matrix} \right] = \left[ \begin{matrix} 2&3-3i \\ 3+3i&5 \end{matrix} \right] = S \\
\]
Eigenvalues of a Hermitian matrix is real, and eigenvectors of a Hermitian are orthogonal.
Unitary Matrices
A unitary matrix Q is a complex square matrix that has orthonormal columns.
Unitary matrix that diagonalizes S : \(Q=\frac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\left[ \begin{matrix} 1&1-i \\ 1+i&-1 \end{matrix}\right]\)
Orthonormal columns : \(Q^HQ=I\)
Square + Orthonormal columns = Unitary matrix : \(Q^{H} = Q^{-1}\)
If Q is unitary the \(||Qz||=||z||\). Therefore \(Qz=\lambda z\) leads to \(|\lambda| = 1\)
9.4 The Fast Fourier Transform
Fourier Matrix
(F_n)_{ij} = w^{ij}, (i,j=0,1,2,...,n-1) \\
w_n = e^{2\pi / n * i} \\
w_n = e^{\pi / 2 * i} = i, w_n = e^{\pi * i} = -1 \\
w_n = e^{3\pi / 2 * i} = -i, w_n = e^{2\pi * i} = 1
\]
example:
\(F_4\) is orthogonal and symmetric.
\left [ \begin{matrix} 1&1&1&1 \\ 1&i&-1&-i \\ 1&-1&1&-1\\ 1&-i&-1&i\end{matrix} \right]
\\
\left [ \begin{matrix} &&& \\ &F_2&& \\ &&& \\ &&&F_2\end{matrix} \right] =
\left [ \begin{matrix} 1&1&& \\ 1&i^2&& \\ &&1&1\\ &&1&i^2\end{matrix} \right]
\\
\Downarrow \\
F_4 =
\left [ \begin{matrix} 1&1&1&1 \\ 1&w_4^1&w_4^{2}&w_4^{3} \\ 1&w_4^2&w_4^{4}&w_4^{6}\\ 1&w_4^{3}&w_4^{6}&w_4^{9}\end{matrix} \right] =
\left [ \begin{matrix} 1&&1& \\ &1&&i \\ 1&&-1&\\ &1&&-i\end{matrix} \right]
\left [ \begin{matrix} 1&1&& \\ 1&i^2&& \\ &&1&1\\ &&1&i^2\end{matrix} \right]
\left [ \begin{matrix} 1&&& \\ &&1& \\ &1&& \\ &&&1 \end{matrix} \right] \\
\]
\(w_4 = e^{\pi / 2 * i} \\
F_4^{H}F_4 = I, \ \ F^{-1}_4 = \frac{1}{4}\overline{F}_4\)
The key idea is to connect \(F_n\) with the half-size Fourier matrix \(F_{n/2}\), and keep going to \(F_{n/4}\),which can be factored in a way that procdeces many zeros, and improve multiply quickly.
Save more than half of time : \(n^2 \Rightarrow 1/2 n log_2^n\)
\left[ \begin{matrix} F_{32}&0 \\ 0&F_{32} \end{matrix}\right]
\left[ \begin{matrix} P_{64} \end{matrix}\right] \\
=\left[ \begin{matrix} \left[ \begin{matrix} I_{16}&D_{16} \\ I_{16}&-D_{16} \end{matrix}\right]&0 \\ 0& \left[ \begin{matrix} I_{16}&D_{16} \\ I_{16}&-D_{16}\end{matrix}\right] \end{matrix}\right]
\left[ \begin{matrix} \left[ \begin{matrix} F_{16}&0 \\ 0&F_{16} \end{matrix}\right]&0 \\ 0& \left[ \begin{matrix} F_{16}&0 \\ 0&F_{16} \end{matrix}\right] \end{matrix}\right]
\left[ \begin{matrix} P_{32}& \\ &P_{32} \end{matrix}\right] \\
D = \left[ \begin{matrix} 1&&& \\ &w^1&& \\ &&\ddots& \\ &&&w^n \end{matrix}\right] \\
P = \left [ \begin{matrix} even-odd \\ permutation \end{matrix}\right]
\]
9. Complex Vectors and Matrices的更多相关文章
- Matrices and Vectors
Matrices and Vectors Matrices are 2-dimensional arrays: A vector is a matrix with one column and man ...
- 理工科应该的知道的C/C++数学计算库(转)
理工科应该的知道的C/C++数学计算库(转) 作为理工科学生,想必有限元分析.数值计算.三维建模.信号处理.性能分析.仿真分析...这些或多或少与我们常用的软件息息相关,假如有一天你只需要这些大型软件 ...
- (转)几种范数的解释 l0-Norm, l1-Norm, l2-Norm, … , l-infinity Norm
几种范数的解释 l0-Norm, l1-Norm, l2-Norm, - , l-infinity Norm from Rorasa's blog l0-Norm, l1-Norm, l2-Norm, ...
- Mathematics for Computer Graphics数学在计算机图形学中的应用 [转]
最近严重感觉到数学知识的不足! http://bbs.gameres.com/showthread.asp?threadid=10509 [译]Mathematics for Computer Gra ...
- The plot Function in matlab
from http://pundit.pratt.duke.edu/wiki/MATLAB:Plotting The plot Function The plot function is used t ...
- Open CASCADE 基础类(Foundation Classes)
1 介绍(Introduction) 1 如何使用Open CASCADE技术(OCCT)基础类. This manual explains how to use Open CASCADE Techn ...
- GNU scientific library
GNU scientific library 是一个强大的C,C++数学库.它涉及的面很广,并且代码效率高,接口丰富.正好最近做的一个项目中用到多元高斯分布,就找到了这个库. GNU scientif ...
- Mathematics for Computer Graphics
Mathematics for Computer Graphics 最近严重感觉到数学知识的不足! http://bbs.gameres.com/showthread.asp?threadid=105 ...
- 在WINDOWS中安装使用GSL(MinGW64+Sublime Text3 & Visual Studio)
本文介绍在Windows下安装使用GSL库,涉及GSL两个版本(官方最新版及GSL1.8 VC版).msys shell.GCC.G++等内容,最终实现对GSL安装及示例基于MinGW64在Subli ...
- Foundations of Game Engine Development Volume 1 Mathematics (Eric Lengyel 著)
http://www.foundationsofgameenginedev.com/ Chapter1 Vectors and Matrices (已看) Chapter2 Transforms (已 ...
随机推荐
- 如何设计一个高性能的图 Schema
本文整理自青藤云安全工程师--文洲在青藤云技术团队内部分享,分享视频参考:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1r64y1R72i 图数据库的性能和 schema 的设计 ...
- hbase报错ERROR: org.apache.hadoop.hbase.ipc.ServerNotRunningYetException: Server is not running yet 采坑记
1.错误异常信息: Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Failed to find me ...
- MVC阶段所有框架完整组合示例
思路:创建工程,导包.编辑配置文件包括 核心spring配置 SpringConfig myBatis 配置文件 mybatisConfig JdbcConfig jdbc.properti ...
- Zabbix6.0使用教程 (一)—zabbix新增功能介绍2
上一篇我们已经介绍了部分zabbix6.0的新增功能,这期我们将继续为家详细介绍下余下的zabbix6.0新增功能,大家可以往下看. 六.监控项 6.1 自动类型选择 监控项配置表单会自动建议匹配的信 ...
- 摆脱鼠标系列 vscode 向右拆分编辑器 ctrl + 右箭头
摆脱鼠标系列 vscode 向右拆分编辑器 ctrl + 右箭头 为什么 今天看见一个两栏工作的,左侧放的是目录大纲,右侧是代码内容 用快捷键 ctrl + 右箭头 快速扩展一个,关闭可以ctrl + ...
- MYSQL 是如何保证binlog 和redo log同时提交的?
MYSQL 一个事务在提交的时候能够保证binlog和redo log是同时提交的,并且能在宕机恢复后保持binlog 和redo log的一致性. 先来看看什么是redo log 和binlog,以 ...
- K8S容器环境下资源限制与jvm内存回收
一.k8s中的java资源限制与可能的问题 与以前单机跑单服务的情况相比,在k8s.docker容器化环境下的宿主机内存.cpu相对更大,所以当运行java类程序的时候,就必然有必要对容器进行内存限制 ...
- Android使用poi遇到的问题
原文:Android使用poi遇到的问题 关于Poi使用可以看这一篇[开源库推荐]#4 Poi-办公文档处理库 本篇主要讲些在Android上使用出现的问题 问题 原本是需要一个导出xlsx表格文件的 ...
- day09-Java数组
Java数组 9.稀疏数组 什么是稀疏数组? 当一个数组中大部分元素为0,或者为同一值的数组时,可以使用稀疏数组来保存该数组. 稀疏数组的处理方式是: 记录数组一共有几行几列,有多少个不同的值 把具有 ...
- api-ms-win-crt-***.dll, api-ms-win-core-***.dll,win7以后kernel.dll,msvc*.dll的改变。api-ms-win-crt-***.dll 有问题就是 c++ redist 版本过低。
api-ms-win-crt-***-|1-1-0.dll是redistributable c++的一部分.以往只会因为msvc*NNN.dll才要去找对应的redistributable c++版本 ...
