马昕璐 201771010118《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十八周学习总结
实验十八 总复习
实验时间 2018-12-30
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 综合掌握java基本程序结构;
(2) 综合掌握java面向对象程序设计特点;
(3) 综合掌握java GUI 程序设计结构;
(4) 综合掌握java多线程编程模型;
(5) 综合编程练习。
2、实验内容和步骤
任务1:填写课程课后调查问卷,网址:https://www.wjx.cn/jq/33108969.aspx。
任务2:综合编程练习
练习1:设计一个用户信息采集程序,要求如下:
1) 用户信息输入界面如下图所示:
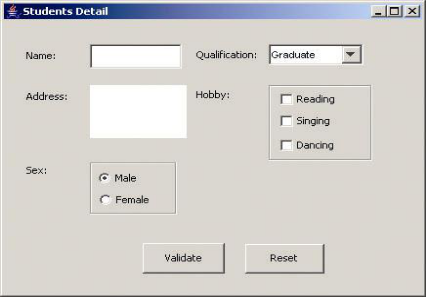
(1)用户点击提交按钮时,用户输入信息显示控制台界面;
(2)用户点击重置按钮后,清空用户已输入信息;
(3)点击窗口关闭,程序退出。
package demo;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
Frame frame = new Frame();
frame.setTitle("Student Detail");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
frame.setResizable(false);
});
}
}
package demo;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
public class Frame extends JFrame {
private JPanel panel;
private JPanel panel1;
private JPanel panel2;
private JPanel buttonPanel;
private JComboBox<String> faceCombo;
private JCheckBox Reading;
private JCheckBox Singing;
private JCheckBox Dancing;
private JPanel panelDanXuan;
private ButtonGroup option;
private JRadioButton optionA;
private JRadioButton optionB;
private static final int DEFAULT_WITH = 800;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 400;
public Frame() {
//框架a
panel = new JPanel();
panel.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(200,160));
panel.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,4));
JLabel lab = new JLabel("Name:", JLabel.CENTER);
final JTextField jt = new JTextField();
JLabel lab1 = new JLabel("Qualification:", JLabel.CENTER);
faceCombo = new JComboBox<>();
faceCombo.addItem("Graduate");
faceCombo.addItem("Not graduated");
JLabel lab2 = new JLabel("Adress:", JLabel.CENTER);
final JTextArea jt1 = new JTextArea();
JLabel lab3 = new JLabel("Hobby:", JLabel.CENTER);
panel1 = new JPanel();
Reading = new JCheckBox("Reading");
Singing = new JCheckBox("Singing");
Dancing = new JCheckBox("Dancing ");
//框架b
panel2 = new JPanel();
panel2.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(200,160));
JLabel lab4 = new JLabel("Sex:", JLabel.CENTER);
panelDanXuan = new JPanel();
option = new ButtonGroup();
optionA = new JRadioButton("Male");
optionB = new JRadioButton("Female");
//框架c
buttonPanel = new JPanel();
buttonPanel.setPreferredSize(new Dimension(200,80));
JButton jButton1 = new JButton("Validate");
JButton jButton2 = new JButton("Reset");
panel.add(lab);
panel.add(jt);
panel.add(lab1);
panel.add(faceCombo);
panel.add(lab2);
panel.add(jt1);
panel.add(lab3);
panel1.add(Reading);
panel1.add(Singing);
panel1.add(Dancing);
panel1.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder(""));
panel1.setLayout(new BoxLayout(panel1, BoxLayout.Y_AXIS));
panel.add(panel1);
panel2.add(lab4);
option.add(optionA);
option.add(optionB);
panelDanXuan.add(optionA);
panelDanXuan.add(optionB);
panelDanXuan.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder(""));
panelDanXuan.setLayout(new BoxLayout(panelDanXuan, BoxLayout.Y_AXIS));
panel2.add(panelDanXuan);
buttonPanel.add(jButton1);
buttonPanel.add(jButton2);
add(panel, BorderLayout.NORTH);
add(panel2, BorderLayout.WEST);
add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
setSize(DEFAULT_WITH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
jButton1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String Name = jt.getText();
if (Name != null) {
System.out.println("Name:"+Name);
}
String m = faceCombo.getSelectedItem().toString();
System.out.println("Qualification:"+m);
String Adress = jt1.getText();
if (Adress != null) {
System.out.println("Adress:"+Adress);
}
System.out.println("Hobby:");
if(Reading.isSelected()) {
System.out.println(Reading.getText());
}
if(Singing.isSelected()) {
System.out.println(Singing.getText());
}
if(Dancing.isSelected()) {
System.out.println(Dancing.getText());
}
System.out.println("Sex:");
if(optionA.isSelected()) {
System.out.println(optionA.getText());
}
if(optionB.isSelected()) {
System.out.println(optionB.getText());
}
}
});
jButton2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
jt.setText("");
jt1.setText("");
faceCombo.setSelectedItem("Graduate");
Reading.setSelected(false);
Singing.setSelected(false);
Dancing.setSelected(false);
option.clearSelection();
}
});
}
}
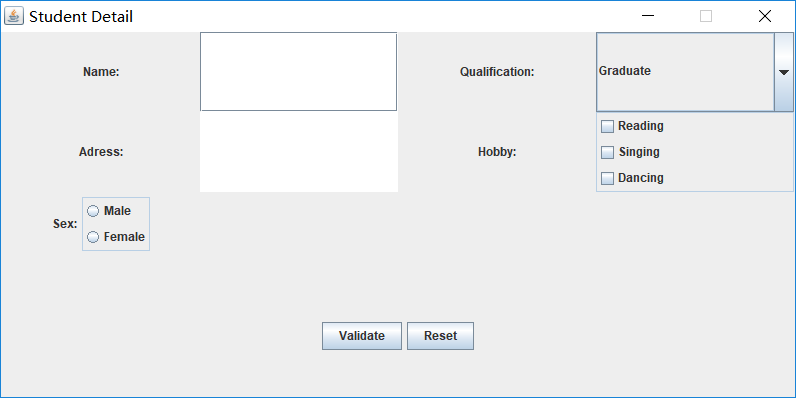
练习2:采用GUI界面设计以下程序:
l 编制一个程序,将身份证号.txt 中的信息读入到内存中;
l 按姓名字典序输出人员信息;
l 查询最大年龄的人员信息;
l 查询最小年龄人员信息;
l 输入你的年龄,查询身份证号.txt中年龄与你最近人的姓名、身份证号、年龄、性别和出生地;
l 查询人员中是否有你的同乡。
l 输入身份证信息,查询所提供身份证号的人员信息,要求输入一个身份证数字时,查询界面就显示满足查询条件的查询结果,且随着输入的数字的增多,查询匹配的范围逐渐缩小。
package 身份查询;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.EventQueue;
import java.awt.Toolkit;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class Out {
public static void main (String args[])
{
Toolkit t=Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
Dimension s=t.getScreenSize();
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new Main1();
frame.setBounds(0, 0,(int)s.getWidth(),(int)s.getHeight());
frame.setTitle("身份查询系统");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
package 身份查询;
public class Person implements Comparable<Person> {
private String name;
private String ID;
private int age;
private String sex;
private String birthplace;
public String getname() {
return name;
}
public void setname(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getID() {
return ID;
}
public void setID(String ID) {
this.ID= ID;
}
public int getage() {
return age;
}
public void setage(int age) {
this.age= age;
}
public String getsex() {
return sex;
}
public void setsex(String sex) {
this.sex= sex;
}
public String getbirthplace() {
return birthplace;
}
public void setbirthplace(String birthplace) {
this.birthplace= birthplace;
}
public int compareTo(Person o) {
return this.name.compareTo(o.getname());
}
public String toString() {
return name+"\t"+sex+"\t"+age+"\t"+ID+"\t"+birthplace+"\n";
}
}
package 身份查询;
import java.awt.BorderLayout;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.Timer;
import javax.swing.*;
public class Main1 extends JFrame
{
private static ArrayList<Person> Personlist;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
File file = new File("F:\\身份证号.txt");
private JPanel Panel;
private JLabel JLabel1;
private JButton Button,Button2,Button3;
private JTextArea text,text1,text2,text3;
boolean tru=true;
public Main1() {
Panel = new JPanel();Panel.setLayout(null);
Button = new JButton("1:按姓名字典序输出人员信息");
Button2 = new JButton("2:查询最大年龄与最小年龄人员信息");
Button3 = new JButton("查询相近年龄");
JLabel1 = new JLabel("输入身份证号或者地址查询");JLabel1.setBounds(900, 50, 400, 30);
text=new JTextArea(30,80);text.setBounds(50, 180, 700, 700);
text1=new JTextArea(1,30);text1.setBounds(900, 80, 400, 30);
text2=new JTextArea(30,80);text2.setBounds(900,180,700, 700);
text3=new JTextArea(30,80);text3.setBounds(420,100,200,40);
Button.addActionListener(new Action());Button.setBounds(50,50,300,40);
Button2.addActionListener(new Action1());Button2.setBounds(50,100,300,40);
Button3.addActionListener(new Action2());Button3.setBounds(650,100,120,40);
Panel.add(JLabel1);
Panel.add(Button);
Panel.add(Button2);
Panel.add(Button3);
Panel.add(text);
Panel.add(text2);
Panel.add(text1);
Panel.add(text3);
add(Panel);
Timer timer = new Timer();
TimerTask timeTask=new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run()
{
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
text2.setText(null);
String place=text1.getText().toString().trim();
for (int i = 0; i <Personlist.size(); i++)
{
String Str=(String)Personlist.get(i).getbirthplace();
if(Str.contains(place)&&!place.equals(""))
{
text2.append(Personlist.get(i).toString());
}
}
for (int i = 0; i <Personlist.size(); i++)
{
String Str=(String)Personlist.get(i).getID();
if(Str.contains(place)&&!place.equals(""))
{
text2.append(Personlist.get(i).toString());
}
}
}
};timer.schedule(timeTask, 0,100);
Personlist = new ArrayList<>();
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis));
String temp = null;
while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) {
Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp);
linescanner.useDelimiter(" ");
String name = linescanner.next();
String ID = linescanner.next();
String sex = linescanner.next();
String age = linescanner.next();
String place =linescanner.nextLine();
Person Person = new Person();
Person.setname(name);
Person.setID(ID);
Person.setsex(sex);
int a = Integer.parseInt(age);
Person.setage(a);
Person.setbirthplace(place);
Personlist.add(Person);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("查找不到信息");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("信息读取有误");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private class Action implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
text.setText(null);
Collections.sort(Personlist);
text.append(Personlist.toString());
}
}
private class Action1 implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
text.setText(null);
int max=0,min=100;int j,k1 = 0,k2=0;
for(int i=1;i<Personlist.size();i++)
{
j=Personlist.get(i).getage();
if(j>max)
{
max=j;
k1=i;
}
if(j<min)
{
min=j;
k2=i;
}
}
text.append("年龄最大: "+Personlist.get(k1)+"\n"+"年龄最小: "+Personlist.get(k2));
}
}
private class Action2 implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
text.setText(null);
int a = Integer.parseInt(text3.getText().toString().trim());
int d_value=a-Personlist.get(agenear(a)).getage();
for (int i = 0; i < Personlist.size(); i++)
{
int p=Personlist.get(i).getage()-a;
if(p==d_value||-p==d_value) text.append(Personlist.get(i).toString());
}
}
}
public static int agenear(int age) {
int j=0,min=53,d_value=0,k=0;
for (int i = 0; i < Personlist.size(); i++)
{
d_value=Personlist.get(i).getage()-age;
if(d_value<0) d_value=-d_value;
if (d_value<min)
{
min=d_value;
k=i;
}
} return k;
}
}
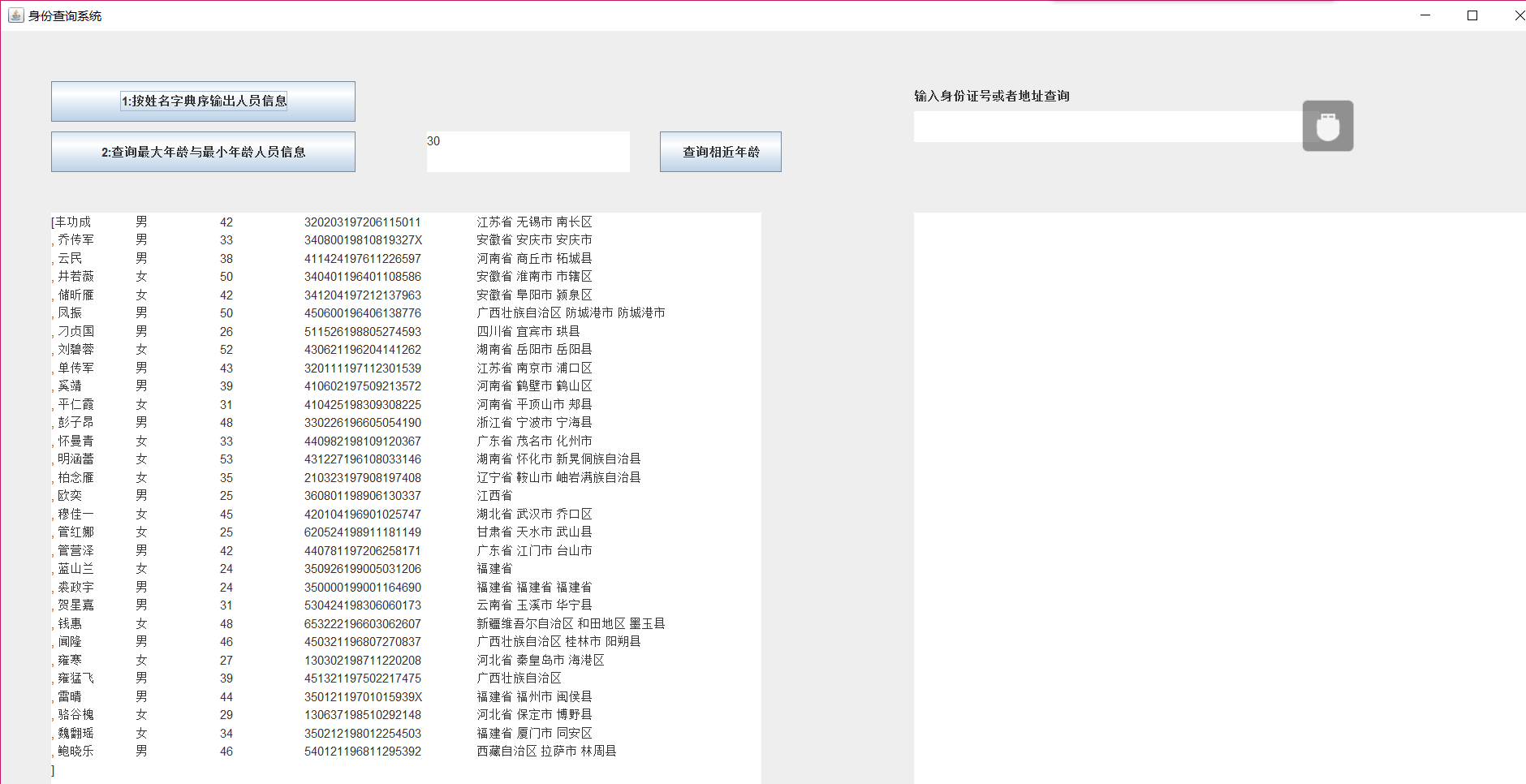
练习3:采用GUI界面设计以下程序
l 编写一个计算器类,可以完成加、减、乘、除的操作
l 利用计算机类,设计一个小学生100以内数的四则运算练习程序,由计算机随机产生10道加减乘除练习题,学生输入答案,由程序检查答案是否正确,每道题正确计10分,错误不计分,10道题测试结束后给出测试总分;
l 将程序中测试练习题及学生答题结果输出到文件,文件名为test.txt。
package 计算器;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.EventQueue;
import java.awt.Toolkit;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
public class New {
public static void main (String args[])
{
Toolkit t=Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
Dimension s=t.getScreenSize();
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new Demo();
frame.setBounds(0, 0,(int)s.getWidth()/2,(int)s.getHeight()/2);
frame.setTitle("计算器");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
package 计算器;
import java.awt.Font;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Scanner;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.math.*;
public class Demo extends JFrame {
private String[] c=new String[10];
private String[] c1=new String[10];
private int[] list=new int[10];
int i=0,i1=0,sum = 0;
private PrintWriter out = null;
private JTextArea text,text1;
private int counter;
public Demo() {
JPanel Panel = new JPanel();Panel.setLayout(null);
JLabel JLabel1=new JLabel("");JLabel1.setBounds(500, 800, 400, 30);JLabel1.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,35));
JButton Button = new JButton("生成题目");Button.setBounds(50,150,150,50);Button.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,20)); Button.addActionListener(new Action());
JButton Button2 = new JButton("确定答案");Button2.setBounds(300,150,150,50);Button2.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,20));Button2.addActionListener(new Action1());
JButton Button3 = new JButton("读出文件");Button3.setBounds(500,150,150,50);Button3.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,20));Button3.addActionListener(new Action2());
text=new JTextArea(30,80);text.setBounds(30, 50, 200, 50);text.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,35));
text1=new JTextArea(30,80);text1.setBounds(270, 50, 200, 50);text1.setFont(new Font("Courier",Font.PLAIN,35));
Panel.add(text);
Panel.add(text1);
Panel.add(Button);
Panel.add(Button2);
Panel.add(Button3);
Panel.add(JLabel1);
add(Panel);
}
private class Action implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
text1.setText("0");
if(i<10) {
int a = 1+(int)(Math.random() * 99);
int b = 1+(int)(Math.random() * 99);
int m= (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 3);
switch(m)
{
case 0:
while(a<b){ b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); }
c[i]=(i+":"+a+"/"+b+"=");
list[i]=Math.floorDiv(a, b);
text.setText(i+":"+a+"/"+b+"=");
i++;
break;
case 1:
c[i]=(i+":"+a+"*"+b+"=");
list[i]=Math.multiplyExact(a, b);
text.setText(i+":"+a+"*"+b+"=");
i++;
break;
case 2:
c[i]=(i+":"+a+"+"+b+"=");
list[i]=Math.addExact(a, b);
text.setText(i+":"+a+"+"+b+"=");
i++;
break ;
case 3:
while(a<=b){ b = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100);a = (int) Math.round(Math.random() * 100); }
c[i]=(i+":"+a+"-"+b+"=");
text.setText(i+":"+a+"-"+b+"=");
list[i]=Math.subtractExact(a, b);i++;
break ;
}
}
}
}
private class Action1 implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
if(i<10) {
text.setText(null);
String daan=text1.getText().toString().trim();
int a = Integer.parseInt(daan);
if(text1.getText()!="") {
if(list[i1]==a) sum+=10;
}
c1[i1]=daan;
i1++;
}
}
}
private class Action2 implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
try {
out = new PrintWriter("text.txt");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
for(int counter=0;counter<10;counter++)
{
out.println(c[counter]+c1[counter]);
}
out.println("成绩"+sum);
out.close();
}
}
}

务3:本学期课程已结束,请汇总《面向对象程序设计课程学习进度条》的数据,统计个人专业能力提升的数据。并从学习内容、学习方法、学习心得几个方面进行课程学习总结,也希望你对课程的不足提出建议和意见。
学习内容:
Java语言特点与开发环境配置(第1章、第2章)
Java基本程序结构(第3章)
Java面向对象程序结构(第4章、第5章、第6章)
类、类间关系、类图
Java JDK预定义类/接口及其API(String-第3章、 Arrays-第3章、Files-第3章62页、LocalDate-第4章、 Object-第5章、对象包装器-第5章、Comparator-第6章、 异常类-第7章、ArrayList-第5+8章、第9章、第10-12章、 第14章)
Java异常处理编程模型
Java GUI编程模型
Java并发程序设计(第14章)
Java应用程序部署(第13章)
学习心得:
通过本学期的学习,掌握了java的一些基本知识,对java有了一定的深入了解,并可以通过java编程来解决一些小问题,在实际问题的解决当中依然有问题。在今后的学习中还会继续努力学习java,提升运用java编程去解决实际生活中的问题的能力。在今后的学习中会尝试着去学习其他一些与java有关的课程。
在这一学期的学习中我收获了很多,同时也感谢老师和助教学长一学期的悉心教导,在课程学习方面对我帮助了许多。
马昕璐 201771010118《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十八周学习总结的更多相关文章
- 201771010118马昕璐《面向对象程序设计java》第八周学习总结
第一部分:理论知识学习部分 1.接口 在Java程序设计语言中,接口不是类,而是对类的一组需求描述,由常量和一组抽象方法组成.Java为了克服单继承的缺点,Java使用了接口,一个类可以实现一个或多个 ...
- 201571030332 扎西平措 《面向对象程序设计Java》第八周学习总结
<面向对象程序设计Java>第八周学习总结 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https: ...
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第八周学习总结
第八周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 一.接口.lambda和内部类: Comparator与comparable接口: 1.comparable接口的方法是compareTo,只有一个参数:comp ...
- 201771010118 马昕璐《面向对象程序设计java》第十二周学习总结
第一部分:理论知识学习部分 用户界面:用户与计算机系统(各种程序)交互的接口 图形用户界面:以图形方式呈现的用户界面 AET:Java 的抽象窗口工具箱包含在java.awt包中,它提供了许多用来设计 ...
- 201771010118 马昕璐《面向对象程序设计java》第十周学习总结
第一部分:理论知识学习部分 泛型:也称参数化类型(parameterized type)就是在定义类.接口和方法时,通过类型参数 指示将要处理的对象类型. 泛型程序设计(Generic program ...
- 201771010118 马昕璐 《面向对象设计 java》第十七周实验总结
1.实验目的与要求 (1) 掌握线程同步的概念及实现技术: (2) 线程综合编程练习 2.实验内容和步骤 实验1:测试程序并进行代码注释. 测试程序1: l 在Elipse环境下调试教材651页程序1 ...
- 马凯军201771010116《面向对象程序设计Java》第八周学习总结
一,理论知识学习部分 6.1.1 接口概念 两种含义:一,Java接口,Java语言中存在的结构,有特定的语法和结构:二,一个类所具有的方法的特征集合,是一种逻辑上的抽象.前者叫做“Java接口”,后 ...
- 周强201771010141《面向对象程序设计Java》第八周学习总结
一.理论知识学习部分 Java为了克服单继承的缺点,Java使用了接口,一个类可以实现一个或多个接口. 接口体中包含常量定义和方法定义,接口中只进行方法的声明,不提供方法的实现. 类似建立类的继承关系 ...
- 201777010217-金云馨《面向对象程序设计Java》第八周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201771010118 马昕璐 《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十三周学习总结
第一部分:理论知识学习部分 事件处理基础 1.事件源(event source):能够产生事件的对象都可以成为事件源.一个事件源是一个能够注册监听器并向监听器发送事件对象的对象. 2.事件监听器(ev ...
随机推荐
- MongoDB代码——Python篇
需要安装的库:pymongo 一.添加文档 from pymongo import MongoClient # 连接服务器 conn = MongoClient("localhost&quo ...
- webpack4.0学习记录
2019/04/28 1.本质上,webpack基于node node跟webpack为最新稳定版,才能更好,更快的打包 安装 1.卸载node 直接在控制面板 卸载 2.安装 从官网下载 然后 ...
- android 应用程序记录AAR
@note:接着读赵波的<android NFC开发实例详解>,单独列出这篇文章一是因为上一篇笔记太长了,网页编辑器不太方便编写,二是这部分的知识是android开发中的知识,以后也许会深 ...
- rsyncd启动脚本
#!/bin/bash ############################################################## # File Name: -.sh # Versi ...
- 024_mac配置屏保命令
注意吃饭等离开工位的时候养成随时开启屏保的功能,养成信息保护的好习惯,mac如何配置屏幕保护呢? 一. 通过mac"设置"里的"Desktop & Screen ...
- linux的cron
linux系统由cron(crond)这个系统服务来控制的,linux系统上原来有非常多的计划性工作,因此,这个系统服务是默认启动的.cron进程每分钟会定期检查是否有要执行的任务,如果有就自动执行该 ...
- WPF 10天修炼 第五天- 内容控件
WPF内容控件 在WPF中,所有呈现在用户界面上的对象都称为用户界面元素.但是只有派生自System.Windows.Controls.Control类的对象才称为控件.内容控件通常是指具有Conte ...
- PHP获取汉字首字母并分组排序
<?php /** * 错误状态码定义 * User: xiucai * Date: 2018/3/11 * Time: 12:23 */ namespace extend; class Wor ...
- python基础--numpy.random
# *_*coding:utf-8 *_* # athor:auto import numpy.random #rand(d0, d1, ..., dn)n维随机值 data0 = numpy.ran ...
- 在js中获取上传图片的宽度和高度
Html: <input type="file" id="MapUploadTd" onchange="getMapPictureSize(th ...
