python爬虫---BeautifulSoup的用法
BeautifulSoup是一个灵活的网页解析库,不需要编写正则表达式即可提取有效信息。

推荐使用lxml作为解析器,因为效率更高. 在Python2.7.3之前的版本和Python3中3.2.2之前的版本,必须安装lxml或html5lib, 因为那些Python版本的标准库中内置的HTML解析方法不够稳定.
如下的html_doc是一个缺少部分闭合标签的html文档
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p>
"""
基本用法
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p>
""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'lxml') # 声明对象并选定解析方式
print(soup.prettify()) # prettify()方法将html格式化并补齐代码
print(soup.title.string) #输出title标签内容
结果:可以看到html缺失的</body>和</html>被补齐了,同时也打印出了title标签的内容

标签选择器
元素选择
在解析对象声明之后,便可以进行元素选择了,会打印输出选择元素的标签及内容
html_doc = """"
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'lxml')
print(soup.prettify())
print(soup.title)
print(soup.head)
print(soup.a)
结果:

获取标签名称:
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc,'lxml')
print(soup.title.name) 结果:
title
获取标签内属性:
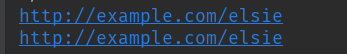
在第一个a标签内有href属性,直接使用['name']或者attrs['name']即可获得属性值,两者是一样的。
html_doc = """ """ from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'lxml')
print(soup.prettify()) print(soup.a['href'])
print(soup.a.attrs['href'])
结果:
获取内容
#如下示例,获取a标签内容
html_doc="""<a>this is tag a</a>""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc,'lxml')
print(soup.a.string)
结果:
this is tag a
嵌套的选择
html_doc = """<html><head></head><a>this is tag a</a><body></body></html> from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc,'lxml')
print(soup.head.a.string)
结果:
this is tag a
一次性获得html文档所有的内容
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p>
""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'lxml') # 声明对象并选定解析方式
print(soup.get_text())
输出:

遍历子节点和子孙节点
html还是示例的,文档中有两个闭合的p标签,这里寻找时总是返回第一个结果,不再向后查询
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'lxml') # 声明对象并选定解析方式
print(soup.p.contents)
结果:第一个闭合p标签的内容被完全打印出,以list形式返回

迭代子节点和子孙节点
soup.p.children实际上是一个迭代器,使用枚举的方式将内容列举出。
html_doc = """
""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'lxml')
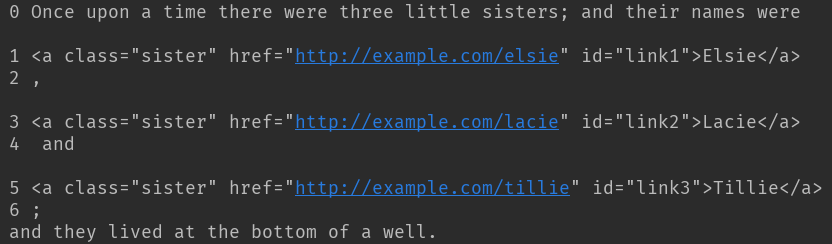
print(soup.p.contents) for i, child in enumerate(soup.p.children): #只迭代子节点,不包含子孙节点
print(i,child) for i, child in enumerate(soup.p.descendants): # 迭代p标签所有子孙节点
print(i, child)
结果:
只迭代子节点,这里p为一级标签,只能迭代出字标签
迭代子孙节点,p为一级标签,可以迭代出所有次级标签

获取父亲节点和祖先节点
html_doc = """
""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'lxml')
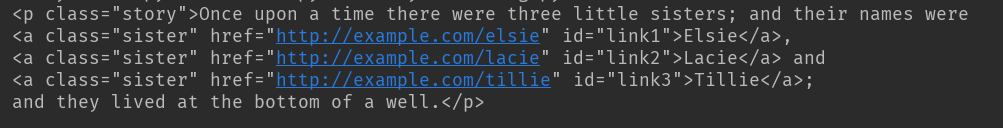
print(soup.a.parent)
结果:p是a的父亲节点,p被完整打印
获取祖先节点
html_doc = """
""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'lxml')
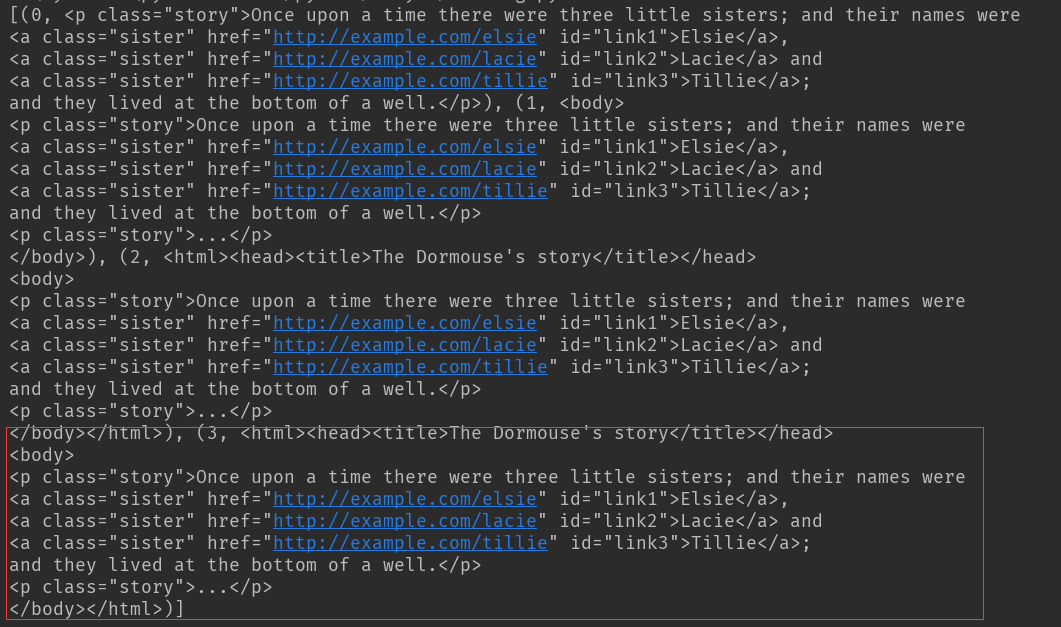
print(list(enumerate(soup.a.parents)))
结果:这个枚举向上迭代通过层级查找,在最后一组元素迭代出所有祖先节点内容
兄弟节点
html = """
""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc, 'lxml') print(list(enumerate(soup.a.next_siblings))) # a以下并列节点
print(list(enumerate(soup.a.previous_siblings))) # a以上并列兄弟节点
结果:

标准选择器
find_all(name, attrs, recursive, text, **kwargs)
可根据标签名,属性,内容查找文档。
使用的html文档如下
html = """
<div class="panel">
<div class="panel-heading">
<h3>hello</h3>
</div>
<div class="panel-body">
<ul class="list" id="list-1" name="elements">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
<li class="element">Jay</li>
</ul>
<ul class="list list-small" id="list-2">
<li class="element">Foo</li>
<li class="element">Bar</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
"""
使用find_all()方法
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print(soup.find_all('ul')) #返回一个list 以bs4的bs4.element.tag方式查找
print(soup.find_all('ul')[0]) #返回一个list 从0开始索引
结果:find_all('ul') 查找到所有ul标签
find_all('ul')[0]只返回第一个查找到的结果
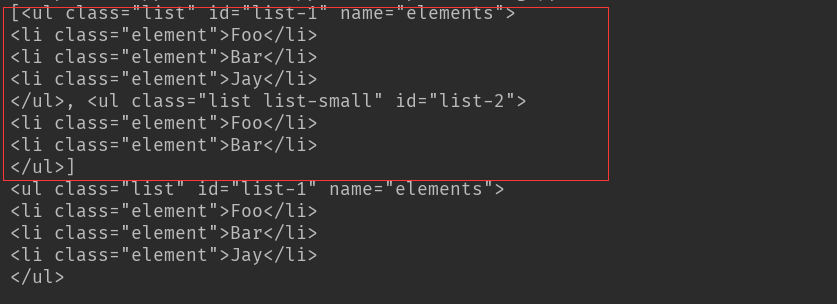
使用find_all方法进行嵌套遍历查找
html = """
""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') #使用find_all()方法的嵌套遍历查找 for ul in soup.find_all('ul'):
print(ul.find_all('li'))
结果:第一个ul标签下的字标签li全部被查找到,结果以list返回
第二个ul下的签同样

以属性进行查找
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') #使用find_all()方法的嵌套遍历查找
print(soup.find_all(attrs={'id': 'list-1'})) #以属性形式查找标签,attrs是一个dict形式,内容为参数名称及属性
print(soup.find_all(attrs={'class': 'list'}))
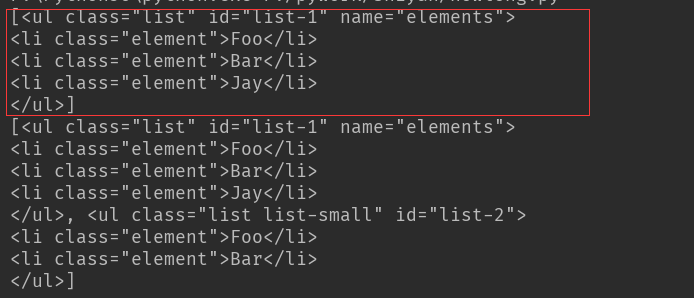
结果:以id=list-1进行查找,结果为红色框内容
以class=list进行查找,结果两个ul全部找到
如有特殊的属性,可以直接以属性名称进行查找
html = """
""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') #使用find_all()方法的嵌套遍历查找 print(soup.find_all(class_='element')) #因为class在python内为关键字,查找时加个下划线就ok
结果:class=element的全部查找到

text以文本方式进行查找
html = """
""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print(soup.find_all(text='Foo')) #直接返回内容
结果:
['Foo', 'Foo']
find(name, attrs, recursive, text, **kw)方法
find返回单个元素,find_all返回所有元素
查找方式及返回结果
html = """
""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print(soup.find('ul')) #返回的是单个的字符串
print(soup.find('li')['class'])
结果:对ul的查找以字符串返回了,而li标签下的class属性则以list 返回

以属性查找同find_all,只是find返回的结果只是字符串
html = """
""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print(soup.find(attrs={'id': 'list-1'}))
print(soup.find(text='Foo'))
结果:

find_parent()和find_parents()
前者只返回父亲节点,后者返回所有祖先节点
find_next_siblings()和find_next_sibling()
前者返回后面所有兄弟节点,后者只返回后面第一个兄弟节点
find_previous_siblings()和 find_previous_sibling()
前者返回前面所有的兄弟节点,后者返回前面的第一个兄弟节点
CSS选择器
通过select()直接传入选择器即可完成选择
如果选择了class属性,则在css选择器中要以.代替,而id以#代替
html = """
""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
print(soup.select('.panel .panel-heading')) # 先选择外层元素,然后里层元素次级标签选择
print(soup.select('ul'))
print(soup.select('ul li')) # 选择ul 次级选li 打印出li标签内容
print(soup.select('#list-2 .element')) # id使用#选择
print(soup.select('ul')[1]) #ul标签选择为一个整体,选择索引从0开始的
选择结果:

以选择器进行迭代
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
for li in soup.select('ul'): #这里使用迭代方式 结果返回list
print(li.select('li'))
结果:同查找的遍历,这里是以选择器方式进行遍历

获取属性
html = """
""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml')
# 获取属性
for li in soup.select('ul'):
print(li['id']) # or print(li.attrs['id'])
结果:
list-1
list-2
获取文本内容
html = """
""" from bs4 import BeautifulSoup soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'lxml') for li in soup.select('li'):
print(li.get_text())
结果:

总结:
lxml是bs最快的解析库,如果不能满足使用,则使用html.parse
查找方式以find_all和find方便
熟悉css选择器则可以使用css select()
python爬虫---BeautifulSoup的用法的更多相关文章
- Python爬虫--beautifulsoup 4 用法
Beautiful Soup将复杂HTML文档转换成一个复杂的树形结构, 每个节点都是Python对象,所有对象可以归纳为4种: Tag , NavigableString , BeautifulSo ...
- python 爬虫括号的用法
首先是文档说明: >>> import re >>> help(re.findall) Help on function findall in module re: ...
- Python爬虫-- BeautifulSoup库
BeautifulSoup库 beautifulsoup就是一个非常强大的工具,爬虫利器.一个灵活又方便的网页解析库,处理高效,支持多种解析器.利用它就不用编写正则表达式也能方便的实现网页信息的抓取 ...
- python爬虫BeautifulSoup库class_
因为class是python的关键字,所以在写过滤的时候,应该是这样写: r = requests.get(web_url, headers=headers) # 向目标url地址发送get请求,返回 ...
- python爬虫 BeautifulSoup
简单来说,Beautiful Soup是python的一个库,最主要的功能是从网页抓取数据. Beautiful Soup自动将输入文档转换为Unicode编码,输出文档转换为utf-8编码. Bea ...
- Python爬虫 | Beautifulsoup解析html页面
引入 大多数情况下的需求,我们都会指定去使用聚焦爬虫,也就是爬取页面中指定部分的数据值,而不是整个页面的数据.因此,在聚焦爬虫中使用数据解析.所以,我们的数据爬取的流程为: 指定url 基于reque ...
- Python 爬虫-BeautifulSoup
2017-07-26 10:10:11 Beautiful Soup可以解析html 和 xml 格式的文件. Beautiful Soup库是解析.遍历.维护“标签树”的功能库.使用Beautifu ...
- Python爬虫-request的用法
import requests if __name__ == '__main__': #基本用法 #response = requests.get("http://httpbin.org/g ...
- Python 爬虫 —— BeautifulSoup
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup % 首字母大写,显然这是一个类 1. BeautifulSoup 类 HTML 解析类(parser) r = requests.get(. ...
随机推荐
- tomcat中配置https请求
一. 创建tomcat证书 这里使用JDK自带的keytool工具来生成证书: 1. 在jdk的安装目录\bin\keytool.exe下打开keytool.exe 2. 在命令行中输入以下命令: ...
- [0413] FFTSHIFT的四种写法
FFTSHIFT的四种写法 前言 matlab说,"你读过书,--我便考你一考.fftshift的函数,怎样写的?"我想,讨饭一样的人,也配考我么?便回过脸去,不再理会.matla ...
- CIKM 18 | 蚂蚁金服论文:基于异构图神经网络的恶意账户识别方法
小蚂蚁说: ACM CIKM 2018 全称是 The 27th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Managemen ...
- 【BZOJ】1085: [SCOI2005]骑士精神
题目链接:http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=1085 $${if (cs+val-1>ans) return ;}$$ #inclu ...
- hdu 6169 Senior PanⅡ Miller_Rabin素数测试+容斥
Senior PanⅡ Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 524288/524288 K (Java/Others) Pr ...
- SHU oj 422 风力观测 线段树
风力观测 发布时间: 2017年7月9日 18:17 最后更新: 2017年7月9日 21:04 时间限制: 1000ms 内存限制: 128M 描述 小Y正在观测y地区的风力情况,他在一 ...
- Centos7默认自带了Python2.7版本,但是因为项目需要使用Python3.x,这里提供一种比较快捷方便的安装方式
安装必要工具 yum-utils: $ sudo yum install yum-utils 使用yum-builddep为Python3构建环境,安装缺失的软件依赖,使用下面的命令会自动处理.$ s ...
- PCA分析和因子分析
#由此说明使用prcomp函数时,必须使用标准化过的原始数据.如果使用没有标准化的raw数据(不是相关系数矩阵或者协方差矩阵),必须将参数scale. = T <result>$sdev ...
- 力扣(LeetCode)412. Fizz Buzz
写一个程序,输出从 1 到 n 数字的字符串表示. 如果 n 是3的倍数,输出"Fizz": 如果 n 是5的倍数,输出"Buzz": 3.如果 n 同时是3和 ...
- 监听浏览器种类,并区分safari和chrom浏览器
//判断浏览器种类函数-处理兼容性 function myBrowser(){ var userAgent = navigator.userAgent; //取得浏览器的userAgent字符串 va ...
