spring——AOP原理及源码(二)
回顾:
在上一篇中,我们提到@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解给容器中加入了一个关键组件internalAutoProxyCreator的BeanDefinition,实际类型为
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的BeanDenation
并且发现这是一个后置处理器,也是一个XXXAware接口的实现类。以及探究了它的继承关系如下。

接下来我们就从后置处理器和BeanFactoryAware的角度来看看AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的BeanDefinition创建完成后都做了什么。
一、设置调试断点
我们分别进入四个有关类,在类中与后置处理器和BeanFactoryAware有关的方法上打上断点。最终效果如下:
AbstractAutoProxyCreator.setBeanFactory
AbstractAutoProxyCreator有后置处理器逻辑
{
postProcessBeforeInstantiation()
postProcessAfterInitialization()
}
AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.initBeanFactory
AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.setBeanFactory
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.initBeanFactory 最后,在配置类中给两个bean方法打上断点。
二、调试过程
开始调试,我们会发现还是先来到上一篇的AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的BeanDenation创建过程。
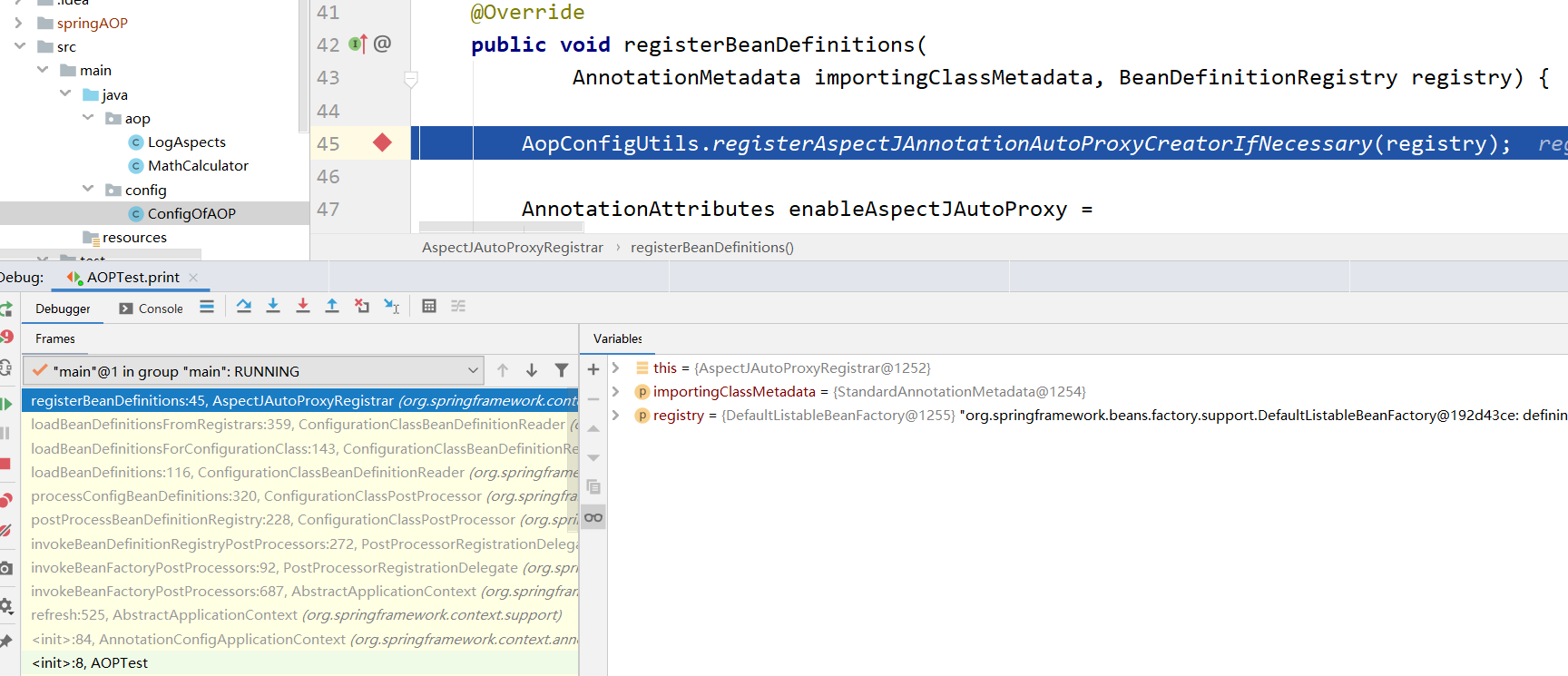
左下角frames框中选到refresh方法可以看到,AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的BeanDenation的创建是invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()方法调用来的。
调用这个方法在上下文中生成后置处理器的BeanDefinition加入容器中。
下一步的registerBeanPostProcessors才是注册后置处理器(利用BeanDefinition的信息注册对应Bean),也是本篇的重点。
为了让它快速创建完BeanDefinition,这里我们直接快进到下一个断点。
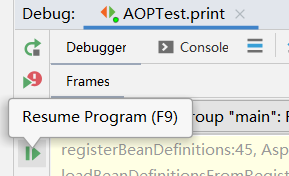
程序先来到了AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator的setBeanFactory方法
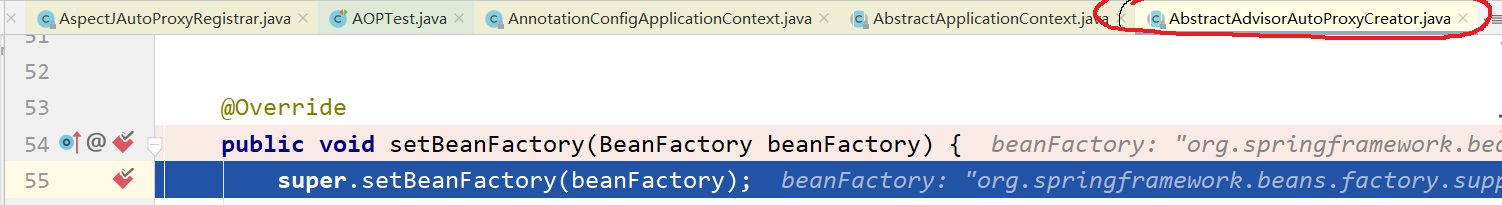
为了从头看起,还是先在frames框中选到refresh方法,可以看到来到了refresh的下一方法,将要开始注册后置处理器。

1、registerBeanPostProcessors()
我们继续在frames中往上点,直到来到PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors()
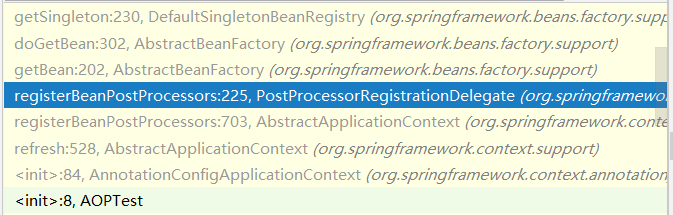
方法有点长,但关键只在其中几个地方,我们将在下面进行针对分析
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) { String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false); // Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount)); // Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
} // First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors); // Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors); // Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors.
List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>();
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors); // Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory);
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors); // Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners,
// moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc).
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext));
}
registerBeanPostProcessors
4:获取所有后置处理器的名字
14~32:对实现不同接口的后置处理器进行分类
35~48:对上面的分类分别进行处理,因为实现的是Ordered接口,我们只关注39~48行

40~46:遍历分好的实现了Ordered接口的后置处理器名,利用beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class)来获取
2、doGetBean()
有了以上的步骤,我们主要来看beanFactory是怎么获取的

可以看到,先来到了getBean方法,然后又进入了doGetBean方法。下面我们来看doGetBean做了什么。
/**
* Return an instance, which may be shared or independent, of the specified bean.
* @param name the name of the bean to retrieve
* @param requiredType the required type of the bean to retrieve
* @param args arguments to use when creating a bean instance using explicit arguments
* (only applied when creating a new instance as opposed to retrieving an existing one)
* @param typeCheckOnly whether the instance is obtained for a type check,
* not for actual use
* @return an instance of the bean
* @throws BeansException if the bean could not be created
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
protected <T> T doGetBean(
final String name, final Class<T> requiredType, final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException { final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean; // Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
logger.debug("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +
"' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference");
}
else {
logger.debug("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
} else {
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
} // Check if bean definition exists in this factory.
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// Not found -> check parent.
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);
if (args != null) {
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
}
else {
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
}
} if (!typeCheckOnly) {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
} try {
final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args); // Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");
}
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
getBean(dep);
}
} // Create bean instance.
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() {
@Override
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
} else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
} else {
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() {
@Override
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " +
"defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton",
ex);
}
}
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
} // Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.
if (requiredType != null && bean != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) {
try {
return getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);
}
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" +
ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex);
}
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
}
return (T) bean;
}
AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean
17:获取后置处理器的名称(这里也就是internalAutoProxyCreator)
21:根据bean名字获取对应单例
22~33:如果获取到的bean不为空,进行一系列操作(这里的internalAutoProxyCreator是第一次获取,bean应该是空,所以我们跳过22~33)
61:getMergedLocalBeanDefinition() 根据传入的后置处理器名称,获取其所有信息,在这里也就是从internalAutoProxyCreator的BeanDefinition中获取必要信息,这是为创建bean做准备。
79:判断如果是单例,调用getSingleton()来获取
这里我们先不急着进入getSingleton()方法,接着往下看先。
130:bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd) 将79行获取的scopedInstance包装为bean
159:返回bean
ok,getSingleton()的获取是要返回的,所以这步是关键,接下来我们来看看getSingleton()。
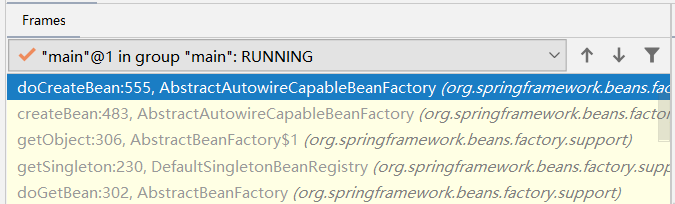
一直往上走,最终我们来到doCreateBean(),说明获取不到,接下来需要创建bean了
3、doCreateBean()
/**
* Actually create the specified bean. Pre-creation processing has already happened
* at this point, e.g. checking {@code postProcessBeforeInstantiation} callbacks.
* <p>Differentiates between default bean instantiation, use of a
* factory method, and autowiring a constructor.
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean
* @param args explicit arguments to use for constructor or factory method invocation
* @return a new instance of the bean
* @throws BeanCreationException if the bean could not be created
* @see #instantiateBean
* @see #instantiateUsingFactoryMethod
* @see #autowireConstructor
*/
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException { // Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
final Object bean = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance() : null);
Class<?> beanType = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass() : null);
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType; // Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition.
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Post-processing of merged bean definition failed", ex);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
} // Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references
// even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware.
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName +
"' to allow for resolving potential circular references");
}
addSingletonFactory(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() {
@Override
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
return getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean);
}
});
} // Initialize the bean instance.
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
if (exposedObject != null) {
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) {
throw (BeanCreationException) ex;
}
else {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex);
}
} if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName,
"Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" +
StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) +
"] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " +
"wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " +
"bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " +
"'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.");
}
}
}
} // Register bean as disposable.
try {
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex);
} return exposedObject;
}
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean
26:创建bean
64:populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper) 给bean的属性赋值
66:initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd)初始化bean
下面我们来看这个初始化bean都做了什么
4、initializeBean()
/**
* Initialize the given bean instance, applying factory callbacks
* as well as init methods and bean post processors.
* <p>Called from {@link #createBean} for traditionally defined beans,
* and from {@link #initializeBean} for existing bean instances.
* @param beanName the bean name in the factory (for debugging purposes)
* @param bean the new bean instance we may need to initialize
* @param mbd the bean definition that the bean was created with
* (can also be {@code null}, if given an existing bean instance)
* @return the initialized bean instance (potentially wrapped)
* @see BeanNameAware
* @see BeanClassLoaderAware
* @see BeanFactoryAware
* @see #applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization
* @see #invokeInitMethods
* @see #applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
*/
protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
} Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
} try {
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
} if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean
一进来我们是停在29行的invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean),这里先不看它
我们来关注一下initializeBean的几个重要流程
1、invokeAwareMethods
2、34行applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization
3、38行invokeInitMethods
4、47行applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization
先执行invokeAwareMethods,调用那些XXXAware方法,然后执行后置处理器的applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization方法,接着执行初始化方法,最后执行后置处理器的applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization方法,这也是我们的后置处理器为什么能在bean初始化前后调用方法的原因了。
现在我们往下进入invokeAwareMethods
private void invokeAwareMethods(final String beanName, final Object bean) {
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(getBeanClassLoader());
}
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.this);
}
}
}
invokeAwareMethods
invokeAwareMethods方法先判断是哪个类型的Aware接口,然后调用对应的set方法,所以它最终来到了我们的断点,setBeanFactory()方法
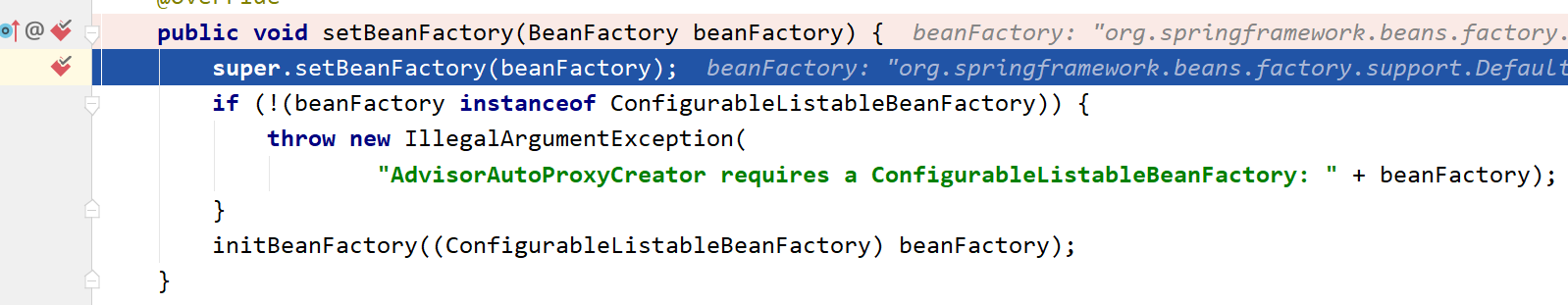
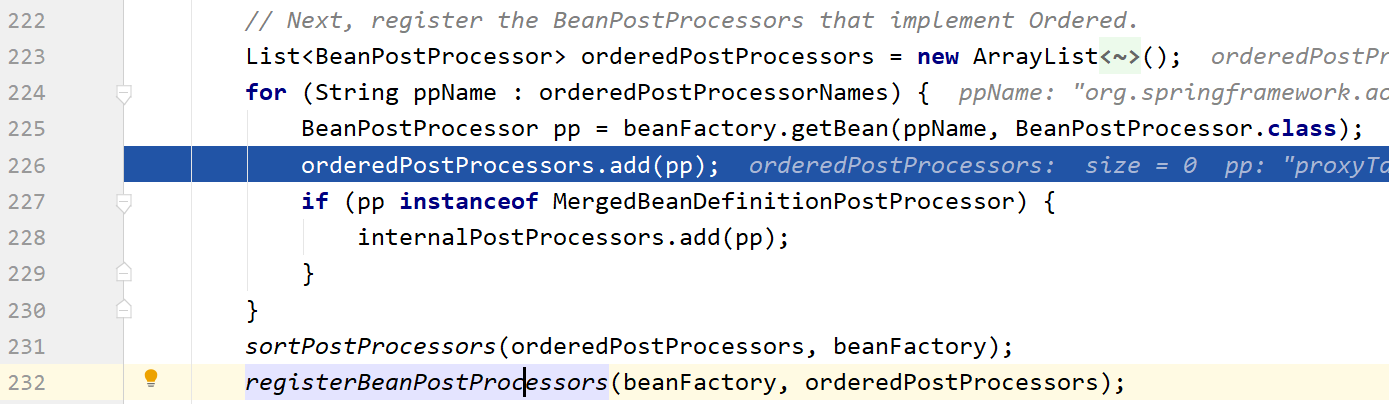
接下来我们一路点击下一步,直到下图,这个BeanPostProcessor就创建完了,并通过orderedPostProcessors.add(pp)先添加到orderedPostProcessors中
再通过registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors)添加到beanFactory中
总结
以上整个过程,是创建完AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator后置处理器bean并存入beanFactory的过程。
下一篇将来探寻AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator在作为后置处理器存入bean工程之后的事。
今天是悲伤,再见了爱人,
spring——AOP原理及源码(二)的更多相关文章
- spring——AOP原理及源码(一)
教程共分为五篇,从AOP实例的构建及其重要组件.基本运行流程.容器创建流程.关键方法调用.原理总结归纳等几个方面一步步走进AOP的世界. 本篇主要为读者演示构建AOP实例及AOP核心组件分析. 一.项 ...
- spring——AOP原理及源码(四)
前情回顾: 上文我们一路分析了从容器创建开始直到我们的AOP注解导入的核心组件AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator执行postProcessBeforeInst ...
- spring——AOP原理及源码(五)
前情回顾: 在上一篇中,通过 wrapIfNecessary 方法,我们获取到了合适的增强器(日志方法)与业务类进行包装,最终返回了我们业务类的代理对象. 本篇我们将从业务方法的执行开始,看看增强器( ...
- spring——AOP原理及源码(三)
在上一篇中,我们创建并在BeanFactory中注册了AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator组件.本篇我们将要探究,这个组件是在哪里以及何时发挥作用的. 调试的起 ...
- 【Spring】Spring IOC原理及源码解析之scope=request、session
一.容器 1. 容器 抛出一个议点:BeanFactory是IOC容器,而ApplicationContex则是Spring容器. 什么是容器?Collection和Container这两个单词都有存 ...
- Spring AOP介绍及源码分析
转自:http://www.uml.org.cn/j2ee/201301102.asp 软件开发经历了从汇编语言到高级语言和从过程化编程到面向对象编程:前者是为了提高开发效率,而后者则使用了归纳法,把 ...
- Spring中AOP原理,源码学习笔记
一.AOP(面向切面编程):通过预编译和运行期动态代理的方式在不改变代码的情况下给程序动态的添加一些功能.利用AOP可以对应用程序的各个部分进行隔离,在Spring中AOP主要用来分离业务逻辑和系统级 ...
- spring MVC 原理及源码解析
首先要知道springmvc的核心控制器dispatcherServlet(继承自httpServlet) 一般httpServlet的请求过程: 1.初始化(创建servlet实例时)时会执行ser ...
- 设计模式(二十一)——解释器模式(Spring 框架中SpelExpressionParser源码分析)
1 四则运算问题 通过解释器模式来实现四则运算,如计算 a+b-c 的值,具体要求 1) 先输入表达式的形式,比如 a+b+c-d+e, 要求表达式的字母不能重复 2) 在分别输入 a ,b, c, ...
随机推荐
- Android之布局LinearLayout
1.weight属性用法 主要用于view对象屏幕适配比例 如下图,左边是等比例,右边是1:2比例 实现代码: <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http:// ...
- git clone 拉取github上面的代码报错:fatal: Authentication failed for xxx解决
1.打开git bash,输入密码:git config --system --unset credential.helper2.结果报错:error: could not lock config f ...
- Angular(一)
Angular开发者指南(一)入门介绍 什么是AngularAngularJS是动态Web应用程序的结构框架. 它允许您使用HTML作为模板语言,并允许您扩展HTML的语法以清晰,简洁地表达应用程 ...
- 39)PHP,选取数据库中的两列
首先是我的文件关系: 我的b.php是主php文件,BBB.php是配置文件,login.html是显示文件, b.php文件代码: <?php /** * Created by PhpStor ...
- linux文件系统与链接
Linux的文件属性图1 图1 linux的文件属性 ls -lhi -l 长格式 -h 人性化 -i inodo -d 看目录自己的信息 inode 源自于文件系统 分区 平面设计图 格式化 施 ...
- nginx做正向代理搭建bugfree
下载地址: Nginx下载地址:http://download.csdn.net/detail/terrly88/9099117 bugfree下载地址:http://download.csdn.ne ...
- com.google.zxing:core 生成二维码的简单使用
String content = ""; int size = 240; Hashtable<EncodeHintType, String> hints = new H ...
- VS编译release版本的出现的LNK1104 无法打开文件“libboost_filesystem-vc140-mt-1_58.lib
最近在用restbed和vs2015做一个项目,debug编译的没问题,但是编译release就有问题,困扰了一天,说下我的出坑过程. 1.我用到了外部的库 restbed ,首先要想正确编译过,你的 ...
- git理论知识
1.Git 有三种状态,你的文件可能处于其中之一:已提交(committed).已修改(modified)和已暂存(staged) 由此引入 Git 项目的三个工作区域的概念:Git 仓库.工作目录以 ...
- 简化Java编程的法宝,让工作更高效
如果你没有看过之前的文章,也不要紧,这并不影响你对接下来的内容的理解,不过为了照顾直接看到第二篇的同学,还是有必要介绍一下HuTool的引入方式. 在项目的pom.xml的dependencies中加 ...

