【OpenCV】SIFT原理与源码分析:关键点描述
《SIFT原理与源码分析》系列文章索引:http://www.cnblogs.com/tianyalu/p/5467813.html
SIFT描述子h(x,y,θ)是对关键点附近邻域内高斯图像梯度统计的结果,是一个三维矩阵,但通常用一个矢量来表示。矢量通过对三维矩阵按一定规律排列得到。
描述子采样区域
 ,如下图所示:
,如下图所示:
源码
Point pt(cvRound(ptf.x), cvRound(ptf.y));
//计算余弦,正弦,CV_PI/180:将角度值转化为幅度值
float cos_t = cosf(ori*(float)(CV_PI/));
float sin_t = sinf(ori*(float)(CV_PI/));
float bins_per_rad = n / .f;
float exp_scale = -.f/(d * d * 0.5f); //d:SIFT_DESCR_WIDTH 4
float hist_width = SIFT_DESCR_SCL_FCTR * scl; // SIFT_DESCR_SCL_FCTR: 3
// scl: size*0.5f
// 计算图像区域半径mσ(d+1)/2*sqrt(2)
// 1.4142135623730951f 为根号2
int radius = cvRound(hist_width * 1.4142135623730951f * (d + ) * 0.5f);
cos_t /= hist_width;
sin_t /= hist_width;
区域坐标轴旋转
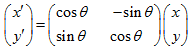
源码
//计算采样区域点坐标旋转
for( i = -radius, k = ; i <= radius; i++ )
for( j = -radius; j <= radius; j++ )
{
/*
Calculate sample's histogram array coords rotated relative to ori.
Subtract 0.5 so samples that fall e.g. in the center of row 1 (i.e.
r_rot = 1.5) have full weight placed in row 1 after interpolation.
*/
float c_rot = j * cos_t - i * sin_t;
float r_rot = j * sin_t + i * cos_t;
float rbin = r_rot + d/ - 0.5f;
float cbin = c_rot + d/ - 0.5f;
int r = pt.y + i, c = pt.x + j; if( rbin > - && rbin < d && cbin > - && cbin < d &&
r > && r < rows - && c > && c < cols - )
{
float dx = (float)(img.at<short>(r, c+) - img.at<short>(r, c-));
float dy = (float)(img.at<short>(r-, c) - img.at<short>(r+, c));
X[k] = dx; Y[k] = dy; RBin[k] = rbin; CBin[k] = cbin;
W[k] = (c_rot * c_rot + r_rot * r_rot)*exp_scale;
k++;
}
}
计算采样区域梯度直方图

源码
//计算梯度直方图
for( k = ; k < len; k++ )
{
float rbin = RBin[k], cbin = CBin[k];
float obin = (Ori[k] - ori)*bins_per_rad;
float mag = Mag[k]*W[k]; int r0 = cvFloor( rbin );
int c0 = cvFloor( cbin );
int o0 = cvFloor( obin );
rbin -= r0;
cbin -= c0;
obin -= o0; //n为SIFT_DESCR_HIST_BINS:8,即将360°分为8个区间
if( o0 < )
o0 += n;
if( o0 >= n )
o0 -= n; // histogram update using tri-linear interpolation
// 双线性插值
float v_r1 = mag*rbin, v_r0 = mag - v_r1;
float v_rc11 = v_r1*cbin, v_rc10 = v_r1 - v_rc11;
float v_rc01 = v_r0*cbin, v_rc00 = v_r0 - v_rc01;
float v_rco111 = v_rc11*obin, v_rco110 = v_rc11 - v_rco111;
float v_rco101 = v_rc10*obin, v_rco100 = v_rc10 - v_rco101;
float v_rco011 = v_rc01*obin, v_rco010 = v_rc01 - v_rco011;
float v_rco001 = v_rc00*obin, v_rco000 = v_rc00 - v_rco001; int idx = ((r0+)*(d+) + c0+)*(n+) + o0;
hist[idx] += v_rco000;
hist[idx+] += v_rco001;
hist[idx+(n+)] += v_rco010;
hist[idx+(n+)] += v_rco011;
hist[idx+(d+)*(n+)] += v_rco100;
hist[idx+(d+)*(n+)+] += v_rco101;
hist[idx+(d+)*(n+)] += v_rco110;
hist[idx+(d+)*(n+)+] += v_rco111;
}
关键点描述源码
// SIFT关键点特征描述
// SIFT描述子是关键点领域高斯图像提取统计结果的一种表示
static void calcSIFTDescriptor( const Mat& img, Point2f ptf, float ori, float scl,
int d, int n, float* dst ) {
Point pt(cvRound(ptf.x), cvRound(ptf.y));
//计算余弦,正弦,CV_PI/180:将角度值转化为幅度值
float cos_t = cosf(ori*(float)(CV_PI/));
float sin_t = sinf(ori*(float)(CV_PI/));
float bins_per_rad = n / .f;
float exp_scale = -.f/(d * d * 0.5f); //d:SIFT_DESCR_WIDTH 4
float hist_width = SIFT_DESCR_SCL_FCTR * scl; // SIFT_DESCR_SCL_FCTR: 3
// scl: size*0.5f
// 计算图像区域半径mσ(d+1)/2*sqrt(2)
// 1.4142135623730951f 为根号2
int radius = cvRound(hist_width * 1.4142135623730951f * (d + ) * 0.5f);
cos_t /= hist_width;
sin_t /= hist_width; int i, j, k, len = (radius*+)*(radius*+), histlen = (d+)*(d+)*(n+);
int rows = img.rows, cols = img.cols; AutoBuffer<float> buf(len* + histlen);
float *X = buf, *Y = X + len, *Mag = Y, *Ori = Mag + len, *W = Ori + len;
float *RBin = W + len, *CBin = RBin + len, *hist = CBin + len; //初始化直方图
for( i = ; i < d+; i++ )
{
for( j = ; j < d+; j++ )
for( k = ; k < n+; k++ )
hist[(i*(d+) + j)*(n+) + k] = .;
} //计算采样区域点坐标旋转
for( i = -radius, k = ; i <= radius; i++ )
for( j = -radius; j <= radius; j++ )
{
/*
Calculate sample's histogram array coords rotated relative to ori.
Subtract 0.5 so samples that fall e.g. in the center of row 1 (i.e.
r_rot = 1.5) have full weight placed in row 1 after interpolation.
*/
float c_rot = j * cos_t - i * sin_t;
float r_rot = j * sin_t + i * cos_t;
float rbin = r_rot + d/ - 0.5f;
float cbin = c_rot + d/ - 0.5f;
int r = pt.y + i, c = pt.x + j; if( rbin > - && rbin < d && cbin > - && cbin < d &&
r > && r < rows - && c > && c < cols - )
{
float dx = (float)(img.at<short>(r, c+) - img.at<short>(r, c-));
float dy = (float)(img.at<short>(r-, c) - img.at<short>(r+, c));
X[k] = dx; Y[k] = dy; RBin[k] = rbin; CBin[k] = cbin;
W[k] = (c_rot * c_rot + r_rot * r_rot)*exp_scale;
k++;
}
} len = k;
fastAtan2(Y, X, Ori, len, true);
magnitude(X, Y, Mag, len);
exp(W, W, len); //计算梯度直方图
for( k = ; k < len; k++ )
{
float rbin = RBin[k], cbin = CBin[k];
float obin = (Ori[k] - ori)*bins_per_rad;
float mag = Mag[k]*W[k]; int r0 = cvFloor( rbin );
int c0 = cvFloor( cbin );
int o0 = cvFloor( obin );
rbin -= r0;
cbin -= c0;
obin -= o0; //n为SIFT_DESCR_HIST_BINS:8,即将360°分为8个区间
if( o0 < )
o0 += n;
if( o0 >= n )
o0 -= n; // histogram update using tri-linear interpolation
// 双线性插值
float v_r1 = mag*rbin, v_r0 = mag - v_r1;
float v_rc11 = v_r1*cbin, v_rc10 = v_r1 - v_rc11;
float v_rc01 = v_r0*cbin, v_rc00 = v_r0 - v_rc01;
float v_rco111 = v_rc11*obin, v_rco110 = v_rc11 - v_rco111;
float v_rco101 = v_rc10*obin, v_rco100 = v_rc10 - v_rco101;
float v_rco011 = v_rc01*obin, v_rco010 = v_rc01 - v_rco011;
float v_rco001 = v_rc00*obin, v_rco000 = v_rc00 - v_rco001; int idx = ((r0+)*(d+) + c0+)*(n+) + o0;
hist[idx] += v_rco000;
hist[idx+] += v_rco001;
hist[idx+(n+)] += v_rco010;
hist[idx+(n+)] += v_rco011;
hist[idx+(d+)*(n+)] += v_rco100;
hist[idx+(d+)*(n+)+] += v_rco101;
hist[idx+(d+)*(n+)] += v_rco110;
hist[idx+(d+)*(n+)+] += v_rco111;
} // finalize histogram, since the orientation histograms are circular
// 最后确定直方图,目标方向直方图是圆的
for( i = ; i < d; i++ )
for( j = ; j < d; j++ )
{
int idx = ((i+)*(d+) + (j+))*(n+);
hist[idx] += hist[idx+n];
hist[idx+] += hist[idx+n+];
for( k = ; k < n; k++ )
dst[(i*d + j)*n + k] = hist[idx+k];
}
// copy histogram to the descriptor,
// apply hysteresis thresholding
// and scale the result, so that it can be easily converted
// to byte array
float nrm2 = ;
len = d*d*n;
for( k = ; k < len; k++ )
nrm2 += dst[k]*dst[k];
float thr = std::sqrt(nrm2)*SIFT_DESCR_MAG_THR;
for( i = , nrm2 = ; i < k; i++ )
{
float val = std::min(dst[i], thr);
dst[i] = val;
nrm2 += val*val;
}
nrm2 = SIFT_INT_DESCR_FCTR/std::max(std::sqrt(nrm2), FLT_EPSILON);
for( k = ; k < len; k++ )
{
dst[k] = saturate_cast<uchar>(dst[k]*nrm2);
}
}
至此SIFT描述子生成,SIFT算法也基本完成了~参见《SIFT原理与源码分析》
【OpenCV】SIFT原理与源码分析:关键点描述的更多相关文章
- 【OpenCV】SIFT原理与源码分析:关键点搜索与定位
<SIFT原理与源码分析>系列文章索引:http://www.cnblogs.com/tianyalu/p/5467813.html 由前一步<DoG尺度空间构造>,我们得到了 ...
- OpenCV SIFT原理与源码分析
http://blog.csdn.net/xiaowei_cqu/article/details/8069548 SIFT简介 Scale Invariant Feature Transform,尺度 ...
- 【OpenCV】SIFT原理与源码分析:DoG尺度空间构造
原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/xiaowei_cqu/article/details/8067881 尺度空间理论 自然界中的物体随着观测尺度不同有不同的表现形态.例如我们形 ...
- 【OpenCV】SIFT原理与源码分析:方向赋值
<SIFT原理与源码分析>系列文章索引:http://www.cnblogs.com/tianyalu/p/5467813.html 由前一篇<关键点搜索与定位>,我们已经找到 ...
- 【OpenCV】SIFT原理与源码分析
SIFT简介 Scale Invariant Feature Transform,尺度不变特征变换匹配算法,是由David G. Lowe在1999年(<Object Recognition f ...
- OpenCV学习笔记(27)KAZE 算法原理与源码分析(一)非线性扩散滤波
http://blog.csdn.net/chenyusiyuan/article/details/8710462 OpenCV学习笔记(27)KAZE 算法原理与源码分析(一)非线性扩散滤波 201 ...
- ConcurrentHashMap实现原理及源码分析
ConcurrentHashMap实现原理 ConcurrentHashMap源码分析 总结 ConcurrentHashMap是Java并发包中提供的一个线程安全且高效的HashMap实现(若对Ha ...
- HashMap和ConcurrentHashMap实现原理及源码分析
HashMap实现原理及源码分析 哈希表(hash table)也叫散列表,是一种非常重要的数据结构,应用场景及其丰富,许多缓存技术(比如memcached)的核心其实就是在内存中维护一张大的哈希表, ...
- (转)ReentrantLock实现原理及源码分析
背景:ReetrantLock底层是基于AQS实现的(CAS+CHL),有公平和非公平两种区别. 这种底层机制,很有必要通过跟踪源码来进行分析. 参考 ReentrantLock实现原理及源码分析 源 ...
随机推荐
- 关于Amazon.com Seller 网络以及IP地址更换 官方回答
Greetings from Amazon Seller Support, I understand your concern that there will be a change of IP ad ...
- 第二次ScrumMeeting博客
第二次ScrumMeeting博客 本次会议于10月26日(四)22时整在3公寓725房间召开,持续15分钟. 与会人员:刘畅.方科栋.辛德泰.窦鑫泽.张安澜. 1. 每个人的工作(有Issue的内容 ...
- rest_framework基础
简介 为什么要使用REST framework? Django REST framework 是一个强大且灵活的工具包,用以构建Web APIs. - 在线可视的API,对于赢得你的开发者们十分有用 ...
- Java中的静态变量static
package com.wangcf; public class Test { String name="你好"; static String sex="男"; ...
- RIGHT-BICEP单元测试——“二柱子四则运算升级版”
RIGHT-BICEP单元测试 ——“二柱子四则运算升级版” ”单元测试“这对于我们来说是一个全新的专业含义,在上了软件工程这门课,并当堂编写了简单的"求一组数中的最大值"函数的单 ...
- P4tutorial实战
Tutorial样例实战 GitHub仓库地址 参考博客 实验一:SIGCOMM_2015/Sourse_Routing 实验环境: OS:Ubuntu16.04 bmv2:behavioral-mo ...
- 404 Note Found队——现场编程
目录 组员职责分工 github 的提交日志截图 程序运行截图 程序运行环境 GUI界面 基础功能实现 运行视频 LCG算法 过滤(降权)算法 算法思路 红黑树 附加功能一 背景 实现 附加功能二(迭 ...
- POJ2528的另一种解法(线段切割)
题目:Mayor's posters 原文地址 首先本题题意是:有一面墙,被等分为1QW份,一份的宽度为一个单位宽度.现在往墙上贴N张海报,每张海报的宽度是任意 的,但是必定是单位宽度的整数倍,且&l ...
- UVALive 6913 I Want That Cake 博弈+dp
题目链接: http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vjudge/problem/96343 I Want That Cake Time Limit: 3000MS 64bit IO Forma ...
- CodeForces 483B 二分答案
题目: B. Friends and Presents time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input s ...
