matplotlib 进阶之Legend guide
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
matplotlib.pyplot.legend
在开始教程之前,我们必须先了解matplotlib.pyplot.legend(),该函数可以用以添加图例。
方法1自动检测
通过这种方式,lendgend()会从artist中获取label属性,并自动生成图例,比如:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
line, = ax.plot([1, 2, 3], label="Inline label")
ax.legend()
plt.show()
或者:
line.set_label("Inline label")
ax.legend()
方法2为现有的Artist添加
我们也可以通过下列操作,为已经存在的Artist添加图例,但是这种方式并不推荐,因为我们很容易混淆。
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
line, = ax.plot([1, 2, 3])
ax.legend(["A simple line"])
方3显示添加图例
我们也可以显示添加图例:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
line1, = ax.plot([1, 2, 3])
line2, = ax.plot([3, 2, 1])
ax.legend((line1, line2), ("line1", "line2"))
参数:
handle: Artist
label: 标签
loc:位置,比如"best":0, "upper right" 1 ...
fontsize
...
控制图例的输入
直接使用legend()命令,matplotlib会自动检测并生成图例,这种方式等价于:
handles, labels = ax.get_legend_handles_labels()
ax.legend(handles, labels)
需要注意的是,只有为Artist设置标签了,通过get_legend_handles_labels()才有效。
有些时候,我们只需要为部分Artist设置图例,这时只需手动传入handles:
line_up, = plt.plot([1,2,3], label='Line 2')
line_down, = plt.plot([3,2,1], label='Line 1')
plt.legend(handles=[line_up, line_down])
当然了,相应的可以传入标签:
line_up, = plt.plot([1,2,3], label='Line 2')
line_down, = plt.plot([3,2,1], label='Line 1')
plt.legend([line_up, line_down], ['Line Up', 'Line Down'])
为一类Artist设置图例
并不是所有的Artist都能被自动设置为图例,也不是所有Artist都需要被设置为图例。
假如我们想要为所有红颜色的玩意儿设置图例:
import matplotlib.patches as mpatches
x = np.arange(1, 4)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
for i in range(1, 10):
ax.plot(x, i * x, color = "red" if i % 2 else "blue")
red_patch = mpatches.Patch(color="red")
# red_patch: <matplotlib.patches.Patch object at 0x00000228D0D4BF60>
plt.legend(handles=[red_patch], labels=["red line"])
plt.show()
如果没理解错,通过patches.Patch构造了一个颜色为红色的Artist类,然后legend()就会对所有满足条件的Artist的类进行处理(其实也用不了处理啊,只是加了图例)。错啦错啦,实际上,就是简单地造了一个颜色为红色的片,价格red line标签而已,跟已有的Artist没啥关系。
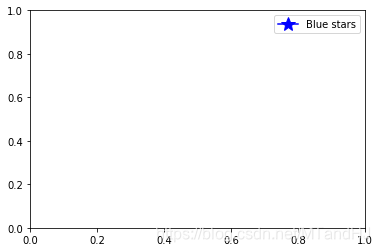
实际上,图例并不十分依赖于现有的Artist,我们完全可以随心所欲地添加:
import matplotlib.lines as mlines
blue_line = mlines.Line2D([], [], color='blue', marker='*',
markersize=15, label='Blue stars')
plt.legend(handles=[blue_line])
plt.show()
Legend 的位置 loc, bbox_to_anchor
legend()提供了loc参数,可以处理一般的位置。而bbox_to_anchor参数可以更加有效强大地来定位:
x = np.arange(1, 4)
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
for i in range(1, 10):
ax.plot(x, i * x, color = "red" if i % 2 else "blue", label="line{0}".format(i))
plt.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1, 1),
bbox_transform=plt.gcf().transFigure)
plt.show()
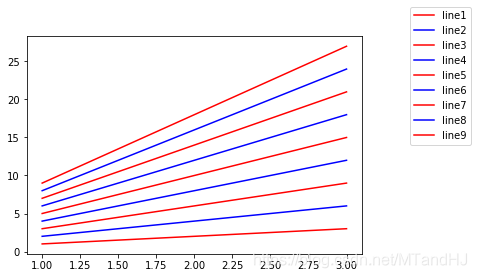
bbox_to_anchor=(1,1)表示legend的位置在右上角,因为bbox_transform,我们将坐标转换为了当前figure的坐标系,也就是图例会放在整个图片的右上角,如果我们去掉这个选项:
plt.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1, 1))
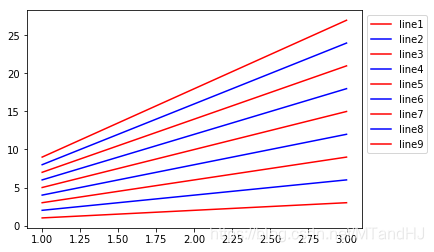
这个时候和下面是等价的:
plt.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1,1),
bbox_transform=ax.transAxes)
即,此时的(1,1)表示的是Axes的右上角。
当我们这么做的时候:
plt.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1, 1),
bbox_transform=ax.transData)
这个时候以数据,也就是我们看到的坐标为依据:
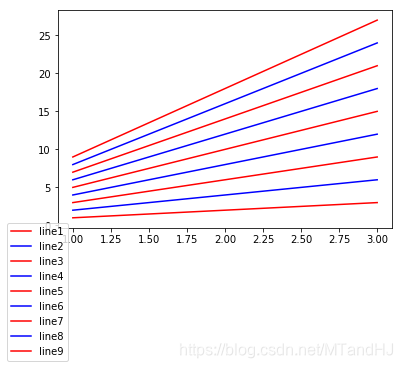
一个具体的例子
下面会用到的一些参数分析:
bbox_to_anchor: (x, y, width, height) 说实话,我并没有搞懂width, height的含义,有的时候能调正宽度,有的时候又不能
ncol: 图例的列数,有些时候图例太多,让他分成俩列三列啊
boderraxespad: axes与图例边界的距离。
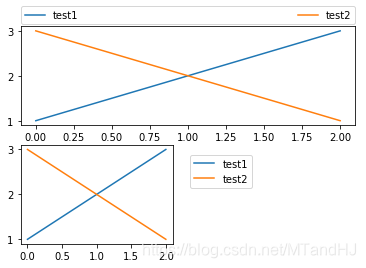
plt.subplot(211)
plt.plot([1, 2, 3], label="test1")
plt.plot([3, 2, 1], label="test2")
# Place a legend above this subplot, expanding itself to
# fully use the given bounding box.
plt.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(0., 1.02, 1., .102), loc='lower left',
ncol=2, mode="expand", borderaxespad=0.)
plt.subplot(223)
plt.plot([1, 2, 3], label="test1")
plt.plot([3, 2, 1], label="test2")
# Place a legend to the right of this smaller subplot.
plt.legend(bbox_to_anchor=(1.05, 1), loc='upper left', borderaxespad=1.)
plt.show()
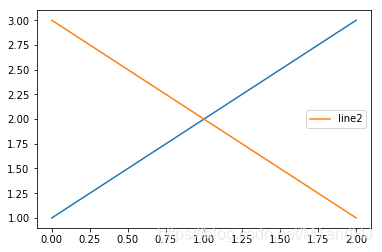
同一个Axes多个legend
如果我们多次使用legend(),实际上并不会生成多个图例:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
line1, = ax.plot([1, 2, 3])
line2, = ax.plot([3, 2, 1])
ax.legend([line1], ["line1"])
ax.legend([line2], ["line2"])
plt.show()
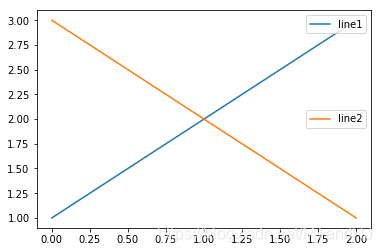
为此,我们需要手动添加图例:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
line1, = ax.plot([1, 2, 3])
line2, = ax.plot([3, 2, 1])
legend1 = ax.legend([line1], ["line1"], loc="upper right")
ax.add_artist(legend1)
ax.legend([line2], ["line2"])
plt.show()
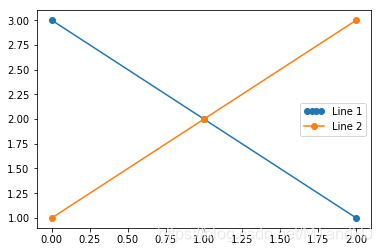
Legend Handlers
没看懂啥意思。
from matplotlib.legend_handler import HandlerLine2D
line1, = plt.plot([3, 2, 1], marker='o', label='Line 1')
line2, = plt.plot([1, 2, 3], marker='o', label='Line 2')
plt.legend(handler_map={line1: HandlerLine2D(numpoints=4)})
from numpy.random import randn
z = randn(10)
red_dot, = plt.plot(z, "ro", markersize=15)
# Put a white cross over some of the data.
white_cross, = plt.plot(z[:5], "w+", markeredgewidth=3, markersize=15)
plt.legend([red_dot, (red_dot, white_cross)], ["Attr A", "Attr A+B"])
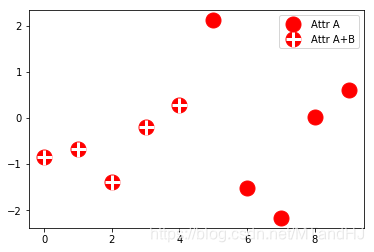
从这例子中感觉,就是legend_handler里面有一些现成,稀奇古怪的图例供我们使用?
from matplotlib.legend_handler import HandlerLine2D, HandlerTuple
p1, = plt.plot([1, 2.5, 3], 'r-d')
p2, = plt.plot([3, 2, 1], 'k-o')
l = plt.legend([(p1, p2)], ['Two keys'], numpoints=1,
handler_map={tuple: HandlerTuple(ndivide=None)})
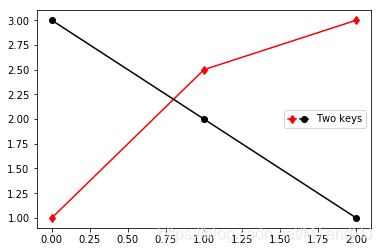
自定义图例处理程序
这一节呢,主要就是告诉我们,如何通过handler_map这个参数,传入一个映射,可以构造任意?奇形怪状的图例?不过参数也忒多了吧,不过感觉蛮有用的。
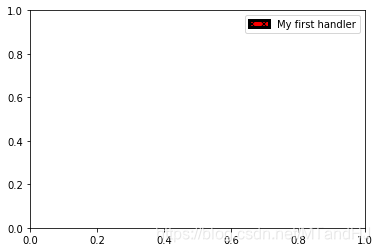
import matplotlib.patches as mpatches
class AnyObject(object):
pass
class AnyObjectHandler(object):
def legend_artist(self, legend, orig_handle, fontsize, handlebox):
x0, y0 = handlebox.xdescent, handlebox.ydescent
width, height = handlebox.width, handlebox.height
patch = mpatches.Rectangle([x0, y0], width, height, facecolor='red',
edgecolor='black', hatch='xx', lw=3,
transform=handlebox.get_transform())
handlebox.add_artist(patch)
return patch
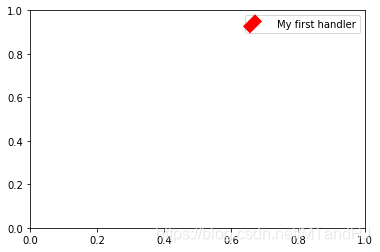
plt.legend([AnyObject()], ['My first handler'],
handler_map={AnyObject: AnyObjectHandler()})
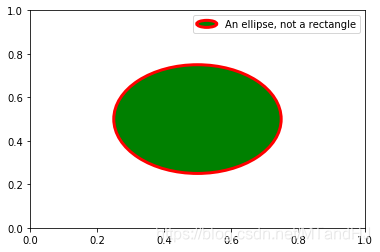
from matplotlib.legend_handler import HandlerPatch
class HandlerEllipse(HandlerPatch):
def create_artists(self, legend, orig_handle,
xdescent, ydescent, width, height, fontsize, trans):
center = 0.5 * width - 0.5 * xdescent, 0.5 * height - 0.5 * ydescent
p = mpatches.Ellipse(xy=center, width=width + xdescent,
height=height + ydescent)
self.update_prop(p, orig_handle, legend)
p.set_transform(trans)
return [p]
c = mpatches.Circle((0.5, 0.5), 0.25, facecolor="green",
edgecolor="red", linewidth=3)
plt.gca().add_patch(c)
plt.legend([c], ["An ellipse, not a rectangle"],
handler_map={mpatches.Circle: HandlerEllipse()})
"""都是啥和啥啊。。。"""
class AnyObject(object):
pass
class AnyObjectHandler(object):
def legend_artist(self, legend, orig_handle, fontsize, handlebox):
x0, y0 = handlebox.xdescent, handlebox.ydescent
width, height = handlebox.width, handlebox.height
patch = mlines.Line2D([1, 2, 3, 4, 6], [1, 2, 3, 4, 6], linewidth=width/2, color='red',
transform=handlebox.get_transform())
handlebox.add_artist(patch)
return patch
plt.legend([AnyObject()], ['My first handler'],
handler_map={AnyObject: AnyObjectHandler()})
函数链接
plt.lengend()-添加图例
get_legend_handles_labels()-获取图例处理对象和对应的标签
matplotlib.patches-包括向量,圆,矩形,多边形等等
legend_artist
matplotlib 进阶之Legend guide的更多相关文章
- matplotlib中的legend()—显示图例
源自 matplotlib中的legend()——用于显示图例 -- 博客园 http://www.cnblogs.com/yinheyi/p/6792120.html legend()的一个用法: ...
- matplotlib 进阶之Tight Layout guide
目录 简单的例子 Use with GridSpec Legend and Annotations Use with AxesGrid1 Colorbar 函数链接 matplotlib教程学习笔记 ...
- matplotlib 进阶之Constrained Layout Guide
目录 简单的例子 Colorbars Suptitle Legends Padding and Spacing spacing with colobars rcParams Use with Grid ...
- matplotlib 入门之Usage Guide
文章目录 Usage Guide plotting函数的输入 matplotlib, pyplot, pylab, 三者的联系 Coding style Backends 后端 matplotlib教 ...
- 【Python学习笔记】调整matplotlib的图例legend的位置
有时默认的图例位置不符合我们的需要,那么我们可以使用下面的代码对legend位置进行调整. plt.legend(loc='String or Number', bbox_to_anchor=(num ...
- 【转】matplotlib制图——图例legend
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/alimin1987/p/8047833.html import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport numpy as ...
- matplotlib中的legend()——用于显示图例
legend()的一个用法: 当我们有多个 axes时,我们如何把它们的图例放在一起呢?? 我们可以这么做: import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import numpy ...
- 【python】matplotlib进阶
参考文章:https://liam0205.me/2014/09/11/matplotlib-tutorial-zh-cn/ 几个重要对象:图像.子图.坐标轴.记号 figure:图像, subplo ...
- matplotlib 进阶之origin and extent in imshow
目录 显示的extent Explicit extent and axes limits matplotlib教程学习笔记 import numpy as np import matplotlib.p ...
随机推荐
- Mybatis相关知识点(二)
Mybatis解决jdbc编程的问题 1. 数据库连接创建.释放频繁造成系统资源浪费从而影响系统性能,如果使用数据库连接池可解决此问题. 解决:在SqlMapConfig.xml中配置数据连接池,使用 ...
- 大数据学习day17------第三阶段-----scala05------1.Akka RPC通信案例改造和部署在多台机器上 2. 柯里化方法 3. 隐式转换 4 scala的泛型
1.Akka RPC通信案例改造和部署在多台机器上 1.1 Akka RPC通信案例的改造(主要是把一些参数不写是) Master package com._51doit.akka.rpc impo ...
- 商业爬虫学习笔记day8-------json的使用
一. 简介 JSON,全称为JavaScript Object Notation(JavaScript对象标记),它通过对象和数组的组合来表示数据,是一种轻量级的数据交换格式.它基于 ECMAScri ...
- Angular Service设计理念及使用
官方认为组件不应该直接获取或保存数据, 它们应该聚焦于展示数据,而把数据访问的职责委托给某个服务. 而服务就充当着数据访问,逻辑处理的功能.把组件和服务区分开,以提高模块性和复用性. 1.依赖注入 注 ...
- Output of C++ Program | Set 11
Predict the output of following C++ programs. Question 1 1 #include<iostream> 2 using namespac ...
- Linux学习 - fdisk分区
一.fdisk命令分区过程 系统一旦重启,分区将消失 1 添加新硬盘 直接在虚拟机上添加 2 查看新硬盘 fdisk -l 3 分区 fdisk /dev/sdb fdisk进入/dev/sdb硬件设 ...
- 【Linux】【Shell】【Basic】Bash
命令历史:shell进程会在其会话中保存此前用户提交执行过的命令: ------------------------------------------------------------------ ...
- SSM和springboot对比
今天在开源中国上看到一篇讲SSM.SpringBoot讲的不错的回答,分享! https://www.oschina.net/question/930697_2273593 一.SSM优缺点应该分开来 ...
- 【Java 8】函数式接口(二)—— 四大函数接口介绍
前言 Java8中函数接口有很多,大概有几十个吧,具体究竟是多少我也数不清,所以一开始看的时候感觉一脸懵逼,不过其实根本没那么复杂,毕竟不应该也没必要把一个东西设计的很复杂. 几个单词 在学习了解之前 ...
- IIS 发布 WebService 连接DB2数据库报错如下图
环境描述: 系统环境: Windows Server 2012 R2 IIS版本:IIS 6.2 C#环境:.NET Framework 4 DB2版本:9.7.500.702 ...
